Symptoms and effects of placental abruption in late pregnancy
In the late stages of pregnancy, a rather dangerous pathology can develop - detachment of the placental tissue. This article will outline the symptoms and effects of placental abruption in late pregnancy.
What it is?
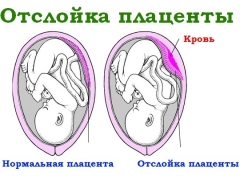
Placental abruption is a pathological condition in which the placental tissue begins to detach from the uterine wall much earlier than the birth. The placenta is a very important organ of pregnancy. It contains blood vessels that provide nutrition and oxygen to the developing baby. Normally, the placental tissue is firmly attached to the uterine wall.
During pregnancy, the placenta is supported by several anatomical structures. It is "held" in the uterus under the influence of:
- muscular framework of the uterus (myometrium);
- gestational sac;
- pressure amniotic fluid.
The special spongy structure of the placental tissue is ensured by the fact that the placenta is rather elastic. This allows it to gradually change its shape and size as the uterus grows, increasing in size during pregnancy. The elasticity of placental tissue allows it to remain complete in the absence of any damaging effects. The looseness of the placenta can cause it to be damaged.
The stronger the impact, the greater the chance of development of placental abruption. In later periods, this condition can be especially dangerous and requires urgent intervention by specialists. Placental abruption, according to statistics, occurs in obstetric practice in approximately 0.5-1.5% of cases. Doctors identify several provoking factors that increase the likelihood of the development of this pathology during pregnancy.
Causes of placental abruption
It often happens that it is difficult to identify any one reason for the development of this pathology. In some cases, several factors affecting the female body simultaneously or sequentially can lead to placental abruption. Doctors distinguish several clinical conditions that lead to the development of detachment of placental tissue from the uterine walls. These include:
- various vascular diseases (vasculopathy);
- pathology, accompanied by a violation of blood clotting;
- effects of mechanical stress (injury, falling on the belly, blows).
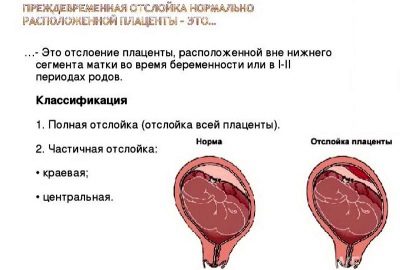
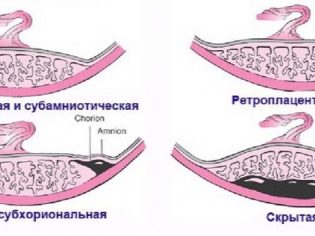
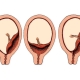
During the development of placental abruption, there is usually a change in intrauterine pressure. This contributes to the fact that the placental tissue begins to exfoliate from the uterine walls more intensely. In some cases, the placenta exfoliates from the uterine wall, section by section. Doctors distinguish several clinical variants of this pathology. Detachment can be of two types.
- Complete. In this case, almost all placental tissue is detached.
- Partial. In this case, only a specific part of the placenta exfoliates from the uterine wall.
With complete placental abruption, the general condition of the expectant mother and fetus usually deteriorates dramatically. This happens against the background of complete well-being. This condition is extremely dangerous. Further prognosis largely depends on how timely medical care is provided. Partial placental abruption has a more favorable prognosis. In this case, as a rule, adverse symptoms develop gradually.
However, this does not exclude the need to seek medical care. The placenta has a particularly important function. It supports the intrauterine development of the fetus at the proper level. If the placenta due to its damage is not able to provide the children's body with nutrients and oxygen, in such a situation its functioning is impaired.
Main symptoms
The most common clinical sign of placental abruption in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy is the development of bleeding. To explain the appearance of bleeding or bleeding can be quite simple. During detachment, mechanical detachment of placental tissue from the uterine wall occurs. At this time, bleeding develops.
However, it is not always possible to accurately and quickly determine the bleeding. In some cases, the placenta begins to flake off gradually. This contributes to the fact that a pregnant woman may first have a vaginal discharge with a reddish or crimson color. The severity of bleeding may be different.
Reviews of many women faced with placental abruption during pregnancy confirm this. Some pregnant women note that they did not have any strong or massive bleeding, and only reddish vaginal discharge appeared. Others describe the appearance of bleeding, which was accompanied by the development of other, not less uncomfortable symptoms. The severity of bleeding depends on several conditions:
- damage localization;
- the intensity of the causative factor;
- the size of the area of detachment;
- individual features of blood clotting;
- the presence of concomitant burden diseases.
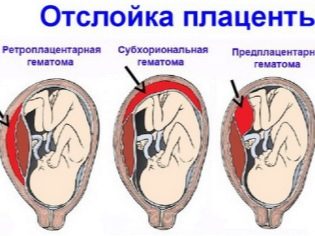
Bleeding that develops when the placental tissue is detached from the uterine wall may be external and internal. When the external version of a pregnant woman appears bleeding from the genital tract or specific bloody discharge. Internal bleeding is characterized by the absence of obvious signs. In this case, blood accumulates inside the uterus, forming a hematoma. Suspected internal bleeding with placental abruption can be.
In this case, a pregnant woman, as a rule, appears brown or brown discharge from the genital tract, may develop pain in the abdomen. It is important to note that external bleeding does not always exclude internal.
It happens that blood accumulates inside the uterus, and part of it flows out. This form of uterine bleeding is quite dangerous. In this case, as a rule, the fetus feels essentially disturbed.
Another symptom that usually occurs with placental abruption is the development of pain in the abdomen. The pain is often permanent. With partial detachment of the placenta, pain in the abdomen gradually increases. If there is a complete detachment of placental tissue from the uterine wall, abdominal pain occurs suddenly, often against the background of complete well-being.
The severity of pain in this pathology is different. In severe cases, with the development of strong functional disorders, a pregnant woman may even lose consciousness. It is not excluded the development of pain shock.
What is dangerous?
Placental abruption is an extremely dangerous obstetric pathology. Expectant tactics in this state should not be applied. The expectant mother who suspected the development of adverse symptoms should immediately seek medical attention. Delay in this situation (especially with complete placental abruption) can be deadly.
Total placental abruption can lead to the development of a strong, and in some cases even massive blood loss. This condition is dangerous for the future mother and her baby. In this case, a woman's blood pressure is greatly reduced, which helps to reduce the blood supply of vital organs.In this case, a pregnant woman can notice the appearance of "fog" in front of her eyes, the "flashing of the flies", and also even faint.
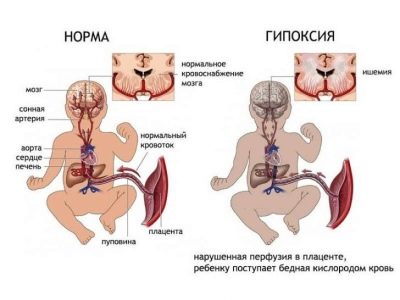
In this situation, the blood flow in the fetus is sharply reduced. The child suddenly feels sharp discomfort. At first, this is manifested in the fact that its heart rate and motor activity increase sharply. As the dangerous condition progresses, the condition of the fetus deteriorates significantly.
In this situation, fetal hypoxia (pronounced oxygen deficiency) occurs in the fetus. The oxygen saturation of the blood decreases, and the level of carbon dioxide rises rapidly.
If at this stage the doctors do not intervene, the further development of the situation may have an extremely unfavorable outcome. If placental abruption occurs suddenly, and medical care is not provided or is carried out untimely, in such a situation the threat to the life of the fetus develops.
Placental abruption, which develops in the late stages of pregnancy, may also be dangerous by the development of preterm labor. Exfoliation of placental tissue from the uterine wall is accompanied by a change in intrauterine pressure. This condition contributes to the fact that the placenta begins to shift downward, exerting a strong pressure on the fetal bladder in which the fetus is located. In such a situation, the possibility of a premature birth of a child increases substantially.
Effects
Placental abruption can also affect delivery tactics. It is possible to fully appreciate the long-term effects of this pathology after delivery. If detachment of the placental tissue occurs before the 36th week of pregnancy, in such a situation, conservative therapy can be applied. In this case, doctors necessarily evaluate the extent of the violations.
If the condition of the future mother and her baby doctors can compensate by introducing conservative drug therapy, they do it. In this case, as a rule, a pregnant woman is left in the hospital under the supervision of specialists. Being in the hospital helps doctors to assess the dynamics of the development of pathology in a timely manner, as well as, if necessary, to resort to surgical obstetrics. Pregnant women who are hospitalized to the hospital with the development of placental abruption, usually conducted dynamic examinations.
For example, she is undergoing ultrasound and cardiotocography. A prerequisite is bed rest. Any physical activity and the lifting of heavy objects are categorically excluded, as this may contribute to the deterioration of the general condition and the progression of placental abruption. If necessary, doctors resort to the appointment of antispasmodics, as well as anti-disintegrating agents. These drugs affect blood counts, and are also good prophylaxis for the development of dangerous complications of this pathology.
Often, with placental abruption, accompanied by massive blood loss, anemia develops. It is characterized by a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and (or) red blood cells in the blood. As a rule, in such a situation, to improve the general condition of the mother and baby, doctors resort to prescribing iron supplements.
If a pregnant woman with placental abruption is hospitalized in a hospital in a critical condition, and conservative therapy does not lead to an improvement in health, in this case, doctors are forced to resort to performing an urgent cesarean section. This emergency operation in this situation is carried out for health reasons.
It is important that specialists decide in time about the necessary surgical obstetrics.
See the following video for symptoms and consequences of placental abruption.