What does brain EEG show in children? Norms and causes of deviations
Electroencephalography is one of the most common methods for diagnosing the state of a child’s brain, which, along with CT and MRI, is considered to be quite effective and accurate. That shows such diagnostics, how to decipher the data and what are the causes of deviations from the norm, you will learn from this article.
What is an EEG and what does it show?
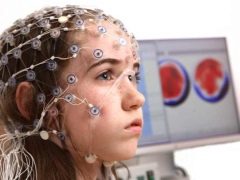
The abbreviation EEG stands for "electroencephalography". It is a method of recording the smallest electrical active impulses of the cerebral cortex. This diagnosis is very sensitive, it allows you to record signs of activity not even in a second, but in milliseconds. No other study of brain function provides such accurate information in a certain period of time.
To establish the morphological changes, the presence of cysts and tumors, the development of the body of the brain and brain tissue, other means of video monitoring are used, for example, neurosonography for children under 1.5-2 years old, MRI, CT for older children. But to answer the question of how the brain works, how it reacts to external and internal stimuli, to changes in the environment, only the electroencephalogram of the head can.
Electrical processes in neurons in general and in the brain in particular began to be studied at the end of the 19th century. This was done by scientists in various countries of the world, but the greatest contribution was made by the Russian physiologist I. Sechenov. The first EEG recording was obtained in Germany in 1928.
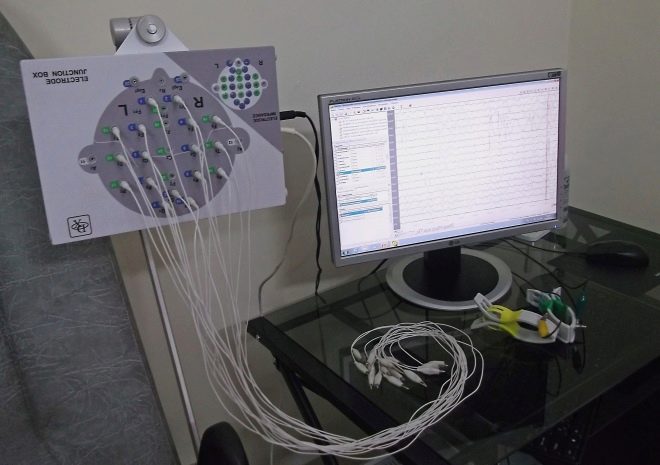
Today, EEG is a rather routine procedure, applied even in small clinics and clinics for diagnosis and treatment. It is carried out on special equipment, which is called an electroencephalograph. The device is connected to the patient through electrodes. Results can be recorded both on a paper tape and on a computer automatically. The procedure is painless and harmless. At the same time, it is very informative: the potentials of the electrical activity of the brain invariably change in the presence of a particular pathology.
With the help of EEG, various injuries, mental diseases can be diagnosed; the method has been widely used in monitoring sleep at night.
Indications for
EEG is not included in the list of mandatory screening studies for children of any age. This means that it is accepted to carry out such diagnostics only for certain medical indications in the presence of certain complaints of patients. The method is assigned in the following cases:
- with frequent headaches, dizziness;
- in the presence of cases of loss of consciousness;
- if the child has a history of convulsions;
- in case of suspected injury to the skull and brain;
- if you suspect cerebral palsy or to monitor the state of the dynamics in case of a previously diagnosed cerebral palsy;
- in violation of reflexes, other neurological conditions that persist for a long time and therapies are poorly amenable;
- with sleep disorders in a child;
- if you suspect a mental disorder;
- as a preparatory diagnosis before brain surgery;
- with delayed speech, mental, emotional and physical development.
In children, EEG is performed to assess the degree of immaturity of the brain. EEG is performed to determine the degree of anesthesia during serious and long-term surgical interventions.
Some features of the behavior of children of the first year of life can also be the basis for the appointment of an EEG.
Regular and prolonged crying, sleep disorders are very good reasons for diagnosing the potentials of neuron electrical impulses, especially if neurosonography or MRI do not show abnormalities in the development of the brain itself.
Contraindications
Contraindications to such a diagnosis is very small. It is not performed only if there are fresh wounds on the head of a small patient, if surgical sutures are applied. Sometimes the diagnosis is denied due to severe rhinitis or exhausting frequent cough.
In all other cases, the EEG can be performed if the attending physician insists on it.
Young children try to carry out a diagnostic procedure in a state of sleep, when they are most calm.
Is the examination harmful?
This question is one of the most pressing for parents. Since the very essence of the method is far from clear to all mothers, the EEG as a phenomenon is overgrown with rumors and speculation in the open spaces of women's forums. There are no two answers to the question about the harmfulness of the study - the EEG is completely harmless, since the electrodes and the apparatus do not have any stimulating effect on the brain: they only fix impulses.
You can do an EEG for a child at any age, in any condition, and as many times as necessary. Reusable diagnostics are not prohibited, there are no restrictions.
Another issue is that in order to allow some time to sit still in small and very mobile children, sedatives may be prescribed. Here the decision is made by a doctor who knows exactly how to calculate the necessary dosage so that your child does not cause harm.
Baby preparation
If the child is scheduled for electroencephalography, be sure to properly prepare him for the examination.
It is better to come to the survey with a clean head, since the sensors will be installed on the scalp. To do this, on the eve it is sufficient to carry out the usual hygienic procedures and wash the child’s hair with baby shampoo.
The baby should be fed immediately before installing the electrodes for 15-20 minutes. It is best to achieve a natural sleep: a well-fed baby will sleep more calmly and longer, the doctor will be able to register all the necessary indicators. Therefore, for babies, take a bottle with a mixture or expressed breast milk to a medical facility.
It is best to schedule a survey with your doctor for the time that your baby’s daily routine is for daytime sleep.
Children older years of EEG carried out in a state of wakefulness. To obtain accurate results, the child must behave calmly, fulfill all the requests of the doctor. To achieve such peace of mind, parents need to conduct a preliminary psychological preparation in advance. If you tell in advance what an interesting game is coming, the child will be more focused. You can promise the fucker that he will be a real space traveler or superhero for a few minutes.
It is clear that for too long a child cannot concentrate on what is happening, especially if he is 2-3 years old. Therefore, you should take a book, a toy with you to the clinic, something that is interesting for the child and can at least temporarily capture his attention.
So that the child is not frightened from the very first minutes, you need to prepare him for what will happen. Choose any old hat at home and play with the child in the "cosmonaut".Put the cap on your head, draw the sound of a walkie-talkie in a helmet, poke and give your cosmoger a team that the doctor on the EEG will give in reality: open and close your eyes, do the same, only in slow motion, breathe deeply and finely, etc. More information about the stages of the survey, we describe below.
If your baby regularly takes any medications as prescribed by the attending physician, you do not need to cancel their admission before electroencephalography. But be sure to tell the doctor before the diagnosis, what drugs and in what dosage the child took the last two days.
Before entering the room, remove the headdress from the child. Girls need to remove hairpins, rubber bands, headbands and remove earrings from their ears, if any. Best of all, all these items for beauty and attractiveness initially left at home, going to the EEG, so as not to lose something valuable in the survey process.
How the procedure is carried out: the main stages
The EEG procedure is done in several stages, about which both parents and the little patient need to know in advance in order to properly prepare. To begin with, the office for electroencephalography is not at all like an ordinary medical office. This is a soundproofed and darkened room. The room itself is usually small.
It has a couch, which will offer to accommodate the child. The baby is placed on the changing table, which is also available in the office.
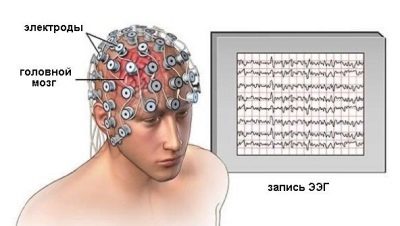
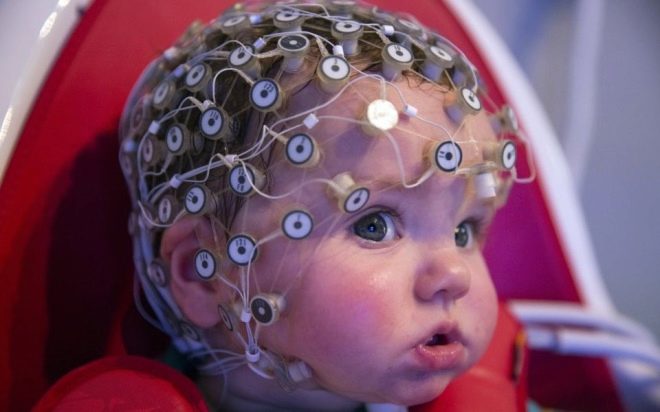
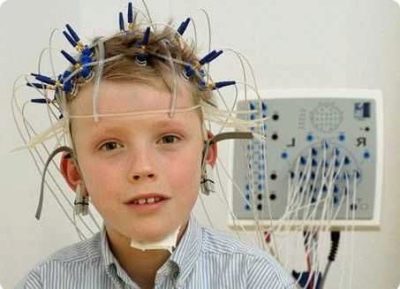
It is proposed to wear a special “helmet” on the head - a cloth or rubber cap with fixed electrodes. On some caps, the doctor installs the necessary electrodes in the required amount manually. Electroencephalographs with electrodes are connected by means of soft thin tubes-conductors.
Electrodes are moistened with saline or a special gel. This is necessary for a better fit of the electrode to the baby’s head, so that no air space is formed between the skin and the sensor receiving signals. Equipment must be grounded. On the ears of a child in the area of the earlobes clips that do not conduct current are attached.
The duration of the study is on average 15-20 minutes. All this time, the child should be as calm as possible.
Grudnichkov is recommended to take on hands - the place on the couch in this case is taken by the mother. The older child is sitting on a half-sitting couch.
What tests are coming depends on the age of the little patient. The older the child, the more difficult the tasks will be. The standard routine procedure involves several options for fixing electrical potentials.
- First, write the background curve - this line on the resulting graph will display the impulses of the neurons of the brain at rest.
- Then check the response of the brain to the transition from rest to activity and work readiness. For this, the child is asked to open and close his eyes at a different pace, which the doctor asks with his teams.
- The third stage is testing of the brain in the state of so-called hyperventilation. For this child are asked to take deep breaths and exhalations with the frequency set by the doctor. At the “inhale” command, inhale is made; at the “expiration” command the child exhales This stage allows you to identify signs of epilepsy, tumors, which led to impaired functionality of the brain.
- The fourth stage involves the use of photostimulation. Potentials continue to be registered, but the doctor turns on and off a special light bulb with a certain frequency in front of the closed eyes of the patient. This test allows you to establish some features of both mental and speech development, as well as a tendency to epilepsy and convulsive syndromes.
- Additional stages are mainly used for older children.They include various teams of the doctor - from clenching and unclenching fingers into fists to answering the questions of psychological tests, if the child is at an age at which answers and understanding are in principle possible.
Parents can not worry - more than the child can and is able, they will not demand from him. If he doesn’t cope with something, they’ll just be given another task.
Rules and interpretation of results
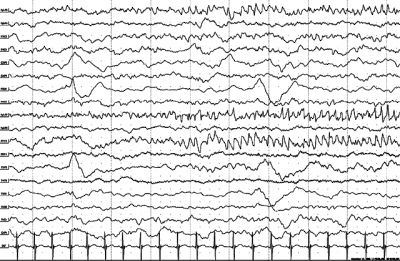
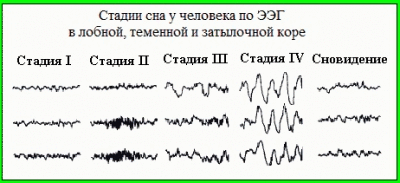
Electroencephalogram, which is obtained as a result of automatic registration of potentials, is a mysterious accumulation of curves, waves, sinusoids and broken lines, which it is impossible to figure out on your own without being a specialist. Even doctors of other specialties, for example, a surgeon or an ENT specialist, will never understand what is shown on the charts. Processing of results takes from several hours to several days. Usually - about a day.
The concept of “norms” in relation to EEG is not entirely correct. The fact is that there are a great many variants of norms. Here every detail is important - the frequency of repetition of the anomaly, its connection with stimuli, dynamics. In two healthy children who do not have problems with the work of the central nervous system and brain pathologies, the resulting graphs will look different.
The indicators are classified according to the type of waves, separately estimate the bioelectric activity and other parameters. Parents do not need to interpret anything, since the conclusion provides a description of the research results and makes certain recommendations. Let's look at several options for conclusions in more detail.
What does epileptiform activity indicate?
If the term is so difficult to understand, it means that sharp peaks prevail in the EEG, which are significantly different from the background rhythm, which is recorded in the resting position. Most often, this form have results in a child with epilepsy. But the presence of sharp peaks and EFA in custody is not always a sign of epilepsy. Sometimes we are talking about epiaktivnost without seizures, but because parents can be surprised a lot, because the seizures and seizures in a child could never occur.
Doctors tend to believe that the EEG reflects patterns that occur even if the child simply has a genetic predisposition for epilepsy. Detection of epileptiform activity does not mean that the child will necessarily be diagnosed appropriately. But this fact necessarily indicates the need to re-examine. The diagnosis may not be confirmed, and may receive confirmation.
Children with epilepsy require a special approach, appropriate and timely treatment from a neurologist, and therefore it is not worthwhile to ignore the appearance of EFA in custody.
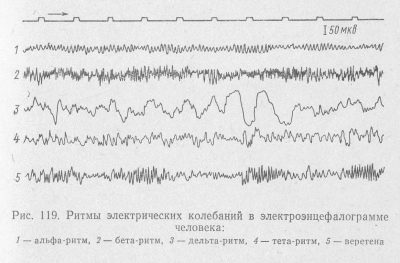
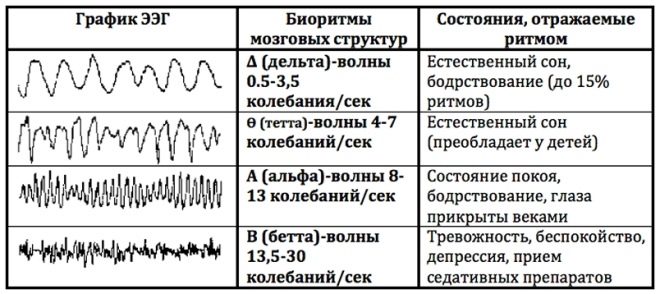
Types and norms of rhythms
Rhythms are of particular importance for decoding results. There are only four of them:
- alpha;
- beta:
- delta;
- theta.
Each of these rhythms has its own norms and possible fluctuations of normative values. To make parents more aware of the brain encephalogram received on their hands, we will try to tell the most complicated things as simply as possible.
Alpha rhythm is called the base, background rhythm, which is recorded in a state of rest and rest. The presence of this type of rhythm is characteristic of all healthy people. If it is not there, they speak about asymmetry of the hemispheres, which is easily diagnosed by ultrasound or MRI. This rhythm dominates when the child is in darkness, in silence. If at this moment to turn on the stimulus, give light, sound, alpha rhythm may decrease or disappear. At rest, he returns again. These are normal values. In epilepsy, for example, spontaneous episodes of an alpha rhythm burst can be recorded on an EEG.
If the conclusion indicates the frequency of alpha 8-14 Hz (25-95 µV), you can not worry: the child is healthy. Deviations of the alpha rhythm can be observed if they are recorded in the frontal lobe, if there is a significant frequency variation. Too high a frequency of more than 14 Hz may be a sign of vascular disorders in the brain, traumas of the skull and brain. Low indicators may indicate a lag in mental development. If the baby has dementia, the rhythm may not be recorded at all.
The rhythm beta is recorded and changed during periods of brain activity. In a healthy baby, the amplitude values of 2-5 µV will be indicated in the conclusion; this type of waves will be recorded in the frontal lobe of the brain. If the values are higher than normal, the doctor may suspect a concussion or contusion of the brain, and with a pathological decrease, an inflammatory process of the meninges or tissues, such as meningitis or encephalitis. Beta waves in the amplitude of 40-50 μV in childhood can speak about a noticeable lag in the development of the child.
Delta rhythm makes itself felt in the period of deep sleep, as well as in patients who are in a coma. Detection of such a rhythm during wakefulness may indicate the fact of the development of a tumor.
Theta rhythm is also characteristic of sleeping people. If it is detected in an amplitude above 45 µV in different lobes of the brain, this is a serious disruption of the central nervous system. In certain embodiments, this rhythm may be in children up to 8 years old, but in older children, it is often a sign of underdevelopment, dementia. A simultaneous increase in the delta and theta may indicate a violation of cerebral circulation.
All types of waves form the basis for fixing the bioelectric activity of the brain. If it is stated that the BEA is rhythmic, then there is no reason to worry. Relatively rhythmic BEA indicates the presence of frequent headaches.
Diffuse activity does not speak of pathology, if there are no other deviations. But in depressive states a reduced BEA may appear in a child.
Frequent abnormalities and possible diagnoses
Based on the EEG alone, no one will diagnose the child. These studies may require confirmation or refutation using other methods, including MRI, CT, ultrasound. The results of electroencephalography can only suggest that the child has a parencephalic cyst, epileptic activity without seizures, paroxysmal activity, tumors, mental disorders.
Consider what doctors may mean by pointing out certain pathologies in the conclusion of an EEG.
- If it is indicated that detected dysfunction of the middle parts of the brain, it is necessary to assume that the child just had stress, that he did not sleep, is often nervous, and therefore he will have enough classes with a psychologist, creating a favorable environment in the family, reducing psychological stress and light sedative preparations of plant origin. This is not considered a disease.
- If the electroencephalogram says that inter-hemispheric asymmetry detected, This is not always a sign of pathology in childhood. The child will be recommended dynamic observation by a neurologist.
- Diffuse alpha rhythm changes in conclusion can also be a variant of the norm. The child is prescribed additional research.
- More dangerous detection of a nidus of pathological activity, which in most cases indicates the development of epilepsy or increased tendency to seizures.
- Wording "Irritation of brain structures" talks about a violation of the blood circulation of the brain, the presence of traumatic lesions after strokes, falls, as well as high intracranial pressure.
- Detection of paroxysms may be a sign of epilepsy in the initial stage, but this is not always the case. More often, the detection of paroxysms indicates a tendency, possibly hereditary, to epileptic seizures. Increased tone of synchronizing structures cannot be considered pathology at all.But according to the established practice, the child is still sent to be observed by a neurologist.
The presence of active discharges is an alarming sign. The child needs to be screened for tumors and neoplasms.
Only a doctor can give an accurate answer to the question whether everything is in order with the baby. Attempts to draw conclusions on their own can lead parents into such jungle, from which it is very difficult to find a reasonable and logical way out.
When do they give an opinion?
Parents can receive an opinion on their hands with a description of the results in about a day In some cases, the time may be increased - it depends on the employment of the doctor and the sequence in a particular medical institution.
Reviews
According to moms, carrying out EEG for children requires iron nerves from parents. First you need to prepare the child, then make sure that he behaves adequately, and then anxiously await the results. The question of passing diagnostics at home has only one answer - this is possible only when the child is monitored for night sleep. Such services are not included in the list provided by the OMS policy; therefore, they are paid and are not provided by all clinics.
Quite often, according to moms, the main reason for the appointment of diagnosis is the lack of speaking in 1.5-2 years and older. By the way, gross anomalies are rarely found, but with the diagnosis “healthy” (in the sense of being completely healthy) few people leave. If there are no abnormalities, according to the EEG results, “immaturity of the brain” or another condition is still indicated, which in childhood is considered the absolute norm and does not need treatment.
For details on the procedure of brain EEG in children, see the following video.