Staphylococcal infection in children
Not only humans live on our planet. We are surrounded by a large number of various microorganisms that can cause various diseases. One of such troubles is staphylococcal infections in children.
What it is?
Coccal flora are various groups of microbes that are spherical in shape. The sizes of these microorganisms can be very different, but they can only be detected in the laboratory - using various microscopes. Perhaps the most common and most frequently encountered microbe of coccal flora is staphylococcus. People talk about it daily from television screens in health programs and write various subject articles.
Such popularity is not accidental. These microorganisms are capable of causing numerous pathologies in a child, which significantly disrupt his general condition. Researchers found staphylococci many years ago - at the end of the 19th century. Since then, the interest of scientists to the study of these microbes does not fade. This is largely due to the prevalence of various diseases that are caused by these microbes.
These microorganisms got their name by chance. When studying them in a microscope, microbes resemble peculiar clusters that are called staphylos in Greek. Not only district pediatricians and doctors of other specialties, but also many fathers and mothers are familiar with staphylococcal diseases. The prevalence of infection caused by these germs is quite high - worldwide.
Staphylococcus family is very extensive. These are several different types of microbes that differ from each other in some physiological and antigenic properties. Currently, scientists have discovered 27 variants of microbes. More than ten of them were found in patients on their mucous membranes.
Many types of microorganisms do not have pathogenic properties. These are peaceful "neighbors" who live near people.
Only three species from the entire family lead to the development of an infectious pathology. The pathogens of these microbes are determined by specific criteria, which are called pathogenicity factors. They talk about how microorganisms can lead to the development of the disease in a particular child. In pathogenic staphylococcal species, these pathogenicity factors (disease) are expressed to the maximum.
Outside, microbes are covered with a dense protective sheath, which protects them from the effects of adverse environmental factors. This feature of the morphological structure helps microorganisms to persist long enough outside the human body, without losing their disease-causing properties. As part of their cell wall contains components that cause a pronounced response from the human immune system, leading to the development of severe inflammation.
Microbes contain specific biologically active substances - hemolysins. These molecules can have a destructive effect on human red blood cells, they can even damage leukocytes. In the course of their vital activity, microbes secrete a large amount of toxic products that have a strong inflammatory effect on the affected children's body.
All pathogenic properties of the microbe and cause a variety of different adverse symptoms that it can cause in sick children. Such a variety of different pathogenic properties makes staphylococcus aureus. one of the most dangerous microbes that are in the external environment.
Three species are considered the most dangerous pathogens of this family. The first - Staphylococcus aureus. Doctors also call this subspecies staphylococcus aureus. In the medical environment adopted various abbreviations and abbreviations.
Doctors use S to designate staphylococcal flora. Usually, this labeling is used for all laboratory tests that are carried out to establish the bacterial flora in various diseases.
This microbe got its name by chance. When viewed in the microscope, you can see that it has a light yellow color. This microbe does not give any concessions - both adults and kids. The combination of various aggressive properties leads to the fact that it causes a variety of clinical variants of the disease and is characterized by a multiplicity of lesions. In adverse environmental conditions, these microbes can persist for a very long time.
The second (no less aggressive) microbe is called epidermal or S. epidermidis. It is the main cause of various infectious skin pathologies. Kids get these infections quite often. It should be noted that both boys and girls are susceptible to infection.
This type of microorganism is quite peaceful. It can be present on the skin in completely healthy babies, without causing any adverse symptoms. The development of clinical signs leads to a strong weakening of the immune system and the depletion of the body after viral or other bacterial infections.
Quite often, microorganisms are transmitted through contaminated hands, medical instruments and during the dental treatment of diseased teeth.
The third type of microbes that can lead to the development of the disease is called saprophytic or staphylococcus saprophyticus. It is important to note that it rarely causes infection in babies. Most often, this pathogen is responsible for the development of pathologies in adults. Women with this sick much more often. Infection is manifested in them by the development of severe inflammation in the urinary tract. Staphylococcal infection is extremely contagious, and you can get infected in a variety of ways. The course of the disease depends on many factors.
These three types of bacterial infections can cause a child of any age. Cases of this infection are quite common in newborn babies and in adolescence.
How is it transmitted?
High spread of microbes in the environment should lead to daily mass outbreaks of infection - or even lead to a pandemic. However, this does not happen. This is explained by the fact that the immune system normally functions every second in the body. Immunity helps to prevent all infections, of which there are many.
Doctors say that the disease begins in babies who, for whatever reason, have significantly decreased the performance of the immune system. The high-risk group includes children who often suffer from colds or have immunodeficiency states of varying severity.
A variety of reasons can lead to a decrease in immunity. Quite often, a provoking factor in the development of staphylococcal infection in babies is a strong hypothermia or overheating, as well as severe emotional stress.
An infection can get into a weakened children's body in a variety of ways.Staphylococci are such universal microorganisms that can live and multiply in any internal organs of a person. The most common method of infection is airborne. In this case, microbes get on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and lead to the development of adverse symptoms.
Contact-household method of infection also often leads to infection. staphylococcal flora. It is especially pronounced in crowded teams. Kids who lead an active lifestyle and attend various educational institutions, sports clubs, are often susceptible to infection by various types of microbes.
Doctors say that germs can even get through the conjunctiva of the eye or the umbilical wound.
Many parents are interested in the probability of infecting babies during the prenatal period. This option is also possible. Pathologies of pregnancy, occurring in violation of the integrity of the placenta or various violations of the placental blood flow, only increase the risk of intrauterine infection of the future baby in the womb of the mother. If a pregnant woman falls ill with a staph infection, then it contributes to the transmission of pathogenic microbes to her baby.
The severity of symptoms depends on the initial state of the child’s immune system. If a baby has had a staph infection a few years ago, and its immune system is functioning well, the risk of a new infection in a child is noticeably reduced. Children with low immunity can get sick several times throughout their lives. Premature babies get sick quite often.
Severe disease is accompanied by the active spread of microorganisms. This happens through systemic blood flow. Pathogenic microbes quite quickly get into different internal organs, causing a strong inflammatory process there. Such a course of the disease is accompanied, as a rule, by the appearance in the infected child of many of the most adverse symptoms.
The nature of violations in staphylococcal lesions can be very different. The presence of various hemolysins in the microbial structure leads to the fact that they have a pronounced damaging effect on various cells. This is usually manifested by the development of ulcerative or necrotic areas. Such "dead" zones are characterized by complete or partial destruction of epithelial cells, which form the mucous membranes of the internal organs.
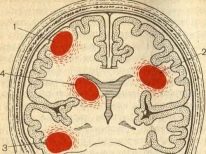
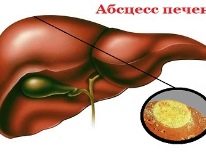
The most severe course of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of purulent infiltrates. Localized forms of such pathologies are called abscesses in medicine. The most dangerous localization of these clinical options - the brain, kidneys, liver and other vital internal organs.
Symptoms
Staph infection manifests itself in different ways. The variety of clinical signs depends largely on the type of microbes that have entered the children's body and led to the appearance of adverse symptoms. The flow can be both light and rather heavy. Without appropriate treatment, very dangerous complications or long-term effects of the disease can occur.
Staphylococcus can cause both local and very common forms of the disease. Massive lesions are also called generalized variants of the disease. Usually they develop in a sick child with severe illness.
It is important to note that local forms can also turn into generalized ones as the disease progresses and without prescribing the correctly chosen therapy.
Staphylococcal infection in children can occur with the appearance of adverse symptoms or be completely asymptomatic. In the latter case, the disease can only be detected by special diagnostic tests. They are carried out in laboratory conditions.In some situations, there may be an erased course in which the adverse symptoms of the disease appear slightly.
The incubation period for infection with staphylococci may be different. It usually ranges from 3-4 hours to a couple of days.
In some babies with marked impairments of the immune system, adverse symptoms of the disease can occur quite quickly.
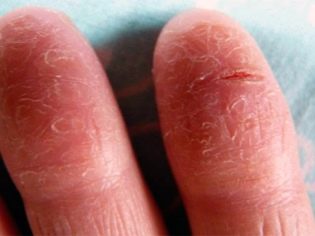
Doctors note that the shortest incubation period is in case of staphylococcal affection of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. This infection often spreads through the skin. In the inflammatory process is often involved and subcutaneous tissue. On the skin there are specific signs that parents find when they examine their baby.
The affected areas have a high tendency to suppurate. Weakening of immunity or exacerbation of chronic pathologies may contribute to the spread of the process. In some cases, the disease becomes a generalized form.
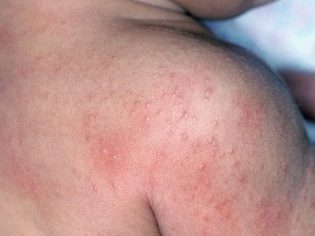
Quite often, the pathology is manifested by various folliculitis, furunculosis, pyoderma, phlegmon, hydradenitis, the appearance of watery pimples. In this case, structural skin elements are also affected - sweat and sebaceous glands.
Skin lesions
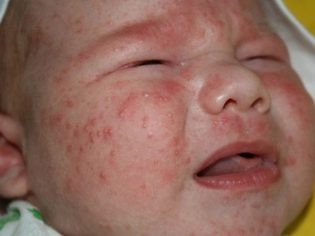
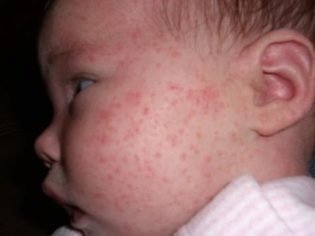
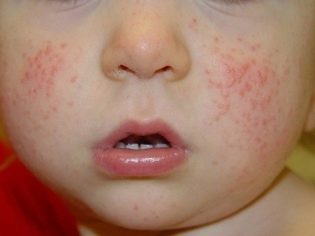
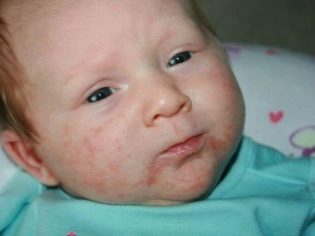
Dermatitis is also not a very rare manifestation of staphylococcal infection. The affected skin gets a bright red color, become hot to the touch. At the peak of the disease, various blisters appear on the skin, filled with pus that looks like a bright yellow liquid.
In severe cases, various ulcers appear on the skin. They look like highly inflamed areas. In the central part of such skin formations visible accumulation of a large amount of pus.
The edges of the wound are usually loosened, when touched, they bleed easily. The wound surface can be the most sizes: from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters. In some cases, the inflamed areas merge together, forming bizarre forms.
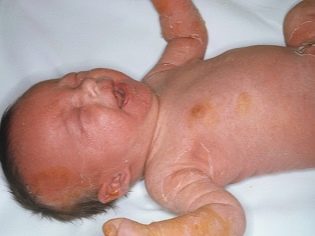
In infants in the first months of life, the most dangerous, most severe forms of the disease are quite common. These include exfoliative dermatitis Ritter, staphylococcal pemphigus, bacterial pustulosis. They are characterized by generalized lesions with the development of strong necrosis (death) of epithelial cells. These forms of the disease occur predominantly in premature babies or children who have had multiple anatomical defects in the structure of internal organs at birth.
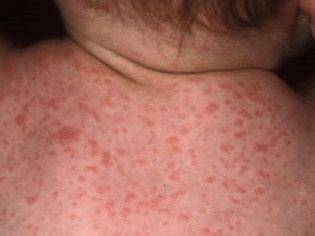
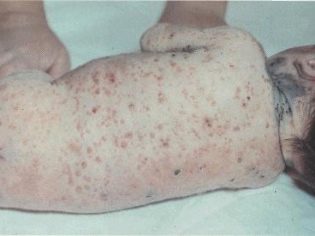
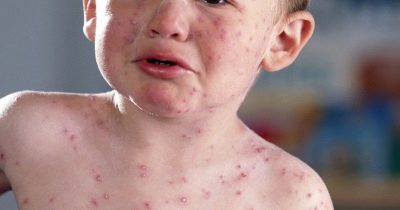
In some cases, when infected with these microbes, a sick child develops symptoms of scarlet-like syndrome. As a rule, it is manifested in the baby by the appearance on the skin of multiple skin rashes.
The rash may spread throughout the body. Its predominant localization is the lateral surfaces. Skin elements are usually quite small.
Skin rash may appear, as a rule, 2-4 days after the onset of the first adverse symptoms of the disease. After their disappearance, numerous dry areas remain on the skin with pronounced desquamation. The appearance of a rash significantly worsens the health of the sick child. The severity of intoxication in this case is very intense.
Mucous membrane lesions
The skin is not the only "favorite" localization for the life of staphylococci. They also actively settle on various mucous membranes. Once in the upper respiratory tract, microbes cause bacterial forms of pharyngitis, laryngitis and tracheitis. Staphylococcus breeding in the nose leads to the development of resistant rhinitis. A runny nose with this variant is usually debilitating, discharge from the nasal passages is yellow or have a greenish tint.
Violation of the gastrointestinal tract
Damage to the organs of the gastrointestinal tract leads to symptoms that are typical for intestinal dysbiosis.Babies have a broken chair. In some cases, this is manifested by the appearance of persistent constipation or severe diarrhea in a child.
Much less often they alternate. Bacterial infection is accompanied by the appearance of non-specific abdominal pain, which can be localized in different areas.
Eye damage
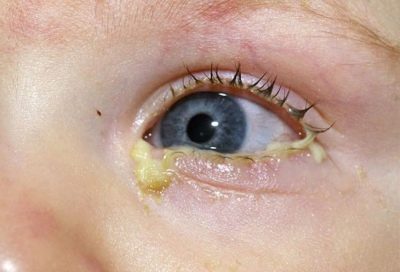
Staphylococcal conjunctivitis is a disease that develops when microbes get on the delicate conjunctiva of babies or under the folds of the eyelids. In this case, the baby has a strong tearing. As part of the secretion of secretion is often present pus. It is difficult for a baby to open his eyes, sunlight getting on an irritated conjunctiva leads only to an increase in the pain symptom.
Angina
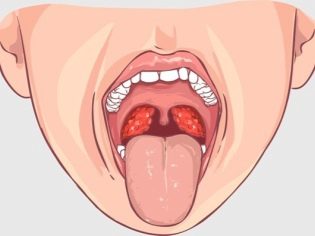
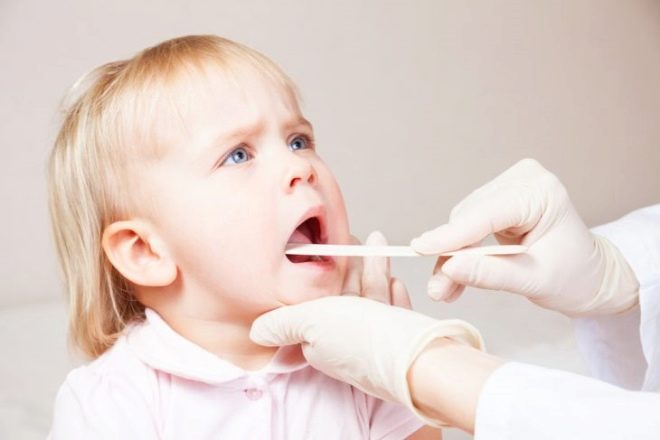
This is a fairly common form of this bacterial infection. It is characterized by the formation of plaque on the affected tonsils. In its color it may be yellow or with a gray tint. Quite often, a sick child has a follicular appearance of acute tonsillitis. The flow of such a sore throat in a baby is quite heavy, it is accompanied by a strong fever and the appearance of a pronounced intoxication syndrome.
It is important to note that staph infection quite often joins viral pathologies. The high-risk group includes children who often suffer from catarrhal diseases or have severe disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs. Such complications appear in children suffering from diabetes or having complicated cardiovascular diseases.
Spread on the respiratory system
Bacterial tracheitis caused by pathogenic staphylococci, proceeds very hard and has a tendency to spread to the organs that are located nearby. A few days later, the small bronchioles, and then the large bronchi, are involved in the inflammatory process. With an unfavorable course of the disease, a staph infection can lead to the development of bacterial pneumonia. Treatment of inflammation of the lung tissue is usually carried out in a hospital.
Stomatitis
In the youngest patients, quite often stomatitis caused by this bacterial flora. It is manifested by pronounced redness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the development of severe inflammation next to the tooth holes.
Quite often, the tongue is also involved in the inflammatory process. He becomes bright red, coated with gray or yellowish bloom, which is poorly removed with a spatula. Severe stomatitis contributes to the appearance of pain when swallowing food.
The severity of intoxication syndrome in various staphylococcal infections may be different. Usually, all forms of this disease occur in children rather hard. They are accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature. The child becomes moody and drowsy, refuses to eat. The baby may have a headache, which is aggravated during staphylococcal meningitis.
Diagnostics
A clinical examination carried out by the pediatrician during the reception can determine the presence of purulent foci on the child’s body or reveal the characteristic signs of mucosal lesions. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a whole range of additional diagnostic tests. These analyzes allow to exclude other diseases occurring with similar symptoms - for example, caused by hemolytic streptococcus.
The most common study to identify pathogens in the blood is considered microbiological test. The essence of this test is a specific immune reaction between a laboratory staphylococcal species obtained in laboratory conditions and biological material.The increased concentration of specific protein-specific immune antibody molecules in the blood indicates the presence of the pathogen in the child’s body.
Microbes can be detected in a variety of biological materials. There are diagnostic methods to detect microorganisms in the feces and urine. During the illness, several studies can be conducted that allow doctors to determine the dynamics of the course of the disease.
Treatment
Therapy for staphylococcal infection is carried out for children with adverse symptoms of the disease. Do not "treat" tests! Many types of staphylococcal flora inhabit completely healthy mucous membranes. When the child’s well-being deteriorates and clinical signs appear, specific treatment should be initiated.
Doctors of several specialties at once deal with the treatment of staphylococcal pathologies, since various internal organs are affected. In the appointment of treatment has its own characteristics. For each particular case, an individual therapeutic scheme is selected, which is built taking into account the characteristics of each sick child.
The basis of the treatment of this disease is the intake of antibacterial drugs. Parents should be aware that giving the sick child antibiotics need as many days as prescribed by the doctor. There should be no independent cancellation of these drugs.
Over time, staphylococcal flora (against the background of the frequent use of various antibacterial drugs) becomes insensitive to their effects. This leads to the fact that there are resistant forms of microorganisms, which powerful drugs simply cease to act.
During antibiotic therapy is very It is important to comply with the prescribed dosage and frequency of use of drugs. Typically, for the treatment of these bacterial infections, clavulanic acid-protected penicillins and a group of last-generation cephalosporin preparations are used. The use of the latest generation of antibiotics and macrolides is extremely rare, since it can lead to the development of microbial resistance to these drugs.
Various symptomatic treatment is used to eliminate the associated symptoms of the disease. It includes the appointment of anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antitussive and fortifying drugs.
During the acute period of illness, doctors recommend the baby to be in bed. The expansion of the regime is carried out gradually, as the restoration of the lost forces.
The specific treatment of severe forms of the disease is purpose anti-staphylococcal drugs. These include plasma, bacteriophages, toxoids or immunoglobulins. All these drugs have a highly targeted destructive action in relation to the staphylococcal flora. Such drugs are prescribed only under strict medical indications, which are established by the attending physician.
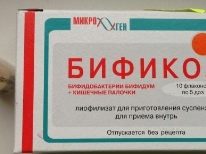
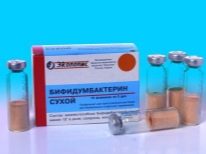
Treatment of the emerging bacterial pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out using complex drugs containing viable lacto-and bifidobacteria in their composition. These funds are usually written out for long-term use. It may take an average of 4-6 months to normalize the beneficial intestinal microflora lost over the period of the disease. "Bifidumbakterin", "Bifikol", "Atsipol"," Linex " and other drugs provide a positive effect and help restore normal digestion in babies.
In some situations, even after medical treatment, the baby has complications of the disease. As a rule, in such cases it is required to conduct already intensive complex therapy, which is carried out only in the hospital. Local purulent processes caused by staphylococcal flora can be treated with surgery.The need for such treatment is determined by the pediatric surgeon.
Prevention
The goal of all preventive measures for staph infections is to reduce the risk of possible infection with highly pathogenic species of these microorganisms. For this, doctors recommend that all children attending educational institutions must observe an anti-epidemic regime.
After visiting public places the child should wash their hands thoroughly with soap. For parents should keep the kids. To date, specific prevention of infection, including vaccinations, unfortunately, has not been developed.
How to deal with a staph infection if you find it in your baby? Dr. E.O. will tell about the causes and prevention of this disease. Komarovsky.