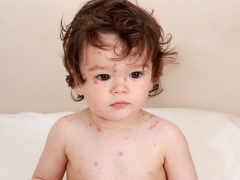
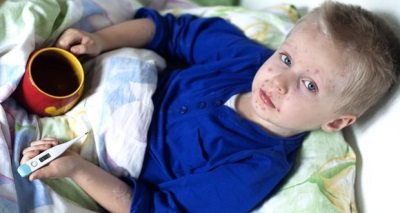
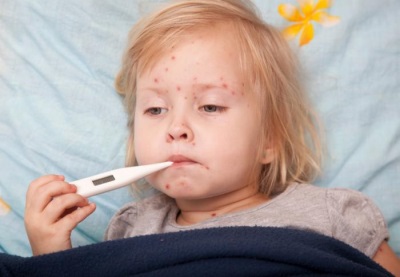
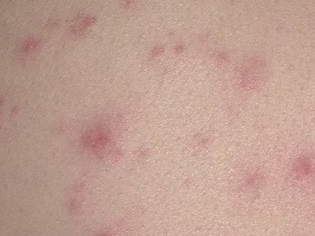
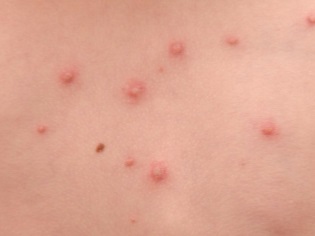
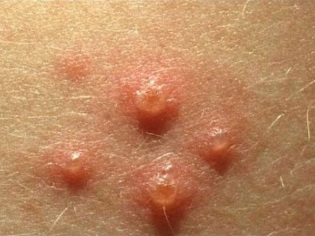
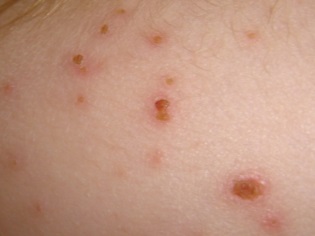
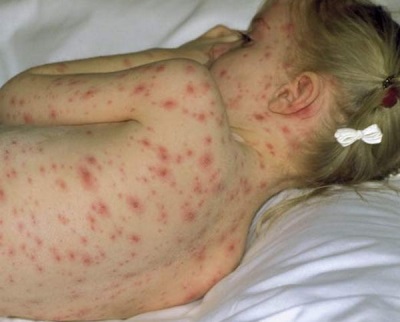
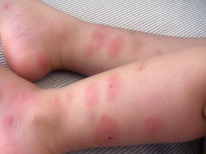
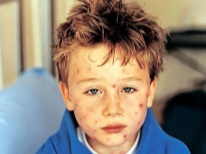
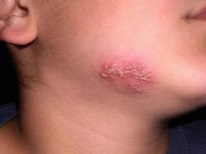
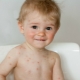
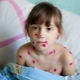
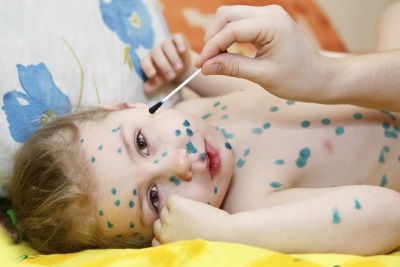
What does chickenpox look like: compare rash with the one in the photo
ChickenpoxIn everyday life, chickenpox is a common childhood infection that is highly infectious. It often appears in preschool and school-age children. That is why all parents should know how the chicken pox looks like in children and how to recognize this infection. In addition, for mothers, information is important, where he gets sick with chickenpox, what signs of this infection are in addition to the rash, and whether there is chickenpox without a rash.
How to catch chickenpox
Transmission of the virus Varicella Zoster, which is the causative agent of chickenpox and a representative of the group of herpes viruses, occurs through airborne droplets. Ill child becomes contagious in the end incubation period, the duration of which is often 14 days, but it can be from 7 to 21 days. You can become infected one day after the appearance of a rash, during the entire acute period of infection and until the crust begins to fall off (up to five days after the last bubbles form on the skin).
Most often, children under 7 years of age are infected with chickenpox. In infants, chickenpox can develop at the age of more than six months, when the child ceases to be protected by maternal antibodies. In the newborn, such an infection practically does not occur, since the baby’s blood contains antibodies to the chickenpox, which his mother had had.
Those who have had chickenpox acquire lifelong immunity to this disease. Because of their high susceptibility to the Varicella Zoster virus, adults rarely get sick, since many people endure such an infection at preschool age. Repeated chicken pox is possible only with severe immunodeficiency.
Chicken Pox Forms
In a typical course, the Varicella Zoster virus enters the child’s body through the mucous membranes, and then enters the bloodstream. It spreads the pathogen through the body, causing the virus to settle in the surface layer of the skin, causing a rash. The reproduction of the virus in a child’s body and the allergic response to it cause fever and other symptoms of intoxication in a child.
Depending on the flow, typical chickenpox is divided into light, moderate and heavy. A mild chickenpox may not affect the general condition of the child. When it rashes a little, and temperature body may remain normal. Severe form is manifested by massive rashes, fever, severe itching, other symptoms of intoxication. It is more common in adults.
Separately allocated atypical chickenpox in children, in which all the symptoms are very pronounced. With such chickenpox in a child, large blisters with pus may form on the body, and then the child will be diagnosed with a bullous form. If the rash contains blood, it is a sign of hemorrhagic chickenpox, and the purulent-bloody contents of the vesicles indicate a gangrenous-necrotic form. The atypical variants include the rudimentary form of chickenpox, which is asymptomatic.
Chickenpox Symptoms
The main manifestation of chickenpox is a characteristic rash. Its main feature, allowing to distinguish rashes from other infections, is called polymorphism. This term designates a variety of elements of the rash on the skin of the child at the same time (next to the healing eruptions, covered with a crust, appear "fresh"). Most babies have a rash that itches.
Other signs of chickenpox in a child:
- Increased body temperature.
- Muscle soreness.
- Weakness.
- Headaches.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Sore throat.
- Restless behavior.
- Reduced appetite.
What do acne do with chickenpox?
Depending on the pathological process that occurs with chickenpox in the skin, the rash is represented by such elements, replacing each other:
- Stains. Their appearance is due to local expansion of the capillaries under the influence of the virus. These are small pink specks from 2 to 4 mm in diameter.
- Papules They appear after a few hours on the spot due to serous edema and look like slightly raised reddish formations resembling insect bites.
- Vesicles Their formation in place of papules is associated with detachment of the epidermis. Such bubbles are single-chamber and surrounded by a “rim” of red color. Inside is a clear liquid, which soon becomes cloudy.
- Sores They are formed on the site of burst bubbles and rather quickly become covered with crusts. The skin heals and crusts disappear within two to three weeks.
On these photos of the rash, you can see all these elements:
Localization of rash
Rash with chickenpox covers almost the entire surface of the child’s body, not only on the palms and on the feet, although these areas are covered by a rash in severe illness. The rash can be seen on the arms, abdomen, back, lateral parts of the body, legs and on the genitals. In some children, rash elements also occur on the mucous membranes. In such cases, the bubbles are visible in the mouth and throat, and can also be located on the eyeball.
Common Questions
What day does the rash appear
In many children, the prodromal period precedes the period of rash, during which the child feels symptoms of indisposition. Its duration is 1-2 days. Sometimes there is no prodromal period in chickenpox and the disease immediately manifests symptoms of intoxication and a rash.
How quickly the rash spreads through the body
The first rash with chickenpox appears, as a rule, on the body. Then they very quickly begin to cover the hands and feet of the child, and then arise on the head. Some children are detected chicken pox in the mouth and on other mucous membranes. With each new wave of eruption, the body temperature rises. After the appearance of the stain and its transformation into a papule and a bubble, the rash crust over a period of one to two days.
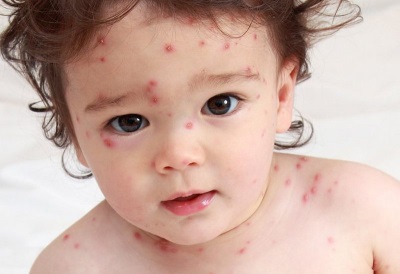
When the rash stops
The duration of the rash with varicella is 2-9 days depending on the course of the infection. For most children, new spots stop appearing on the fifth or eighth day of the disease, after which the recovery period begins.
Whether traces remain with chickenpox
If the sores are not combed, they will not leave marks, since the vesicles in chickenpox do not affect the skin growth zone. But when combing and entering a bacterial infection are traces. Such holes or scars after a chickenpox remain until the end of life.
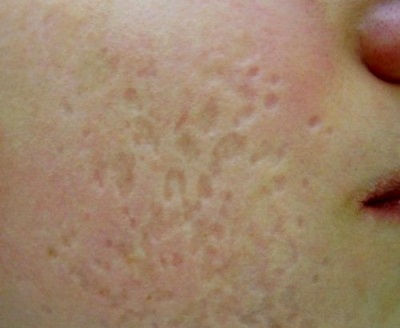
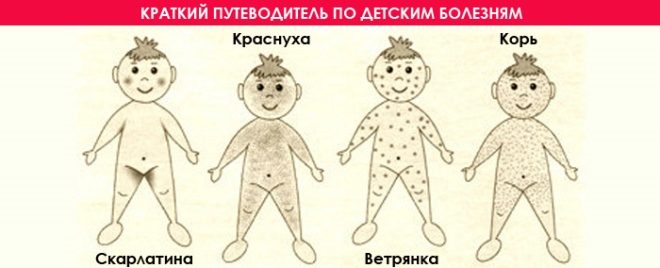
What diseases of rash are similar to those with chickenpox
In the diagnosis of chicken pox, its rash should be distinguished from insect bites, vesicular rickettsiosis and herpes rash. Similar rashes are also observed in streptoderma, atopic dermatitis and atypical measles infection.
Can there be no rash
A rash occurs in most children with chickenpox. In mild form, they can be represented by several vesicles that heal quickly. Chicken pox without a rash is extremely rare.
What happens if you do not treat chicken pox
There is no specific treatment for chickenpox, so all therapy for such an infection is aimed at eliminating or alleviating the symptoms. The child is shown bed rest during the fever and is given antipyretic drugs, and when expressed itch prescribe antihistamines. If you do not use this treatment, the general condition of the child will be worse and there is a high probability of scratching the rash.
Locally, the rash is treated with disinfectant solutions. If this is not done, the risk of bacterial infection of the elements of the rash (the appearance of pustules) increases. However, even without treatment, the vesicles become covered with a crust and then heal without a trace.
About what to treat rash in a child, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.