What to do if a child has hard, heavy or fast breathing, wheezing?
Any changes in the child's breathing immediately become noticeable to parents. Especially if the frequency and nature of breathing changes, there are extraneous noises. About why this can happen and what to do in each specific situation, we will discuss in this article.
Special features
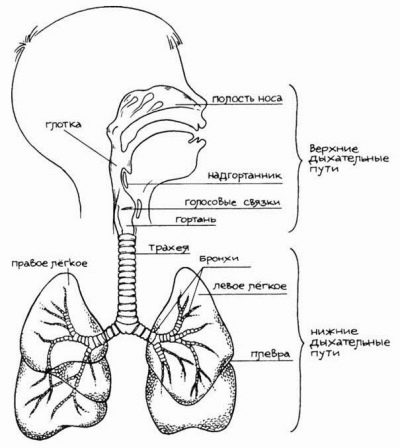
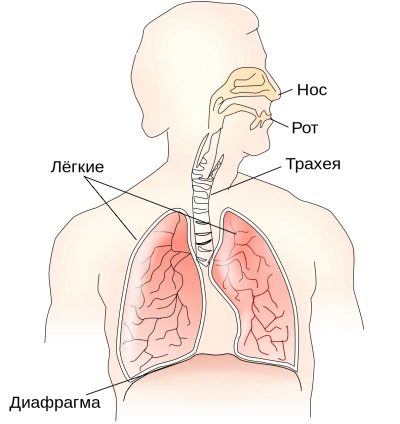
Children do not breathe like adults. First, babies breathing is more superficial, shallow. The volume of inhaled air will increase as the child grows, in babies it is quite small. Secondly, it is more frequent, because the volume of air is still small.
Children's airways are narrower, they have a certain deficiency of elastic tissue.
This often leads to a violation of the excretory function of the bronchi. With a cold or a viral infection in the nasopharynx, larynx, in the bronchi, active immune processes begin to fight the penetrating virus. It produces mucus, the task of which is to help the body cope with the disease, “bind” and immobilize alien “guests”, and stop their progress.
Due to the narrowness and inelasticity of the respiratory tract outflow of mucus is difficult. Most often, problems with the respiratory system in childhood are experienced by children born prematurely. Due to the weakness of the entire nervous system in general and the respiratory system in particular, they have a significantly higher risk of developing serious pathologies - bronchitis, pneumonia.
Babies breathe mainly "belly", that is, at an early age because of the high location of the diaphragm abdominal breathing prevails.
At the age of 4, chest breathing begins to form. By age 10, most girls breathe through their breasts, and most boys have diaphragmatic (abdominal) breathing. A child’s need for oxygen is much higher than the needs of an adult, because babies are actively growing, moving, they have much more transformations and changes in their bodies. To provide all organs and systems with oxygen, the baby needs to breathe more often and actively, for this purpose there should be no pathological changes in his bronchi, trachea and lungs.
Any even a minor, at first glance, cause (nose blocked, sore throat, tickling appeared), may complicate children's breathing. During illness, it is not so much the abundance of bronchial mucus that is dangerous, as its ability to thicken quickly. If, with the nose stuffed, the baby was breathing with his mouth at night, then with a high degree of probability, the next day the mucus will begin to thicken and dry out.
Not only the disease, but also the quality of the air it breathes can disturb the child’s external breathing. If the climate in the apartment is too hot and dry, if the parents turn on the heater in the children's bedroom, then there will be many more breathing problems. Too humid air, too, will not benefit the baby.
Oxygen deficiency in children develops faster than in adults, and for this it is not necessarily the presence of some serious illness.
Sometimes there is a fairly small swelling, minor stenosis, and now hypoxia develops in the toddler. Absolutely all departments of the children's respiratory system have significant differences from the adult. This explains why children under 10 years of age most often suffer from respiratory ailments.After 10 years, the incidence is declining, with the exception of chronic pathologies.
The main problems with breathing in children are accompanied by several symptoms that are understandable to each parent:
- the child's breathing became hard, noisy;
- the baby breathes heavily - inhaling or exhaling is given with visible difficulty;
- respiratory rate has changed - the child began to breathe less often or more;
- wheezing appeared.
The reasons for such changes may be different. And only a doctor in tandem with a specialist in laboratory diagnostics is able to establish the true ones. We will try to explain in general terms what causes most often underlie the change in breathing in a child.
Varieties
Depending on the nature, experts distinguish several types of difficulty breathing.
Hard breathing
Hard breathing in the medical sense of this phenomenon is such a breathing movement in which the breath is well heard, and the exhalation is not. It should be noted that harsh breathing is the physiological norm for young children. Therefore, if a child does not have a cough, runny nose or other symptoms of the disease, then you should not worry. The baby breathes within the age norm.
The hardness depends on the age - the younger the peanut, the harder his breath. This is due to the insufficient development of the alveoli and weakness of the muscles. The baby usually breathes loudly, and this is quite normal. In most children, breathing is softened by 4 years, for some it can remain quite hard up to 10-11 years. However, after this age, the breathing of a healthy child always softens.
If a child has noise on expiration accompanied by cough and other symptoms of the disease, then we can talk about a large list of possible illnesses.
Most often, such breathing accompanies bronchitis and bronchopneumonia. If exhalation is heard as clearly as inhalation, then you should definitely consult a doctor. Such harsh breathing will not be the norm.
Hard breathing with a wet cough is characteristic of the recovery period after acute respiratory viral infection. As a residual phenomenon, such breathing indicates that not all excess sputum has left the bronchi. If there is no fever, runny nose or other symptoms, and breathing is accompanied by a dry and unproductive cough, maybe it's an allergic reaction to some antigen. With the flu and acute respiratory viral infections at the very initial stage, breathing can also become harsh, but the accompanying symptoms will be a sharp increase in temperature, a clear liquid discharge from the nose, possibly redness of the throat and tonsils.
Hard breath
With heavy breathing, breathing is usually difficult. Such difficulty breathing causes the greatest concern to the parents, and it is not at all in vain, because normally a healthy child should breathe in audibly, but light, it should be given to the child without difficulty. In 90% of all cases of difficulty breathing when breathing in, the cause lies in a viral infection. These are all familiar flu viruses and various acute respiratory viral infections. Sometimes heavy breathing accompanies serious illnesses such as scarlet fever, diphtheria, measles and rubella. But in this case, changes in breath will not be the first sign of the disease.
Usually, heavy breathing does not develop immediately, but as an infectious disease develops.
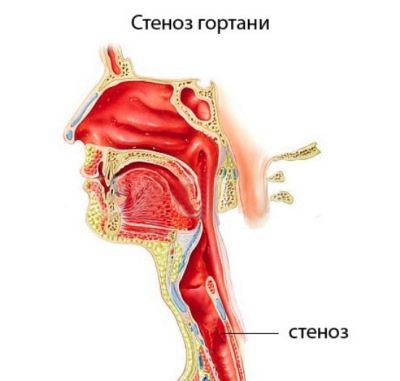
With the flu, it may appear on the second or third day, with diphtheria - on the second, with scarlet fever - by the end of the first day. Separately, it is necessary to say about this reason for difficulty in breathing, as croup. It can be true (for diphtheria) and false (for all other infections). Intermittent breathing in this case is due to the presence of stenosis of the larynx in the region of the vocal folds and in nearby tissues. The larynx narrows, and depending on the degree of the croup (how narrowed the larynx is) depends on how difficult it is to inhale.
Severe intermittent breathing is usually accompanied by shortness of breath. It can be observed both under load and at rest.The voice becomes hoarse, and sometimes disappears completely. If the child convulsively, jerks breaths, while breathing is clearly difficult, well heard, when trying to breathe in the baby, the skin over the clavicle sinks a little, you should immediately call an Ambulance.
The croup is extremely dangerous, it can lead to the development of instant respiratory failure, suffocation.
It is possible to help a child only within pre-medical first aid - open all the windows, provide fresh air (and do not be afraid that it is winter outside!), Put the child on his back, try to calm him down, because too much excitement makes the breathing more difficult and aggravates the situation. All this is done from that period of time, while an ambulance team is going to the kid.
Of course, it is useful to be able at home to self-rudely intubate the trachea with improvised means, in case of suffocation of the child, this will help save his life. But not every father or mother can, having overcome fear, make a cut in the area of the trachea with a kitchen knife and insert the nose from a porcelain teapot into it. This is how intubation is done for health reasons.
Breathing along with a cough in the absence of fever and signs of a viral disease may indicate asthma.
General lethargy, lack of appetite, shallow and shallow breaths, pain when trying to inhale more deeply may indicate the onset of a disease such as bronchiolitis.
Breathing fast
A change in respiratory rate is usually in favor of an increase. Rapid breathing is always a clear symptom of a lack of oxygen in the child’s body. In the language of medical terminology, fast breathing is called tachypnea. A failure in the respiratory function can manifest itself at any time, sometimes parents may notice that the infant or newborn often breathes in sleep, while the breathing itself is shallow, it is similar to what happens in a dog that is “out of breath”.
Detect the problem without much difficulty can any mother. but You should not try to independently find the cause of tachypnea, this is the task of specialists.
The rates of respiratory rate for children of different ages are as follows:
- from 0 to 1 month - from 30 to 70 breaths per minute;
- from 1 to 6 months - from 30 to 60 breaths per minute;
- from six months - from 25 to 40 breaths per minute;
- from 1 year - from 20 to 40 breaths per minute;
- from 3 years old - from 20 to 30 breaths per minute;
- from 6 years old - from 12 to 25 breaths per minute;
- from 10 years and older - from 12 to 20 breaths per minute.
The technique of counting the frequency of breathing is quite simple.
It’s enough for mother to arm herself with a stopwatch and put a hand on the child’s chest or tummy (this depends on age, because abdominal breathing prevails at an early age, and at an older age, it can change in the chest. It’s necessary to calculate the number of times the child breathes will fall) in 1 minute. Then you should check with the age norms presented above and make a conclusion. If there is an excess, this is an alarming symptom of tachypnea, and you should consult a doctor.
Quite often, parents complain of frequent intermittent breathing in their baby, unable to distinguish tachypnea from banal dyspnea. To make it in the meantime rather simply. It should be carefully observed whether the inhalations and exhalations of the baby are always rhythmic. If frequent breathing is rhythmic, then we are talking about tachypnea. If it slows down and then accelerates, the child breathes unevenly, then we should talk about the presence of shortness of breath.
The causes of increased breathing in children are often neurological or psychological.
Strong stress, which the crumb can not because of age and insufficient vocabulary and figurative thinking to express in words, still needs to exit. In most cases, children begin to breathe more often. It is considered physiological tachypnea, there is no danger of violation.The neurological nature of tachypnea should be considered first of all, remembering which events preceded the change in the nature of inhalation and exhalation, where the baby was, who he met, had he not had a strong fright, resentment, hysteria.
The second most common cause of rapid breathing lies in respiratory diseasesfirst of all in bronchial asthma. Such periods of frequent breaths are sometimes harbingers of periods of shortness of breath, episodes of respiratory failure typical of asthma. Frequent fractional inhalations are often accompanied by chronic respiratory illnesses, for example, chronic bronchitis. However, the increase does not occur during remission, but during exacerbations. And along with this symptom, the baby has other symptoms - cough, fever (not always!), Loss of appetite and general activity, weakness, fatigue.
The most serious reason for frequent breaths and exhalations lies in diseases of the cardiovascular system. It happens that the pathology of the heart can be detected only after the parents bring the baby to the reception about the increase in respiration. That is why in case of violation of the frequency of breaths, it is important to check the child in a medical institution, and not to self-medicate.
Hoarseness
Bad breathing with wheezing always indicates that there is an obstruction in the airways for the passage of a stream of air. On the way of air, there may be a foreign body that the child inadvertently inhaled, and dried bronchial mucus, if the baby was coughed incorrectly, and a narrowing of any part of the respiratory tract, the so-called stenosis.
The wheezing is so varied that you need to try to give the right characteristic of what the parents hear in the performance of their own children.
The wheeze is described by duration, tonality, by coincidence with inhalation or exhalation, by the number of tones. The task is not easy, but if you successfully cope with it, then you can understand what exactly the child is sick.
The fact is that wheezing for various diseases is quite unique, peculiar. And they can really tell a lot. So, wheezing (dry rales) may indicate a narrowing of the airway, and wet rales (noisy gurgling accompaniment of the breathing process) - the presence of fluid in the airways.
If the obstruction has arisen in the bronchus wide in diameter, the tone of the rattle is lower, bass, and deaf. If the bronchi are thin, the tone will be high, with a whistle on the exhale or inhale. When inflammation of the lungs and other pathological conditions leading to changes in the tissues, wheezing is noisier, loud. If there is no severe inflammation, the child wheezes more quietly, more muffledly, sometimes hardly distinguishable. If the child wheezes, as if sobbing, it always indicates the presence of excess moisture in the airways. Experienced doctors can diagnose the nature of wheeze by ear with a phonendoscope and percussion.
It happens that wheezing is not pathological. Sometimes they can be seen in an infant up to one year old, both in the state of activity and in the state of rest. The kid breathes with a bubbling "accompaniment" and also noticeably "grunts" at night. This is due to congenital individual narrowness of the airways. Such wheezing should not disturb parents if there are no accompanying painful symptoms. As the child grows, the airways will grow and expand, and the problem will disappear by itself.
In all other situations, wheezing is always an alarming sign, which necessarily requires an examination by a doctor.
Rattles are wet, gurgling in varying degrees of severity may accompany:
- bronchial asthma;
- cardiovascular problems, heart defects;
- lung diseases, including edema and tumors;
- acute renal failure;
- chronic respiratory diseases - bronchitis, obstructive bronchitis;
- SARS and flu;
- tuberculosis.
Dry whistling or barking rales are more common in bronchiolitis, pneumonia, laryngitis, pharyngitis, and may even indicate the presence of a foreign body in the bronchi. In the formulation of the correct diagnosis helps the method of listening to wheezing - auscultation. Each pediatrician owns this method, and therefore a child with wheezing must be shown to the pediatrician in order to determine the possible pathology in time and begin treatment.
Treatment
After the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment.
Hard breathing therapy
If there is no temperature and there is no other complaint, except for the rigidity of breathing, then there is no need to treat the child. Enough to ensure him a normal motor mode, it is very important that the excess bronchial mucus out as quickly as possible. It is useful to walk on the street, play in the fresh air in active and active games. Breathing usually returns to normal within a few days.
If harsh breathing is accompanied by cough or fever, it is imperative that the child be shown to a pediatrician to rule out respiratory diseases.
If the disease is found, treatment will be aimed at stimulating bronchial secretion. For this, the baby is prescribed mucolytic drugs, abundant drinking, vibration massage.
How the vibration massage becomes, look in the following video.
Hard breathing with a cough, but without respiratory symptoms and fever needs a mandatory consultation with an allergist. It is possible that the cause of the allergy can be eliminated by simple household actions — wet cleaning, airing, eliminating all household chemicals based on chlorine, and using a hypoallergenic children's laundry detergent when washing clothes and linen. If this does not work, then the doctor will prescribe antihistamines with calcium.
Measures with heavy breathing
When a viral infection is breathing, special treatment is not needed, since the underlying disease must be treated. In some cases, antihistamines are added to standard prescriptions for influenza and ARVI, since they help to relieve internal edema and facilitate breathing easier for the child. In case of diphtheria croup, a child is hospitalized without fail, since he needs the prompt introduction of anti-diphtheria serum. This can be done only in the hospital, where, if necessary, the baby will be provided with surgical assistance, the connection of a ventilator, the introduction of antitoxic solutions.
False croup, if it is not complicated, and the child is not an infant, may be allowed to heal at home.
For this, it is usually prescribed courses of inhalation with drugs. Medium and severe croup require hospital treatment with glucocorticosteroid hormones (“Prednisolone"Or" Dexamethasone "). The treatment of asthma and bronchiolitis is also carried out under medical supervision. Severe - in the hospital, in the light - at home, subject to compliance with all the recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor.
Increased rhythm - what to do?
Treatment in the case of transient tachypnea, which is caused by stress, fear or excessive impressionability of the child, is not required. It is enough to teach the child to cope with their emotions, and over time, when the nervous system becomes stronger, the attacks of frequent breathing will disappear.
You can stop another attack with a paper bag. It is enough to offer the child to breathe into it, breathing in and out. At the same time it is impossible to take air from the outside, you only need to inhale what is in the bag. Usually a few such breaths are enough to make the attack retreat. The main thing is to calm down and calm the child.
If the increased rhythm of inhalation and exhalation has pathological causes, the main disease should be treated. Cardiovascular problems of the child are engaged pulmonologist and cardiologist. A pediatrician will help with asthma. ENT doctor, and sometimes an allergist.
Treatment of wheezing
None of the doctors deals with the treatment of wheezing, since there is no need to treat them. Treatment should be the disease, which was the cause of their appearance, and not a consequence of this disease. If wheezing is accompanied by a dry cough, to alleviate the symptoms, along with the main treatment, the doctor may prescribe expectorant drugs, which will facilitate the rapid transition of dry cough to productive with sputum.
If wheezing caused stenosis, narrowing of the respiratory tract, the child may be prescribed drugs that relieve swelling - antihistamines, diuretics. With a decrease in edema, wheezing usually becomes quieter or disappears altogether.
Whistling wheezes that accompany abrupt and difficult breathing are always a sign that the child needs emergency medical care.
Any combination of character and tonality of wheezing against the background of high temperature is also a reason to hospitalize a child as soon as possible and entrust his treatment to professionals.
What parents can not do?
Remember:
- You can not try to cure a child with a changed nature of breathing folk remedies on their own. This is dangerous for the reason that herbs and substances of natural origin used in alternative medicine can cause a strong allergy in a child. And with allergic changes in respiration, with croup, with stenosis of any part of the respiratory tract, this can be fatal.
- Even if there is an inhaler and nebulizer at home, Do not do inhalation on their own, without a doctor's prescription. Steam inhalations do not always benefit the child; sometimes they do harm. Nebulizer should generally be used only on the recommendation of a specialist, since this device is designed to create a fine suspension of drugs, and not to spray chamomile or essential oil decoction. Children suffer more from inappropriate and abnormal inhalations than from bronchitis or pharyngitis.
- You can not ignore the symptoms impaired breathing and respiratory failure, even if there are no other obvious signs of the disease. In many cases, a child even with severe pathologies can be helped if a doctor is called in time.
Infant mortality as a result of the development of respiratory failure, according to statistics, takes place mainly after late appealing to a medical institution.
- There are much more pathological reasons for the appearance of difficult or hoarse breathing in nature than natural and harmless causes, and therefore you should not hope that everything will "resolve" by itself. Waiting for a doctor or an ambulance can not leave a child without a minute without attention. The harder and harder the breath, the more vigilant the control must be.
- Do not use any medication without the consent of your doctor. This is especially true of widely advertised sprays and aerosols, which, according to TV commercials, “instantly facilitate breathing.” Such drugs can cause an instant spasm of the larynx in children who have not yet turned 3 years old.
- Another common parental mistake, which is costly for children, is to give when coughing appears. "Something coughing." As a result, when a child coughs, the child is given antitussives, which suppress the work of the cough center in the brain, and this leads to stagnation of sputum, pneumonia and the development of respiratory failure.
In order to prevent a total error, it is better not to give any medication for breathing problems until the doctor arrives.
General recommendations
If you have problems with your respiratory function in a child, you should follow a certain algorithm action:
- calm down and calm the child;
- carefully listen to the nature of the violations, measure the frequency of breathing, pay attention to the skin color - cyanosis, pallor indicate the onset of oxygen starvation, redness of the skin and the appearance of rashes - the development of infection;
- pay attention to the presence and nature of cough;
- measure the pulse rate and blood pressure of the child;
- measure the child's temperature;
- call a doctor or an ambulance by telling the phone about the fact of respiratory failure and their observations;
- put the baby in a horizontal position, do with it, if possible, breathing exercises (a smooth breath - a smooth exhalation);
- open all windows and air vents in the house, if the opportunity permits, to carry the child out onto the street or on the balcony so that he has unlimited access to fresh air;
- if the condition worsens, give the child artificial respiration, an indirect heart massage;
- not to refuse hospitalization, if the visiting doctors insist on it, even if the ambulance doctors managed to stop the attack. Relief may be temporary (as with croup or heart failure), and with a high degree of probability, the attack will recur in the coming hours, only it will be stronger and longer, and the doctors may not have time to get to the little patient.
What should be first aid for breathing difficulties? Dr. Komarovsky will answer this question in our next video.