Symptoms, signs and treatment of varicella in children
Every mother is at risk of chicken pox, because this childhood infection is highly infectious. What is it, how is chickenpox spread and how is it usually tolerated? At what age is it better to have chickenpox? What is the treatment of this infectious disease and how to protect against the pathogen of chickenpox? Is it possible to quickly get rid of chickenpox rash? Answers to these and other questions about chicken pox should be known to all parents.
The reasons
Chickenpox is a viral infection caused by the DNA virus Varicella Zoster. It belongs to the viruses of the herpes group, in particular, is a herpes virus of the third type. In addition to chickenpox, the same pathogen provokes the appearance of the disease "herpes zoster", which is also called shingles.
The susceptibility of a previously ill person with chickenpox to the Varicella Zoster virus is up to 90-100%. For infection, it is enough to be near the sick child for 5-10 minutes. In addition, such a pathogen is highly volatile, as it can fly with particles of mucus up to 20 meters.
At the same time, the chickenpox virus is unstable to the action of external conditions. If the causative agent of such an infection is outside the human body for more than 10-15 minutes, it dies. Sun rays, disinfectants, high temperatures and other external factors help to speed up his death.
When the chicken pox has passed, and the child has recovered, the virus Varicella Zoster does not disappear from the body of the patient for good. It remains inactive in the nerve tissues. In people over 40 years old, this virus becomes active in 15% of cases, which is manifested by symptoms of herpes zoster.
Ways of Transmission
Chickenpox is transmitted from sick people to healthy babies and adults who do not have immunity to this infection in the following ways:
- Airborne. This is the most common variant of the spread of chickenpox virus. The pathogen is transferred with particles of mucus after sneezing or coughing, as well as during normal breathing. A sick person begins to isolate the varicella-zoster virus at a time when there are no signs of the disease (on the last day of the incubation period). Further, it is a source of infection during the entire period of rash (this is the most active period of infection). As soon as five days after the formation of the last new bubbles on the patient's skin, the child ceases to be infectious.
- Contact. This route of transmission of the Varicella Zoster virus is more rare. With it, the pathogen gets to healthy people when it comes in contact with chickenpox bubbles, which contain a lot of viruses inside. Theoretically, you can transfer the virus to linen and various objects, but in practice, infection through household items or third parties almost never happens.
- Transplacental. This way the chickenpox infects the fetus if the mother did not have this infection before the pregnancy and did not get the vaccine. At the same time, infection at an early stage of gestation threatens with the development of serious pathologies in a child.If the virus penetrated the body after 12 weeks of gestation, the risk of congenital chickenpox, an infection that manifests itself clinically immediately after birth and is quite difficult, increases. Especially dangerous is the period 5 days before birth, because with earlier infection to the baby gets not only the pathogen, but also antibodies developed in my mother's body. If the baby gets infected just before childbirth, the antibodies do not have time to develop and are not transferred to it, which leads to congenital chickenpox.
Referring to where the chickenpox comes from, it is worth noting the possibility of transmission of the virus Varicella Zoster from patients with shingles, because in the bubbles that appear on their body there is a lot of virus. And if a child who has not had chickenpox, will accidentally come into contact with such bubbles, he will have chickenpox. That is why the patient who has had chickenpox can be a carrier of the disease, but provided that such a person has an active stage of herpes zoster.
At what age are sick more often
Chickenpox is most often diagnosed in children older than two years old, but less than ten years old, and children 4-5 years old are considered to be extremely susceptible to the Varicella Zoster virus. At the same time, the course of the disease in preschool and junior school children is predominantly easy.
Infants up to 6 months of chicken pox practically do not get sick. They are protected by maternal antibodies, which are obtained during pregnancy and during breastfeeding. Newborn babies can get chickenpox only if the mother did not suffer from such an infection before (they have no protection).
From 6 months of age, the antibodies received from the mother in the child's body become less, so babies from this age, 1 year and older, can get chickenpox when in contact with a sick person. In such a situation, a one-year-old child also suffers the disease mostly in a mild form.
Adolescents can also get chickenpox if they haven’t been ill at an earlier age. As in adults, the course of the disease is often severe, the development of an atypical form is possible, and the risk of complications is increased.
You can learn more about this by looking at the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.
Stages of the disease
Since the moment of contact of Varicella Zoster with a healthy child, the disease goes through the following stages:
- Incubation period. In it, the pathogen actively multiplies and accumulates in the cells of the mucous membranes, and the symptoms of the disease are absent.
- Prodromal period. This is the time when the virus enters the bloodstream and the infection begins to manifest indisposition, but it is still impossible to accurately diagnose chicken pox.
- The period of rash. In it, the pathogen attacks the skin cells and a rash characteristic of chickenpox appears on the body, and the baby’s general condition is worsened.
- The recovery period. At this time, antibodies are formed, new elements of the rash cease to appear, and all the existing bubbles heal.
Incubation period
The duration of this period can vary from seven days to 21 days, but most often in childhood, chickenpox manifests itself two weeks after contact with the virus. A decrease in the incubation period is observed in babies up to a year, as well as in immunocompromised babies. A longer incubation period occurs in adolescents — they rarely first symptoms infections begin 23 days after infection.
Symptoms
First signs
The onset of chickenpox is similar to the onset of any viral infection and manifests itself:
- Weakness
- Headache.
- Worsened appetite.
- Complaints that sore throat.
- Muscle aches.
- Moody behavior, irritability.
- Disrupted sleep.
In severe form, the child may experience vomiting, enlarged lymph nodes are detected. Cough and runny nose with uncomplicated chicken pox are not found.
As the chickenpox manifests itself in the early days, you can look at the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.
Temperature rise
Fever is one of the most common symptoms of chickenpox, and its severity is directly related to the severity of the infection. If the disease is mild, then the temperature of the body may remain within the normal range or slightly increase. In the case of moderate flow, mother sees 37-38 degrees on a thermometer, and severe chickenpox usually proceeds with a temperature above + 39 ° C.
Chickenpox rash
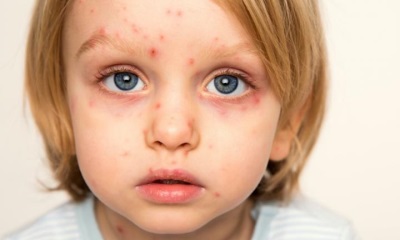
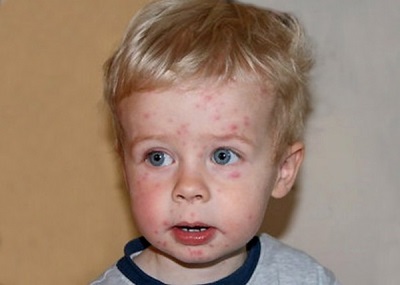
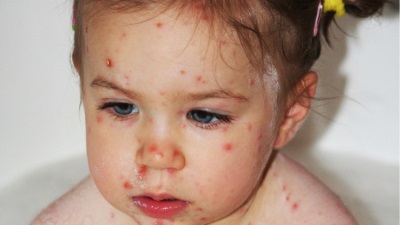
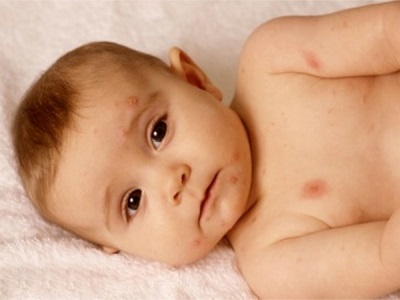
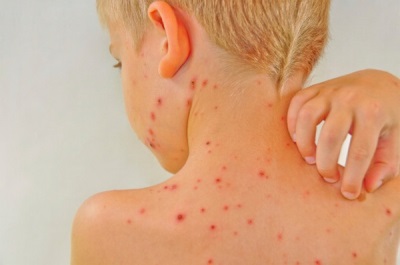
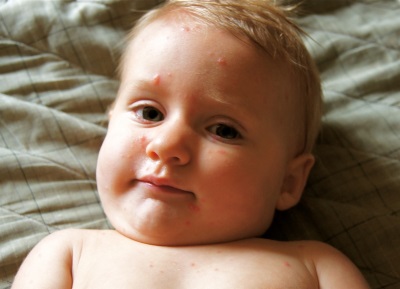
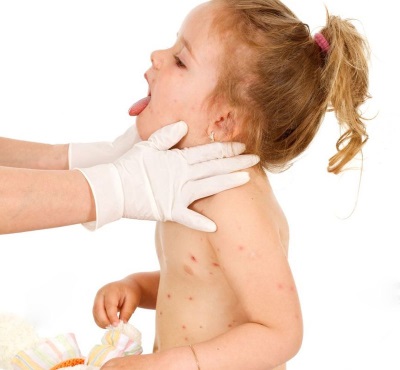
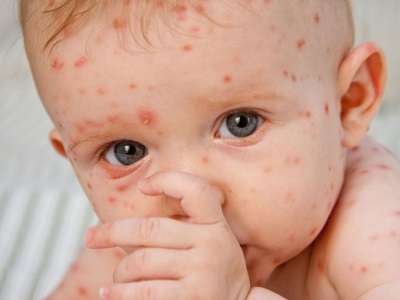
Rash can be called the most characteristic sign of chicken pox. Cases of chickenpox without rashes are practically not found. Even with a very light course on the body of the child at least a few bubbles appear.
As a rule, a rash is found on the body of the child at the same time as the temperature rises. The first elements are marked on the body, and then they appear on the arms and legs, as well as on the head. They are quite itchy, causing children severe discomfort. It is also important to note that varicella acne does not occur on the palms and feet, but can occur not only on the skin surface, but also on the mucous membrane, for example, on the tongue, on the soft palate, on the eyes or on the genitals.
At first, chickenpox rash is represented by small reddish spots, which quickly become papules (at this stage, the rashes look like insect bites). After some time, the top layer of the skin in the papules begins to flake off, and inside the transparent liquid accumulates, resulting in the formation of single-chamber vesicles in place of the papules. Around these bubbles is visible red rim of inflamed skin.
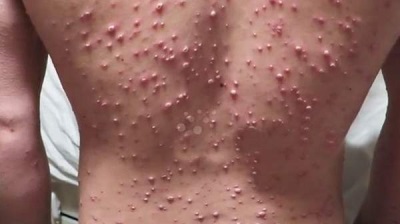
The contents of the vesicles soon become turbid, the bubbles burst and become covered with crusts. Under the crusts, the skin gradually heals, and if you do not scratch the rash, no trace of it will remain. Simultaneously with the formation of crusts, new spots appear on the skin of the child, from which vesicles are also formed.
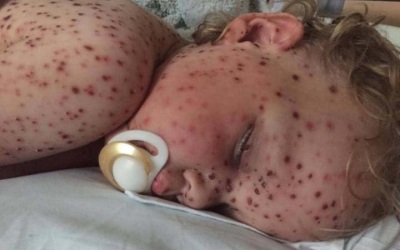
If the baby has a light chickenpox, new “waves” of rash may not be observed, and with a severe form, vesicles form within a week or longer, and their number is very large. At the same time, as a new “wave” of bubbles appears, the body temperature also rises.
Forms
Taking into account the clinical manifestations and the course of chicken pox, a typical form is distinguished, the symptoms of which are described above, as well as such atypical forms:
- Bullous, in which the rash is represented by large vesicles filled with pus.
- Hemorrhagic, with bloody contents inside the vesicles.
- Gangrenous-necrotic, in which the vesicles contain both blood and pus.
These types of chicken pox are commonly found in severe illness. However, there is a rudimentary form of the infection with an asymptomatic course.
Duration of illness
It’s impossible to answer exactly how many days the chicken pox goes, because every child suffers such an infectious disease in its own way. The prodromal period in most children lasts 1-2 days, but sometimes it is so short that the rash begins to appear almost immediately after the baby has felt bad.
The period of rash depending on the course of the disease can last 2 days and 9 days, but on average, new vesicles cease to appear after 5-8 days from the beginning of the clinical symptoms of the infection.
Complete healing of the skin after the formation of crusts on top of all vesicles lasts 1-2 weeks.If a child has light chickenpox, then the disease can completely end in 7-8 days, and with more severe course and complications, the child can get sick for several weeks or longer.
Complications
The occurrence of complications of chickenpox can be provoked by the virus itself or by the addition of a bacterial infection.
Severe chicken pox can be complicated by:
- Pneumonia (the most frequent complication).
- Encephalitis (the most dangerous complication).
- Bacterial infections of the skin (due to scratching of the bubbles on the skin).
- Stomatitis (when infected with bubbles in the mouth).
- Otitis (in the formation of bubbles in the ear).
- Corneal lesions.
- Jade.
- Hepatitis.
- Myocarditis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the joints, muscles, genitals and others.
Many are wondering if you can die from chickenpox. Such a risk does exist, since the mortality rate for complications, such as chickenpox encephalitis, reaches 10%. No less dangerous and provoked by chickenpox pneumonia, and chickenpox croup.
Diagnostics
Most often, the diagnosis of chicken pox is made on the basis of complaints and clinical manifestations of such an infection, because with a rise in temperature and a rash, almost all mothers cause a pediatrician, and an experienced doctor often has no problem how to determine if the child has chicken pox. However, the question of how to distinguish chickenpox from allergies, enterovirus, streptoderma, allergies, measles and herpes can be quite complicated, because with such diseases, rashes and other symptoms are very similar to chicken pox.
In such cases, it is possible to understand that this is really chicken pox, with the help of an additional examination of venous blood. From the first days of the disease, it is possible to detect the virus using the PCR reaction (this study reveals the DNA of the pathogen), and from 4-7 days from the onset of chickenpox in the blood of a sick child using ELISA, antibodies (M immunoglobulins) to the herpes virus type 3 are detected.
Chicken Pox Treatment
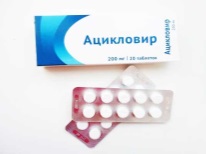
- In childhood most cases windmills are treated at home without the use of antiviral drugs. The child is given only medications aimed at alleviating the symptoms of the infection. Antiviral agents, for example, tablets Acyclovir, apply only in severe. Antibiotics for varicella are prescribed only when bacterial complications appear.
- Children and adults with chickenpox are isolated to eliminate the risk of infecting people without immunity. This is especially important for such categories of people as pregnant women, patients with immunodeficiency, people with chronic pathologies and some others.
- If the temperature is very high, bedding is prescribed for the child with chickenpox. It is not required to be constantly in bed at a low or normal temperature, but it is desirable to limit physical activity.
- Food with chickenpox should be light, Therefore, the menu includes soups, dairy products, fish and steamed meat, fruit purees, vegetable dishes. Special diet in mild form is not required, but parents should know what to eat with chickenpox. This is considered to be spicy, fried, smoked, as well as everything that is hard to digest. If bubbles appear in the mouth, food is given in a semi-liquid form.
- A child with chickenpox is advised to give more warm drink. He is offered morsy, weak tea, broth hips, clear water, unsweetened compote and other drinks.
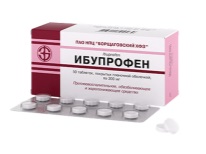
- To reduce the temperature, use antipyretic drugs approved in childhood - Paracetamol and ibuprofen. Both drugs effectively fight fever, but their dosage must be coordinated with the pediatrician. Do not use aspirin for chickenpox.
- To reduce the nervous excitability and capriciousness of a child with chickenpox, Often use homeopathic or herbal preparations, for example, Nervohel or Nott.
- Treatment of bubbles in chickenpox is aimed at reducing itching and protecting the skin from infection. The use of brilliant green and fucorcin is quite common. Also often used antiseptics such as potassium permanganate (preparing a pale pink liquid) and hydrogen peroxide.
- To reduce the activity of the pathogen, The baby’s skin can be treated with gel or Viferon ointment.
- For reducing itching and faster healing Zinc-based products are often used, for example, Zindol suspension or Calamine lotion. Such drugs are allowed from birth.
- Children over 2 years old can smear the skin with PoxCline. It is a gel based on aloe vera and other natural ingredients (packaged as a spray). The product is easy to apply, fast acting, non-toxic and non-addictive.
- To accelerate the healing of the bubbles, you can lubricate them with tea tree oil. Also, regeneration processes in the skin are stimulated by treatment with salicylic alcohol.
- If the rash is very itchy and bothers the child, you should discuss this with your doctor, which can prescribe antihistamines to reduce itching. It may be drugs such as Suprastin, Zodak, Claritin, Loratadine other. From local preparations use the gel Fenistil.
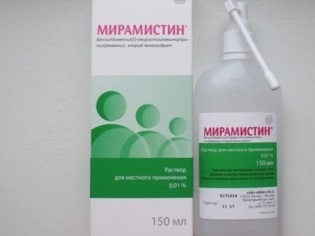
- With the appearance of bubbles on the oral mucosa baby is recommended to gargle Miramistin, herbal decoctions, furatsilina solution. If painful sores have formed in the mouth, they should be lubricated with anesthetic gels used in teething (Calgel, Kamistad other).
- Some parents are wondering if you can cauterize the chickenpox vesicles with iodine. This is not recommended since such treatment will cause itching.
- To remove scars due to the scratching of the bubbles and the penetration of the infection, use local products such as Counter-Tubex, Medgel, Rescuer, Dermatiks, Mederma and others.
The opinion of Dr. Komarovsky on how to treat chickenpox, you can find out by watching his transfer.
Immunity after chickenpox
In children who have had chickenpox, immunity remains, which is persistent and lifelong (it protects against this infection for life). Again You can rarely get chickenpox. Such cases are diagnosed in no more than 3% of those who have been ill and are associated primarily with immunodeficiency states.
Tips for parents
Frequent short hygienic baths help to reduce itching. Bathe with chickenpox not recommended only at high body temperature. When the child is better, the baths are allowed up to 4-6 times a day, but you should not use detergents and washcloths, and after the procedure, do not rub the body with a towel, but only lightly dab the water. For more on this, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.
- Make sure the room is not too hot, and the child’s clothing was natural and rather spacious, since overheating contributes to the enhancement of pruritus.
- Pay attention to preventing the scratching of the bubbles, because then you will not have problems, how to remove traces and scars after an illness. Briefly cut the nails or wear gloves to the child (if he is a baby), and also constantly distract if you notice that the baby is trying to scratch the rash.
- The fact that a child has developed complications may suggest such symptoms like cough, blue skin, shortness of breath, frequent vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, convulsions, photophobia, conjunctivitis and other symptoms. When they appear, you should immediately call a doctor.
- Do not hesitate to seek medical help and at high temperatures, especially if it's hard to shoot down. Also, you should be alerted by a rise in temperature a few days after the normalization of the general condition. Contact a pediatrician should be after 2 weeks from the onset of the disease, if the rash has not yet passed.
- Although a child with chickenpox is no longer contagious 5 days after the last new vesicles have been detected on the skin, do not rush to go out with him to crowded places. It is best to consult a doctor about returning to the children's team, because the time when you can go to school after chickenpox or start kindergarten again will be individual for each child.

To make the child understand what is happening to him, tell him about the chicken pox and show a cartoon, for example, about kitty Musti. Through viewing, a child in an understandable and interesting form can understand how the disease is manifested and transmitted. In addition, the cartoon shows why patients with chickenpox should not receive guests.
Prevention
To prevent the spread of the virus, chickenpox use the following measures:
- Isolation of patients for the period of their infectiousness.
- Allocation of separate dishes, linen and other hygiene items to a child.
- Separate washing clothes sick child.
- The use of gauze dressings.
- Frequent airing and wet cleaning of the room in which there is a sick child.
This can help to avoid infection of households who did not suffer from such an infection in childhood, but often ineffectively, because the infection is transmitted even during the incubation period.
A more effective way to protect yourself or a child is called varicella vaccination. In our country, it is not mandatory, so parents can purchase a vaccine and make it at will.
There are 2 varicella vaccines - Okavaks and Varilriks. They contain a weakened virus and are predominantly well tolerated.
Chickenpox vaccination can be done from 9 months of age. If you vaccinate a child under the age of 13, then the vaccine is placed only once. Over the age of 13 years, for complete protection against the Varicella Zoster virus, two vaccinations are required, which are carried out with a break of 6-10 weeks. The injection is done intramuscularly or subcutaneously in the shoulder area.
You can learn more about chicken pox by watching Dr. Komarovsky’s program.