Why do amniocentesis during pregnancy and what does it show?
Examinations aimed at identifying various pathologies in the fetus are carried out at very different periods of carrying a baby. One of them is amniocentesis.
What it is?
This study appeared in medical practice quite recently. For many centuries, doctors have not had the opportunity to identify various pathologies of fetal intrauterine development at the earliest stages of its development. Modern techniques allow doctors to do it quite successfully and effectively.
Doctors call amniocentesis an invasive technique. She is in the puncture of the amniotic membrane. This is done by a special medical instrument, which is preliminarily subjected to serious treatment and is sterile.
During the survey A small amount of amniotic fluid is collected. The study of this biomaterial is carried out in the laboratory. Also during this procedure, doctors can introduce drugs into the amniotic bladder.
You can conduct research using different methods. For this, doctors can use a special puncture adapter or use the technique "Free hands".
Both of these methods allow you to identify chromosomal pathology in babies quite effectively.
When is it held?
Doctors say that it is possible to carry out this procedure in the most different periods of pregnancy. Optimally, if such a study is carried out at the 17-20 week of intrauterine development of the fetus.
If the examination is performed during the first trimester of pregnancy, then it is called early. Doctors do late amniocentesis after the fifteenth week of intrauterine development of the baby.
Indications
The main purpose of this procedure is diagnostic. Amniocentesis shows already in the early stages of the intrauterine development of a baby that he has various genetic pathologies. Such an intestinal diagnosis is indicated for all pregnant women with a family history or predisposing risk factors.
If, after passing through genetic screening, the future mommy revealed possible signs of the presence of chromosomal diseases, then doctors will also recommend her to undergo amniocentesis. This study may also be assigned. genetic doctor after consultation. If, during screening, a woman showed in the laboratory tests and an ultrasound scan for signs of the presence of genetic abnormalities in the fetus, then the amniocentesis is highly indicated.
This procedure can also be carried out in the presence of the mother and her baby Rh-conflict. In this clinical situation, the risk of the formation of various pathologies increases markedly. With the help of the study of amniotic fluid, these diseases are easily identified. Such a study is usually prescribed. with a complicated course of pregnancy.
During the 2 nd and 3 rd trimesters, physicians may resort to the appointment of this procedure in order to establish the severity of functional impairment of the vital organs of the fetus.
Using the amniocentesis, one can obtain information on the maturity of the lungs and the presence of surfactant in them, assess the severity of hemolytic disease, or diagnose various infectious diseases.
Amniocentesis can also be not only a diagnostic, but also a medical procedure. It is assigned in this case to women with signs of polyhydramnios. During the procedure, the doctor with a special tool can remove excess amniotic fluid. With a properly performed method of this manipulation the risk of undesirable consequences for the fetus is virtually absent.
Some women in the second half of pregnancy develop pathologies that may require the introduction of drugs into the amniotic bladder. Doctors call this technique intraamnial. This procedure is carried out only by experienced professionals with quite a long clinical experience.
Fetosurgery is one of the newest methods of fetal treatment. In this case, doctors still during intrauterine development can eliminate certain pathologies and gross malformations. Immediately it is worth noting that this method is quite new and is currently being improved.
Preliminary preparation
Before the study, the expectant mother will need to pass several laboratory tests. They are necessary for doctors to be able to identify possible contraindications for this examination. Such tests include a general analysis of blood and urine, as well as a biochemical study (if indicated).
Also, the gynecologist usually makes a vaginal smear for the detection of various infections in it. Exacerbation of infectious diseases may be a relative contraindication for amniocentesis.
Before performing this diagnostic procedure, the doctor usually prescribes the expectant mother to undergo an ultrasound. It is necessary to establish pathologies, as well as to assess the condition of the fetus before the procedure. Some specialists do not carry out a preliminary ultrasound examination, but perform it already before the immediate amniocentesis.
In order not to provoke bleeding during this procedure, doctors recommend women Do not use any antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants during the week prior to the survey.
These drugs contribute to blood thinning, which can lead to severe bleeding during or after a diagnostic examination.
In that case, if the study is carried out after 21 weeks of pregnancy, the doctor will recommend the expectant mother to come to the study with a filled bladder. If the diagnostic procedure is performed at an earlier date, then this is not necessary.
Before performing this invasive examination, the doctor must warn the expectant mother about all sorts of complications and consequences of this test. After such a conversation with the doctor, she signs voluntary informed consent. This medical document must be attached to a medical card.
How is it done?
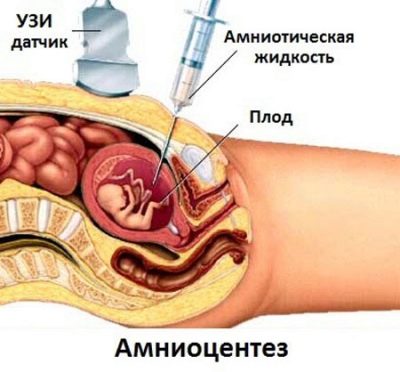
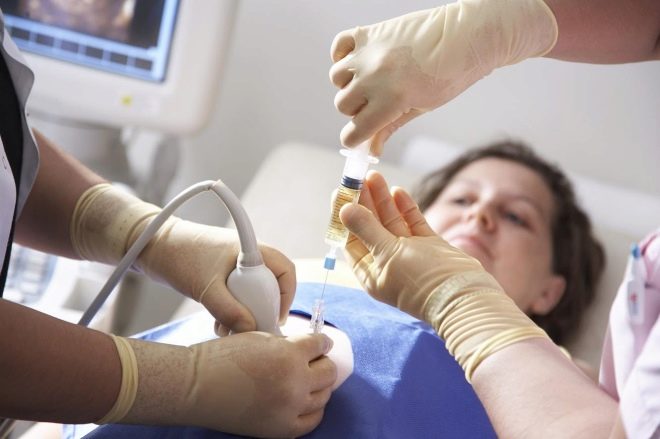
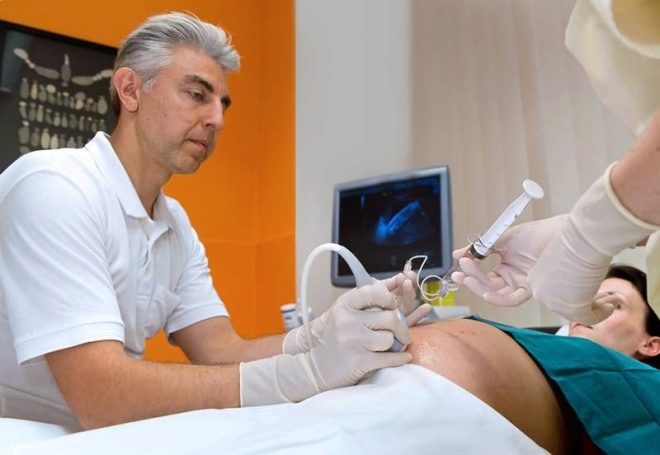
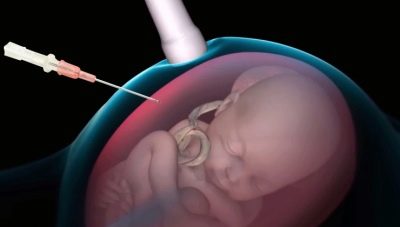
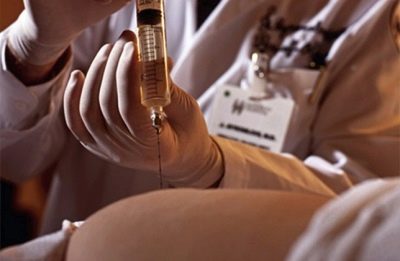
The technique of this procedure is quite complicated. For its holding a special ultrasonic device is used. Using the sensor, the doctor finds the best place for sampling the amniotic fluid. The best localization is a place not in contact with the umbilical loops.
To introduce a medical instrument will be transplacental way. To do this, doctors try to determine the thinnest area where the thickness of the placenta is minimal. During the procedure, special puncture needles are used. In the process of conducting research, the doctor necessarily monitors the performance of their actions. He sees the result on a special screen - the monitor.
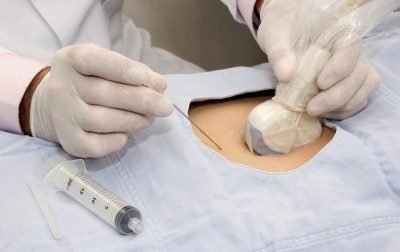
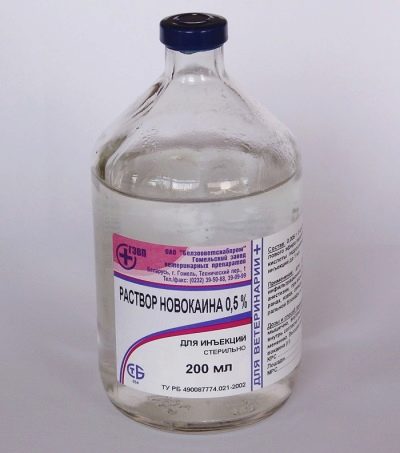
For the procedure, as a rule, no additional anesthesia is required. In some cases, the doctor may use local anesthesia to reduce the pain component. To do this, use a 0.5% solution of novocaine. Before the needle is inserted into the belly, the doctor will necessarily treat the future mother's belly with an alcohol disinfectant solution. Such disinfection will help reduce the potential risk of infection.
After the needle is in the place required for the puncture, the doctor attaches a syringe and takes the necessary amount of amniotic fluid. Usually the first 0.6 ml of the obtained biomaterial is poured. According to doctors, it is not suitable for the study.
In the first volume of amniotic fluid may contain many mother cells. They can lead to the fact that the results of the study will be unreliable. For laboratory diagnostics 18-20 ml of amniotic fluid is required.
After the entire procedure, the needle is pulled out. The puncture site is treated with special disinfectant solutions.
After the entire procedure, the doctor necessarily evaluates the condition of the fetus. For this, he counts his heartbeat. If this study is carried out in the final period of pregnancy, the doctors will monitor the condition of the baby for some time. In some cases, subsequent antimicrobial prophylaxis may be indicated for certain medical conditions.
For a couple of days after the procedure, the woman may feel a sensation of pain in the lower abdomen. To reduce the pain symptom, doctors prescribe painkillers and symptomatic agents in this situation. Quite often, the pain disappears on its own, without the use of any medication.
On the first day after the amniocentesis, gynecologists recommend more in bed. Exercise is excluded. It is necessary to eat light food which is easily acquired and does not cause gas formation.
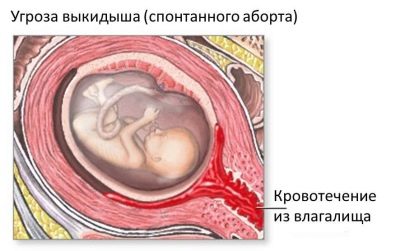
If, after a few days, the intensity of the pain syndrome in the abdomen does not decrease, and a woman has a spotting from the genital tract or the body temperature rises, then in this case she should immediately consult a doctor. It is possible that she had complications after the study.
What can be diagnosed?
This study allows to identify hereditary and genetic diseases in the fetus. This examination is scheduled for all expectant mothers who have a burdened family history of developing such pathologies.
With the help of cytogenetic and molecular analysis of amniocytes, prenatal diagnosis of many congenital diseases of the genetic apparatus can be effectively carried out.
With the help of chorionic villus biopsy, it is possible to obtain more accurate research results on the detection of certain chromosomal pathologies. It is fairly accurate and extremely invasive.
What are the results of the study?
Experts note that the accuracy of the survey is 98.5-99%. More accurate results are recorded if the survey methodology was not impaired.
To conduct research, The resulting biomaterial is seeded on nutrient media. It helps the active growth of fruit cells. After this cytogenetic examination is carried out.
Poor research results can be recorded with ventriculomegaly in the fetus.
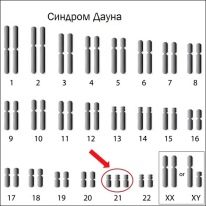
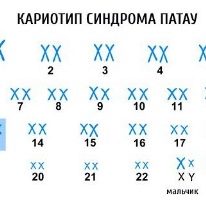
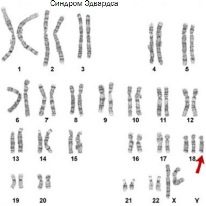
Normal in the genetic material there must be 23 pairs of chromosomes. With poor results, this amount may vary. This is how many genetic defects appear. A change in the number of chromosomes occurs in Down's disease, as well as in Patau and Edwards syndromes.
Also a bad result of an amniocentesis. may indicate the presence of a child with severe malformations of his intrauterine development - Anencephaly or spinal hernia.After the study, experts can eliminate such dangerous conditions as cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia. Both of these pathologies are extremely dangerous for the future life of the fetus and can lead to the formation of various anomalies of the development of internal organs.
Laboratory analysis of amniotic fluid allows you to determine the presence in the waters of various dangerous pathologies, such as herpes and rubella infections. These diseases can lead to the formation of various congenital developmental abnormalities in the fetus.
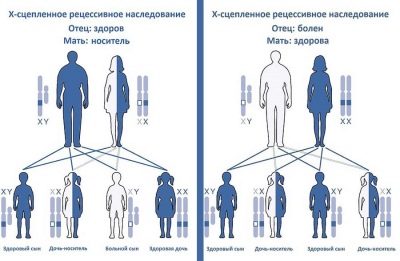
In some cases, the results of the survey can determine the presence of various hereditary diseases associated with sex X and Y chromosomes in a baby developing in the mother’s tummy. An example of such a disease is hemophilia. This disease is manifested in boys and significantly impairs their quality of life.
When the results of biochemical studies of amniotic fluid are ready, then the degree of maturity of the fetal lungs can be identified. To do this, experts evaluate two indicators - lecithin and sphingomyelin. To make a forecast, their ratio is used.
If the value obtained is within 2/1, then this indicates the full maturity of the baby’s lung tissue. Displacement of the indicator from 1.5 to 1.9 / 1 is a possible sign of developing distress syndrome.
If this criterion is 1.5 / 1, then this is, as a rule, a consequence of distress syndrome.
Consequences and complications
All injection procedures are quite dangerous. The risk of adverse effects after such manipulations does exist. Doctors identify several clinical situations that may develop after complicated amniocentesis. These include:
- untimely discharge of amniotic fluid;
- the allocation of amniotic fluid (especially on the first day after the procedure);
- detachment of the membranes;
- ingress into the amniotic fluid of various pathogenic microbes and the development of infection;
- traumatic damage to the blood vessels that feed the fetus;
- uterine artery injury with the development of massive bleeding;
- alloimmune cytopenia in a developing baby in the womb.
Contraindications for
Amniocentesis can be performed only under strict medical indications. Any interventions in the integrity of the amniotic membranes can lead to rather sad consequences for both the future mother and her baby.
For this procedure, doctors distinguish a number of contraindications. Thus, amniocentesis cannot be performed during the acute period of an infectious disease. High body temperature and catarrhal symptoms are a relative contraindication for the study.
After the future mother recovers from a viral or bacterial infection, this study can still be performed. Before holding it, a pregnant woman should be sure to visit the therapist, so he gave her a conclusion about the possibility of the procedure after an infection.
The presence of a large myoma node or other neoplasm in the future mother in the uterus is also a contraindication for this study. The risk of injury to such structures is very high. In this case, amniocentesis is usually not performed. An alternative to research in such a situation is laboratory tests and analyzes, which allow to identify various signs of genetic and chromosomal pathologies.
A high risk of spontaneous abortion or miscarriage is also a contraindication for this examination during pregnancy. If a woman, for some reason, has already begun to detach the placenta, then this procedure is also impossible. In this case, the risk of fetal death increases several times.
See more on amniocentesis in the next video.