What to do if the child’s gums are swollen?
When the baby's gums swell, it affects the child's well-being and requires an immediate reaction from the parents. With the swollen gums the baby is hard to chew, and sometimes talk.
In some babies, a gum tumor is accompanied by fever and other unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, it is important to understand as quickly as possible why the gums have swelled and increased in size, and what to do to alleviate the condition of the child.
Possible reasons
Swollen gums are a symptom of a child’s situation:
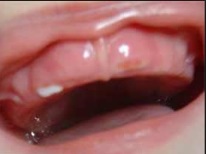
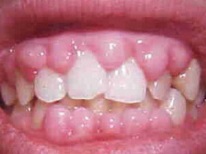
- Teething milk teeth. This is the most common reason for which karapuz gums grow in size. Most often, such manifestations are observed in children over the age of 5-6 months, but in some babies you can notice swelling of the gums even at 3 months.
- Caries. Such a disease affects children's teeth quite often, especially if their cleaning is not thorough enough, and there are a lot of carbohydrates in a child's diet. The first signs of caries are often ignored by the parents, as they are represented by white spots. When the teeth begin to turn black and pain appears, the infection has already penetrated deep into the dental tissues and can provoke the development of a complication called periodontitis. It is a swelling of the gums above the aching tooth. Inside such a swelling is going pus, which can break through the gums and form a fistula in it.
- Gingivitis. Swollen gums in children older than 5-6 years are often a symptom of their inflammation. The disease is also manifested by increased bleeding (especially when the child eats or brushes his teeth), painful sensations, an unpleasant smell from the mouth and other symptoms.
- Gum trauma If a child has damaged a gum mucosa with a sharp object, food that is too hard, or burned, it will lead to inflammation, one of the symptoms of which will be swollen gums.
- Removal of a tooth. For some time after the doctor removes a tooth, the gum at the site of manipulation will remain swollen.
- Teething permanent tooth. As a rule, molars do not climb as painfully as milk teeth, but there is an exception - the wisdom teeth eruption. These teeth, called "eights", begin to erupt during adolescence and cause severe discomfort, and also cause swelling of the gums at the site of their "hatching."
- Vitamin C deficiency. If the baby does not receive this vitamin with food, its gums will become more loose and increased in size.
How to help a child
- If the gums have increased in volume and have become swollen due to teething, you can help the toddler relieve the itching and soreness with a light massage of the gums, cooled teething toys or anesthetic gels. When expressed discomfort crumbs should show the dentist.
- If a child has gum swelling over a baby tooth affected by deep caries, and the doctor has diagnosed periodontitis, the tooth is often removed, even if the child is only 3 years old or 5 years old, and before the change of teeth is still far away. This is done in order to prevent the transition to the germ of the molar tooth.
- If the gum swelling is observed around a permanent tooth with caries, they try to preserve that tooth, so it is treated, as in adults, with the removal of infected tissues and the installation of a filling.
- When gingivitis is the cause of swelling, the doctor will clean the teeth in the dental office, remove the entire plaque, and then prescribe rinsing with antiseptic and local treatment with anti-inflammatory action.
- If the gum swell is triggered by trauma, the baby must be shown to a doctor. The dentist will determine the severity of the lesion and prescribe the necessary treatment.
- If the child does not have enough vitamins and minerals, it is important to balance the nutrition of the toddler, as well as to consult with a pediatrician for the choice of a suitable complex vitamin preparation.