Azithromycin for children: instructions for use
Timely administration of the antibiotic helps in the fight against infections of the respiratory tract, urogenital system and other organs. And one of the most popular drugs in this group is Azithromycin. It attracts by its low toxicity and long-lasting effect, due to which the medicine is taken only once a day, and the course of antibiotic therapy with Azithromycin is often short. But is it possible to give this medicine to children, in what dose it is used in childhood and when it is not necessary to treat the child with Azithromycin?
Composition and trade names
The active ingredient in the drug Azithromycin is represented by a compound with the same name. At the same time, the domestic drug Azithromycin is not the only one with this active ingredient. Azithromycin acts as a basis for other drugs:
- Sumamed
- Hemomycin
- Azitrox
- Azitral
- Nitrolide
- Ecomed
- ZI factor
- AzitRus
- Azimycin
- Sweetrox
- Sumatrolide Solutab
- Zytrotsin and others.
All of these drugs containing azithromycin can replace each other, therefore, we will consider the features of all these drugs at once, calling them Azithromycin.
Auxiliary ingredients depending on the form of the drug may be lactose, sucrose, silica, magnesium stearate, gelatin, xanthan gum, colors, flavors and other substances. Therefore, when When purchasing any of the Azithromycin options for a child with an allergic tendency, attention should be paid to additional components.
Watch an interview with a practicing doctor-dermatovenerologist in which he answers questions regarding ezithromycin preparations:
Release form
Azithromycin is available in many forms, which allows you to choose the most suitable medicine for children of different ages. The medicine is represented by the following options:
- Powder. It is represented by white granules or crystals, which may have a creamy yellow hue. The powder is packaged in bottles, where you need to add water to make a suspension. In the package, as a rule, there is a dosing syringe, as well as a dosing spoon. Azithromycin powder form is represented by two dosages - a medicine, in 5 ml of which, after preparing the suspension, will be 100 mg of the active substance (Sumamed, Hemomitsin, Sweetrox, Azitrox, AzitRus, Azithromycin Zintiva, Azithromycin Sandoz) and the preparation, 5 ml of which solution will contain 200 mg azithromycin (AzitRus, Azithromycin Zintiva, Hemomitsin, Azithromycin Sandoz, Azitroks, Sweetroks). The prepared liquid has a sweet taste and a pleasant smell, so many children drink this syrup without any problems.
- Pills. This form of Azithromycin is represented by both dispersible tablets (Sumamed, Sumatrolide Soluteb) and tablets in the shell (Sumamed, ZI-factor, Azithromycin, Hemomycin, Azithromycin Forte, Azithromycin Zintiva, Ecomed, Azitromus Forte, Zitnob). The content of the active substance in these tablets is often 125 or 500 mg, but there are also drugs with 250 or 1000 mg of azithromycin. Most drugs are packaged in a blister of 3 or 6 tablets.
- Capsules. Sumamed, Zitrolid, AzitRus, Ecomed, Azithromycin, ZI-factor, Hemomycin, Azitrox, Azitral, Azithromycin-OBL are produced in this form. Each capsule contains 250 mg (less frequently 500 mg) of azithromycin, and 1 pack may contain 3, 6, 10, 12, or more capsules.
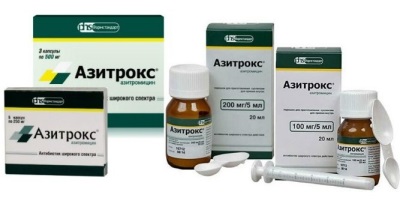
There is also Azithromycin for injection, for example, Sumamed or Hemomitsin lyophilisate. This drug injections is in demand for very serious infections, but in childhood is not used.
Operating principle
Azithromycin belongs to the group of macrolides. Such antibiotics have a fairly wide range of effects on harmful bacteria. After entering the patient's body, they are transferred to the site of inflammation and penetrate both through tissue barriers and through cell walls.
Azithromycin is absorbed quickly enough, so that after 2-3 hours its concentration in the bloodstream will be maximum. After discontinuation of the drug is circulated in the plasma for another 5-7 days, providing a therapeutic effect.
In a moderate dose, Azithromycin is able to suppress the formation of proteins in bacterial cells, which causes their reproduction to slow down. High concentration of the drug is bactericidal (kills the pathogen).
Taking Azithromycin is effective in infecting:
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Epidermal Staphylococcus.
- Streptococcus group B and other groups.
- Pneumococcus.
- Pyogenic streptococcus.
- Hemophilic wand.
- Moraxella.
- Pertussis wand.
- Stick parakoklyusha.
- Campylobacter.
- Legionella.
- Gonococcus.
- Gardnerella
- Bacteroids.
- Peptostreptokokk.
- Clostridia.
- Chlamydia.
- Mycobacteria.
- Ureaplasma
- Mycoplasma.
- Pale treponema.
- Borrelia.
However, it happens that the drug does not help if microorganisms develop resistance to such an antibiotic. This situation requires replacement of the drug after determining the sensitivity of the pathogen to other antimicrobial agents.
Indications
Containing azithromycin drugs are advised to take for the treatment of such diseases:
- Angina.
- Laryngitis.
- Tick-borne borreliosis.
- Bronchitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Sinusitis and other sinusitis.
- The pharyngitis provoked by streptococci.
- Otitis media
- Whooping cough.
- Erysipelas and pustular skin lesions.
- Infectious dermatitis.
- Urethritis and other urinary tract infections.
- Gastrointestinal ulcer.
Quite often, the cause of the appointment of Azithromycin is a cold that has been improperly treated., as a result, it was complicated by a more serious bacterial infection. Also, this antibiotic may be prescribed to children when popular antibacterial agents such as penicillins and cephalosporins (eg Amoxicillin proved ineffective).
At what age is it allowed to take?
Azithromycin is not used in the treatment of children under 6 months. If the child is already half a year old, the doctor may prescribe such medicine in the form of a suspension. The tablet form or Azithromycin capsules give older children who can swallow such drugs. The dosage is calculated on the basis of the body weight of the child. Azithromycin infusions are contraindicated until the age of 16.
Contraindications
Any form of Azithromycin should not be taken with hypersensitivity to such an active substance. The drug is contraindicated in case of allergy to other macrolide antibiotics. Also, the drug does not give:
- With severely impaired liver function.
- With severe renal diseases.
Azithromycin should be prescribed with caution when it is prone to arrhythmias, imbalances in water and electrolytes, problems with kidney or liver function, diabetes mellitus (for drugs with sucrose), carbohydrate metabolism disorders (for suspensions).
Side effects
The children's body sometimes reacts to Azithromycin by the appearance of:
- Dizziness.
- Excited state.
- Fatigue.
- Drowsiness.
- Feeling tingling or numbness of the limbs.
- Headache.
- Anxious mood.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Sleep disturbance
- Chest pains.
- Sensations of palpitations.
- Nausea
- Flatulence.
- Jaundice.
- Liquid stool.
- Stomach ache
- Vomiting.
- Decreased appetite.
- Inflammation of the stomach.
- Candidal mucosal lesions.
- Pruritus
- Muscle aches.
- Urticaria.
- Rash on the skin.
More rare side effects of azithromycin preparations are:
- Hearing impairment or tinnitus.
- Visual impairment.
- Constipation.
- Liver damage.
- Inflammation of the intestine.
- Nephritis.
- Quincke swelling.
- Increased sensitivity to ultraviolet.
- Changes in blood tests.
- Anaphylactic shock.
- Pancreatitis.
Instructions for use
- Azithromycin reception frequency - once a dayand the duration of treatment is usually 3 days. For tick-borne borreliosis, the drug is prescribed for 5 days.
- Note that the absorption of the active substance Azithromycin is affected by food intake. For this reason, the medication should not coincide with the feeding of the child. The drug is given either after about 2 hours after a meal, or 60 minutes before a meal.
- Azithromycin powder is diluted with boiled cool water. To find out how much water is needed and how to dilute the medicine, you should clarify such information in the instructions. For example, in powder Sumamed need to pour 12 ml of water.
- Shake the vial with suspension before each use., then select the desired dose with a syringe or pour it into a spoon.
- If the next dose of Azithromycin is missed, it must be taken immediately, as soon as this fact was discovered. The next dose should be 24 hours after taking the missed dose.
- Tablets or capsules should be swallowed without biting. and then drink water. What if the child chewed this form of Azithromycin? It does not pose any danger, but for a more effective action it is not recommended to break the drug shell.
Dosage
Suspension
The dose of this form of Azithromycin is calculated by weight of the child. - for one kilogram of body weight of a sick baby you need 10 mg of the active substance. If you use the drug with a dosage of 100mg / 5ml, then 10 mg of azithromycin will be in 0.5 ml of the prepared solution. It turns out that a child with a weight of 5 kg should be given 2.5 ml of the drug (this is 50 mg of the active substance), with a body weight of 6 kg - 3 ml of the drug, with a weight of 7 kg - 3.5 ml and so on.
With a weight of 10-14 kg, for example, at 2 years old, a baby is given 100 mg of azithromycin, which corresponds to 5 ml of suspension. If a child is 3 years old and his weight is already 15 kg, then for treatment he will need 150 mg of azithromycin, so they are switching to a more concentrated medication - 200mg / 5ml. A single dose of this suspension is also determined by weight:
- Children weighing 15–25 kg (for example, at the age of 6 years or 8 years) are given 5 ml of medication per dose, containing 200 mg of the active substance.
- A child who weighs 25-35 kg (approximately aged 9-10 years) requires 300 mg of azithromycin, which corresponds to 7.5 ml of the drug.
- Children weighing 35-45 kg (11–12 years old) have a therapeutic dosage of azithromycin 400 mg, so they are allowed to drink 10 ml of suspension.
- With a weight of over 45 kg (12-13 years), a single portion of the drug is 12.5 ml, which corresponds to 500 mg of the active substance and allows you to use tablets or capsules.
125 mg
This dosage of Azithromycin is presented only in tablets.If they are coated, the drug is recommended not earlier than the age of 3, when the child can already swallow it.
250 mg
Azithromycin with this dosage is prescribed from 12 years of age. A child is given 2 capsules or 2 tablets at a time in case of diseases of the respiratory system, soft tissues or ENT pathologies. When borelliosis on the first day a single dose will be 4 capsules or tablets, and then reduce the dose to two capsules / tablets per reception.
500 mg
This dosage of Azithromycin is used in the treatment of children over 12 years old and adults. The drug is taken on 1 tablet or 1 capsule per day.
Overdose
If a child accidentally drinks Azithromycin in a very high dose, it will lead to vomiting, severe nausea, or diarrhea. It is also possible hearing loss for some time. To help your baby, you should immediately flush the stomach and consult a doctor for a symptomatic treatment.
Interaction with other drugs
If the child is already taking any medication and Azithromycin has been prescribed, this requires attention from the pediatrician.After all, many drugs should not be combined with such an antibiotic. For example, if you give your baby antacid agents, it will worsen the absorption of azithromycin and affect the results of treatment.
Other antibacterial agents also affect the activity of the drug, for example, the prescription of tetracycline will increase the effect of Azithromycin, and the antibiotics lincomycin will weaken its therapeutic effect.
In azithromycin, effects on carbamazepine, theophylline, zidovudine, cetirizine, fluconazole, digoxin, phenytoin, warfarin and many other drugs are also noted. That is why the appointment of Azithromycin to children who are taking other medicines should be carefully monitored by a doctor.
Terms of sale
You can buy Azithromycin in a pharmacy only after presenting a prescription from a doctor. The price of the medicine will depend on many factors, including the form of release, dosage, manufacturing company and others. Domestic drugs are cheaper (their price is from 30 rubles), and foreign ones are more expensive.
Storage conditions and shelf life
Azithromycin should be kept in a place where a small child cannot reach. Storage temperature is room temperature (up to + 25 ° С). It is impossible to take a medicine that has expired (Azithromycin is 2 or 3 years depending on the manufacturer and form of the drug). The suspension prepared from powder form is not stored for more than five days.
Reviews
On the use of Azithromycin in the treatment of children there are a lot of positive reviews. Moms say that this antibiotic is very effective for bronchitis and pneumonia. It helps to eliminate cough, reduce body temperature and quickly deal with the disease. It is also often used for otitis and angina, because these bacterial infections are very common in childhood.
The benefits of Azithromycin are many dosage forms and ease of use of the suspension for young children. All mothers like that they give medicine only once a day, and the duration of treatment is short. Negative reviews of Azithromycin include complaints of treatment failure (if the pathogen was resistant to the drug) and frequent side effects (allergies, headaches, nausea, and others).
Analogs
If it is not possible to use Azithromycin in the treatment of a child, such a drug may be replaced by other antibacterial agents from the macrolide group:
- Clarithromycin. This drug is effective against bacterial infections and is permitted from 6 months of age.
- Macropene. The active ingredient of this drug is midecamycin. The drug is produced in granules, of which make a suspension, as well as tablets.
- Erythromycin. This antimicrobial drug was the first macrolide used to treat various infections, so this drug has quite a few side effects.
- Roxithromycin. It is an effective macrolide approved for use from 2 months of age. The drug is produced in tablets, which are dissolved before giving to the baby.
- Vilprafen. This antibiotic contains effective macrolide josamycin, so it is prescribed for serious infectious diseases. In childhood use a form of dispersible tablets.
- Rovamycin. The main component of this medication is spiramycin. The tablet form of this macrolide is prescribed to children aged 3-4 years and older.