Perthes disease in children
Osteochondropathy of the hip joints is found in children's orthopedic practice more and more every day. Proceed such diseases are usually very difficult. One of these pathologies is Perthes disease. This article describes how the disease manifests itself in babies.
What it is?
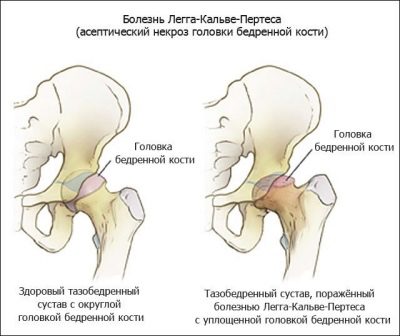
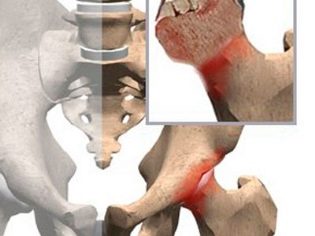
Children's orthopedists call this disease Legg-Calvet-Perthes disease. Also, this pathology is called osteochondropathy of the femoral head. This disease is accompanied by necrosis (death) of cells that form bone and cartilage.
During the development of the disease occurs severe blood supply failure. This causes necrosis of the elements forming the hip joint. According to statistics, this pathology often sick boys.
The peak incidence occurs at the age of 4 to 14 years. It should be noted that in some cases, the disease may occur at an earlier age.
Children's orthopedists note that most often this disease affects the right hip joint. Double-sided lesions are also common. In this case, the course of the disease becomes very difficult. The prognosis of bilateral lesions is usually poor. In some cases, this can even lead to the development of signs of disability in a sick baby.
Causes
Doctors have not yet established the true cause of this disease. There are a huge number of different scientific theories that explain the occurrence of this disease:
- Some experts believe that various traumatic injuries. The consequences of such injuries lead to the development of anatomical defects in the joints.
- Strong hip load also contributes to the fact that the child in the future may receive various circulatory disorders. Frequent infectious diseases that occur especially in weakened babies, lead to the development of necrotic changes of the hip head.
- Congenital diseases large joints can also be a provoking cause of Perthes disease. In this case, the development of specific changes leads to a violation of the anatomical integrity of the structures that form the hip joint. In adolescents, the pronounced displacement of the fourth lumbar vertebra becomes a fairly common cause of this pathology. This situation provokes pinching of the intervertebral nerve and the supplying blood vessels.
- Impaired blood supply contributes to the gradual development of dystrophic changes in the hip joint. After some time, the child develops pronounced necrosis of bone and cartilage tissue. This condition is manifested in violation of the architecture of the hip joint. A long course of the disease provokes the development of multiple adverse symptoms in a child.
Doctors identify several high-risk groups for the development of this disease:
premature babies and toddlers with a critically low birth weight;
children who had rickets in early childhood;
toddlers who do not receive adequate nutrition, as well as babies who are on artificial feeding;
children who often have colds and respiratory diseases;
babies with signs of malnutrition;
children suffering from various types of allergies.
Stages
In the development of the disease several clinical stages alternate.The initial one is accompanied by the appearance of necrosis of the nucleus of ossification of the femoral head. Stage 2 is characterized by the appearance of a compression fracture of the head of the hip bone.
Stage 3 causes multiple fragmentation and destruction of the main anatomical structures that form this bone joint. At the fourth stage, a large amount of connective tissue appears on the site of the former bone and cartilage tissue. The final stage 5 is accompanied by ossification of the newly formed areas, due to deposition in the damaged areas. calcium.
Symptoms
The manifestation of clinical signs depends on the stage of development of the pathological process. All adverse syndromes develop gradually. Late stages are characterized by the presence of pronounced clinical signs, which are quite clearly manifested in a child.
A rather frequent manifestation of the disease is the appearance of pain in the hip joint. At first, the child feels only a pulling pain that spreads throughout the affected leg. The baby feels maximum pain in the region of the head of the hip joint. At this time, the child often appears weakness of gluteus muscles.
Sick baby first starts to limp a little. During the development of the pathological process, the child begins to limp much more. This violation is particularly pronounced in a one-sided process. Double-sided damage may not appear for quite a long time.
Over time, the child’s gait begins to suffer. When walking, he tries not to step on the damaged leg and spares it. This leads to the fact that the child relies more on a healthy foot. This gait is preserved in the baby almost constantly.
As the inflammation in the joint develops, this symptom in a child only progresses.
Soreness when trying to turn a damaged leg outwards - Another characteristic symptom that develops in this pathology. Rotational motions are also disturbed. At first, this symptom is manifested by the appearance of soreness during the abduction or rotation of the leg. Then active and then passive movements are limited.
Restriction of hip joint flexion occurs in all babies with Perthes disease. The affected leg swells severely. This symptom is most pronounced when assessing a sore limb with a healthy one. If the process is bilateral, that edema appears immediately on both legs.
Circulatory impairment leads to pulsation of blood vessels is noticeably reduced. Doctors identify this clinical sign during a clinical examination of a sick child. The development of a pathological process of 2–3 degrees is accompanied by the appearance of a subfebrile condition in a child. In this case, the body temperature rises to 37.2-37.5 degrees.
Expressed stages of the pathological process are characterized by increasing pallor of the skin. The affected leg becomes cold to the touch. Some babies have severe sweating of the feet.
Diagnostics
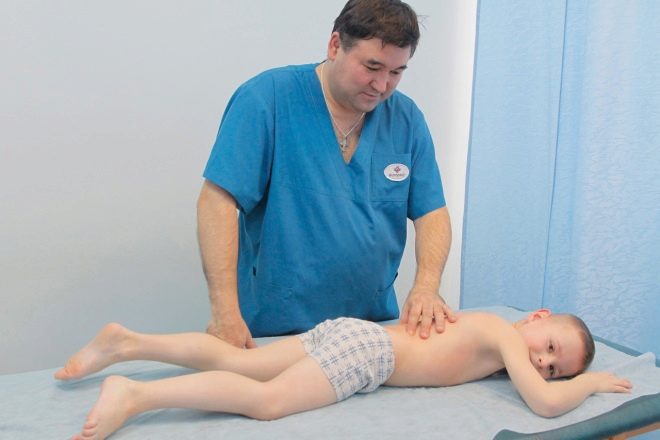
Clinical examination plays a very important role in establishing the diagnosis. Usually, the first adverse symptoms do not go unnoticed. Attentive fathers and mothers in this case immediately bring the baby to the doctor. Children's orthopedists and traumatologists are engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of Perthes disease.
Seeing a doctor is necessary. The doctor will be able to establish not only the correct diagnosis, but will also control the development of the disease. Little patients suffering from Perthes disease are forced to be in the dispensary for orthopedists throughout their lives.
To control the development of the disease, they are necessarily carried out a whole range of tests and research.
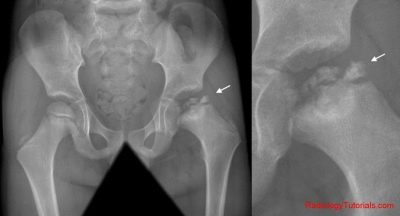
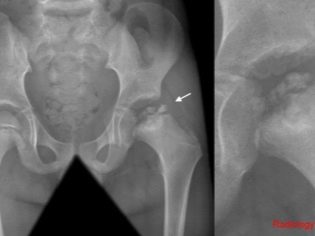
In the diagnosis of Perthes disease in children plays an important role x-ray This research is carried out both in a direct, and in a special lateral projection - according to Launshteyn. This double examination allows you to establish the diagnosis at the earliest stages.
There are a number of additional diagnostic methods that are used to confirm the diagnosis. Such studies include: ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Doppler ultrasound imaging allows you to accurately determine the severity of circulatory disorders. CT and MRI are used mainly in complex diagnostic cases where diagnosis is difficult.
Children's orthopedists prefer to use methods magnetic resonance imaging in the very first and early stages of the development of this disease. In this case, they still do not appear on X-rays, since at this time in most cases there are no pathological changes in the bone tissue. X-rays can usually be performed at 5-6 weeks after the appearance of the first violations that occurred. Such changes are characterized by expansion of the cavity of the joint space and pronounced softening of the growth zone of the femur.
X-ray examination helps to identify first the initial signs of bone destruction. Then you can determine the symptoms of squeezing the femoral head. Pathological disorders that occur in the third stage are identified as numerous patches of softened bone tissue. Stage 4 is determined by the emergence of newly formed zones.
With the active development of the process, the acetabulum becomes flattened, and not a regular spherical shape.
Treatment
Pediatric orthopedists note that Perthes disease is best treated, if possible, in the very early stages. The main goal of treatment of this pathological condition is to preserve the anatomically correct spherical shape of the hip joint head. For this purpose, a whole range of different methods is used.
To carry out the treatment of Perthes disease at home without the supervision of doctors is impossible. Such self-medication can only provoke the progression of adverse symptoms. It is especially dangerous to carry out such treatment in young children.
An integrated approach to the treatment of this disease can improve the blood supply to the damaged area, reduce the inflammatory process in the cartilage and bone tissue, and also normalize the tone of the muscles surrounding the hip joint. Doctors identify several ways to treat this type of osteochondropathy. These include standard conservative therapy, as well as surgical procedures.
To reduce the static load on the joint, the sick child is limited to any physical activity. Strongly rely on the sick leg of the child should not. In the acute period of the disease, doctors recommend to observe bed rest. This will help reduce the load on the damaged hip joints and improve the child's well-being.
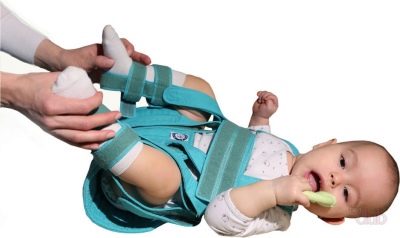
At marked stages in order to stop the progression of the disease, various orthopedic splints, dressings and gypsum constructions are used. They allow you to fix the damaged leg in the desired functional position.
Such forced traction also helps to reduce the dynamic load on the hip joint.
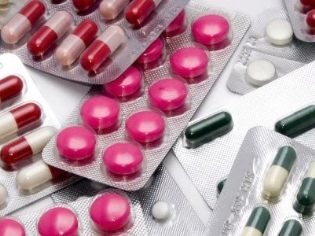
Drug therapy not only eliminates the adverse symptoms of the disease, but also prevents the development of the disease. Pain relievers based on ketorol and nimesulide will help reduce pain. For the reception of these funds, there are a number of medical contraindications. Use these funds should be only on demand, as long-term use can cause serious damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract in the baby.
For drugs that help preserve the integrity of the articular cartilage a little longer are chondroprotectors. These funds are assigned to children suffering from Perthes disease, just for a long reception. Such medicines are perfectly combined with vitamin complexes, enriched with vitamins of group B. This combined drug therapy has not only a positive effect on the cartilage of the hip joints, but also helps to improve the blood supply to the affected area.
Medical massage and specially selected complex exercise therapy assigned to all babies with this disease. These methods help to improve the well-being of the child, as well as reduce the manifestation of muscle hypotrophy and help to normalize the blood supply in the hip joints.
Physical therapy plays a very important role in eliminating all the adverse symptoms of the disease. Warming techniques using paraffin, as well as electrical stimulation have a beneficial effect on muscles and bone and cartilage formations.
All children with Perthes disease, doctors recommend to undergo annual rehabilitation treatment in a sanatorium. In such a medical facility, a whole range of different procedures is performed that have a pronounced therapeutic effect.
With the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment are held. surgeries. They are performed in the case when the child has a rather high risk of disability. After the surgical treatment, as a rule, the child's overall well-being improves and the gait is restored. Adverse effects after a technically correctly performed operation in most cases do not occur.
Surgical treatment is usually shown in cases of marked necrosis of the head of the hip bone, as well as in the presence of severe deformities. In some cases, the lesions are already so massive that the joint needs to be replaced. Different endoprostheses are used for this. The use of such technical means allows to normalize the volume of movements lost in the hip joint.
About the fact that Perthes disease is dangerous, see the next video.