What tests take during pregnancy?
During the term of carrying the child, the expectant mother has to pass a great many different tests, starting with general blood and urine examinations and ending with specific laboratory diagnostic tests that can tell a lot about how the baby develops in the womb. In this article we will talk about what exactly and why a woman who is expecting a baby needs to pass, and also at what time it is better to do it.
Why get tested?
Most of the future moms treat the process of testing negatively, perceive their purpose as an unpleasant necessity, and they regularly complain that they were “driven into the classrooms” and “tortured”. This position can not be considered responsible and reasonable for an adult and a future mother, because modern diagnostic capabilities - This is a real chance to see the pathology and abnormalities in the development of the baby, problems with carrying mom at the beginning. And the timely identification of the problem in most cases allows to completely and very successfully solve the problem as a whole.
It is reasonable to start testing before pregnancy, during the planning period. This approach is very popular in Europe, America, Japan and China. But in Russia, while walking around the offices on the threshold of conception, unfortunately, has not become a good tradition.
That is why it is important not to skip tests that are appointed by the obstetrician-gynecologist after it became known about the fact of pregnancy of the woman.
Immediately make a reservation that the analyzes, according to Russian law, are not a prerequisite for monitoring pregnant. Any woman for personal reasons and motives can refuse to pass any analysis. That is why it is important to know what tests are recommended for what, what they show and why they are necessary. Then a woman who is waiting for a baby will no longer regard diagnostic measures as a burden and will begin to more consciously treat the settings.
Research prior to registration
The first analysis of a pregnant woman is a test, the main task of which is to convert a woman into the category of pregnant women. She can do it herself at home. To do this, it is enough to use the test strip, which responds with a signal line (second strip) to an increase in urine of a concentration of a special hormone - chorionic gonadotropin. It is produced by the chorion cells immediately after implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity.
Usually this significant event happens. 7-8 days after conception, and the hormone level increases every two days. With the onset of the delay, it is possible to establish the fact of an “interesting situation” with the help of pharmacy tests. A little earlier, you can donate blood from a vein to determine the concentration of hCG, because the pregnancy hormone appears in the blood earlier, its concentration increases faster.
A few days before the delivery of venous blood you must give up fatty foods and all bad habitsTo which smoking and alcohol belong, it is advisable not to eat at all 6-8 hours before visiting the laboratory. If the result indicates that hCG is higher than 5 units, then pregnancy may be suspected.But it is still too early to go to the consultation, it is advisable to repeat the blood test after 2-4 days in order to get the growth of the hormone in dynamics.
When the level of hCG is growing at a good pace, you can safely contact your local gynecologist at your place of residence with a request to take you on the account of pregnancy.
The list of surveys for registration
Typically, the fair sex turn to their gynecologist for 10-15 days delayed menstruation. In addition to general questions, finding out the date of the last menstruation, the future mommy will receive The list of diagnostic examinations recommended for all women in the “interesting position”:
general analysis of a urine sample;
analysis for the identification of blood groups and rhesus accessories;
biochemical examination of a blood sample;
detailed blood test (total);
a blood test to identify existing or past infections (PB Wasserman, HIV, TORCH infection);
cytology smear vaginal discharge.
These are the main diagnostic purposes, it is they who give the doctor the opportunity to get a "starting" picture of the health of the woman who is about to become a mother. As additional diagnostic prescriptions, having studied the personal history of the lady, the characteristics of previous pregnancies, miscarriages, childbirth, sometimes such diagnostic methods are assigned as:
a blood test for the concentration of hormones, especially progesterone;
analysis of hemolysins and Rh antibodies (in pregnant women with a negative Rh factor);
sexually transmitted infection test (STD).
Table of mandatory analyzes
In short, the diagnostic plan for the next nine months looks something like this:
Obstetric term (weeks) | Assigned examinations |
5-7 |
|
7-11 |
|
11-14 (up to 13 weeks + 6 days) |
|
15-16 |
|
16-19 (up to 19 weeks inclusive) |
|
20-22 |
|
24-28 |
|
30 (exactly) |
|
31-36 |
|
36-37 |
|
37-40 |
|
This is only an approximate list of diagnostic measures, in each specific situation it may be supplemented by other studies that require it. If we talk about longer periods - trimesters, then it is advisable to go through the following studies in each of them.
First trimester
Up to 12-13 weeks, it is advisable for a woman to undergo the first screening study, the so-called genetic test or analysis for theoretically probable deformities of the baby. The ratio of the concentration of hcgb (human chorionic gonadotropin) and plasma protein substance PAPP-A, together with the data shown by the fetometry of the baby, the computer program will calculate the individual risk of having a child with chromosomal disorders, such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome and other total and incurable diseases . The ultrasound will also evaluate markers of genetic pathologies - TVP (thickness of the collar space) and visualization of the nasal bones.
General studies like diagnosis of infectious diseases, are of great importance, because when establishing the fact of certain fluctuations from the norm and anomalies, the doctor will be able to choose the right tactics for managing the pregnant woman. Important doctors believe and examination to clarify the group and rhesus blood.
When the future mommy discovers the absence of a specific protein, that is, the negative Rh factor is confirmed, her husband will also have to visit the treatment room during pregnancy and donate blood for the same analysis in the same antenatal clinic so that the doctor can verify that the man’s Rhesus and timely assess the risk of developing Rh-mother and fetus.
Midwife future mom in 1 trimester will visit approximately once in 3 weeks, if in the process of gestation there are no complications and unforeseen situations. During this period, she will be recommended to visit other doctors - ENT, cardiologist, ophthalmologist, dentist and endocrinologist.
At each scheduled visit to your consultation, you will need to pre-pass urine for a general analysis, and also they will measure the pressure and weigh it.
Second trimester
In the middle of pregnancy, the main examination is the second screening study. Blood for biochemistry is donated from the 16th to the 20th week, it is permissible to conduct an ultrasound scan at any time up to and including 21st week. As with the previous screening, a quantitative measure of hCG will be evaluated, as well as the level of alphafetoprotein and free estriol.
Together with ultrasound and a general history of pregnant women, a computer program for screening studies will be able to summarize the picture and calculate the risks of having a baby with pathologies and developmental abnormalities.
As in the earlier periods, it is advisable to take care to appear at the scheduled reception after passing urine for an overall analysis (OAM). At each visit, the woman will measure the level of pressure, weigh it, evaluate the lower and upper extremities for the possible appearance of edema. Visit the doctor will have more often - about twice a month.
In the third trimester
The greatest number of tests will have to pass when making maternity leave. By the 30th week, almost everything that has already been surrendered during the admission of a pregnant woman to the dispensary registration is surrendered. A urinalysis is still required before each visit to the doctor. Expectant mother starts to apply visits to the gynecologist every 7-10 days. Diagnostic tests can be performed from week 31 - Fetal CTG and the so-called Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound), whose task is to establish the intensity of blood flow in the uterine vessels.
Before giving birth, a woman again has to pass an impressive list of tests, including cytological examination of vaginal mucus. Screening for 3 trimesters is limited to ultrasound for periods 26 to 32 weeks.
Description of tests during pregnancy
Not all doctors tell patients that any tests performed by pregnant women can show to patients, whose duties include deciphering these tests and making decisions about the possible treatment or correction of the identified disorder.And it is very important for future mothers to know what and why she rents.
Clinical blood test
More recently, it was taken exclusively separately, piercing a woman’s finger with a scarifier, now doctors are trying to combine this process with venous blood sampling, since such material is quite suitable for conducting clinical analysis on a par with a capillary blood sample. Such a study is also called expanded, in the direction it can be indicated briefly - "UAC" or "AS".
The analysis allows you to set the blood content of pregnant erythrocytes, hemoglobin level, the exact number of leukocytes, lymphocytes and platelets, as well as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Donate blood should be on an empty stomach.
An experienced doctor can be told by a laboratory assistant after extensive testing to tell a lot about the well-being of the future mother and her baby - whether a pregnant woman has inflammatory processes or an allergy or anemia. Leukocytes and ESR during childbirth always slightly elevatedit is completely natural due to nature itself. But the decrease in hemoglobin is considered an alarming indicator and requires medical correction, because with anemia, the mother suffers from a child.
Hematocrit - the ability of the blood to carry oxygen, under this concept doctors and encrypt the number of red blood cells, cells that give blood its color and carry oxygen. Excess platelet counts may well indicate thrombophilia - a very dangerous condition in general and in particular in pregnancy.
Determination of blood type and Rh factor
For the first time a person is determined by these characteristics immediately after birth, in the maternity hospital. However, not every woman, especially if she has ever been in hospital, has a clear idea of what group she has and what her Rhesus is. And this information is very important for understanding the tactics of pregnancy. Venous blood is collected at the initial stage of the child's term.when the expectant mother comes to get registered. This is one of the first analyzes that is of great importance.
If it turns out that a man and a woman who are preparing to become parents have different blood types, the doctor will be able to assume the probability (slight) of a conflict in the blood group. Much more often there is a conflict on the Rh factor. If a woman has a negative, and her husband has a positive one, then the risk of an immune conflict between the mother and the fetus that the father’s rhesus can inherit is great.
Preparation for the analysis is not required, a sample of venous blood will be taken simultaneously with the samples for general laboratory analysis. Repeat the group and Rh status are determined in the maternity hospital, just before the birth of the baby, in order to eliminate any probability of error.
Antibody titer tests
Such an analysis is needed not for everyone, but only for women who are at risk of developing a conflict on the type of mother-fetus due to the difference in Rh factors or blood groups. The analysis makes it possible to detect antibodies in a woman’s blood that are aimed at destroying the child as an agent alien to the mother’s body. The antibody titer is expressed as 1: 16, 1: 32, etc. If there is no conflict, then the antibody titer is negative. The higher the value, the stronger the conflict.
The analysis is given from a vein, on an empty stomach. For the first time, he is appointed to a future mother from a risk group after registration, once a month. In the second trimester, the analysis is carried out at least 1 time in 2 weeks, and after 34 weeks - once a week.
Blood for sugar
Glucose is very important for energy metabolism both in the mother’s body and for the metabolic processes in the small body of the baby. But the excess of sugar in the blood can lead to irreversible changes in the development of the child. Therefore, this simple and clear analysis be sure to do while carrying a baby.
For the first time, blood sugar will be determined at the time of registration for the dispensary registration of pregnancy. If there are no deviations, then such a study is repeated only at the end of pregnancy, after 34 weeks. If the doctor has suspicions about the so-called diabetes of pregnant women, then the analysis will have to pass more often. You can use the glycemic profile - a special method that is used at home.
With it, a woman’s blood should be analyzed using a home glucometer several times a day - on an empty stomach before breakfast, every two hours after meals, and also before bedtime. At night, the procedure is carried out every 3 hours. The results are recorded, the daily glucose profile is analyzed after a correctly performed daily measurement.
Normally, blood sugar in a pregnant woman is at the same values as non-pregnant. No more than 5.9 mmol / liter in venous blood should be detected in its blood, not higher than 8.9 mmol / liter two hours after a meal. High glucose levels are fraught with miscarriage, abnormal development of the fetus.
Hormonal blood test
Hormones are responsible for maintaining pregnancy, they contribute to the growth and normal development of the baby. Changes in the hormonal background are causes of the threat of miscarriage, developmental pathologies. This rather impressive group of studies includes blood tests for hCG, estriol, progesterone. The first two hormones are determined during the second prenatal screening, and the level of progesterone is important both in the early stages (it contributes to the delivery of the fetus) and at the end of the term of the infant’s (he talks about the condition and work of the placenta).
For the proper development of the internal organs of the child need a sufficient amount of thyroid hormones. They can be identified in the blood of a pregnant woman as free T4 (thyroxin) and T3 (triiodothyronine). Tests on free T3 and T4 will not be prescribed to everyone but only for women who used to have thyroid problemsnd, as well as the appearance of such problems during the carrying of the child.
Popular is the analysis of placental lactogen. This hormone is produced by the placenta itself, it normally grows by weeks of pregnancy, so its decline may be a sign of placental insufficiency. The concentration of prolactin is also investigated.
Of great importance on the reproductive health of the future mother has the hormone estradiol, which is responsible for the normal functioning of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, the uterus itself. The closer to childbirth, the higher the concentration of estradiol. It is dangerous not so much the excess of this hormone as its deficiency, since it is fraught with termination of pregnancy and other unpleasant consequences.
Sometimes you want to determine the level of male sex hormone testosterone in the blood of a pregnant woman. This hormone, although considered to be male, is also present in certain concentrations in women, and its level rises several times during the carrying of a child, especially in women pregnant with boys. It is also sometimes necessary to determine the so-called AMT - an anti-Mullerian hormone, which is important for the reproductive function of a substance. Such an analysis is often prescribed to women before and after IVF, as well as to pregnant women who have a history of unsuccessful attempts to become mothers - miscarriages and frozen pregnancies.
All tests for the determination of hormonal levels should be taken in the morning before eating. 8 hours before that you should not take fatty foods, for an hour you can not smoke. A blood sample is taken from a vein. Many factors can affect test results, from medications taken by a woman to the severe stress she is experiencing. It is also worth temporarily refraining from donating blood if any infectious disease has recently been postponed.
Blood chemistry
This common laboratory diagnostic method allows you to form a fairly accurate idea of how the internal organs work, how the metabolic processes take place. The current level of laboratory development allows setting several dozens of different indicators in a venous blood sample.
In pregnant women, laboratory workers determine the glucose level, urea level, creatinine, total protein, iron and serum iron, bilirubin, cholesterol, homocysteine, ferritin as part of a biochemical study. Thus, the concentration of bilirubin can talk about the state and functioning of the liver, and urea and creatinine indicate the functionality and health of the kidneys and the entire excretory system. AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT (alanine aminotransferase) are enzymes that “signal” with their level of possible disturbances in the functioning of the heart and liver, respectively.
C-reactive protein can be a sign of inflammation in the body of a pregnant woman. In addition, the biochemical method of research allows to establish the content in the blood of pregnant calcium and potassium, sodium and chlorine, which are so necessary in the period of gestation of the baby.
If you are assigned such an analysis, take it seriously. To appear in the treatment room should be strictly on an empty stomach, preferably for 2-3 days before donating blood from a vein, do not eat fatty and fried foods, you should abandon a lot of spices and sweets.
Determination of blood clotting
This is a whole group of tests that should not be refused at least because the outcome of the upcoming delivery depends on it. The ability of blood to clot does not allow a woman to die during childbirth, because blood loss at this moment is quite large. For several reasons, the future mom's blood may have an increased or decreased ability to clot. This is checked both at the beginning of the pregnancy and in its final, immediately before the birth.
The main danger in childbirth is abundant uterine bleeding, which can occur after the placenta is “born”, in which there is no longer any need after the birth of the baby. Women prepare for this crucial moment in advance. From the second trimester, the blood becomes more "thick", ready for increased blood clots if necessary.
During pregnancy, such an analysis will have to be taken several times - at the very beginning, in the middle and immediately before the birth. The main indicators are APTTV (time required for clotting), platelet level and fibrinogen, lupus anticoagulant.
A coagulogram includes the definition of an INR - international normalized attitude. The survey determines the time required for the formation of a clot, the so-called prothrombin time. Normally, it ranges from 17 to 20 seconds.
The concentration of the complex complex complex is also determined - soluble fibrin-monomer complex. The result of this value is important for diagnosing developmental problems or premature aging of the placenta. And since the fibrin monomers do not rise by themselves, but are usually associated with the number of platelets, TEG is also performed with a thromboelastogram. Hemostasis - the balance of the blood, which does not allow it to thicken or thin out excessively - is very important.
Any violations require prompt medical correction.
Hepatitis B and C Analysis
Hepatitis in pregnant women often occur without symptoms, but the effect of viruses on the baby can be devastating, and the probability of intrauterine infection is lower than the probability of infection during childbirth. The treachery of hepatitis is that a woman can not guess about the disease and not associate it with recent sex, visiting a dentist, piercing, eating raw milk and oysters.
Hepatitis C is more dangerous than hepatitis Bbecause it often leads to intrauterine infection in the fetus, as well as the death of the baby both in the womb and in the first hours after birth. For many future moms, the positive result of this laboratory blood test is unexpected. Hepatitis for them is opening up.
Therefore, you should not refuse to undergo such a diagnosis, because it does not require a separate visit to the treatment room — venous blood will be taken along with the material for biochemical or clinical analysis.
If the result is doubtful, false positive or false negative - the diagnosis is repeated.
Test for syphilis and hiv
To protect the child from being infected with the human immunodeficiency virus, special antiretroviral treatment is provided during pregnancy. In this case, the probability of infecting a baby is less than one percent. But in order to start such treatment and properly lead such a pregnancy, the doctor must be confident in the HIV status of the pregnant woman.
The analysis is done twice for the pregnancy, not because the doctor wants so. This is due to the incubation period - it is from 3 monthsbut because at the beginning of pregnancy, when a woman registers, the analysis can be negative, and already at 30 weeks can become positive.
In laboratory conditions, in the venous blood of the future mother determine antibodies to HIV. Normally they should not be. The analysis of syphilis is also carried out repeatedly during the term of carrying a baby. This is also due to the duration of the incubation period of the disease.
Syphilis is dangerous during pregnancy because it can lead to miscarriage, to premature birth, to intrauterine infection of the baby. To speak with confidence about whether there is syphilis, no woman can. Even if all of her sexual contacts are under control, then the same cannot be said about the partner, besides the disease is transmitted by household means. Long enough syphilis can not manifest itself.
A blood test for this unpleasant venereal disease is performed by two methods - precipitation microreaction or Wasserman reaction. More common is the second method. Both during pregnancy can give false positive results, plunging the expectant mother into shock. Unfortunately, this happens quite often during pregnancy. Only an additional examination will help establish whether syphilis really is.
It is recommended to take these tests on an empty stomach. Blood is taken from a vein. Often, the analysis is combined with the collection of material for research on other infections.
TORCH Infection Analysis
TORCH is an abbreviation, behind which are the capital letters of the Latin names of the most common and most dangerous infections for future mothers - toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus infection, herpes. If a woman suffered some of these ailments earlier, before the onset of pregnancy, then antibodies of the IgG type, which indicate the presence of antibodies to these infections in the body, will be detected in her blood. The child, therefore, is also under their protection.
If antibodies detected in the blood are characteristic of the active phase of the immune response - IgM and IgA, then the woman urgently needs the help of an infectious disease specialist, and, possibly, termination of pregnancy for medical reasons. Such antibodies suggest that a woman suffers from these ailments, and this increases the likelihood of anomalies of the baby’s development, death, and disability birth by a factor of ten.
For rubella, toxoplasmosis, herpes viruses and cytomelovirus, blood will be taken from a vein. Preparation for the analysis is not required, that is, you can not starve before visiting the treatment room.
Additional analyzes
In addition to tests that can be prescribed and carried out in the conditions of the antenatal clinic, sometimes there is a need for additional research. These include the complex IPD - invasive prenatal diagnosis.It is usually carried out in conditions of medical genetic centers.
It allows you to accurately determine whether the baby is healthy. A woman may be referred to such examinations. in which the results of the first and second screenings showed high and extremely high risks birth of a child with chromosomal abnormalities.
At first, the woman is provided with advisory assistance - she is sent to a reception for genetics, who chooses and offers the expectant mother one of the ways to confirm or refute the alarming screening results.
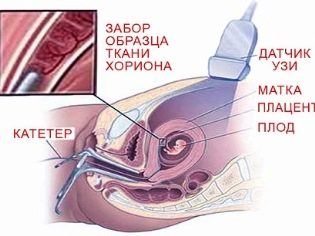
Chorionic biopsy is a study that can be scheduled at the earliest time, as early as 10-12 weeks. Through the cervix with a special catheter or through a long needle puncture in the anterior abdominal wall are taken for analysis of chorionic tissue. This study makes it possible, with a probability of 99%, to establish in a child Down syndrome and other congenital chromosomal abnormalities, neural tube defects, hereditary diseases, hemophilia, the sex of the child, and even establish paternity if necessary.
A plus method is that the conclusion is prepared within a few days, and, if the sad diagnosis is confirmed, the woman and her relatives have time to decide on the further fate of the pregnancy - to leave the child with the pathology or to interrupt her for medical reasons.
Minus biopsy is the risk of infection of the membranes of the fetus, the embryo itself, as well as the occurrence of bleeding and abortion. A woman with a negative Rh factor invasive diagnosis can provoke a conflict. Risks are estimated at 2-5%.
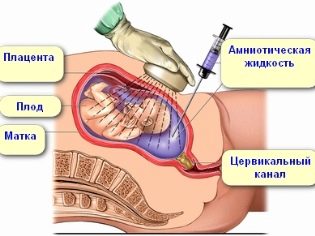
In the second trimester, a placentocentesis can be performed for a woman - taking a sample of placental tissues for genetic analysis in the same manner as described. On week 15-16, obstetric calculation of the term for a woman can offer an amniotic fluid test - amniocentesis.
The amniotic fluid intake passes through a long needle through the anterior abdominal wall. The whole process is tirelessly monitored by an ultrasound technician. The procedure is tracked on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner. The painful sensations of a woman are stopped by local or general anesthesia. This analysis is shown not only to those whose screening shows high risks of having a child with genetic diseases, but also to women who have high antibody titers in the blood, since the method will allow to determine the nature and course of the Rh-conflict, as well as women who have a doctor suspects severe fetal hypoxia.
The risk of negative consequences for the state of the pregnant woman and her baby in this case is lower than with a chorion biopsy. It is estimated at about 1-3%. The minus of the method lies in its duration - sometimes it takes up to 6 weeks to get the result.
In the second trimester, from week 18, it is possible to carry out cordocentesis - collection for analysis of the baby's cord blood. Her "mined" in the same way - through the anterior abdominal wall. From the middle of pregnancy a baby biopsy can also be indicated. The most traumatic method, in 8-10% of cases leading to spontaneous abortion, is fetoscopy. A flexible probe is inserted into the uterus and the baby is carefully examined on a monitor. You can do this procedure at 18-19 weeks of pregnancy, but the procedure for understandable reasons is prescribed quite rarely.
Non-invasive methods are not particularly accurate, and they are less dangerous for women and children. Among the exact non-invasive ways to learn everything about the health of the baby can only be noted non-invasive DNA test. It is carried out in special genetic clinics and medical centers. In the blood of a pregnant woman, red blood cells of the baby are identified and released, which appear in it already from the 8th week of pregnancy. Then, in the blood cells of a child, his unique DNA is isolated, which allows us to judge whether there are pathologies and developmental abnormalities with an accuracy of up to 98-99%.The downside of the analysis is that it is very expensive - several tens of thousands of rubles.
Conclusion
Pregnancy tests can be assigned a variety of, it all depends on how the carrying of the child proceeds. All of them, if there is a doctor's prescription (except for innovative non-invasive DNA test), are carried out for the future mother absolutely free. However, the right of a woman is to choose a laboratory and clinic where to be examined, and if she chooses not to have a consultation laboratory, she will have to take tests for a fee at the rates of the selected clinic.
In the next video you will find a useful calendar of pregnancy by week and a list of necessary tests.