Eye examination in children: norms and deviations
Eyesight helps children learn more about the world around them. However, the visual system is rather fragile, vulnerable, and it is not always possible for the child to maintain good visual perception, and for some babies it has congenital abnormalities. The development of violations contributes to many factors, both external and internal order. In this article we will tell you how to check a child’s vision, what to do if deviations are detected.
Children's vision - features
The visual system performs essential functions, giving the child an idea of the world in which he lives. Without a good vision, this picture will be incomplete, in the development of the baby “gaps” are formed. The load that falls on the organs of vision is great. And not always a small organism can cope with it successfully.
Children's vision differs from an adult in the first place in the structure of the organs responsible for the visual perception of the world. Eyeballs in children are proportionally shorter. It is for this reason that the light beams are focused in the child not on the retina, but directly behind it. Such a condition is characteristic of farsightedness, and on this basis we can safely say that physiological farsightedness is inherent in all newborns.
Eyeballs grow at the fastest rate in the first year of a baby’s life. By 12 months, the physiologically conditioned far-sightedness gradually recedes. One can speak about its complete disappearance only when the process of normal parameters of the eyeball is completed. This usually occurs between the ages of 3 and 5 years.
Vision begins to form during the period of my mother's pregnancy. And its first trimester is especially important. Most of the practically incurable or intractable congenital malformations of the organs of vision are usually associated with this period when a serious “mistake” arose in the process of laying and forming organs.
A newborn child practically does not distinguish the size and shape of objects. He sees the world as a patchwork - a cluster of more and less bright spots. The baby begins to focus his eyes at the age of 1 month, and already in 2-3 months of independent life he normally knows how to follow the moving object with his eyes.
With each subsequent month, the repository of visual images of the crumbs increases, replenishes. He masters speech, not only because he hears sounds, but also because he sees the articulation of adults and tries to mechanically repeat it. He begins to sit, crawl and get up, not only because his spine and muscular system are ready for this, but also because he sees mom and dad moving and trying to imitate them.
The optic nerve and muscles in preschool children are weak, very vulnerable.
That is why it is so important to limit watching TV, playing at the computer, as well as any strain on your eyesight. If parents are attentive and correct in the prevention of vision problems, by 6-7 years old the child’s visual apparatus becomes strong enough, the baby is ready for school and the training loads ahead.
Unfortunately, it is at this age that the first pathologies mostly begin to emerge. The child is taken for a physical examination before the school, and the optometrist reveals a particular deviation.Of course, this is not a sentence, because most of these acquired violations can be corrected successfully. But parents must make an eye examination mandatory. And to take the child to a specialist not only for medical examination, but also for his own comfort, so as not to miss the beginning disease.
How to check?
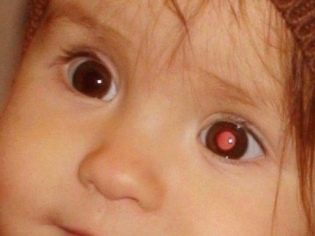
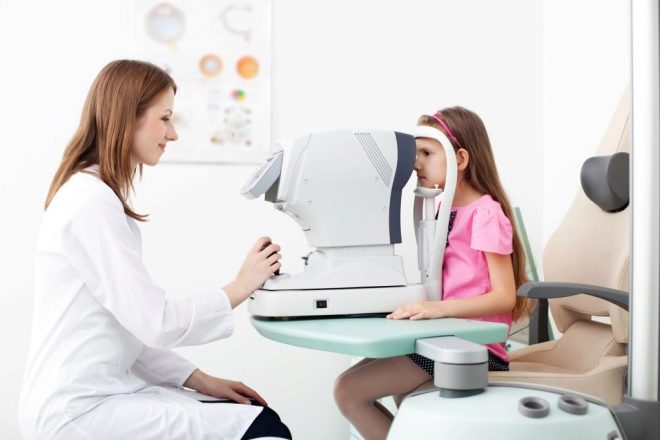
All babies, without exception, are first examined in the maternity hospital. This examination is superficial, it is carried out without special ophthalmic equipment. Such a diagnosis allows you to see gross congenital defects of the organs of vision - cataracts, retinoblastoma, glaucoma, ptosis. It is much more difficult to see such congenital pathologies as atrophy of the optic nerve and rhinopathy of prematurity on such examination. The rest of the disease on the first inspection is almost impossible to see.
Scheduled visits to an ophthalmologist are scheduled for 1 month, 3 months, 6 and 12 months. On these examinations, the doctor will be able to assess the condition of the fundus, the ability of the pupil to shrink when a beam of light hits it, and to identify some pathologies that have gone unnoticed in the hospital. In the first year of life, parents, no worse than any doctor, may suspect vision problems in their children.
The main thing - to closely monitor the child. If in 3-5 months he does not focus his gaze on a toy, if his eyes “jerk” relative to the center up and down or left-right, if by this age the baby does not recognize his relatives' faces, then this is an occasion to turn to an ophthalmologist off-schedule.
For children from 6 months to a year, doctors use special striped plates. Mum will close one eye of the child with her hand, and the doctor will show a white sign, half of which is filled with black stripes. Normally, the baby should begin to consider this particular striped part. Then the same experience is carried out with the second eye. This test gives the doctor an opportunity to evaluate whether both eyes respond to a visual object. Using a hardware method, the doctor will examine the state of the fundus, the contractility of the pupil.
In children from two years of age, a wider range of indicators of normal vision is estimated:
- the physical condition of the organs of vision;
- synchronization of eye movement following a moving object;
- the presence or absence of prerequisites for the development of strabismus;
- focusing eyes on a close and distant subject;
- depth of perception of volumetric spatial objects.
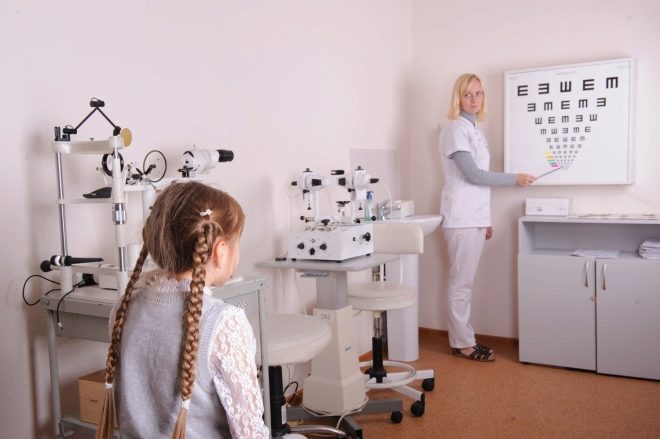
Examination of the organs of vision with the use of special equipment, as well as a series of tests, will provide answers to these questions. Polarizing glasses are used to assess the volume of the visual function, and Orlova's table is used to assess visual acuity. It does not have letters and complex objects that the child is still unable to understand due to age. There are simple images familiar to him - a duck, an elephant, a star, a Christmas tree, a teapot, an airplane, etc. At the request of the doctor to show a duck or a plane, the child will be able to respond, if not by moving his hand in the right direction, at least with the direction of his gaze.
An experienced ophthalmologist of this reaction will be quite enough to understand whether the baby sees the black and white images drawn and whether they are different in shape. If at a distance of five meters the child distinguishes the tenth line from the top, then his vision is considered to be one hundred percent. Difficulties can arise only with the names of objects, because not every kid will be able to know the outlines of a teapot or a car. Therefore, it is recommended that parents first at home discuss the table with the child in a calm atmosphere, show him all the objects and clearly name them.
At the next age stage, at school age, the child will be tested for visual acuity on the Sivtsev table. This is the most famous table in Russia, which is based on the image of letters. There are 12 lines in the table and only 7 letters that are repeated in a different order - Ш, Б, Ы, К, М, Н, and I.
An excellent result is considered if the child sees the tenth row from a distance of 5 meters from the table. A decrease and increase in the number of lines seen can tell the doctor what type of visual impairment is present in the child and what correction is needed. It should be noted that using the Sivtsev table it is impossible to establish hyperopia. It only determines the presence of myopia.
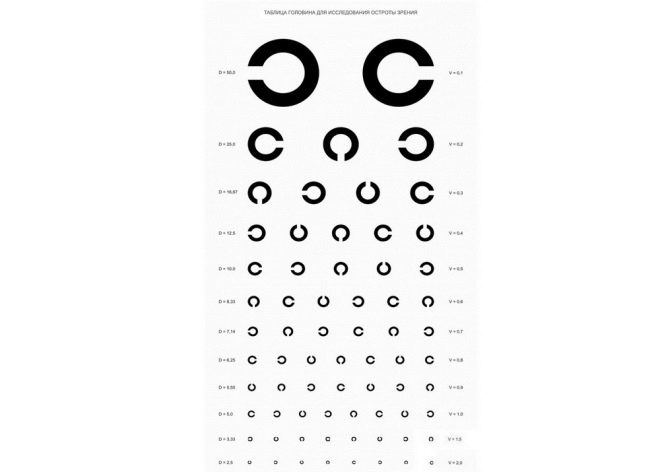
Another popular eye examination chart is the Golovin table. There are no letters, no pictures in it, only open rings turned in different directions. All rings in all 12 rows have an equal width, but with each row on top of them, they decrease in size. Opposite each line is the distance from which a person normally should see the image. It is denoted by the Latin letter D.
It is clear that the doctor on the basis of only information about the objects or letters seen by the patient, will not make a diagnosis.
For the diagnosis of eye diseases in children, additional studies are scheduled:
- Diaphanoscopy. This method makes it possible to establish the possible clouding of the internal media of the eye, as well as detect tumors or foreign bodies inside the eye. The babies are examined under general anesthesia, children of middle and high school age under local anesthesia. Survey is supposed to be only in a dark room. The diaphanoscope is pressed against the eyeball and pressed with varying strength, moving along the sclera. Thus, it is possible to see the intensity of the glow of the pupil. If the luminescence is difficult or completely absent, this may indicate a pathological hardening, a disease.
- Tonometry. This examination is also carried out in the hospital, by anesthetizing the child's organs of vision or by introducing it into a state of medication sleep. A special device - a tonometer when pressed against the eyes, gives the doctor an idea of the level of intraocular pressure.
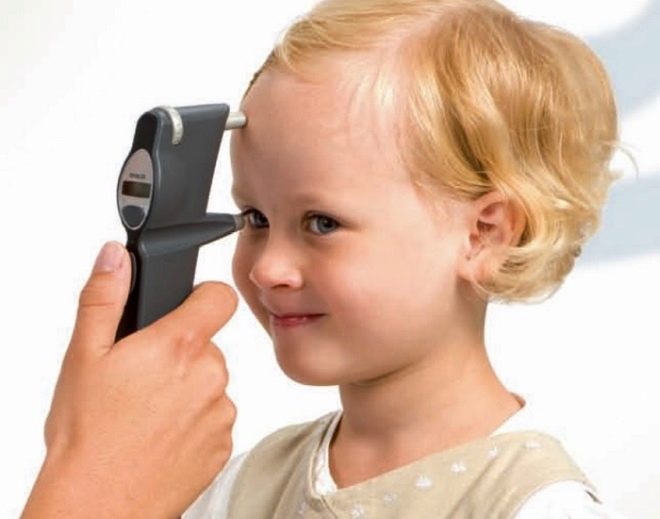
- Exophthalmometry. This method allows you to install eye protrusion from the orbit and thus diagnose lymphomas, thrombosis and hemorrhage, as well as other pathologies of the organs of vision. To do this, the ophthalmologist uses a special device that resembles a ruler.
- Aglesimetry The method allows to establish the sensitivity of the cornea. To do this, the child from the side of the temple, the doctor quietly brings to the eye a piece of cotton, extends the eyelids and lightly touches the eyeball. The degree of sensitivity is judged by the intensity of the reaction to such a touch. Sometimes doctors do not use cotton, but a special set of diagnostic hairs (according to the Samoilov method).
- Probe Vesta. This method allows you to specify the state of the lacrimal sac and the nasolacrimal duct permeability. A special contrasting compound, a collargol or a solution of fluorescein, is instilled into the child’s eyes, the nasal passages are closed with cotton swabs. If on the wool for the allotted time (no more than 7 minutes) traces of the drug appear, the tear ducts are passable.
- Fluorescein test. This method allows you to find out if the cornea is intact, if there is any mechanical damage on it. Fluorescein solution is instilled into the child’s eye, and then the eye is washed very quickly with saline. With the help of a binocular loupe and a mirror, the doctor examines the eye. The lesion sites will be stained with a contrast agent, instilled earlier.
There are other tests and methods of examination of the eye, which can be assigned to a child individually, if the initial examination has caused some concerns at the ophthalmologist.
Self check
Many parents are interested in whether it is possible to check the child’s visual acuity at home. In principle, this will not make much work, although parents will not receive much information from such a survey. Answer the main question - see if the baby, you can at home. But to establish the reason why he sees insufficiently or does not see, it is impossible in any way at home.
The child's vision from 3 months to a year can be checked with a bright toy. If a child watches her with his eyes, if at a distance of 1.5-2 meters he sees the toy in his mother’s hand and reacts to it, this is quite enough to conclude that the baby sees it as a whole.
For a child from 2 years old, mom can print Orlova's table on a regular A 4 sheet. Show and name all the items on the sheet, and only then, hanging the sheet at the level of the child’s eyes at a distance of 5 meters from him, ask what item you are showing.
It is considered normal if the child sees with each eye all the images of the tenth row (count from top to bottom). No more than 1 error is allowed. Testing is needed in a room that is well lit, best in daylight. When thinking, the child is given no more than 2-4 seconds; one eye should be closed while checking the second. It is important that the child does not squint.
A student who already knows how to read and knows the letters well can be verified in a similar way using the Sivtsev table. It can also be printed on an A 4 sheet and hung at eye level at a distance of 5 meters from the child. One eye is closed with a bandage of black opaque fabric, a piece of cardboard or plastic. Show the letters you need from the top rows, going down below. If the child calls all the letters in the tenth line without errors, he probably has no problems with his eyesight.
Home eye tests should not be done too often. It will be enough to test the child every 3-4 months. Using such techniques is especially useful if the child does not have eye pathologies at the next examination by an ophthalmologist, but there are prerequisites for the development of such ailments:
- genetic factor - mom or dad has poor eyesight;
- features of birth - if the baby was born prematurely;
- if the family has relatives suffering from glaucoma.
You should know that many visual impairments develop in childhood gradually. In this case, the baby will have no special complaints, and it will be difficult to see the symptoms until the pathology is felt, and this happens already in the final stages. Home tests will help in time to notice the warning signs. If this happens, you should not postpone the visit to an ophthalmologist.
Children's diseases
The most common eye diseases among children:
- Cataract. In this disease the lens becomes cloudy. As a result, the glow in the pupil is disturbed. The pupil does not look black, but grayish. The disease causes a variety of options for the fall of vision until its complete loss. Congenital cataract is caused by intrauterine processes of the formation of organs of vision at 8-10 weeks of pregnancy. Acquired may be due to genetically, as well as be the result of injury to the eye, the effects of radiation. It is treated mainly by surgery, and not every kind of cataract can be operated on in early childhood.
- Congenital and acquired glaucoma. At the same time, the intraocular pressure increases, the outflow of fluid from the organs of vision is disturbed. Accompanied by the loss of visual acuity, progressing, can lead to optic nerve atrophy, complete blindness. The disease is treated comprehensively - with the use of medicines and surgical intervention. In most cases, with the timely detection of the disease, laser correction can improve vision.
- Retinoblastoma. This is a malignant tumor of the retina, the manifestations are very similar to cataracts. If the disease is detected early, for example, in the maternity hospital or in the first months after the birth of a child, it is possible to preserve and restore his vision by hemming a special plate with radioactive material to the sclera. Late pathology detection involves only one form of treatment — the complete removal of the affected eye.
- Retinopathy. This is a lesion of the retina of the eyeball. The most common cause of vascular disorders is when the vessels of the membrane expand and interfere with the normal blood supply to the organs of vision. If the disease progresses, the child gradually loses sight until its complete loss. In premature babies, retinopathy is diagnosed in the maternity hospital. In full-term, it can be detected much later. The illness is treated by conservative methods and promptly.
- Atrophy of the optic nerve. When the function of the optic nerve dies out, the child essentially loses his sight, and his return and preservation is a big question. With a congenital disease, it may be complete, and vision will be completely absent. But this happens infrequently. Partial atrophy gives chances of preserving the visual function in a certain amount. Treatment depends on the location and extent of nerve damage. Most often, doctors prescribe vascular medication.
- Inflammatory ailments. Some loss of vision in a child can be observed in inflammatory processes. Such conditions include dacryocystitis (obstruction of the tear ducts and inflammation of the lacrimal sac), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes), blepharitis (inflammation of the ciliary edge of the eyelids), keratitis (inflammation of the cornea with the appearance of turbidity and ulceration). Usually, the forecasts in this case are quite optimistic - with proper and timely anti-inflammatory treatment, the disease retreats, and the visual capabilities are restored completely. In certain cases, with neglected diseases, it is impossible to fully return the function, but in 99% of cases it is possible to stop its decline.
- Nystagmus This term refers to the involuntary movements of the eyeballs. Often in the people pathology is called "eye twitching." Often, nystagmus is, in fact, a manifestation of and congenital visual weakness, and a condition associated with the defeat of some parts of the brain. Virtually no cure, but antispasmodics temporarily improve the condition of the child.
- Retinitis pigmentosa. This is a hereditary disease that is associated with gradual degenerative changes in the retina. Quite often, it is manifested by deterioration of vision as early as childhood. Correction of the disease almost can not be. There are no known methods of treatment. It continues to progress until the loss of photoreceptors becomes critical and the person is completely deprived of the opportunity to see.
- Strabismus. With complaints of possible squint, parents of babies come to the doctors more often. However, the squint is not always pathological. For young children, even with good vision, some "obliquity" is considered a variant of the physiological norm. Pathology is manifested in the fact that it is very difficult for a child to focus his gaze on a specific object, since his eyes cannot act in sync. In most cases, strabismus can be corrected with a simple operation. Often doctors use light stimulation. However, strabismus itself rarely happens, more often it accompanies such common disorders as myopia or hyperopia.
- Myopia (myopia). A nearsighted kid poorly distinguishes objects that are far away from him. The smaller the distance from which the small patient sees the object, the greater the stage of myopia. Physiologically, the process is explained by the fact that the image as a result of focusing does not appear on the retina, which is considered a normal sign of eye health, but in front of it. Myopia is most often diagnosed in children experiencing significant loads on their eyesight - in schoolchildren, for example.
To restore the child's vision in case of myopia is a quite feasible task, even though it will take a lot of time. For the correction assigned to wearing glasses, contact lenses.In some cases, surgery is possible, which can effectively improve vision. If myopia is insignificant, then it is often possible to “outgrow” it, and also to eliminate it with the help of special effective exercises.
- Hyperopia (hyperopia). With this violation, the child’s image is not projected onto the retina, but into the space behind it. If the disease is minor, then the child will see a few blurry objects that are close to him. In case of moderate and severe pathology, objects in the distance and objects near will be blurred.
A small children's farsightedness is the norm due to the peculiarities of physiology for children up to 4-5 years. It is usually not necessary to treat such hyperopia, and it passes as the eyeballs grow. If the disease develops later than this age or does not pass, then treatment with the wearing of glasses, contact lenses, and in some cases even surgery is required.
- Astigmatism. Quite rarely, this pathology is independent. Usually it acts as an accompaniment for myopia or hyperopia. Vision falls due to a violation of focusing mechanisms. This becomes possible with the curvature of the shape of the eyeball and lens. The child sees objects vague, since the image is focused in the "stereo" - a double effect. For treatment, the child is prescribed wearing glasses. A rather effective method is laser correction.
There are many other diseases, many of which are due to congenital malformations of the organs of vision, optic nerve, retina, and cornea.
Classification of violations
The classification of all deviations from normal visual function is based on the determination of the type of disorder and the degree of its development. First of all, the doctor prescribes all the necessary diagnostic measures to find out what kind of illness the child is having. Then he will set the stage.
According to the stage of violation, all patients are divided into:
- the blind (with a complete loss of vision, as well as with the loss of the ability to see, but the possibility of feeling bright light or darkness);
- partially blind (with light sensation and residual vision);
- totally blind (in the absence of vision in general and of all the possibilities of light sensation in particular);
- visually impaired (with vision from 0.05 to 0.3).
The ability to see two luminous points with a minimum distance between them - this is the criterion for assessing visual acuity. The degree of violation is determined in relation to the deviation from the norm, which is 1.0. By this criterion, it becomes clear that the popular definition of "minus 3" is nothing more than mild myopia, and "plus two" is a slight long-sightedness.
Social adaptation of children with minor disabilities is not difficult, as babies with rates of 0.3 or higher can attend regular schools, then study at universities and even serve in the army. With the established degree of violation from 0.05 to 0.3, the child will have to study in a special school for the visually impaired. When vision is less than 0.05, a child will be able to attend only specialized schools for the blind and be trained according to a special methodology.
Causes of violations
Vision in children may begin to decline as a result of the progression of certain congenital abnormalities. That is why it is so important to visit the ophthalmologist regularly and examine the baby, because the positive results of the past examination cannot indicate that the child’s vision is still in order.
Acquired vision problems can be triggered by the following reasons:
- medium eyes have lost their transparency;
- weakened eye muscles;
- the retina is affected and cannot perform its functions;
- optic nerve affected;
- there were irregularities in the cortical center of the brain.
Severe viral infections and bacterial lesions of the organs of vision can make their own “corrections” to the normal functioning of the organs of vision.Not least occupy eye injuries, as well as head injuries. Sometimes parents themselves “indulge” the development of disorders - they allow the child to watch TV for a long time, play at the computer, use gadgets.
Symptoms and signs
Each of the above diseases has its own symptoms, however, there are general symptoms of reduced vision, which attentive parents simply must pay attention to. A child with visual impairment may not complain about anything, but he will feel some discomfort anyway. Therefore, the first change in behavior and habits of the baby.
Here are just some of the signs that a child’s eyesight is declining:
- the baby begins to blink frequently, and when he is very interested in an object or a picture, he can begin to squint with one eye;
- when a child looks at an object, one of his eyes mows a little in the other direction;
- the child does not always succeed in immediately seizing the desired object, sometimes he “misses”;
- the child often complained of headaches and fatigue;
- the baby can read, draw and sculpt only for a very short time, he gets tired quickly;
- when teaching self-reading, the kid starts to drive his finger along the lines in the book;
- the child does not respond to a subject shown from a distance if he does not make any sounds;
- in the street, a child aged one and a half years and older does not see planes flying in the sky, does not notice insects;
- the child is difficult to determine the colors;
- in some situations when the child is in a hurry or emotionally excited, his coordination of movements may be disturbed.
Even if a child has three or more symptoms from this list, this is a good reason to make an unplanned visit to the office of an ophthalmologist. The earlier eye pathologies are detected, the easier it is to treat and correct them.
Treatment methods
Most of the eye diseases with the time of the detected problem can be eliminated in childhood. Modern medicine is ready to offer a lot of ways to correct the problem. The most effective and frequent in pediatrics are as follows:
- Laser Correction. This is not an operation, but a complex of therapeutic procedures. This treatment allows you to bring to normal or completely return the vision with myopia, hyperopia and some forms of astigmatism. Even serious degrees of deviation are perfectly amenable to such treatment.
- Photostimulation. With this treatment, multicolored signals with a given rhythm are sent to the child's retina. These signals stimulate the body's hidden resources for a more enhanced mode of operation of the organs of vision. This improves blood supply to the retina and the optic nerve, and also allows the brain, more precisely, that part of it, which is responsible for the perception of visual images, to form and absorb new neural connections. Such treatment is prescribed for pathologies of the optic nerve, for glaucoma and after surgery, for astigmatism and myopia.
- Magnetotherapy. This method is based on the ability of the magnetic field to beneficially affect the process of tissue regeneration. And because such physiotherapy is prescribed after surgery on the eyes, with inflammatory diseases of the eye, which led to a decrease in vision, with hemorrhages inside the organs of vision, with injuries of the cornea. Magnetic field treatment is effective for blepharitis, conjunctivitis, dystrophic changes in the retina, myopia and accommodation disturbances, as well as amblyopia.
- Electrostimulation. Stimulation of the eyesight of visually impaired children and children with minor deviations from the norm with this method is due to the impact on the optic nerve by electrical impulses. At the same time, nerve conduction is restored, the eye muscles are strengthened. Due to the impulse effect improves metabolism, metabolism in the organs of vision. This procedure is prescribed for atrophy of the optic nerve, myopia, and strabismus.
- Glasses and lenses. Quite often, children are instructed to wear glasses with certain diopters. However, the child is not always comfortable and comfortable with glasses, often you want to hide a visual defect, besides an active child can lose or break glasses. Therefore, quite often parents wonder how old they can wear contact lenses. Soft and hard contact lenses should be prescribed by a doctor who will decide on the appropriateness of wearing them at a given age on an individual basis.
In medicine, it is believed that lenses can be worn with 14 years. However, modern ophthalmologists more loyally look at this problem, and allow the wearing of soft medical lenses from 8-9 years.
- Night lenses - This is a relative method of night vision correction. They are more rigid, their task is to act on the cornea and retina during sleep, distributing the load, exerting some physical pressure. In the morning, the lenses are removed, and the vision for the whole day ahead is significantly improved. A therapeutic course with such lenses for moderate and mild forms of pathology of the organs of vision provides restoration of eye function without the use of additional methods.
Night lenses for children can be worn from 11-12 years. In any case, the question of whether it’s time for a child whose glasses have a noticeable effect on self-esteem should go to the lenses should be taken by both the doctor and the parents. After all, the use of lenses requires a child to be careful, comply with all hygiene procedures, certain skills and responsibility.
If the child is quite ready for this, then the doctor is unlikely to object to the lenses.
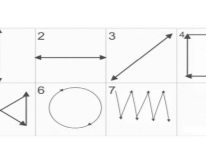
- Charging to restore vision. You can do exercises for the eyes by several methods. Most often, pediatricians and ophthalmologists advise you to engage in gymnastics with the child according to Professor Zhdanov's system. It provides for certain exercises. There are seven of them. “Watch dial”, “Snake”, “Rectangle” and other figures that need to be “drawn” by eye movement - this is only the basic part of the technique. It also includes eye massage according to Zhdanov (palming) and morning exercises for the organs of vision.
There are also separate eye charges for myopia and hyperopia. Their basic exercises are shown and explained by an ophthalmologist who treats a child.
Features of the development of children with disabilities
Mental and psychological development of a child with visual impairment has its own characteristics. Such children are more vulnerable, more sensitive to criticism. Due to the fact that often while playing or learning, they cannot see something, such children perceive their own failures very painfully.
If they are not timely provided with support and psychological help, the children may develop aggression, apathy, stubbornness and negativism.
During training and during classes, these children are more inhibited, because due to the lack of visual images, their ideas about the world are narrower than those of healthy peers. Involuntary memory suffers, which is based on receiving and fixing visual images. The motor memory also suffers, and in boys it is worse than in girls. Short-term verbal memory is well developed in such children, but long-term memory suffers greatly.
Insufficient vision also affects physical development, because it is much more difficult for a child to navigate in space. And if at the age of nine a visually impaired child experiences impaired coordination of movements by approximately 28% of the total number of movements, then at 16 years old, provided that the vision does not improve, the coordination problems reach 52%.
Psychologically, a child in 3-5 years old feels much more comfortable than at an older age, when he learns to understand the difference between himself and his peers around him. This understanding may be accompanied by reticence, unwillingness to participate in events, attend school. That is why parents, in addition to treatment, it is important to engage in the socialization of the child.
With a significant loss of vision, the child is better to attend a specialized kindergarten for children with visual impairment. They use completely different methods of development of children, aimed at a more complete formation of their worldview. Most preschool institutions of this type work according to the Plaksina program, a complex of classes for training and developing visually impaired children.
Parents are also encouraged to master this technique, as they will be at home with the child. It is important to understand that such a special child should be surrounded by large and bright things, contrasting combinations, because the color perception of most children with visual impairment persists, and it is important to maintain it. It is not necessary to demand too much from a kid with vision problems. But each of his achievements must be encouraged, the only way the child will gradually form the motivation and will to adapt, heal, and learn.
Prevention
It is necessary to engage in the prevention of eye diseases from the very first day the child is in the house. The crib must be positioned so that there are no sources of bright light, mirrors nearby, so that the child cannot constantly “look” in one direction. Access to the baby should be on all sides so that the baby is not forced to look only in one direction. Toys, mobility and everything that parents want to hang above the crib should be placed at a distance of at least 40 centimeters from the eye level of the crumbs.
At an older age, it is important that the child’s room is well lit, the baby watching his posture, not bending too low over a book or sheet of paper when drawing. A preschooler must spend enough time outdoors, play active games. Computer and TV do not benefit children’s eyesight - it’s better to limit their use to 20-30 minutes a day.
Periods of visual activity (study, drawing, reading) should always be alternated with rest periods for the eyes - a walk, a ball game, a run or a bike ride. Changing the type of activity must necessarily be a fundamental factor in the preparation of the child's day regimen. And the older the child becomes, the more important this rule.
From a very young age, you need to teach your child to observe eye hygiene - do not touch eyes with dirty hands, do not rub them, do not injure with foreign objects, do not look at bright light, including solar light, do not weld on toxic substances or alcohol-containing substances. which can be in household chemicals, cosmetics. A child should not be in smoke filled spaces for a long time.
Child nutrition should be full and rich in vitamins. Products that improve vision, must be included in the diet. These are fresh carrots, fresh parsley, sea fish, sea kale and seafood, blueberries, sweet cherries, wild rose, peaches, pumpkin, corn, potatoes, melons, nuts, honey and citrus fruits.
From the video below you will learn some of the most common vision myths. The children's doctor E. Komarovsky will tell about them.