Placental hyperplasia during pregnancy
A thickening of the placental tissue may lead to changes in the course of pregnancy. Placental hyperplasia has a number of features that can affect the fetal intrauterine development.
What it is?
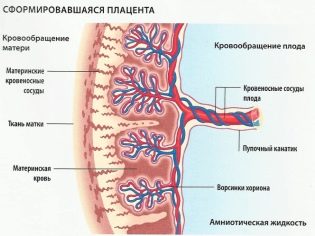
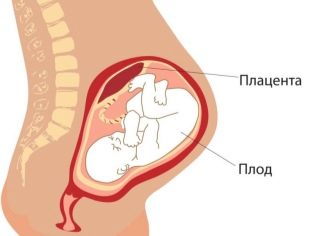
Normally, the placenta has a certain size. Every day of pregnancy, the thickness of the placental tissue increases. The rate of thickness of the placenta depends on the duration of pregnancy. If it is thickening, then doctors call this condition hyperplasia.
By birth, the thickness of the placenta is approximately 2-4 cm. If the placenta becomes very thick before the prescribed period, then the course of the pregnancy may change.
The reasons
The development of a thickening of the placental tissue can lead to a variety of reasons. As a rule, if a too thick placenta is diagnosed during pregnancy, this is evidence that there are some pathologies in the future mother's body.
Various viral and bacterial infections can lead to the development of placental hyperplasia. Pathogenic microbes cause inflammation, which leads to disruption of the formation of the placenta. Ultimately, this contributes to the fact that placental tissue is excessively thickened, which leads to the development of its hyperplasia.
Also, a change in the thickness of the placental tissue may develop under anemic conditions, which are accompanied by a strong decrease in hemoglobin in the blood. Diabetes mellitus can also lead to the development of placental hyperplasia. A persistent increase in blood glucose leads to the development of damage to the placental tissue.
Vascular pathologies can also lead to the development of hyperplasia - it can develop with arterial hypertension. In this case, the development of damage contributes to a persistent increase in blood pressure. The higher these figures are in the expectant mother, the higher the risk of developing placental pathology.
Hyperplasia can also develop after past infectious pathologies. So, ureaplasmosis, toxoplasmosis, as well as a number of sexually transmitted diseases can lead to a thickening of the placenta.
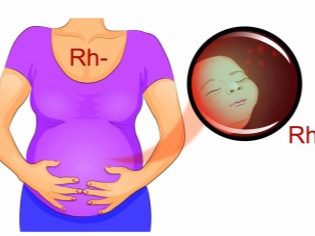
Rhesus-conflict between mother and baby can also contribute to the development of characteristic changes in the placenta. In this case, the intrauterine development of the fetus may be disrupted due to the development of complications.
Late toxicosis of pregnancy can also affect the development of placental disorders. This pathology is dangerous because the prognosis of pregnancy, as a rule, worsens. The future mother will have severe edema, the general condition is disturbed, and a violation of uteroplacental blood flow may also develop.
How can it manifest itself?
In most cases, placental hyperplasia is asymptomatic. It is simply impossible to suspect the presence of this pathology in this case for some clinical signs. That is why most often placental hyperplasia becomes a real “find”, which is detected during planned ultrasound scans during pregnancy.
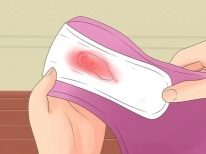
In some cases, a thickening of the placenta can lead to the development of dangerous complications. In this case, the future mother will be disturbed by adverse symptoms that affect her well-being. So, a woman may have discharge from the genital tract or a slight soreness in the lower abdomen.
Sometimes it also happens that the only symptom that worries the future mother, who has placental hyperplasia during pregnancy, is poor health and general weakness. Such a nonspecific manifestation, as a rule, is not a reason for going to a doctor, which leads to an untimely diagnosis of pathology.
Diagnostics
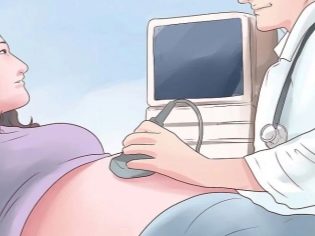
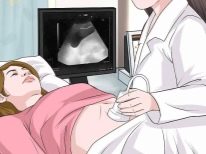
The main diagnostic method that allows to identify this pathology is ultrasound examination. During the ultrasound, the doctor can determine the thickness of the placenta, as well as identify various anatomical defects. Quite often, a thickening of the placenta is first diagnosed at 18-20 weeks of pregnancy, but this pathology can be detected much later.
During the determination of the thickness of the placenta, the ultrasound specialist also assesses its density. The structure of placental tissue depends largely on the duration of pregnancy. So, in the second trimester, it is fairly smooth and uniform.
As the delivery approaches, the placenta changes its density. Diffuse changes appear in it, as well as areas of compaction. For example, the structure of placental tissue at week 32 of pregnancy is significantly different from that at 20–22 weeks. Such changes are absolutely normal and indicate a healthy pregnancy.
If, for some reason, the placenta changes its thickness before the prescribed period, then the ultrasound doctor will diagnose the presence of her hyperplasia. At the same time, he necessarily carries out accurate measurements of the thickness of the placental tissue and indicates the results in his medical report, which is issued after the examination of the expectant mother. This conclusion in the future necessarily invested in the medical card. Assessment of the thickness of the placenta in dynamics allows doctors to track how this pathology develops.
If the future mom was diagnosed with hyperplasia of the placenta, then she was also prescribed a number of additional examinations. A pregnant woman will need to:
- to pass a biochemical blood test, as well as general blood and urine tests;
- undergo cardiotocography;
- be screened for sexually transmitted infections;
- determine the presence of antibodies (according to indications);
- visit the Doppler room to identify various violations of uteroplacental blood flow;
- visit an obstetrician-gynecologist for a clinical examination and collection of smears from the genital tract for analysis.
Possible consequences
Severe thickening of the placenta most often threatens with the development of an extremely dangerous condition - fetoplacental insufficiency. This pathology is accompanied by a strong violation of the uteroplacental blood flow, as a result of which the fetus does not receive oxygen, which means that the oxygenation process of the child’s body is disrupted. Persistent oxygen deficiency can even lead to the development of fetal growth retardation syndrome. In this case, the normal course of intrauterine development of the fetus is disturbed.
A decrease in the growth rate of a baby in such a situation may also lead to the fact that he will grow more slowly and gain weight. In the end, severe placental hyperplasia can contribute to the fact that the baby will be born low in weight and much earlier than the prescribed period.
If hyperplasia of the placental tissue is also accompanied by lack of water, then in such a situation the fetus has a high risk of developing disorders in the structure of its musculoskeletal system. The child may develop curvature of the limbs, as well as various pathologies of the skeleton.
Treatment
The choice of therapy depends on many factors. The doctor necessarily assesses the general condition of the future mother and her baby, the degree of violations that have occurred, the risk of developing complications, the duration of pregnancy and much more. Only such a comprehensive assessment allows professionals to choose the right tactics for further pregnancy management.
Treat hyperplasia of the placenta in different ways.Basically, basic therapy involves prescribing medications. They are selected individually, taking into account the features of the future mother. Also, when prescribing drugs, their effect on the fetus is necessarily evaluated.
Reviews of many women who were diagnosed with hyperplasia of the placenta during pregnancy indicate that for the treatment of the resulting disorders, they were prescribed vascular preparations.
Such drugs are indeed often included in the treatment regimens of the thickened placenta. They help to improve blood flow in the body, which has a positive effect on its functioning.
With placental hyperplasia, hemostasis pathologies may also develop. They are related to the fact that blood coagulability is changing. In order to correct the resulting disturbances in this case, drugs that affect the blood coagulation system may be prescribed. Most often, therapy with such drugs is carried out in a hospital. This is due to the fact that during its implementation it is often necessary to control the blood for clotting.
Survey data is more convenient to conduct in the hospital. During such therapy it is very important to monitor the condition of the woman and her baby. A pregnant woman in this case should always be under medical supervision.
In case of hyperplasia of the placenta, the blood supply to the placenta is often disturbed. This process is accompanied by the development of tissue oxygen deficiency - hypoxia.
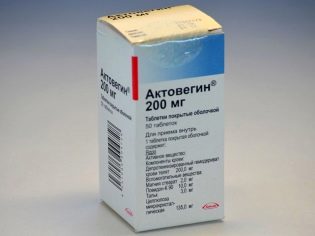
In order to improve the oxygenation and well-being of the fetus, special preparations are prescribed. One of these means is “Actovegin».
In order to prevent massive damage to cell membranes, in some cases, preparations containing essential phospholipids are used. They help maintain the structure of the cell wall, thus providing a building function.
Vitamin therapy is another component of the complex treatment of placental hyperplasia. Receiving vital substances helps to improve the functioning of the body. Assigned to various multivitamin complexes during pregnancy, as a rule, for a fairly long reception.
If viral or bacterial infections have caused the thickening of the placental tissue, they should also be treated. To do this, doctors resort to the appointment of antiviral and antibacterial agents. It should be noted that some of them may have an adverse effect on the fetus. In order to avoid such an impact, only the most safe and effective drugs that improve the general condition of both the very future mother and her baby are selected.
For more information about the placenta during pregnancy, see the following video.