MRI of the brain of a child
Modern technologies allow to detect various diseases at the earliest stages. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain has already saved hundreds of thousands of small lives.
What is the essence of research?
Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI of the brain is used to diagnose various diseases. Modern pediatric neurology does not appear without the use of this highly accurate diagnostic method. Every day, thousands of babies living in different parts of the world undergo this study.
For the first time, the medical community began talking about brain MRI at the end of the last century. This method was an unconditional breakthrough in the diagnosis of various diseases. Quite often, brain pathologies remained "dumb." Many malignant tumors and neoplasms were detected only in the later stages. The possibilities of magnetic resonance imaging allowed us to recognize even the most dangerous pathologies in the initial period of their development.
Daily devices for magnetic resonance imaging are improved. In the world there are several well-known recognized leaders in this industry. These corporations are located in Japan and America. European tomographs also provide decent quality research. Different models allow examinations of children of different ages, including the smallest patients.
With the help of magnetic resonance, doctors get an accurate descriptive picture of all the anatomical structures of the brain. To correctly evaluate the result obtained, the study is carried out in several projections at once. This gives specialists and clinicians a spatial description of where a specific pathology is located. For proper interpretation, a system analysis of all the projections made at once is necessary.
The research method is absolutely safe and does not carry increased radiation exposure.
Such safety research allows its wide use even in infants. In America, without performing an MRI scan of the brain, no clinical examination is performed. Before establishing the diagnosis, doctors send all patients to magnetic resonance imaging.
The essence of the study is to conduct high-frequency impulses generated in the tomograph to the organs of the central nervous system. In most cases, this procedure is non-invasive (contactless). Only in some situations requires the prior introduction of a special coloring matter - contrast. It has a targeted and selective action and accumulates only in the nervous tissue.
Contrast studies are carried out mainly in difficult diagnostic situations, when simple magnetic resonance imaging is not enough to get the correct diagnosis. Usually, such invasive procedures are contraindicated and are carried out only on the strict recommendation of the attending physician who observes the child.
The most common contrast in pediatric oncology is to identify some types of malignant tumors and cystic formations.
Magnetic resonance imaging has several advantages over the usual diagnostic methods that are carried out daily. These include:
- No radiation exposure. When conducting radiography, X-ray irradiation is essential.Such a high radiation load is possible only for a limited period of time, so research can only be carried out a maximum of a couple of times a year. For magnetic resonance imaging such terms do not exist. It can be done as long as necessary to establish the correct and complete diagnosis.
- High resolution. Some diseases of the brain is almost impossible to detect using ultrasound. In this case MRI comes to the rescue. It shows the pathology of the brain and spinal cord, even in the very early stages.
How is it done?
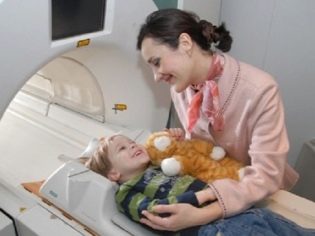
For the study usually does not require special special training. In some cases, children who are emotionally stable and prone to neurotic states are advised to give an age-old dosage of sedative (e) before the day before. This will help reduce the excitement of the child during the study.
If there are any metallic elements in the child's body (braces, brackets, fixing pins and others), you should first tell the doctor about this. In some cases, this will be considered a contraindication for this study.
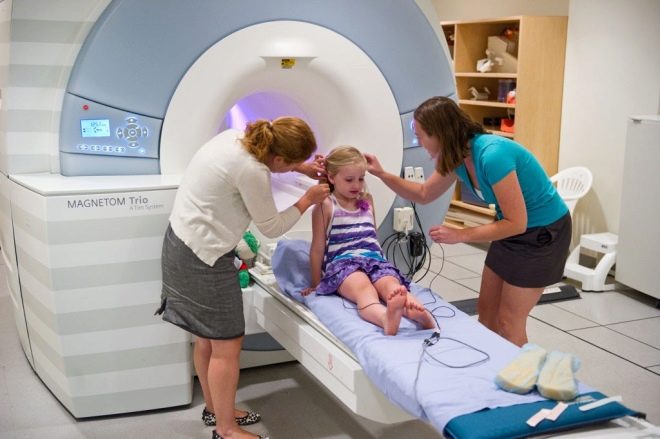
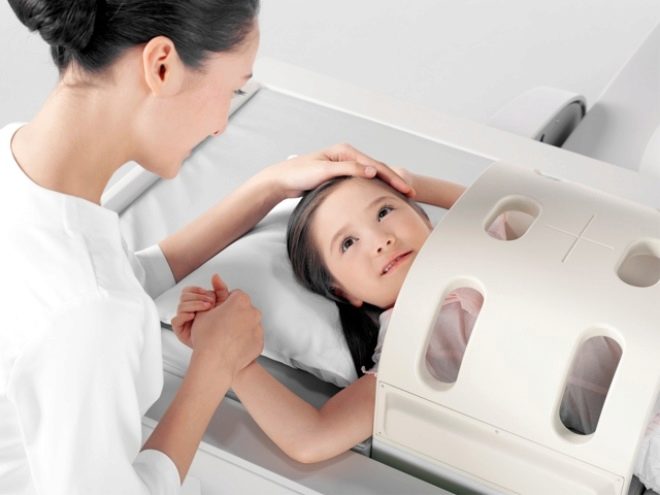
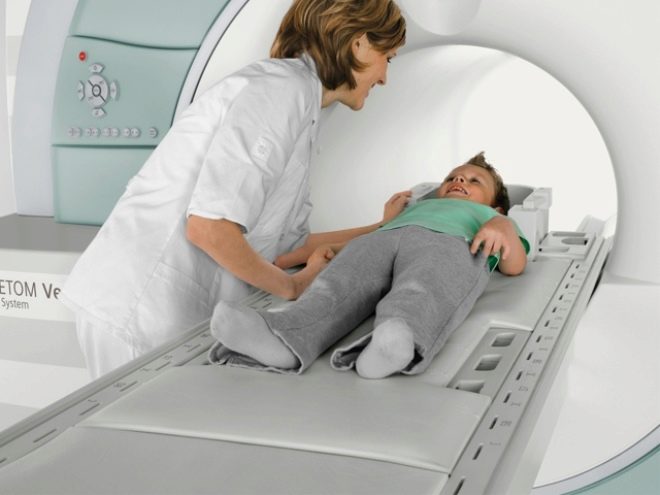
Diagnosis is carried out in a magnetic resonance imager. It can be open and closed. For babies with claustrophobia or soreness in conditions of confined space, it is better to conduct a diagnosis on open scanners for conducting a study. Such devices are designed specifically for such patients.
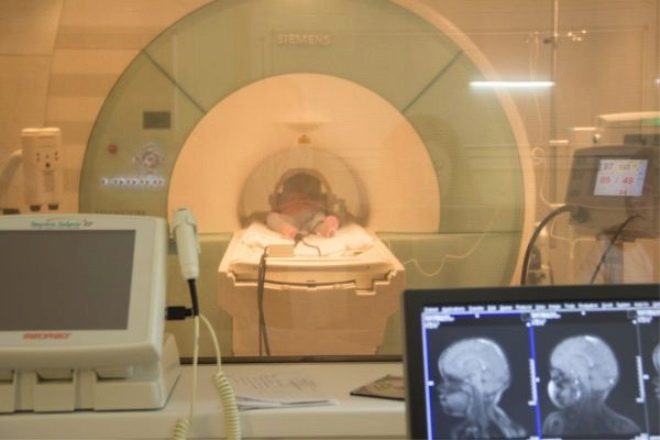
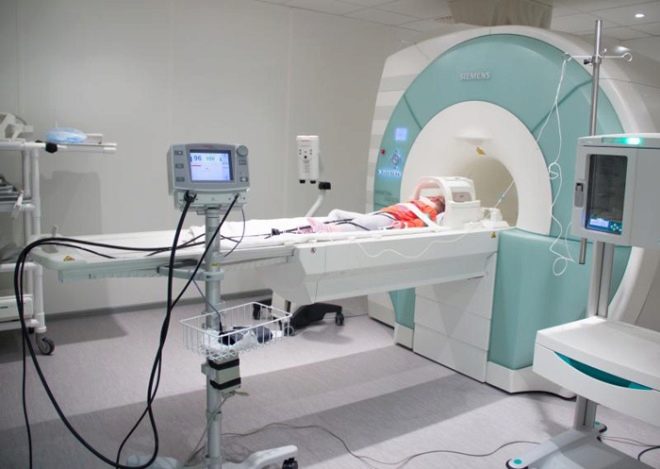
Tomographs are in the form of a cylinder that has holes on both sides. A sliding viewing table is attached to the fixed part. A small patient is placed on this table and fixed with straps. It is not painful at all, but it is necessary, because during the procedure the child should not move. Typically, the duration of the study is 40-60 minutes. Contrast tomography takes longer to practice.
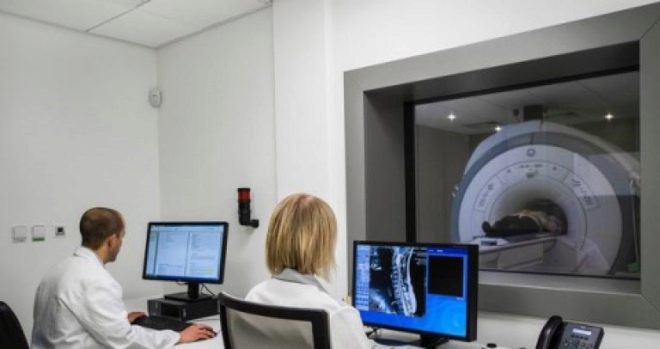
Next to the head of the baby, special sensors are fixed, sending magnetic impulses to the brain, which will then be transmitted to special software. This program gives a descriptive picture of the anatomical structures present in the brain and makes it possible to identify pathological anomalies, as well as dangerous tumors and neoplasms. The doctor conducting the study is in the next room behind the glass from the treatment room where the study is being conducted.
Little kids tolerate the procedure is difficult. They cannot remain still for a long time. There are techniques when anesthesia is administered to babies, and then the brain is examined. Usually such a study is conducted in children aged 1-3 years. Research under anesthesia can be carried out to a newborn and an infant. However, the evidence in this case is very limited.
Preparations for general anesthesia are usually administered to babies on an empty stomach. Prior to the introduction of anesthesia, the baby is necessarily examined by the resuscitator. After examining the child, the doctor will be able to select the required dosage of the drug that will be given to the baby for anesthesia.
If the baby has an MRI of the brain under general anesthesia, then stop eating in advance. Babies should not eat 2 hours before the procedure, babies older than a year - 4 hours before the study, children aged 5 years-7 years and older - 8 hours.
There are several ways of immersion in drug sleep: through the introduction of drugs into a vein or through mask anesthesia. Some clinical situations involve a combination of these methods.
The choice of the method of anesthesia remains for the resuscitator, who will carry out this procedure.
What makes reveal?
Brain MRI is one of the most accurate and safe methods for diagnosing various pathologies of the central nervous system today. During the study, the doctor has the opportunity to get not only a static picture, but also to see the work of the body in real time. This allows doctors to diagnose some neurological diseases that are difficult to diagnose using alternative methods.
Reviews of the MRI is the most favorable. Parents who were forced to carry out such research to their children note that the child did not experience any pain during the procedure. They note only that some of the kids were very much afraid of the noise and sounds that the tomograph made while working.
The advantages of this study include high information content and accuracy. Minus - the cost of research.
A brain tomography is recommended when the following pathological conditions are detected in a child:
- various headaches that occur at any time of the day (periodic or permanent);
- pain in the head after performing various physical activities or after a strong psycho-emotional shock;
- impairment of speech, hearing and vision (the most dangerous cases of sudden-onset conditions);
- dizziness of varying severity;
- disturbances of consciousness and short-term loss of consciousness, in the event of fainting;
- noise in the head and ears;
- the emergence of motor disorders, gait disorders, not related to orthopedic diseases;
- sudden loss of attention and impaired memorization;
- with the appearance of various intellectual disorders;
- with the occurrence of numbness in the arms and legs, as well as tingling or "crawling" on the fingers.
Contrast MRI of the brain is carried out with suspected cancer, neoplasms and certain types of cystic formations. The study is also informative for the diagnosis of pathologies that have arisen in the pituitary gland. Contrasting allows you to identify metastases of malignant tumors, multiple sclerosis. Also, this type of research is used to monitor the state and timely detection of recurrences of certain diseases of the brain after surgical treatment.
Contraindications
Many parents believe that magnetic resonance imaging is harmful for a child. This opinion is not entirely correct. In some cases, it is simply impossible to establish the correct diagnosis without an MRI. The advantages of magnetic resonance imaging are unconditional. The ability to detect oncologic neoplasms at the earliest stages has saved more than one life.
Magnetic resonance imaging, like any other research method, has contraindications. If they are present in the child, then the conduct of such a diagnosis should be forgotten. In this case, the baby may have strong problems, so the study is not conducted. There are relative and absolute contraindications. If the reason why the study is not possible, can be eliminated after some time, then the restriction is considered relative.
Contraindications of this method include:
- claustrophobia or tenderness of being in a confined space for a long time;
- various metal elements that are inside the body;
- hemolytic anemia (for contrast).
How to prepare a child for an MRI, see the next video.