Symptoms and treatment of tonsillitis in children
Diseases of the throat are very common in childhood. There are a lot of physiological and age reasons for this. However, ailment is a disease, and they require different treatment. After reading this article, you will learn how to recognize tonsillitis in children, what are the symptoms, how to distinguish it from sore throat, pharyngitis and other diseases of the throat, how treatment is carried out.
What it is?
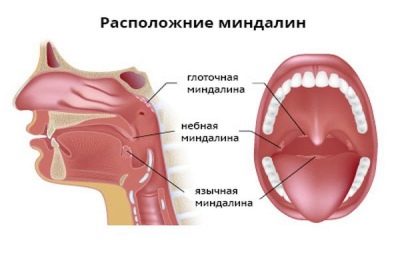
Tonsillitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the tonsils. These tonsils are paired, they are located in a small depression between the soft palate and the tongue of the child. In medicine, they are called simply ordinal numbers - the first and second.
They consist of lymphoid tissue, like the spleen, and perform immune functions. The first and second tonsils form a protective barrier, whose task is to stop viruses and bacteria that enter the body through the nose (when breathing), through the mouth (with food and water).
Tonsils not only provide protection, but also actively participate in the complex process of blood formation. If a child gets sick, a virus or bacteria penetrates the throat, then the tonsils react to this with inflammation, thereby creating the most unfavorable conditions for development and reproduction to the uninvited “guest”.
If the child is sick often, the tonsils do not have time to cope with the increased load and begin to grow, hypertrophied. Increasing the size temporarily helps them to function according to a given nature of the program, but rather quickly these tonsils themselves turn into a source of infection and danger.
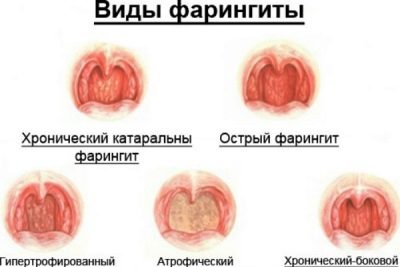
When tonsillitis affects not only the first and second palatine tonsils, sometimes inflammation spreads to the unpaired pharyngeal tonsil. That is why the people such illnesses mistakenly called angina.
Angina in the understanding of doctors is an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis or acute tonsillitis. But chronic tonsillitis in remission continues to be a disease and angina is not considered.
None of the children is immune from tonsillitis - infants can develop in infants and older children. However, at the age of 1 to 3 years, the disease is less common - in 3% of children. In 3 years and older, the incidence increases 2 times - about 6% of children under the age of 7 years have such a diagnosis in their personal medical history. The highest incidence is in children over 7 years old (it is about 15%).
Classification
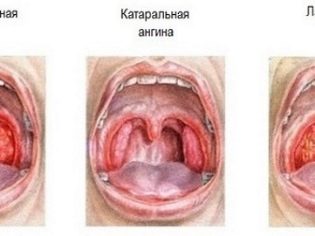
Tonsillitis can be acute and chronic. Acute (angina) in turn is catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, fibrinous and herpetic. As follows from the name of each subspecies, the difference is in the causes of the occurrence and course of the disease.
Acute tonsillitis is often bacterial in nature; it can be streptococcal, staphylococcal, pneumococcal, depending on the microbe that attacked the child. Inflammation of the tonsils caused by microbes is always accompanied by purulent phenomena - ulcers, plaque on the tonsils.
In the second place are viral acute tonsillitis, they are caused by viruses that have entered the lymphoid tissue. The fungal nature of the disease is not excluded - candidal tonsillitis is a rather dangerous disease.
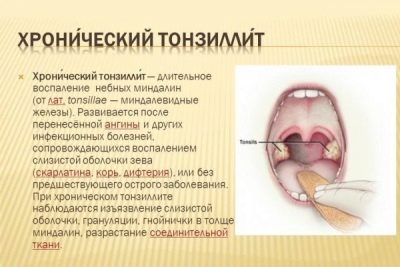
However, once a sore throat is transferred, there is still no reason for the child to be diagnosed with tonsillitis.The chronic form of this disease usually appears in children who have had angina for at least 4 times a year, as well as in babies who have not had an acute form of the disease properly.
Chronic tonsillitis is also not as simple as it may seem. He has a lot of manifestations and appearances. Thus, the disease is compensated and decompensated. In the first case, the child's body, which has a high capacity for compensation, "smoothes" the disease, not allowing it to develop, and the baby is not disturbed by anything. The infection peacefully “slumbers” for the time being. When the decompensated stage of inflammation becomes frequent, they are complicated by the ailments of neighboring organs - ear, nose.
The simplest is considered to be lacunar chronic tonsillitis, with inflammation with it extends only to the lacunae. In more serious cases, the inflammatory process also covers the tissues of the entire tonsil, and this is already lacunar parenchymal tonsillitis.
Phlegmonous is called such a disease in which mainly palatine tonsils are affected. The most complex form is sclerotic tonsillitis, it affects not only the tonsils, but also the neighboring areas, and there is a strong proliferation of connective tissue.
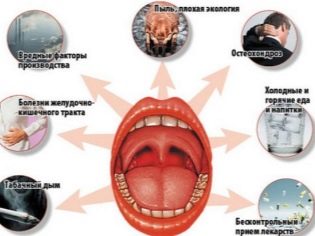
The reasons
To establish the true origin of tonsillitis is not so difficult, the disease is well studied, and the most frequent causes of its occurrence are known to physicians literally "by sight":
- Bacteria. These are widespread in the environment of staphylococci, streptococci, hemophilus bacillus, moraxsella, pneumococci.
- Viruses. This whole family is very common among people adenoviruses, some herpes viruses - for example, Epstein-Barr virus, Coxsackie viruses, flu viruses.
- Fungi, chlamydia and mycoplasma.
- Allergens.
Pathogens, entering the body of a child, do not always act destructively. In some children, they cause tonsillitis, while others do not.
It is believed that the most likely development of the disease in children with weakened immunity, who recently had an infectious disease or are currently suffering from it.
Other risk factors:
- Sources of infection in the mouth or throat. This includes unhealed sore teeth and stomatitis.
- Protracted rhinitis and nasopharyngeal diseases. If the child’s nasal breathing is difficult, but he begins to reflexively breathe through his mouth, as a result, he inhales practically unpurified, cold air, which is often too dry. The mucous membranes of the oropharynx dry up and cease to perform immune functions, which contributes to the reproduction of bacterial microflora.
Often the development of tonsillitis all the forces "help" the adenoids, which suffers from a child, chronic rhinitis, sinusitis.
- Adverse climate. If the child inhales too dry or too humid, too gassed, polluted air, the risk of developing tonsillitis increases significantly.
- Hypothermia or overheating.
- Malnutritionwhich led to metabolic disorders.
- Constant stress. If a child is in a situation of constant scandals or in a situation of divorce of parents, if he has difficulty in communicating with peers in the children's team, the likelihood of developing tonsillitis increases. This is a well-founded medical report, which is based on the experience of observation and treatment of hundreds of thousands of children with tonsillitis.
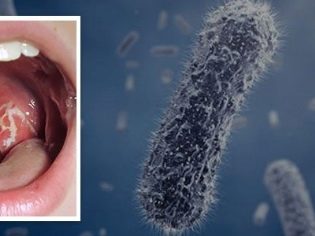
Symptoms and signs
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) and attacks of chronic tonsillitis always occur with increasing temperature. Moreover, the fever can be very pronounced, the temperature can rise to 39.0-40.0 degrees - in some forms of angina. The temperature usually lasts for 3-5 days - depending on how quickly and how correctly the throat began to heal.
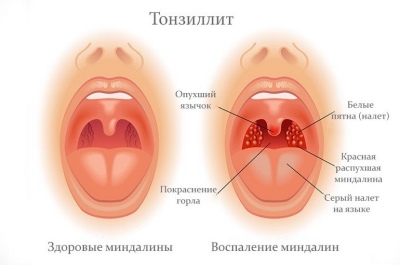
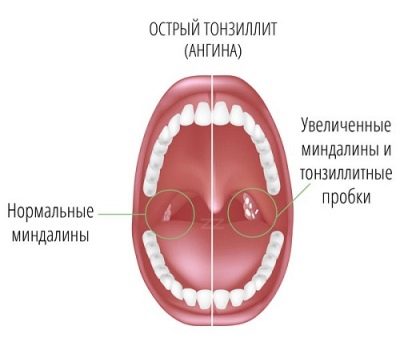
Sore throats are intense, the child sometimes can not eat, drink and even swallow his own saliva. In catarrhal sore throat, most often the tonsils just blush and look swollen.When the follicular on the tonsils appear yellowish purulent points, which increase in size, merge and turn into a rather large purulent formation.
When lacunar quinsy with the naked eye can be seen accumulation of liquid pus in the gaps, as well as the appearance of purulent-caseous traffic jams on the tonsils.
When a child has a sore throat, a very unpleasant smell goes out of his mouth. The stronger the pus is, the stronger it is. Regional lymph nodes are inflamed and grow in size (under the jaw, in the occipital region, behind the ear).
If the child is allergic, during this period he may become allergic, if there are problems with the joints, then there is an increase in joint pain.
Chronic tonsillitis in remission does not give any special symptoms, the child leads a normal life, does not complain about anything, he is not contagious. However, in the acute stage, the symptoms become very similar to the classic sore throat, except that the course of the disease is slightly less acute.
Suspected parents have chronic tonsillitis in a child for several reasons:
- After eating cold foods or drinks, temporary discomfort appears in the throat.associated with tickling sensations, difficulty swallowing, slight pain.
- Body temperature rises to 37.0-37.9 and lasts a long time.. Most often, it rises in the evenings, before bedtime.
- Appears unpleasant smell from the mouthwhich is especially strongly felt in the mornings - after a night’s sleep.
- The child's sleep is disturbed, he sleeps uneasily, often wakes up.
- Increased fatigue, the child becomes dispersed and inattentive.
- Exacerbations can be up to 10-12 times a year. - almost every month.
Danger of illness
Tonsillitis cannot be considered a harmless disease, since if left untreated or inadequate treatment, it can cause serious complications:
- Paratonsillar abscess. It manifests itself as a one-sided severe pain in the throat when swallowing, when viewed from a child there is a marked asymmetry - one amygdala is much larger than the other.
- Myocarditis. This is a lesion of the heart muscle, which is manifested by shortness of breath, swelling, pain in the heart, a violation of heart rhythm. Requires long and serious treatment.
- Rheumatism. With this complication, systemic damage to the connective tissue occurs, most often in the region of the heart.
- Glomerulonephritis. This is a complication that is associated with the destruction of the kidney cells - glomerul. Requires long and complicated treatment.
In severe form, can lead to severe intoxication and death of the child. In case of severe lesions, a donor kidney transplant is required, as well as lifelong maintenance therapy on an artificial kidney machine.
- Skin diseases It has been established that long-term chronic tonsillitis is one of the main causes of the development of neurodermatitis and dermatosis of the most diverse etiology in a child.
- Other diseases. In chronic tonsillitis, the focus of infection is permanent, it can cause some diseases of the lungs, metabolism, and joints.
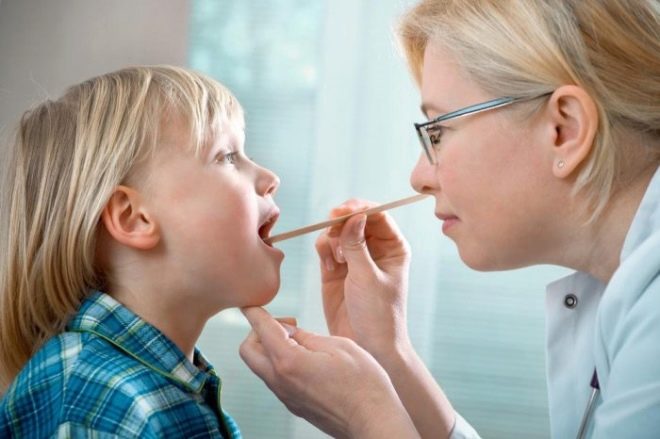
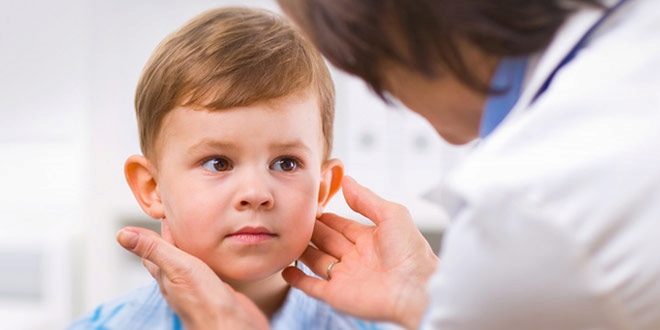
Diagnostics
Detection of the disease involved a pediatric otolaryngologist. Other specialists can also join the treatment - a nephrologist (if complications arise from the kidneys), a cardiologist (if there are complications in the heart), an allergist (if the disease occurs with worsening allergies or caused by allergens), a surgeon (if surgical treatment of the tonsils is required).
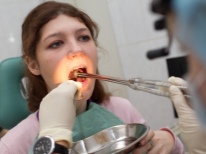
The doctor begins to diagnose with an external examination of the tonsils. The clinical picture of tonsillitis is characterized by a variety of specific signs with enlarged tonsils. These include rashes on the first and second tonsils, purulent or non-purulent lesion of the pharyngeal tonsil, and inflamed follicles that look like small or medium sized pustules.
A smear is always taken from the surface of the tonsils.His research laboratory - for the content of bacteria, fungi. If they are detected, the laboratory technician gives an answer to another question - what specific microbe caused the disease.
This is important in order to implement the correct treatment. After all, some antibiotics are active against staphylococcus, while others are best suited to fight pneumococcus. Fungal lesions are treated with antifungal drugs, it is a different story altogether.
A general blood test, which makes all children with tonsillitis, shows how strong the inflammatory process takes place in the body, whether it is systemic. A virological analysis allows you to determine whether the disease is caused by certain types of viruses. After all, with such an origin tonsillitis will be treated without the use of antibiotics.
If a child has neglected and severe tonsillitis, the ENT doctor can give referrals to a nephrologist and a cardiologist. You will have to go to the first one with the ready results of urine on your hands in order to rule out possible complications of the kidneys. The cardiologist will conduct an ECG and an ultrasound of the heart (if necessary) to see if the inflamed tonsils are not complicated by heart ailments.
Treatment
Acute (and chronic) tonsillitis is treated using different methods and regimens.
Acute form
Treatment of acute tonsillitis (depending on the pathogen causing it) is carried out by drugs active against a particular microorganism.
That is why angina in no case can not be treated independently at home. This "treatment" in 90% of cases leads to the fact that tonsillitis goes into a persistent chronic form.
For bacterial sore throat, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. It is best if the medicine is as effective as possible against a specific microbe. But in small towns and villages, where there are often no bacteriological laboratories in hospitals, it is sometimes very difficult to establish whether staphylococcus or streptococcus is to blame for the illness. The doctor determines the bacterial infection literally "by eye" - and in this case prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics.
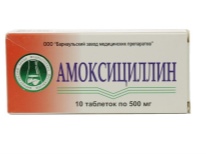
As a rule, treatment begins with the penicillin group of antibacterial drugs. Well proven "Amoxicillin"And"Amosin". For young children, let us take drugs in the form of syrups.
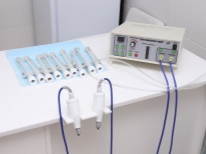
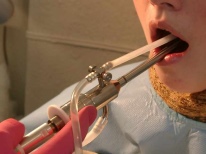
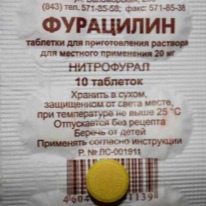
In parallel with this, the child is prescribed local therapy - washing the glands with a special Tonsilor apparatus, rinsing with furatsilina solution, and treatment with antiseptics.
For this, spray is most commonly prescribed. ”Miramistin", Herbal antiseptic" Tonsilgon. "
In the case of viral tonsils, antibiotics are completely and absolutely contraindicated. Their admission in this case can not reduce the risk of complications. Moreover, these risks increase 6-8 times.
Sometimes doctors recommend taking antiviral drugs. It is up to parents to buy them or not, since the clinical efficacy of most of these agents has not been officially proven. "Anaferon" or "Ergoferon" does not in any way affect the speed of recovery of the child.
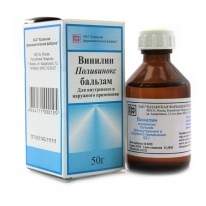
More hope for local processing. Affected tonsils are treated with balm.Viniline", Designate gargling with furatsilina solution, treatment with antiseptics.
Fungal tonsillitis is considered one of the most difficult to treat. They are prescribed a course of antifungal therapy, which includes both the ingestion of appropriate drugs, and local treatment with antifungal sprays and ointments. The course is quite long - from 14 days, after a short break it is repeated.
To reduce fever in acute tonsillitis, antipyretic drugs are allowed - Paracetamol, Tsefekon (candles for children), anti-inflammatory nonsteroid drug Ibuprofen. They allow not only to remove the heat, but also moderately anesthetize.
You should not treat the throat with angina solution "Lugol".This drug contains a large amount of iodine, which is perfectly absorbed and absorbed by the children's body. The more extensively the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils is affected, the faster and more aggressive iodine is. This is fraught with serious overdose and iodine poisoning.
At the stage of recovery, the child is prescribed physiotherapy treatment - warming up, procedures for treating the tonsils with ultrasound, phototherapy.
Chronic form
The treatment of chronic tonsillitis is a whole complex of measures that are aimed at neutralizing the inflammation center and at improving immunity, including local. Parents are advised to review the regime of the child’s day, his diet and physical activity. Long walks, a sufficient amount of vitamins in food, sports are excellent help with simple forms of illness, periods of remission become long and persistent.
If a child’s disease does not cause serious complications and is manifested mainly only by frequent episodes of angina, then conservative treatment is indicated. It includes local processing - washing the glands, processing with antiseptics (with the exception of iodine and alcohol solutions). In the acute stage, antibiotics are prescribed (for a bacterial disease) or antifungal agents (for fungal).
Such courses are usually prescribed twice a year (in spring and autumn, when the immunity of children is weakened). Individually, the doctor can increase the number of courses to 3-4 per year, if the child is sick often, he has exacerbation of tonsillitis.
Today, treatment of tonsillitis with low-frequency ultrasound is considered to be a rather effective method. During the procedure, the sound on the tonsils first occurs, then the pus is sucked in by the vacuum method, and only then by the hardware method the tonsils are irrigated with antiseptics and, if necessary, with antibiotics. Such procedures are performed by an ENT doctor, the average course of treatment is 10-15 days.
If conservative treatment does not help, the frequency of exacerbations does not decrease or some complication is detected, the surgical method of treating tonsillitis is recommended to the child.
The operation called "tonsillectomy" involves the complete removal of the tonsils - together with the connective tissue capsule. This operation is the only effective way to cope with the problem, there are no alternatives, but it is she who is most often criticized by opponents of the surgical method of treating tonsillitis.
The essence of criticism is that the organ that is important for the work of immunity is removed - the tonsils. As a result of this intervention, immunity is weakened, especially local, and children after tonsillectomy are more likely to suffer from diseases of the throat, bronchi, lungs, and nasopharynx.
However, official medicine has plenty of evidence that the benefits of surgery significantly exceed the harm, because sometimes it can stop the dangerous process of complications from the kidneys, heart and joints.
It should be noted that this operation is not shown to all children, there are diseases and conditions in which the complete excision of the tonsils is unacceptable. Then the child may be assigned another operation - tonsillotomy. It consists in removing not the entire amygdala, but only parts of it, especially overgrown and damaged infections. Most often it is carried out for children aged 5 to 10 years, because earlier without special need there is no point in surgical treatment at all.
Both operations are performed under both local and general anesthesia. Both tonsillotomy and tonsillectomy can be performed not with a special surgical knife (tonsillotomy), but with the use of modern laser technologies.
The recovery period does not last long, after 8 hours the child can eat and drink, and after a day he is sent home from the hospital.In the near future he will have to eat on a sparing diet, which excludes spicy and spicy, salty, sour and fried, and also after each meal, rinse the throat and mouth first with ordinary boiled water and then with antiseptic solutions.
General recommendations for treatment:
- Acute tonsillitis treatment (or exacerbation of chronic illness) always requires abundant warm drinking. It is important to preserve the moisture of the mucous membranes and prevent dehydration at elevated temperatures.
- Herbs can be used for gargling. (chamomile or sage), but only if the tonsillitis is not allergic.
- Enhance immunity contribute to walking in the fresh air. This can be done immediately after the body temperature drops. Hardening is useful, as well as active games on the street.
- Do not interrupt treatment at the first sign of improvement. Untreated infection is chronic, and then it will be even more difficult to treat, because the microbe develops resistance to previously used types of antibiotics.
- After a sore throat or during remission of chronic tonsillitis (when the child is not worried about anything) parents should be engaged in strengthening local immunity - tempering the throat. To do this, the child is given ice cream, cool drinks, practice cool gargles with a gradual decrease in the temperature of the gargle.
Prevention
Preventive measures that will help protect the child from tonsillitis are quite simple.
They do not require the use of expensive drugs or time consuming:
- During a massive increase in the incidence of ARVI, it is better not to drive the child to crowded placesshould avoid traveling in public transport. Instead, it is better to walk a few stops on foot or take a walk in the park.
- If you have a sore throat, redness, enlarged tonsils, you should immediately call a doctor.. Only the correct, emergency and complete treatment of diseases of the throat (including sore throats) will help avoid the occurrence of such an unpleasant illness as chronic tonsillitis.
- The child needs to be tempered, led to the sports section, not to overfeed or re-entangle. Only under such conditions a normal, strong, strong immunity is formed.
- It is important to do everything according to age. mandatory vaccinations.
For the causes of chronic tonsillitis, the conditions under which the removal of the glands is shown, and the treatment of enlarged palatine tonsils, see the following video.