Symptoms and treatment of adenoiditis in children
Often sick children, snotty and coughing almost constantly - not such a unique phenomenon. Many parents are faced with the fact that a child from one hospital goes to another, and so almost all year round.
Perhaps it is not weak immunity that is to blame, as grandmothers and mothers think, but adenoids. About what it is and how to treat a child with adenoiditis, we will describe in detail in this article.
What it is
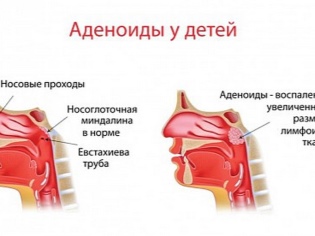
Adenoiditis - A disease that refers to pathological changes in the pharyngeal tonsil. The tonsils (palatal, lingual, tubal, pharyngeal) have a specific purpose, which is to protect the body against the penetration of viruses and bacteria. They consist of lymphoid tissue. When a disease pathogen attacks the nasopharynx, the tonsils respond to this by hypertrophy (i.e. an increase in size).
In the people tonsils are called simply - the tonsils. Normally, in a healthy child, they are small, do not cause anxiety and do not interfere with breathing. If the tonsils are enlarged, it always indicates that the body is desperately fighting some kind of alien pathogen or bacterium.
If the child is sick more often than their peers, then the unpaired pharyngeal tonsil ceases to cope with a constant load and begins to grow. This property of lymphoid tissue, which, in fact, is the body’s natural filter, is also characteristic of other tonsils. Hypertrophied tonsils themselves become a big problem, because their inflammation causes adenoiditis.
This disease rarely affects adults and is considered truly childish in medicine.
At risk - babies from 2 to 7 years, and in 2 years it is less common, and the majority of patients are between 4 and 6 years old. Adenoids are concerned about 6% of children of different sexes, while it does not matter in the northern or southern regions they live.
Classification
Depending on how long the child has suffered a violation of nasal breathing, coughing, adenoiditis is acute, subacute and chronic.
The acute form of the disease occurs in parallel with SARS or another viral disease, and lasts about a week. Subacute adenoiditis is a disease that lasts no more than three weeks, it is usually recorded in children with already hypertrophied tonsils. The illness in a chronic form is a disease that is more than six months long, with it usually complaints not only that the overgrown pharyngeal tonsil prevents normal breathing with the nose, but also the insufficient functions of neighboring organs - the child starts to hear worse, he often has a sore throat.
According to the combination of clinical manifestations of inflammation, there are catarrhal adenoiditis, serous (exudative) and purulent. Allergic adenoiditis, which develops as a result of prolonged contact with allergens, should be considered separately.
For a better understanding of the child’s condition, it is important for parents to know even non-morphological and clinical types of the disease, but its degree, because they most fully reflect the real picture and allow making predictions for treatment:
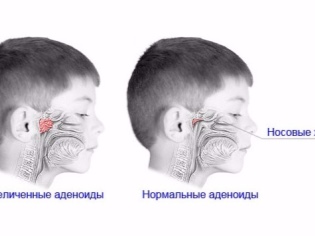
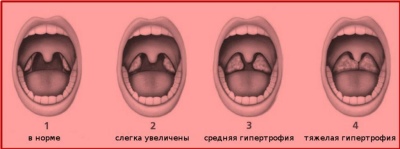
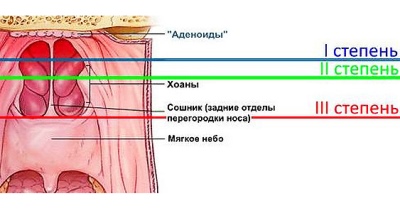
- Adenoiditis 1 degree. When it is overgrown, the pharyngeal tonsil covers about a third of the vomer (the bony part of the nasal septum). Nasal breathing is possible, although it is difficult.
- Adenoiditis 2 degrees. Hypertrophied tonsil blocks half of the vomer, and therefore breathing is often difficult.
- Adenoiditis 3 degrees. Nasal breathing is very difficult, the child almost always breathes through the mouth, because the amygdala is so enlarged that it covers two thirds of the lumen.
- Adenoiditis 4 degrees. In principle, a child cannot breathe with a nose, since the overgrown lymphoid tissue completely covers the nasal passages. The fourth degree is not recognized by all doctors, some estimate the disease by three degrees and the extreme is considered the third. What matters here is not so much the sequence number before the word “degree”, as the share of nasal passages closing.
In case of a disease, 1-2 degrees of manifestation can be only on one side - only one nostril is permanently laid or hearing loss has occurred only on one ear. However, both nasal passages or both auditory tubes are more often affected.
The reasons
- The main reason for the proliferation of adenoids lies in the acute respiratory viral infections that are common among children. SARS, influenza, acute respiratory infections most often provoke increased growth of the tonsils. If for some reason the child’s immunity is not strong enough, is temporarily weakened, for example, due to a recent illness, then the likelihood of tonsil hypertrophy increases significantly.
Child immunity cannot compete with an adult at all, and if in the first six months of a child’s life protect antibodies from the mother during pregnancy (which explains the very low prevalence of adenoiditis in infancy), then, when there is no innate protection, the entire burden falls on own, not yet fully formed immunity of the child.
- The second most common reason for enlarged tonsils is the individual propensity for allergies. If a child suffers from allergic reactions with manifestation of a repiratory - allergic rhinitis, cough, then the risk of developing chronic adenoiditis increases, which will worsen each time there is contact with an allergen (during seasonal flowering, for example).
If the child lives or most of the time is in a room where it is hot and breathes excessively dry or dusty air, then the probability of developing pathological adenoids is higher. Under these conditions, nasal mucus dries out faster, and pathogens can pass through the nose almost unhindered and settle in the throat. Inflamed tonsils will grow at a faster rate.
Chronic disease of the nose and throat also has a significant effect on the formation of the disease. If a child has a runny nose for a couple of months, it creates excellent conditions for the growth of adenoids. Therefore, every respiratory disease must be treated on time and correctly.
Contrary to popular belief, adenoiditis is not contagious to others. The child is contagious only during the acute stage of the disease viral infection, since the vast majority of viruses are transmitted by airborne droplets. At the same time, the child will “share” with others not by adenoiditis, but by a flu virus or other infection.
Viruses usually cause acute adenoiditis. In children with chronic illness, they can cause an exacerbation. Purulent adenoiditis is often evidence of a secondary bacterial infection.
Symptoms and signs
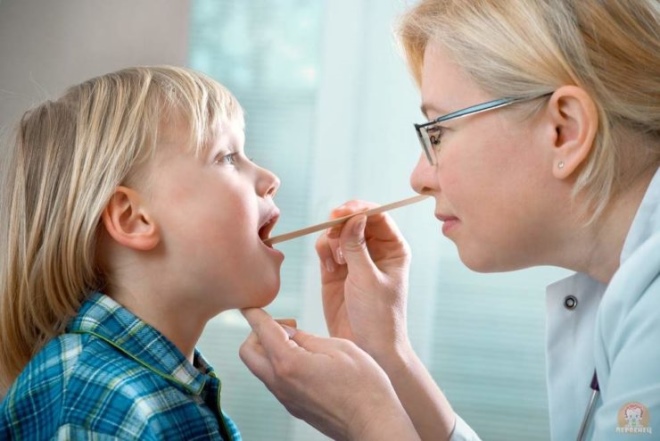
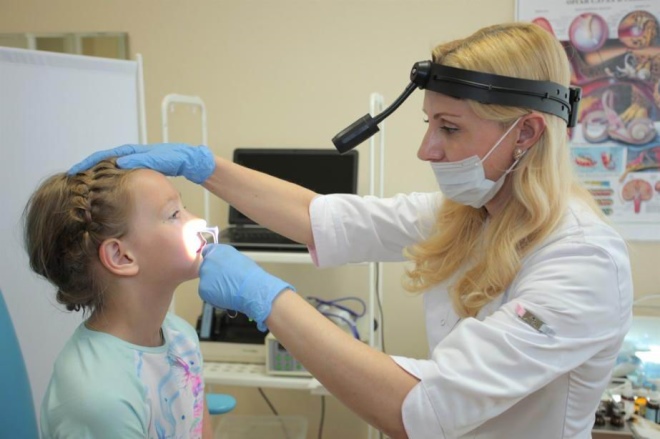
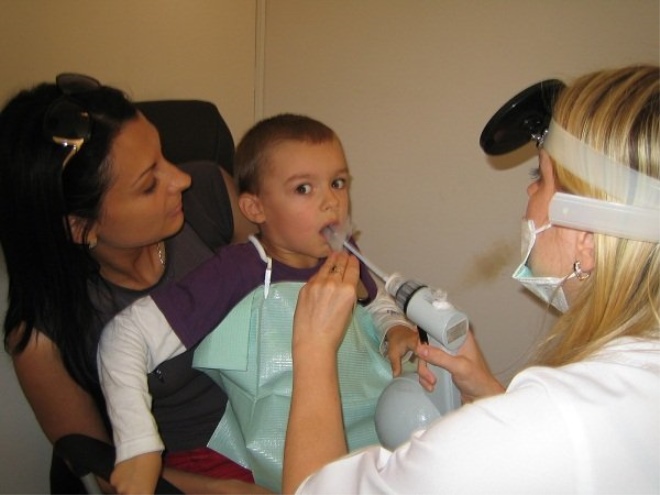
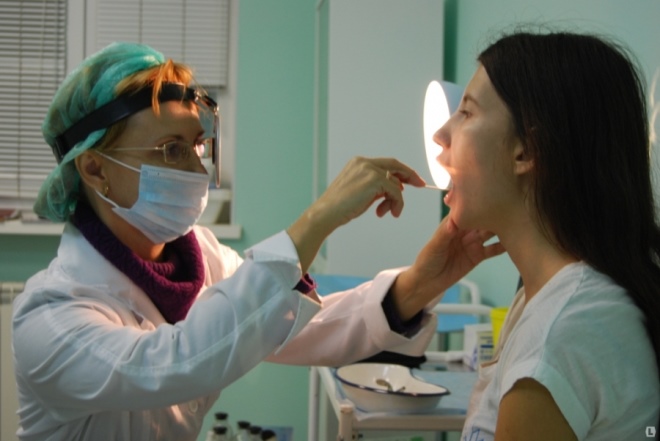
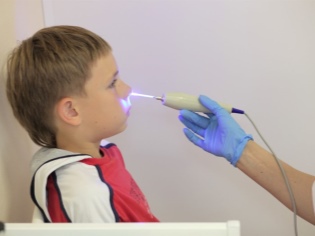
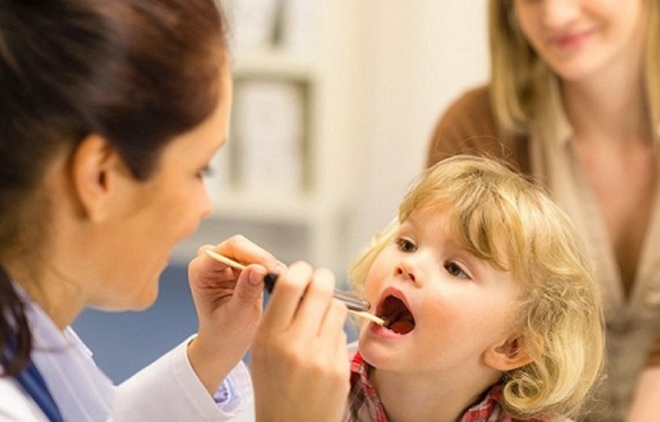
Symptoms are varied and extensive, and are not limited to runny nose and cough, as it may seem at first glance. Unlike most diseases of the oropharynx, adenoiditis cannot be seen at home when viewed from the throat. Adenoids are located in the arch of the nasopharynx; only the ENT doctor can see there, and then using a special mirror with a flashlight on a long handle.
However, parents may suspect problems with the pharyngeal tonsil without a visual assessment of the adenoids.
There are several signs that may indicate a disease:
- Long runny nose. Difficult nasal breathing up to the complete lack of the ability to breathe through the nose. In this case, the child begins to breathe through the mouth.
- Excessive nasal mucus secretion, which not only shoots, but also flows into the nasopharynx. With purulent adenoiditis, the discharge has a greenish color and a very unpleasant odor.
- Body temperature in acute and purulent adenoiditis can be quite high (up to 38.0-39.0 degrees). Chronic large tonsils usually do not cause fever, symptoms run without fever.
- The child's sleep is disturbed due to the fact that in a dream he has to breathe mainly through the mouth. The baby sleeps uneasily, often wakes up. A clear sign of the disease is snoring.
- Happy baby sluggish, sedentary, inactivehe has a reduced ability to memorize new information, an interest in everyday affairs that used to be important to him.
- Older kids may complain of headaches, hearing loss.
- The voice loses a bright color, becomes more hoarse and monotonous.
- Cough does not always appeartherefore, it cannot be considered a mandatory symptom of adenoiditis. If it is, it is in the nature of a chronic, dry unproductive.
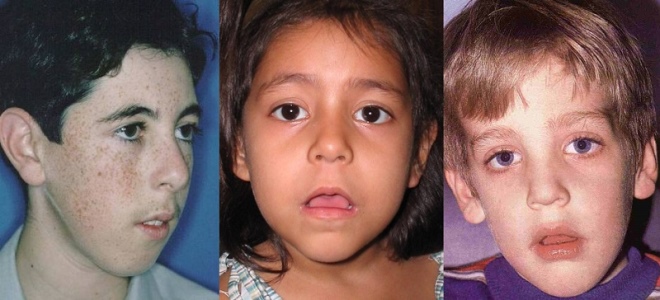
- The appearance of the so-called adenoid mask. With long-term chronic adenoiditis, the child's facial expression changes. Due to the constantly open mouth the child looks somewhat retarded, the expression of the eyes is not very meaningful. Nasolabial folds are smoothed, there is a strong drooling, changing the bite. The chest may become hollow.
Diagnostics
Children's ENT for the diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease will use several methods.
First, he will examine the pharyngeal tonsil on his own. Not so long ago, she felt out manually. The procedure is unpleasant. Now it is officially recognized as less informative, because the size of the pharyngeal tonsil is quite individual, and palpation cannot be a way to determine the pathological growth of adenoids.
However, the manual method of examination has one undoubted plus - the doctor gets an idea of the consistency of the tonsils. If they are not just big, but loose, it will certainly alert the specialist. If softness is observed with systematic observation and in the dynamics of a child's tonsils are constantly enlarged, this is the reason for a more detailed examination.
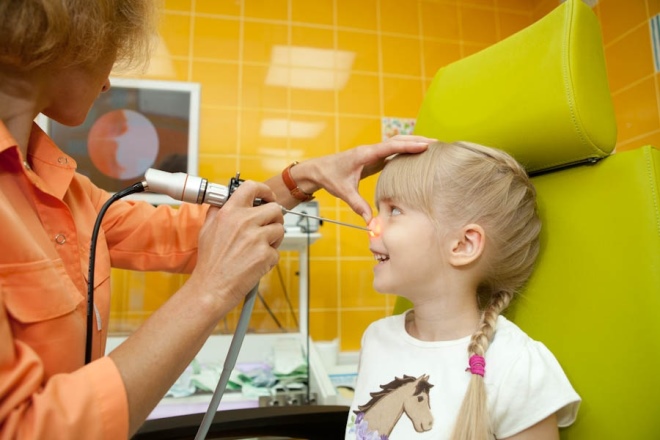
Visual inspection is called "back rhinoscopy." With her, the doctor examines the pharyngeal tonsil and the surrounding space with a special mirror that enters through the mouth. If the child is small, then it is incredibly difficult to do this manipulation. Then another method comes to the aid of the ENT system - anterior rhinoscopy, when the tonsils are inspected with instruments that are inserted through the nose.
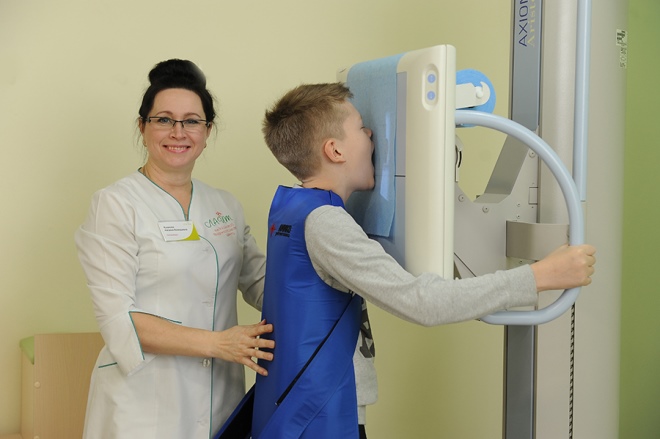
The most informative method is x-ray of the nasopharynx, however, not all parents agree to it, and not all doctors offer it, because the procedure is connected with the irradiation of the child’s body. If there is a need for a detailed snapshot of the nasopharyngeal area, the doctor may order a CT scan, which also provides informative and accurate data.
The tomograph is not in every hospital and clinic, and it can be quite expensive for parents to conduct research at their own expense. Endoscopic examination is considered the most common method for the diagnosis of adenoiditis. With it, the doctor inserts a soft, flexible endoscope tube into the nasopharynx through the nose or mouth and receives a fairly accurate picture of the surface of the adenoids.
All these methods and the combination of several of them with each other allow the doctor to determine the presence or absence of adenoiditis, its clinical features (purulent or catarrhal), to determine the extent of the disease by the area of nasal breathing over the norm,when the baby breathes unhindered. In addition, the physician should exclude the presence of tumors in the nasopharynx, polyps and other diseases that may give similar symptoms. All these data are very important for making decisions about treatment tactics.
Treatment
All parents care about only one question - how to reduce the tonsils and alleviate the child's condition. The answer is unequivocal - the child needs to be treated. Without therapy, adenoiditis always goes into a chronic stage that can cause a lot of trouble - from the appearance of a “adenoid mask” on the face to serious complications in the heart and kidneys.
If the doctor assesses the disease by grade 1-2, then treatment is prescribed conservative. If a child has a 3-4 degree, in which the lumen is closed by an overgrown pharyngeal tonsil by two thirds or more and is complicated by inflammation, then surgical intervention is recommended. The operation is also recommended for children, in whom the growth of the tonsil (even 2 degrees) led to the overlapping or partial closure of the Eustachian tubes, as a result of which the hearing has decreased significantly.
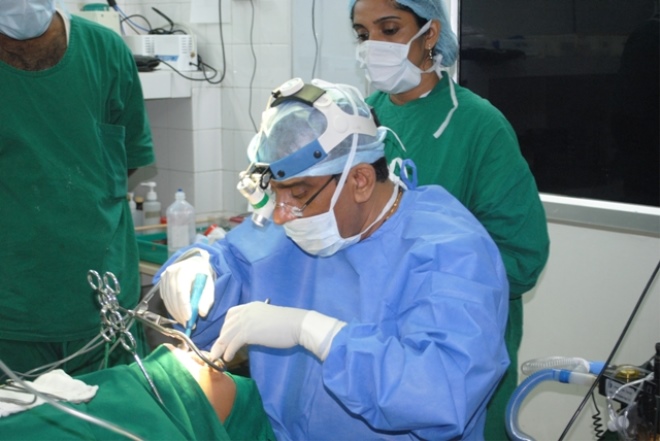
Surgical methods
The operation to remove the adenoids is called "adenotomy." The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. Many representatives of the older generation remember that earlier the tonsils were removed without anesthesia at all, because the adenoids themselves are deprived of nerve fibers. It was not so much pain, how much scary, but because anesthesia is today not even used for pain relief, but in order for the child to more comfortably undergo surgery.
Today in medicine there are several ways of conducting such an operation:
- Classical adenotomy using a round-shaped knife, which is used for cutting off overgrown tonsils;
- Laser adenotomy using high-precision laser equipment instead of a knife;
- Cold plasma adenotomy using the bloodless method.
The first method, although "rolled back" on many generations of young patients, is considered the most traumatic. After it, the recovery is longer, there is a chance of relapse. Laser operations are more accurate and less traumatic. Cold plasma techniques are relatively new, they show excellent results in the quality of the intervention and in the short duration of the recovery period. The choice of method and method of anesthesia is the task of doctors, because each individual child may have individual indications and contraindications.
Opponents of surgical treatment often indicate that it is undesirable to remove tonsils as an important immune organ.. Indeed, doctors may prescribe not complete removal, but cutting or partial removal of the inflamed and hypertrophied tonsil, if there is reason to believe that the remaining part of the lymphoid tissue will not grow further.
Fearing adenotomy is not necessary, experts say, because the operation lasts about 15 minutes, after a few hours the child feels great. In the absence of postoperative complications, he is discharged home after 3-5 days.
Treatment without surgery
With uncomplicated adenoiditis 1-2 degrees, the baby is prescribed conservative treatment, which includes several areas at once. It is important not only to reduce inflammation in the tonsils, but also to stop the process of their growth, and this can be done only by strengthening the child’s immunity.
The removal of edema and inflammation is facilitated by rinsing the nose and throat and washing the nasopharynx. Usually for this purpose they use saline, furatsilina solution, local antiseptic "Miramistin". If a purulent course of the disease is diagnosed in a child, the doctor, after analyzing the nasal mucus bakposev, will be able to prescribe the most accurate antibiotic against the "culprit" of purulent inflammation. Antibiotics of the penicillin group are commonly used. Perhaps as a local instillation in the nose, and taking antibiotics in pills.
In the treatment of purulent adenoiditis, antibiotics are not used at all. The doctor prescribes drugs - glucocorticosteroids ("Beclomethasone", "Fliksonaze", etc.) in the nasal form, that is, they will need to be buried and sprayed into the nose. In allergic adenoiditis, the doctor prescribes antihistamines in combination with calcium preparations. In various forms of the disease, the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug Ibuprofen may be prescribed.
The duration of the course and dosages are determined by the doctor taking into account the age of the small patient and the severity of the symptoms. In addition to medications, the doctor prescribes a whole range of measures to strengthen the immune system. It is advisable for the child to do a general strengthening massage, to do breathing exercises according to the Strelnikova system. Officially, medicine has not been proven, but climate therapy is widely practiced for adenoiditis. Parents are advised to take the child to the sea, breathe the sea breeze and bask in the sun.
Physical procedures may be prescribed associated with exposure to heat, rays, and therapeutic aerosols on the glands. And only if after six months the result of the therapy is not followed, the child’s condition remains the same or worsens, then the parents will be recommended to consent to the operation.
Postoperative period
Most of the guys will like the rehabilitation period after the operation on the glands very much, because doctors recommend giving the operated ... ice cream! Eating it can be difficult because swallowing will hurt for at least a week after surgery. In some babies, after a surgical procedure, the temperature rises, even if it was not at all before the operation. Doctors do not advise giving in this case antipyretic drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid, as this may cause bleeding.
In the first 7 days the child should not take a hot bath, go to the bath and even just sunbathe in the sun. After adenotomy, a special diet is recommended, based on the use of pureed, puree products, cereals, jelly, broths, which will not further irritate and injure the throat.
Strengthened physical activity, sports should be postponed for at least a month, but a lot of walking in the fresh air is possible and necessary, it helps to strengthen the immune system and more rapid recovery.
If the operation was carried out in the fall or winter, when an increase in seasonal viral diseases is observed, after it you need to protect the child from contact with other people for at least a couple of weeks. This will increase the likelihood that he will not “pick up” another virus again and will not start to hurt again. If the city has a salt chamber, where the child can go for several sessions, this will be an additional advantage. In itself, inhalation of salt ions does not help to be cured, but sterile air (in such chambers it is such) will be beneficial in the process of realitization.
Folk remedies
Parents whose child has been diagnosed with adenoiditis must be sent to the Internet to look for a remedy that “without pills and surgery” will help cure the child. Such recipes are sought even by those whose children have 100% indications for surgery. Believing in a miracle cannot be forbidden, but it should be understood that everything folk remedies can be both useful and harmful, if the child has a stage no more than 1-2. And in the case of stage 3-4, home treatment is a real parental crime.
However, traditional medicine can be very useful at the stage of recovery after surgery, and even the “old school” doctors, who don’t accept the "sorcery" in any way, say so.
To safe means include:
- Saline solution. It is prepared from a teaspoon of salt and a liter of water. The solution can be used to wash the nasopharynx during conservative treatment and for the prevention of adenoiditis at the first signs of a novice SARS or flu.
- Decoction of chamomile or sage. Broths made from the pharmacy fees of these herbs can be used for gargling, for washing the nasopharynx, for drinking both during treatment without surgery (with a slight increase in the tonsils) and after surgery (as a drink). For rinsing and washes, you can use the St. John's wort and calendula decoctions. The main thing is not to replace the treatment prescribed by a doctor with handwritten herbal rinses. Home-based methods can only slightly complement the basic therapy, and not replace it.
- Separately, focus on inhalation. Many parents believe that a child with adenoids who breathes over boiled potatoes under a blanket is treated this way. In fact, hot inhalations can only aggravate the process of inflammation, especially if it is purulent. Moreover, such a method (over a potato or a basin of boiling water) can cause burns to the respiratory tract, and this will only worsen the condition of the baby and may require hospitalization.
Inhalations with steam inhalers, if they are in the house, can be relatively useful only for acute catarrhal adenoiditis, when additional hydration of the mucous membranes is an obvious benefit. For all other forms of the disease, such procedures are useless. And with a purulent form - dangerous to life and health. Nebulizers for the treatment of adenoids are not used, since they are intended for procedures with the use of drugs in the treatment of diseases of the lower respiratory tract (bronchi, lungs).
To remove the swelling and reduce the tonsils in size can only competent doctor's actions and the patient's desire to follow all the recommendations. Magic weed or pills from adenoiditis does not exist.
Prevention
Measures to prevent this disease should be aimed at strengthening the immune protection of the child. By and large, prevention needs to be engaged from the very birth of a baby.
- Creating optimal conditions. If a child breathes dry and dusty air, as well as chemical vapors, by 3-4 years he will have formed not only a persistent adenoiditis, but also a couple of other chronic diseases of the respiratory system.
It is best if the children's room is no higher than 20 degrees Celsius with a relative humidity of 50-70%. Under such conditions, the mucous membranes of the nose and oropharynx will not dry out, and this is an excellent prevention (and treatment!) SARS, influenza, bronchitis, laryngitis and other diseases, including problems with the tonsils.
- Prevention of allergies. In the child’s room there should not be objects and things that are potentially dangerous in terms of allergies - carpets, large soft toys that stand in the corner and perform the function of collectors of house dust. Books should be stored in the closet behind the glass. To clean the house mom is best to use household chemicals that do not contain chlorine, and if the child is prone to allergies, then wash the floors without household chemicals at all. Things and bedding baby to wash hypoallergenic baby washing powder.
- Strengthening immunity. The ability of the body to repel attacks of viruses and bacteria directly affects which way of life a baby leads. A moving child who has enough time to spend the day in the fresh air is less likely to have illnesses, and if they do, they are much faster, without serious complications. From a very early age, the child needs to be hardened, attached not to a computer, but to sports and walks. Local immunity (in the throat) will be higher if the child drinks not only warm but also cold drinks, as well as systematically eat ice cream.
- For any infectious diseases parents should be able to act competently to minimize the possible negative consequences, which include adenoiditis. You can not prescribe a child antibiotics, antiviral and other medicines. The only exception is antipyretic drugs, and even then - at temperatures above 38.5-39.0.All the rest should be prescribed exclusively by the doctor, whom the prudent and sensible mom and dad will call the house on the very first day.
Reviews
On the surgical treatment of adenoiditis on the Internet, parents wrote whole volumes of reviews. Therefore, those who are to undergo the operation may well familiarize themselves with them and draw their own conclusions. Most mothers, who for a long time could not decide on the surgical removal of the tonsils in a child, and even with the 3rd degree of the disease continued to struggle with conservative methods, eventually still went with the children to the operation and did not regret it. Permanent persistent diseases stopped, children became more active, inquisitive.
Particularly noteworthy reviews of repeat operations. Unfortunately, adenoiditis often returns, and some children have to undergo the intervention two or even three times. There is not much difference in which clinic to undergo treatment. In any case, mothers who chose paid private organizations for their children point out only one advantage - they let them go home in a day or even earlier. The rest of the level of equipment, the qualifications of surgeons are about the same.
Reviews about the treatment of adenoids without surgery, though numerous, but more like advertising brochures, because at the end of every sad story about 3-4 degrees of adenoids in a child, there is necessarily a mention of a certain “balm”, “Dr. Ivanov from such a clinic” or “ author's methodology.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell about adenoids in the next video.