Symptoms and treatment of pharyngitis in children
Inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract are quite common in pediatric practice. Throughout life, every person at least once gets pharyngitis. What you need to know about this disease to successfully cope with it, this article will tell.
What it is?
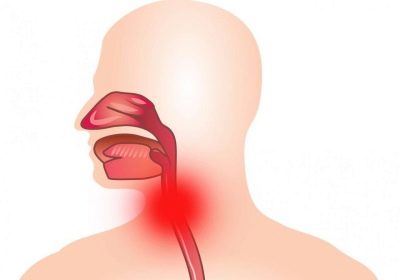
The pathological condition localized in the oropharynx is called pharyngitis. This disease is equally affected by both boys and girls. Baby can get pharyngitis at any age. Doctors report cases of illness even in newborn babies and infants.
The disease is spread throughout the world.
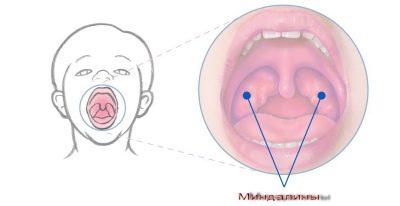
The inflammatory process in pharyngitis is mainly localized. Edema mainly extends to the region of the posterior pharyngeal wall, certain parts of the upper palate, the root of the tongue, and in some cases the tonsils and lymphoid tissue. This process is characterized by the occurrence of pronounced edema and an acute local immunity reaction.
The predominant method of infection is airborne. In this case, the smallest viruses or bacteria easily fall on the mucous membranes. Transmission of infection occurs from a sick person to a healthy one. In some cases, the “transmitter” of an infectious disease may not suspect that there are pathogens in its body. Such a person also lacks the corresponding symptoms of pharyngitis. In medicine, this condition is called "carrier of the infection."
According to statistics, the greatest number of cases of inflammation of the pharynx occur in the cold season. The end of autumn, winter, and early spring are the most likely months for pharyngitis.
Kids who attend various educational institutions and leisure centers get sick much more often. This feature is due to the low prevalence of viruses and bacteria in the environment. Many microorganisms are very resistant to the effects of adverse environmental factors and can maintain their vital activity for a long time. In children aged 2-3 years, the disease is much harder than in older children. This is due to the immaturity of the immune system: it usually develops during the first 5-6 years of a baby’s life. The failure of the local and systemic immune response leads to the fact that any infection spreads quite quickly throughout the child’s body and can cause serious complications in the child.
During life, each person can have pharyngitis more than once. This is due to the fact that with each infection it becomes infected with completely different subtypes of viruses or bacteria.
The immune system "remembers" the causative agents of the disease, but does not form a stable memory mechanism. The exceptions are only a few viral and bacterial childhood infections, which are also called "quarantine".
The reasons
A variety of causes can cause inflammation in the oropharynx in a child. Their impact can be short in time or long enough. Such a variety of different causal factors leads to the fact that quite a lot of clinical variants of the disease are recorded.
The most common causes of inflammation in the oropharynx are the following:
Viral infections
Getting on the delicate mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, viruses easily cause an inflammatory process. Different antigenic variants of these microorganisms can cause the appearance in the child of symptoms of different severity. Quite often, viral infections cause illness in babies up to a year.
The most common in pediatric practice sources of disease are: adenoviruses, parainfluenza and influenza viruses, rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, Coxsackie viruses, Epstshyn-Barr viruses, and many others.
Bacterial infections
Bacterial infections are quite common causes of various types of pharyngitis in young patients. A fairly common variant of the disease is streptococcal. Bacterial pharyngitis can be quite difficult, with severe intoxication syndrome. The elimination of adverse symptoms requires the appointment of an optimal antibiotic regimen.
Chronic diseases of internal organs
Some pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the endocrine system and immunodeficiency states are common causes of the occurrence of adverse symptoms of pharyngitis in a baby.
To eliminate the clinical signs of the disease in this case, initial therapy of the underlying disease is required.
Sick teeth
The presence of carious or periostitic teeth in the oral cavity is often the cause of the disease. An infected tooth cavity is an excellent breeding ground for the development of pathogens. Prolonged infection leads to the fact that microbes begin to spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. The organs that are located in the neighborhood, including the oropharynx, are more affected.
Herpes infection
Herpetic or vesicular pharyngitis occurs predominantly in weakened or often ill children with colds. The causative agents of the disease in this case are different types herpes. Settling in the body, they affect the lymphoid tissue, causing a strong inflammatory process. Treatment of herpetic pharyngitis is usually longer than viral or bacterial.
Allergic Pathologies
Allergic reactions occur in babies who have individual sensitivity to various types of allergens. Allergy substances can be various foods, inhalation of polluted air, some chemicals. The course of allergic pharyngitis is usually undulating: periods of exacerbations are replaced by remissions. If an allergen enters the child’s body as soon as possible, it can cause an allergic reaction, which also involves the oropharynx.
Local hypothermia
The mucous membranes of the oropharynx are very tender. The impact of adverse temperatures contributes to their damage and the beginning of the inflammatory process. Inflammation quickly goes to the lymphoid tissue, which is well represented on the back of the pharynx.
Drinking your favorite ice cream during the cold season or walking in windy weather without a scarf very often leads to the fact that in the morning the baby wakes up with clinical symptoms of pharyngitis.
Long-term use of certain medications
All pharmaceuticals have side effects.One of which is the emergence of nonspecific (non-infectious) pharyngitis. It is often enough that the occurrence of adverse symptoms of inflammation in the oropharynx in a child is caused by prolonged use of clozapine, sulfasalazine or carbimazole.
Smoking
This causal factor is relevant for adolescents. The components of smoke inhaled while smoking contain quite a lot of various toxic substances that irritate the mucous membranes of the oropharynx.
Smoking in cold weather significantly increases the risk of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
Candidiasis
Also, this disease is often called "thrush". It is most common in debilitated toddlers, as well as children suffering from obesity or endocrine diseases. Diabetes mellitus can also cause signs of candidal pharyngitis in a child. It should be noted that this clinical form is rare in children.
Classification
The development of this disease leads to the impact of a variety of reasons. This causes a large number of nosological variants of the disease. For the convenience of setting the correct diagnosis, all of them are collected into special classifications used by doctors in their daily practice. In order to establish the correct form of the disease, in many cases, pediatricians have to carry out a rather large complex differential diagnosis. This is necessary to establish the correct cause of the disease, as well as to draw up further tactics for treating a baby.
For the duration of onset of symptoms
For the duration of the onset of symptoms, doctors distinguish several clinical variants of oropharyngeal inflammation.
- Acute. All adverse symptoms develop, usually in 5-7 days. After an acute period of the disease, full recovery occurs. Immunity after the illness, unfortunately, is unstable. According to statistics, children from 6 to 14 years old suffer mainly from acute pharyngitis.
- Chronic. Chronic form has a wave-like flow. Acute periods of the disease are replaced by periods of relative or absolute clinical well-being. During periods of remission, babies usually do not feel any discomfort in the oropharynx area. The duration of the exacerbation period in chronic pharyngitis can be different: from several days, weeks or up to a couple of months. In their work, pediatricians and pediatric otolaryngologists take into account not only one classification by the age of occurrence of clinical symptoms. They also use another division of the disease, taking into account morphological (structural) changes. This classification includes the following anatomical variants of pharyngitis.
On structural changes
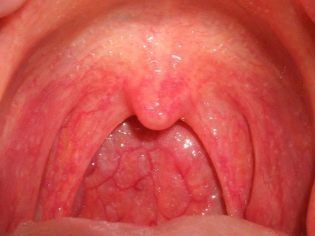
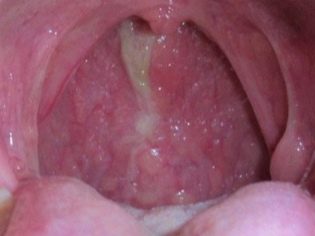
- Catarrhal The mildest form of the disease. It is characterized by minor inflammatory changes in the oropharynx and pharynx. The severity of adverse symptoms is moderate. Complications in this form of the disease, as a rule, do not arise.
- Hypertrophic. It is the next stage of the process chronization. It is characterized by a pathological increase in the tissue of the oropharynx. Hypertrophic form is divided into lateral and granular. The granular variant is characterized by the formation of numerous red granules on the back of the pharynx, which are accumulations of lymphoid tissue. The course of the hypertrophic version of the disease is much harder than the catarrhal.
- Atrophic. It is considered the most unfavorable projected clinical form of the disease. Causes a sick child a lot of adverse symptoms that significantly impair his health and are rather difficult to tolerate. When atrophic pharyngitis in the oropharynx is formed a sufficiently large number of dense crusts.Often the process moves to the nasal cavities, which significantly impairs the well-being of the baby.
Symptoms
The duration of the incubation period may be different. It depends on which pathogen caused the disease in a particular child. So, the first clinical signs of viral pharyngitis usually appear after 1-3 days from the moment of infection. In some cases, this time is significantly reduced. For example, having visited a kindergarten in the afternoon, in the evening the baby may already feel bad, and by the morning he will have all the adverse symptoms of the inflammatory process in the oropharynx.
The first clinical signs of the disease with bacterial pharyngitis appear after 5-7 days from the moment of infection. This time is necessary for the development and reproduction of bacteria in the children's body. The duration of the incubation period in various clinical variants of pharyngitis may be different: from a couple of hours to several days. At this time, the child's illness, as a rule, does not bother. Only in some cases, attentive parents may notice that the baby has become somewhat sluggish and less active.
Inflammation in the pharynx is characterized by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- Soreness when swallowing. It appears immediately after the end of the incubation period. The severity of this symptom may be different: from mild to significant pain. In severe illness, it may be difficult for a child to swallow even chopped or mashed food. Too hot or cold dishes noticeably increase pain.
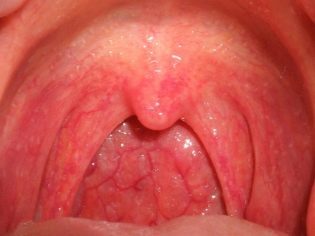
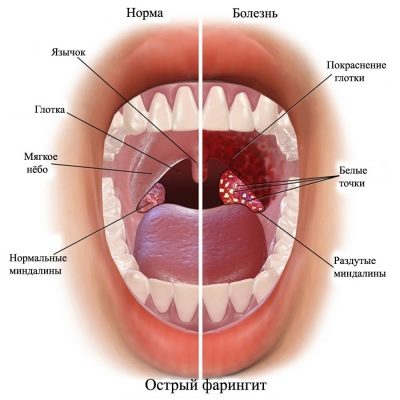
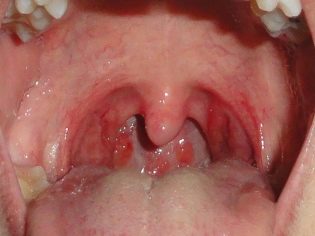
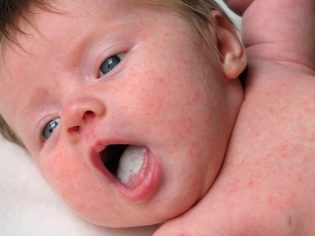
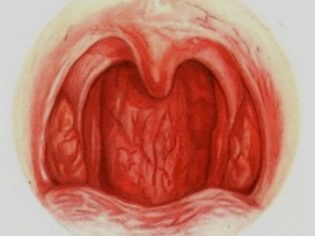
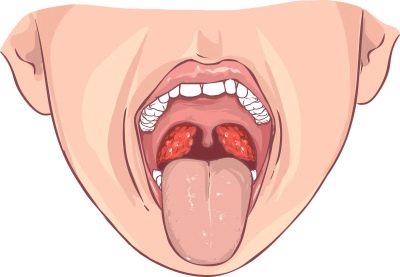
- Redness of the back wall of the throat. This symptom is the most specific for pharyngitis. The back wall of the throat, tonsils, palate and root of the tongue become hyperemic (bright red). When viewed from the oropharynx with a spoon or spatula, pronounced puffiness and "granularity" are visible.
- Increased body temperature. It can reach different values. With a mild course of the disease, the body temperature rises to 37-35.5 degrees. More severe forms of the disease cause pronounced febrile condition in sick children. Heat usually lasts 3-5 days and then gradually decreases. During the exacerbation of persistent chronic tonsillitis, subfebrile condition may persist somewhat longer.
- Intoxication syndrome. In the acute period of the disease, the baby has a headache, severe weakness. Changing the behavior of a sick child. He becomes more sluggish, apathetic, he loses interest in his favorite games and activities. Sick kids spend more time in bed, they can be capricious and whimper.
- Accumulation of excess mucus. The inflammatory process leads to the increased formation of various secrets, one of which is mucus. It accumulates on the back of the throat, increasing the appearance of adverse symptoms.
- Hot cough. This symptom occurs mainly in the smallest patients. The accumulation of mucus on the back of the pharynx irritates the receptors, which leads to the appearance of cough in the child. It can be different: both dry and wet. The cough usually lasts 1-1.5 weeks, then this unfavorable symptom gradually disappears.
How does the disease manifest in babies up to three years old?
The most severe course in newborn babies and infants has streptococcal pharyngitis. It causes the child to have numerous adverse symptoms and significantly worsens his overall well-being. During a streptococcal infection, the oropharyngeal mucosa becomes bright red, and in some cases even "burning". When viewed from the throat visible pronounced hyperemia of the inflamed areas and severe swelling.
Body temperature in this clinical form of the disease is increasing rapidly. Its values often reach 38-39 degrees.Such a pronounced febrile can persist for 4-7 days.
Reduction and normalization of elevated body temperature is a very favorable symptom, which indicates the beginning of recovery. During streptococcal infection in a child there is a strong discharge from the nasal passages. Usually they are yellow or green, quite thick. The discharge is bad. Parents should remove them from the nasal cavity of babies, as babies do not know how to blow their own nose. Quite often, this infection causes various complications in sick babies: inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis), severe otitis, and in some cases - bacterial conjunctivitis.
The disease occurs in a child is quite difficult. The severity of intoxication syndrome increases with each passing hour. A one-year-old child becomes sluggish, his appetite decreases, and sleep is disturbed. Infants may refuse breastfeeding or poorly attached to the breast. A sick child increases daytime sleepiness. In many cases, systemic disorders also join the symptoms of pharyngitis in bacterial infections. These include: muscle and joint pain, abdominal pain, abnormal stool, headache, increased sensitivity to various sounds and photophobia.
The severity of these symptoms may be different. Treatment of bacterial forms of pharyngitis in children under three years old, especially in severe cases of the disease, is given in the hospital setting.
Diagnostics
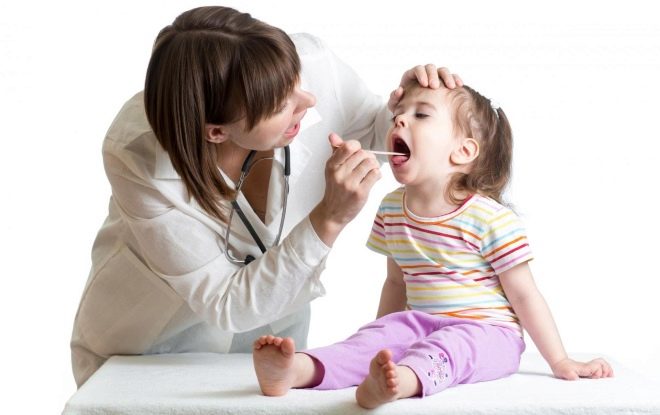
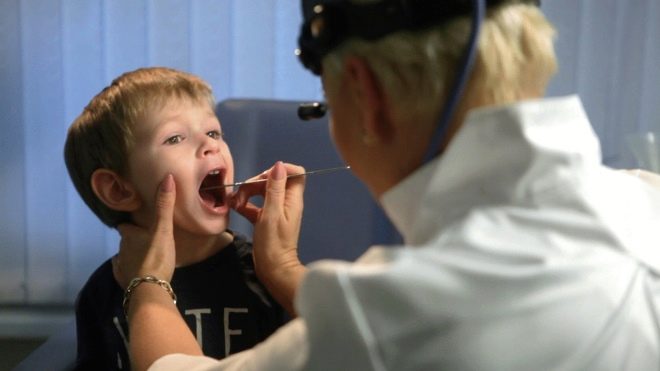
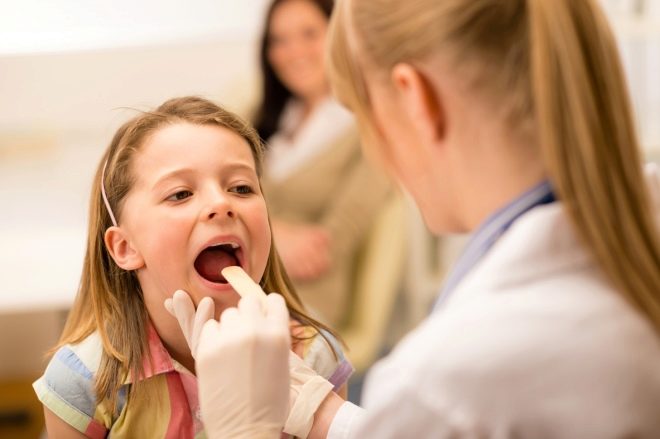
The appearance of adverse symptoms of the disease should be a good reason for seeking advice from a pediatrician. To establish the correct diagnosis, he must conduct a clinical examination. During the examination of the child, the doctor will necessarily examine the oropharynx and pharynx, and also will hold a palpation of the abdomen to rule out complications of a viral or bacterial infection. After a clinical examination, pediatricians prescribe a whole range of laboratory tests, which is necessary to determine the severity of functional disorders, as well as to determine the cause of the disease. Seek advice can not only to the pediatrician. Also the treatment of pharyngitis, especially chronic, are engaged in children's otolaryngologists. Bacterial variants occurring with the appearance of pus from the nasal passages or in the cavity of the pharynx are treated only in lora.
To assess the condition of the upper respiratory tract, a children's otolaryngologist conducts a special examination - pharyngoscopy. The essence of this study is a visual inspection of the oropharynx and the identification of all pathological conditions existing there. To exclude associated complications, the doctor also conducts rhino- and otoscopy. With the help of a special tool (retractor), he evaluates the visual state of the visible mucous membranes of the ear and nasal passages. If the doctor also needs to examine the larynx, then he uses another device called a laryngoscope.
Conducting such a comprehensive study allows for a fairly complete differential diagnosis, the result of which will be the formulation of a correct diagnosis. To establish the cause and severity of the disease to the sick child, general clinical blood and urine tests are performed. An increase in the total number of leukocytes and arising deviations in the leukocyte formula indicate a viral or bacterial cause of the disease.
The acute form or exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis is accompanied by a significant acceleration of ESR. In some cases, it can increase to 30-50 mm / hour.
Bacteriological research to determine the causative agent of the disease is also an important component of a successful diagnosis.The biological material for this study is usually discharge from the nasal cavity or mucus collected on the back of the oropharynx. This laboratory test allows to establish the exact cause of the disease, as well as to determine the sensitivity of the detected microorganisms to various antibiotics and bacteriophages. Bacteriological examination is quite sensitive and helps to establish the correct diagnosis.
Complications
The most frequent complication of acute pharyngitis is the transition of this pathological condition to the chronic form. It occurs mainly in frequently ill children, as well as children with serious long-term diseases of internal organs. Chronic disease is more unfavorable in prognosis than acute. That it contributes to the progression of the disease and the appearance of adverse long-term complications in the baby.
The spread of the inflammatory process to neighboring organs leads to the development of pathologies in these organs. One of these pathological conditions is tracheitis. It is often a complication of viral and especially bacterial pharyngitis. Acute tracheitis is characterized by a strong inflammatory process in the trachea, which is manifested by the appearance of a strong cough in a baby. The spread of inflammation leads to the fact that the process involves the cervical lymph nodes.
One of the most dangerous complications considered pharyngeal abscess. It can develop in a child and independently. However, quite often this pathology develops precisely as a complication of bacterial pharyngitis. Zaglottic abscess occurs in the oropharyngeal space due to the spread of the inflammatory process in this anatomical zone. It is characterized by a pronounced increase in temperature and an increase in intoxication syndrome.
The state of health of a child with this pathology is significantly impaired. The kid categorically refuses to eat, more is in bed. Daytime sleepiness can be quite strong. At night, on the contrary, the baby is more difficult to sleep and can wake up several times. A characteristic symptom of the pharyngeal abscess is unbearable pain when swallowing, which does not diminish after taking local antiseptic and painkillers and sprays. Zagothy abscess is an extremely difficult pathology. The treatment of this pathological condition is surgical. For the treatment of the sick child is urgently hospitalized in the hospital. After the surgery, the child is given special recommendations that will help the baby to recover and gain strength sooner.
Treatment in children
Pharyngitis therapy includes the appointment of a whole complex of various therapeutic techniques. The period of treatment of the acute form usually takes 5-7 days. The exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis is quite difficult and requires the appointment of a more intensive treatment regimen. Selection of the necessary treatment is carried out either by a pediatrician or a children's otolaryngologist.
To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease the following recommendations should be followed.
- Use a variety of medicines. According to its mechanism of action medications can be anti-inflammatory and analgesic. As a rule, modern pharmacological preparations have a complex effect and also have an excellent antiseptic effect. These funds can be discharged in various forms of release: lozenges for sucking, sprays, aerosols, solutions for inhalation and use through a nebulizer and others. When using these drugs, it is very important to remember that prolonged use may cause addiction and lead to a decrease in the desired effect.
- Observe the mode of the day. For a quick recovery and prevention of undesirable complications of the disease, the entire acute period of the illness the baby should spend at home. A visit to a kindergarten or school is not acceptable. Forced quarantine is also an excellent measure to prevent mass outbreaks of infectious diseases. During high body temperature, the child should be kept in bed.
- Discard water treatments. It is impossible to bathe a child during a high temperature. From hygiene procedures in the early days of the disease should be abandoned. Prolonged hot baths can lead to pronounced disturbances in thermoregulation. During the acute period of the disease, it is better to limit yourself to a quick hygienic shower or flushing. It is possible to bathe the baby while normalizing the body temperature and improving the well-being of the child.
- Cancel walks. You can not walk with temperate crumbs, especially in the cold season. The first days of the disease are quite difficult for the baby. In order not to cause the progression of the disease and not aggravate the course of the disease - it is necessary to limit active walks on the street for several days. Subsequently, after the normalization of the child’s well-being, it is possible to carry out walks only by carefully choosing for this purpose comfortable and warm clothing according to the season.
- Monitor nutrition. You need to carefully plan the diet of the baby. The daily caloric content of the sick baby should be 10% higher than the age norm. The main components of nutrition - protein foods and complex carbohydrates. All dishes should be prepared in a gentle way and grind. Cooked food should be at a comfortable temperature, free of spicy spices, and also well ground.
- Follow the drinking regime. The result of the inflammatory process is the formation of a huge amount of toxins and decomposition products. Accumulating in the child's body, they lead to the preservation of intoxication syndrome. Only water can remove waste substances from the body. As drinks during illness, various compotes and fruit drinks made from berries and dried fruits are perfect.
Preparations
To eliminate the adverse symptoms of pharyngitis are prescribed a variety of medications.
Anesthetic Lozenges
Anesthetizing lozenges help eliminate pain and redness in the throat. These medicines are produced in the form of various animal figures or letters of the alphabet. Such treatment will be interesting even for the smallest patient. Lozenges are used in children older than three years. At an earlier age, it is dangerous to use these medicines, as the child may swallow or choke on them.
The sprays
Sprays to relieve sore throat, in addition to the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, also have a pronounced antiseptic effect on the affected inflammatory tissues of the oropharynx. As a local antibacterial treatment can be used various nasal sprays, for example, "Isofra". They help effectively eliminate the adverse symptoms of bacterial nasopharyngitis.
Antibiotics
This is the most effective means for the treatment of bacterial pharyngitis. Currently, doctors give preference to tools with a wide spectrum of action. For the treatment of pharyngitis in children are used: "Amoxiclav», «Sumamed», «Ceftriaxone" other. Dosage, frequency and duration of use are chosen by the attending physician. Usually antibacterial therapy is prescribed for 3-7 days with the obligatory monitoring of effectiveness.
Antitussives
Appointed at the accession of complications and the spread of the inflammatory process on the trachea and bronchial tree. These remedies help eliminate pronounced coughing, and also improve sputum discharge. "Lasolvan», «Erespal», licorice root syrup - Excellent means for the normalization of bronchial respiration.
Antipyretic drugs
Should only be used when the temperature rises above 38 degrees. As antipyretic agents in children, drugs based on paracetamol and ibuprofen are widely used. Prolonged use of these drugs for prophylactic purposes is not advisable, since it may contribute to the appearance of adverse side effects.
Local Immunostimulating Therapy
Immunostimulatory drugs help to strengthen the immune response, which leads to faster recovery of the baby. In the local treatment, Derinat is an excellent drug. It is available in various forms of release. Immudon has a systemic effect, which is prescribed for use by a strictly treating physician.
How to treat at home?
It is possible to treat pharyngitis that occurs in a mild form at home. However, even in this case, the course of the disease should be closely monitored. First aid for pharyngitis is the removal of the pain component that is present when swallowing. Medicinal pastils or decoctions of herbs, which also have a good anti-inflammatory and local anesthetic effect, can help in this.
As a home treatment is perfect: chamomile, calendula, sage. For the preparation of infusion will need 2 tablespoons of crushed vegetable raw materials. This amount should be filled with 1-1.5 cups of boiling water and covered with a towel to infuse, after 30-35 minutes the infusion will be ready. Rinse the inflamed oropharynx should be 3-4 times a day one hour after meals. This simple method has positive reviews, time-tested, and allows you to quickly cure the adverse symptoms of pharyngitis.
Prevention
Strengthening immunity is an important preventive task. A strong immune system is able to cope with various pathogens entering the children's body. Active walks and games in the fresh air, healthy nutrition and good night rest contribute to the strengthening of immunity and give the child the necessary strength to combat various infections.
How to correctly determine the cause sore throat have a child, will tell Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.