Vulvitis in girls
Pediatric gynecology - the question is very intimate and often quite closed. Diseases of the female genital organs can occur even in newborn girls and babies of a very young age.
What it is?
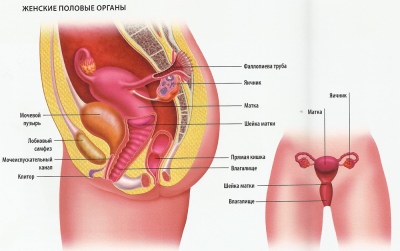
Inflammations of the external female genital organs are called vulvitis. These include: the eve of the vagina, small and large labia, clitoris and the outer part of the urethra. Vulvitis is most common in babies under 10 years old. The disease in infants is much less. In adolescents, after puberty, vulvitis is also formed quite infrequently.
This anatomical region is very well supplied with blood and innervated. Any inflammatory changes in this zone provoke the appearance of very unfavorable symptoms that bring the baby severe discomfort. According to statistics, vulvitis is recorded most often in babies and at a later age in women suffering from dystrophy of the genital organs.
The impact of hormones on the reproductive system is very significant. Any vibrations affect the epithelial cells of the female genital organs. With prolonged exposure, this may provoke the development of vulvitis. Inflammations of the female genital organs are very dependent on the basal level of hormones. Diseases of the endocrine system contribute to the development of vulvitis.
Sexual external organs of the baby are sterile. By the end of the first week, conditionally pathogenic microorganisms settle on them and the pH of the vagina is shifted. In infants, it is neutral or slightly alkaline. Already by the age of 10, the vagina is colonized by lactobacilli. Their normal concentration leads to a shift in the pH of the medium to 4-4.5.
Before the onset of menstruation, babies have virtually no local immunity. Any infections that settle on the walls of the external genital organs can lead to the development of local inflammation. With reduced overall immunity, this leads to the rapid progression of the disease.
The reasons
Various causes can lead to the development of inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. According to the initial appearance of symptoms, all vulvitis may be acute and chronic. When the process is chronized, the adverse manifestations of the disease can be repeated again and again for several years. For chronic vulvitis requires the selection of the correct treatment and regular monitoring by the pediatric gynecologist.
The following provoking reasons may lead to the development of vulvitis in babies:
- Feature of the anatomical zone. Large labia in girls are more open than in older age. A reduced amount of lactobacilli leads to a change in the pH of the vaginal environment. Quite loose and easily traumatized mucous membranes of the genital organs are excessively susceptible to any infectious and non-infectious influences.
- Poor quality personal care. Excessive lavage can lead to an even greater change in the pH of the vagina. This contributes to the development of inflammation in the external genitalia. If the schedule of personal hygiene is constantly violated, then it can also contribute to the appearance of vulvitis.
- Incorrectly chosen diapers. Their prolonged wearing can lead to a permanent effect on the external genital organs. The use of diapers in girls for a long time can provoke a change in pH in babies.Also, girls may experience various irritations and rashes in the genital area.
- Helminth infestation. Most often vulvitis occurs when infected with ascaris or pinworms. In the process of vital activity, these parasites secrete various toxic products. They cause severe irritation and redness in the genital area. Also, helminth eggs can get into the anogenital zone, causing strong allergic variants of vulvitis in a baby.
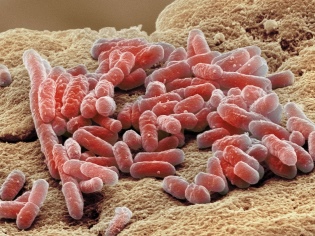
- Various infections. Infection with viruses, bacteria or fungal infections can provoke inflammation on the vulva. Usually such vulvitis is accompanied by the appearance of a large number of adverse symptoms. To eliminate them requires the appointment of complex treatment.
- Mechanical damage. In early childhood, the development of vulvitis results in various small objects entering the external genitals. The babies of the first three years of life love to actively explore their bodies. Inadvertently, they can cause themselves various injuries that provoke the development of vulvitis.
- Chronic diseases. Various infections that occur in different internal organs lead to the development of inflammation in the female genital area. With an additional decrease in immunity, the process can take a rather severe course.
- Violation of personal hygiene during sexual intercourse. Actually for girls in adolescence.
- Intrauterine infection. It occurs only in 1% of cases. Infection of the genitals of babies occurs as a result of various infections in the bloodstream from mother to child. The first symptoms of vulvitis occur after birth. To eliminate them, an appeal to the pediatric gynecologist is required in the first days after the discharge of the baby from the hospital.
Kinds
Taking into account provoking reasons, several types of vulvitis can be distinguished:
- Bacterial. Occurs as a result of infection with various types of bacteria. Staphylococci, streptococci and anaerobic microorganisms lead to the development of purulent forms of vulvitis in young girls. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 3 to 7 years. For treatment requires different forms of antibiotics.
- Viral. Provoked by various viruses. Most often, the development of viral vulvitis is caused by infection with the herpes viruses of various subtypes. They proceed, as a rule, in acute and subacute variants. Accompanied by the appearance of discomfort symptoms. Antiviral agents are used for the treatment, as well as local treatment.
- Allergic. Occurs in girls with individual hypersensitivity to various allergens. In some cases, can occur with atopic dermatitis. To eliminate the adverse symptoms requires the appointment of antihistamines and baths with antiseptics.
- Parasitic. Occur due to invasion by various helminths. Parasites emit various toxic substances that have an irritant effect on the external genital organs. With a long course of the disease, inflammation can become chronic. Antiparasitic drugs may be required for treatment.
- Traumatic. These nonspecific variants of vulvitis occur as a result of the consequences of a slight trauma to the mucous membranes of the external genital organs. They are the most sensitive and easily traumatized in babies of the first year of life. To eliminate the adverse symptoms, it is necessary to administer ointments that have a regenerating effect.
- Secondary. Occur in girls with chronic diseases of internal organs. Most often, vulvitis occurs in endocrine pathologies, as well as in allergic diseases. To eliminate the adverse symptoms of vulvitis, it is first necessary to treat the underlying disease and strengthen the immune system.
All processes that appear during the first month are called acute. If the adverse manifestations of the disease occur for three months, then the course of the disease is called subacute. When the process is chronized, the symptoms of the disease may appear within six months or more. Typically, chronic vulvitis occurs in weak and frequently ill children.
Symptoms
The severity of adverse symptoms depends on the severity of the disease. With a slight course, the baby may appear only a slight itching and redness in the genital area. These adverse symptoms are easily eliminated. Acute vulvitis, occurring in a mild form, practically does not become chronic.
Among the symptoms of inflammation in the area of the external genital organs, the following are noted:
- Severe swelling of the mucous membranes. In severe cases, the labia majora become enlarged. Excessively swollen mucous membrane of the urethra leads to increased urination. At the same time, the amount of urine discharge does not change, only urges become more frequent.
- The appearance of itching or burning. With a mild course of this symptom almost does not bring the baby any discomfort. Severe forms of the disease significantly disrupt the general condition of the child. Baby begin to constantly comb the anogenital zone. A bacterial infection often gets into the scratching places, which can lead to the development of secondary infection.
- The presence of discharge. They can be of different types and textures. With bacterial infections, vaginal discharge is yellowish and green. In viral vulvitis, the discharge becomes gray or whitish. Fungal infections are accompanied by the appearance of secretions that crumble easily.
- The appearance of a fetid odor. Usually this symptom appears in bacterial forms of vulvitis.
- Soreness Touching the external genital organs leads to the appearance of pain. In severe cases, the pain is greatly enhanced.
- Redness of the skin in the anogenital zone. Inflamed skin becomes a bright red color. The external genitals become hot to the touch. When worms and allergic vulvitis on the skin, traces of scratches appear.
- Impaired urination Swollen, inflamed genitals lead to moderate compression of the duct of the urinary canal. Also, inflammation can go to the urethra and the ascending path from the vagina. Baby asks to the toilet much more often. Portions become small, but frequent. The total amount of urine per day does not change.
- Increased temperature, in some cases - fever. With the development of infectious vulvitis symptoms of intoxication increase. With a slight current body temperature rises to subfebrile numbers. More severe forms of the disease are accompanied by the appearance of febrile.
- Behavior change. Babies are becoming more emotionally depressed. They are often naughty, are in a depressed mood. Severe itching in the anogenital zone contributes to increased irritability and nervousness. In babies sleep is disturbed, insomnia appears.
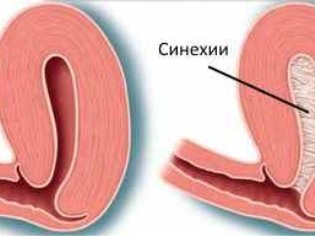
- With a long course of the disease, adhesions or synechiae appear. Their moms are usually found in babies during daily hygiene procedures.
Diagnostics
If adverse symptoms occur, first of all, show the child to the pediatric gynecologist.
The doctor will conduct the necessary examination, as well as all additional tests and examinations. Be sure to perform a complete blood count. The appearance of leukocytosis with elevated ESR indicate the presence of infectious diseases.
For secondary vulvitis, a biochemical blood test should also be performed. For this, the levels of bilirubin, creatinine, and hepatic transaminases are examined.The increase in these indicators indicates the presence of changes in the gastrointestinal tract. Chronic diseases of the digestive system often cause vulvitis.
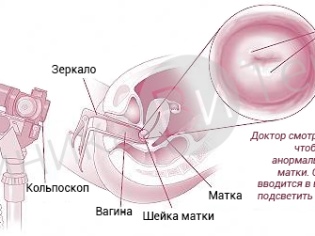
Also, a gynecologist will definitely perform a colposcopy.
With the help of special medical instruments, he can examine the external genitals well and determine the cause of the disease. During the consultation, the doctor will also take a biomaterial for carrying out bacpossev secretions. This analysis will help identify the causative agent, as well as its sensitivity to antibiotics.
If necessary, you must also show the child to an endocrinologist, an allergist and a gastroenterologist. These consultations will be necessary for the differential diagnosis of various types of vulvitis.
Treatment of chronic inflammation of the genital organs is impossible without the establishment and elimination of the underlying disease, which has led to the appearance of adverse symptoms.
Drug therapy
Treatment of acute vulvitis must necessarily be selected based on the cause, which contributed to the development of the disease. Usually, therapy for a disease takes about 2-3 weeks. The purpose of treatment is carried out by a gynecologist after examining the child and conducting all the necessary research. The names of the drugs may be different depending on the active substances in them.
For the treatment of vulvitis appointed:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Apply locally. Baths, lotions and hygienic treatment are suitable with substances that relieve inflammation in the anogenital zone. These include miramistin, furatsilin, hydrocortisone ointment, bepanten and other means. They are assigned to coursework, usually 10-14 days.
- Antibacterial drugs. Appointed with purulent vulvitis. Discharged by a doctor. Appointed usually for 7-14 days. Antibiotics with a broad spectrum of action are suitable for the treatment of purulent vulvitis: macrolides, various forms of cephalosporins, and also fluoroquinolones.
- Antiviral. Used to eliminate viral forms of vulvitis. Appointed for 5-7 days. Discharged in the form of ointments and pills.
- Restorative. The use of multivitamin complexes helps to improve the immune system. In chronic forms of the disease, regular courses of vitamins are recommended. Usually they are discharged in spring and autumn for 1 month of admission.
- Stimulating immunity. Assigned as rectal suppositories. Successfully used to treat chronic forms of vulvitis. Interferon-based preparations are used. Usually appointed for 10-14 days.
- The appointment of antifungal agents for the treatment of fungal forms of vulvitis. Effectively used: intraconazole, flukanozol, clotrimazole and others. In severe and often progressive vulvitis, tablet forms are used. When a vulvitis occurs for the first time, local antifungal preparations are used, which are produced in the form of ointments and vaginal creams.
Home treatment
It is also possible to eliminate itching and burning in the anogenital zone by using medicinal plants. These tools are usually always in every home medicine chest. Medicinal plants have a good tolerability spectrum, and are also practically incapable of provoking various side reactions in babies. It should only be careful when using them, as they can still cause allergic reactions in the presence of individual susceptibility.
The most effective home remedies include decoctions made from chamomile, calendula, oak bark. These plants have a pronounced antiseptic effect. They help eliminate itching and burning in the anogenital zone, as well as eliminate inflammation from irritated genital organs.
To prepare homemade medicine, you will need to take 2 tablespoons of crushed vegetable raw materials and pour 1.5-2 cups of boiling water.Insist should be within an hour. After that, the resulting infusion is filtered through cheesecloth or a fine sieve.
The finished home remedy can be added to the sit-down bath or the anogenital zone can be treated with gauze napkins.
To achieve a good effect, you should apply the medicinal infusion at least 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is prescribed for two to three weeks. After 5-6 days, well-being improves significantly. In babies, inflammatory secretions from the genitals are reduced, and itching and burning gradually disappear. In chronic vulvitis, these hygienic procedures can be used 2 times a year to prevent new exacerbations.
Prevention
To maintain reproductive health for many years requires regular monitoring of the state of the genitals. From an early age should teach the baby how to properly conduct the toilet and daily hygiene. If any adverse symptoms occur, a child must be taken to a pediatric gynecologist. It is very important that the girl is not afraid to visit this doctor. This will create a positive attitude for the future.
Treatment of respiratory infections and colds, as well as strengthening the immune system will help prevent the development of inflammatory vulvitis. Baby should avoid severe hypothermia, as well as wear quality underwear, which is made from natural materials. In infancy, diapers should not be worn for a long time. This simple measure will help prevent the development of vulvitis in the future.
You can learn more about this disease in the video below.