Deformation of the gallbladder in a child
In the modern world, children with various digestive problems are increasingly registered. Many of them are associated with the deformation of the gallbladder in a child.
What it is?
Not everyone knows what the gallbladder is responsible for in the body. This small reservoir is needed to store bile reserves, which is regularly formed in the liver. It is possible to live without a gallbladder, but the quality of life deteriorates significantly.
In gastroenterological practice, there are many different diseases of the gallbladder, caused by anatomical defects in its structure. Such anomalies lead to disruption of the functioning of the body, leading to the appearance of adverse symptoms. As a rule, they manifest in a child dyspepsia, disorders in digestion.
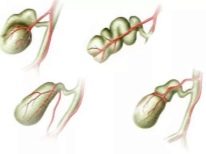
Anatomical defects of the structure of the gallbladder can manifest themselves in different ways. Most often they appear as bending, bending, or deformation. Under these conditions, the correct anatomy of the organ changes.
Various excesses of the gallbladder lead to disruption of its work, the digestion in this case is disturbed. The severity of adverse symptoms depends on the true cause of the condition.
Norm
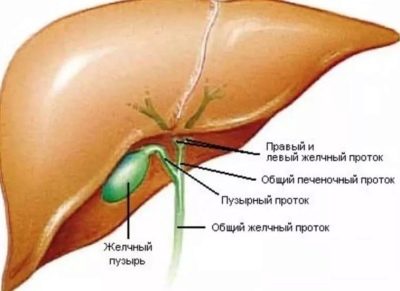
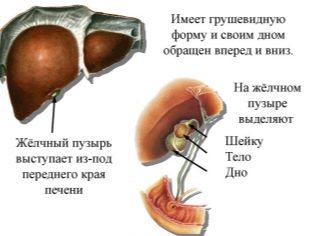
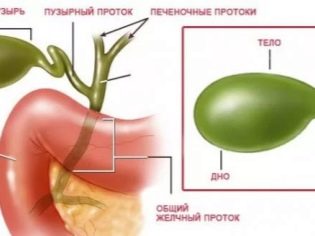
The projection of the gallbladder on the body is the area under the right costal arch. It is in this zone is the body responsible for the storage of bile. In a healthy person, the gallbladder is a pear-like reservoir. It consists of several parts: the body, the bottom and the neck.
The accumulation of bile occurs directly in the area of the body. In the process of digestion, the necessary amount of it moves to the neck area before the anatomical narrowing - the Lutkens sphincter. This mechanism of biliary excretion invented by nature. It allows you to select the required amount of bile with each meal.
Bile moves along the bile duct and reaches the "fork". One part of the digestive secretion is sent to the liver, and the other enters the intestine with the help of another anatomical formation, the sphincter of Oddi.
The reasons
The development of various pathologies associated with anatomical defects in the structure of an organ results from the following factors:
- Various pathologies in intrauterine development. Violation of the course of pregnancy, infection of the future mother with various infections or hereditary diseases contribute to the violation of organogenesis in the fetus. The most dangerous period is the first trimester. It is at this time that most organs appear, including the digestive system. Symptoms of gallbladder dyskinesia may appear already in a newborn baby (immediately after birth) or in infants.
- Malnutrition. This factor leads to the appearance of signs of dyskinesia already at an older age. Abuse of fatty and fried foods, as well as fast food contributes to the active work of the body. If the baby constantly eats such food, then the gallbladder may start to work incorrectly. For the processing of fatty foods requires the release of a greater amount of bile, which contributes to the development of various torsion and kinks in the neck of the body.
- Traumatic injury. Injuries to the abdomen can lead to the curvature of the anatomical shape of the organ. The gallbladder becomes deformed or bent. The change in the shape of the organ appears after the fall of the child on the belly. In this case, it becomes wrong.
- Heredity. In families where parents have signs of a change in the anatomical shape of the gallbladder, children are more likely to be born with the same characteristics. This pattern is due to the presence of specific genes, which from generation to generation pass on certain parameters of the structure of organs. With this option, congenital anomalies of the structure of the gallbladder are possible.
- Concomitant diseases of internal organs. Pathologies of the liver and pancreas often contribute to the development of various anatomical defects in the structure of the gallbladder. This is due to the proximity of the adjacent abdominal organs.
Kinds
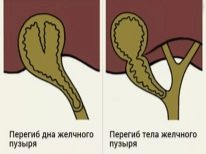
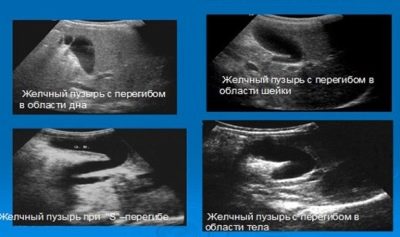
Usually the shape of a healthy gallbladder is fixed. When deformation occurs, it changes. In some cases, additional constrictions or jumpers are present in the gallbladder. They are formed in utero, in normal they should not be. Such bridges contribute to the fact that the shape of the gallbladder changes and becomes S-shaped.
It is important to note that the anatomically correct form of the body contributes to the physiological secretion of bile - as a result of food intake. Any jumpers in the organ cause a violation of its outflow.
Ultimately, this leads to manifestations of dyskinesia and the formation of chronic cholecystitis.
The curved shape of the gallbladder is also not conducive to the normal secretion of bile. Usually, with this pathology, bile can accumulate in the body or bottom. Prolonged accumulation can lead to the development of gallstone disease. Usually, the first signs of the disease appear only at an older age.
Symptoms
Most forms of anatomical organ defects are asymptomatic. Many people live their whole lives, not even knowing that they have any anomalies of the gallbladder. Mild flow is not accompanied by the appearance of adverse symptoms. Quite often, the diagnosis is made spontaneously, after an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity.
If the anatomical defect is quite pronounced, then this can lead to the development of various adverse symptoms in the child.
They can be expressed in different ways. The development of these uncomfortable symptoms associated with the stagnation of bile.
The following signs of dysfunction of the gallbladder are especially common:
- Nausea. Usually it occurs after eating fatty or fried foods. Nausea is mild. Often runs independently, without the use of drugs. Any errors in the diet lead to the appearance of this symptom.
- Vomiting. It is extremely rare. It usually occurs after family feasts and eating various fatty foods. Vomiting develops 30-40 minutes after ingestion of food. Quite often, it is a one-time, it goes back to the eaten contents.
- Soreness in the right hypochondrium. This symptom does not occur in all cases. Usually pain or pulling pain occurs when there are errors in the diet. The intensity of the pain syndrome is from mild to moderate. The use of enzyme preparations and antispasmodics significantly alleviates the condition.
- Increased gas formation. Abuse of fatty and fried foods leads to the fact that the supply of bile is not enough for the implementation of digestion. Prolonged stagnation contributes to the development of putrefactive processes in the abdominal cavity and gas formation. This symptom is also often combined with bloating.
- Breaking stool Small patients with dyskinesia of the gallbladder or signs of stagnation of bile often have constipation. Maybe spastic chair. With the involvement of the pancreas, diarrhea can occur, but this is quite rare.
- Fever. Usually it does not increase above subfebrile values. An increase in body temperature to 37.5 may be the first sign of trouble in the gallbladder.This condition often causes the child to feel hot and increases general weakness.
- Disturbed appetite. In babies who have problems with the work of the gallbladder, various taste preferences may appear. This is usually a tendency to add acidic foods to food. Often, little patients with impaired bile outflow like to eat lemons or other citrus fruits.
Diagnostics
To suspect anatomical defects of the gallbladder at home is impossible. Even conducting a clinical examination and palpation of the abdomen by a doctor gives only a preliminary diagnosis. To determine the anatomical defect requires additional research.
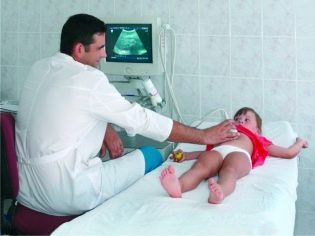
To date, the most informative and safe examination of the abdominal organs is an ultrasound examination.
This method has been successfully used in pediatric practice for many years to identify various pathologies of the gastrointestinal organs. This study is very informative. It helps to establish the diagnosis in almost 100% of cases.
During the study, the ultrasound doctor can detect any deformity of the gallbladder. In the presence of an inflammatory process, the contour of the organ changes, it becomes double. Contour investigation is very important. It allows you to install all the defects of the gallbladder wall that occur with various anatomical problems.
The first early sign of the presence of anomalies in the body is the amplification of the echo signal from the reflected walls. This suggests that bile stasis is present in the organ or there are signs of inflammation. Ultrasound also helps determine the amount of secretion in the gallbladder. With this method, you can eliminate chronic cholecystitis, as well as detect the presence of stones in the body at the earliest stages.
Doctors use various laboratory tests to assess functional disorders. With pathologies of the gallbladder, biochemical blood tests are prescribed. Evaluate the work of the body helps the analysis of indicators of bile enzymes: bilirubin and its fractions. There are age norms. The excess of indicators indicates the presence of violations in the secretion of bile and the presence of diseases of the liver or gallbladder.
Treatment
Therapy of anatomical defects of the gallbladder is usually performed by a pediatric gastroenterologist. He prescribes treatment after all the necessary examinations and determination of the exact diagnosis. With a mild course of the disease, it is enough just to diet regularly. Such medical nutrition should be prescribed in a timely manner, on a diet will need to sit throughout life.
With the appearance of adverse symptoms requires the appointment of special medicines. To improve the flow of bile, antispasmodic drugs are prescribed. Regular use of these drugs is not required. They are assigned either to the course acceptance, or on demand. Such funds remove the spasm and normalize the discharge of bile through the bile ducts.
Contribute to the excellent work of the gallbladder and various physiotherapeutic procedures. They help to improve the blood supply to the body, after which it functions better. Physical therapy also helps to improve the secretory functions of the gallbladder and eliminate various spasms of the gastrointestinal organs.
Sanatorium treatment is necessary for all children suffering from digestive diseases. Regular nutrition with regard to pathologies allows achieving positive results.
Doctors recommend such treatment at least once a year. During the rest, the kid improves the digestive processes, he becomes more healthy.
For the treatment of stagnant bile, a special diet is required. All fatty and fried foods are absent from this therapeutic diet. The kid should use high-quality protein foods that do not contain fat, but have good saturating properties.Vegetables and fruits are important components of therapeutic nutrition.
It should be eaten in small portions, up to 5-6 times a day. This fractional nutrition allows you to normalize the flow of bile from the gallbladder. When abdominal pain occurs, choose dishes cooked in a gentle way (steamed or baked).
You can supplement the diet with any fruit juices and compotes. Perfectly also suitable broth hips. This drink is good thirst quencher, and also contributes to good biliary excretion.
Usually, conservative therapy is sufficient for the treatment of gallbladder deformity. Surgical operations are shown only in the presence of persistent anatomical defects that lead to severe disruption of the functioning of organs.
Diseases that occur fairly easily do not require intervention from the surgeons.
The disease is controlled by a gastroenterologist. Babies with gallbladder deformities should visit this doctor every year. You can perform an ultrasound examination of an organ once every few years. The annual implementation of the survey is not necessarily.
On what problems can be with the gall bladder and how to treat them, see the next video.