All about the umbilical cord: indicators of the norm, function during pregnancy and appearance
During pregnancy, new organs appear in the female body, which are necessary for the full intrauterine development of the fetus. One of them is the umbilical cord. This article will tell about this unique organ, vital for the growth and development of the baby in the womb.
What it is?
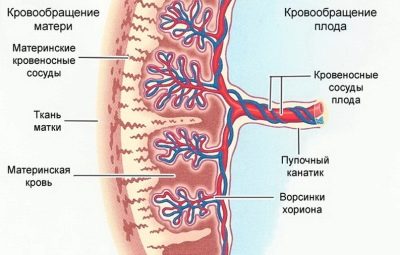
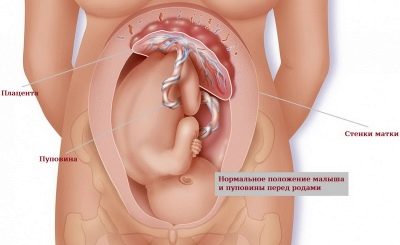
Doctors call the umbilical cord the umbilical cord that connects the small embryo, and then the fetus with the placenta. Through this special “bridge” the child’s body is connected to the mother. This relationship occurs almost in the very first months of pregnancy and persists until the onset of labor.
Interestingly, the umbilical cord is found not only in humans. This organ is also found in all vertebrates, which form embryonic membranes during pregnancy. However, the structure of the umbilical cord in humans is different. It is much more complicated than other mammals.
The umbilical cord has two ends. One of them is attached to the abdominal wall of the fetus, and the other to the placental tissue. In the place where the umbilical cord is attached to the baby’s tummy, in the future there will be a well-known “label” - the navel. It will appear after the baby is born and the doctor cuts the umbilical cord with a special tool.
Histologically, the umbilical cord largely consists of connective tissue. It also contains elements from previous embryonic membranes, amniotic cover, as well as other components.
Appearance
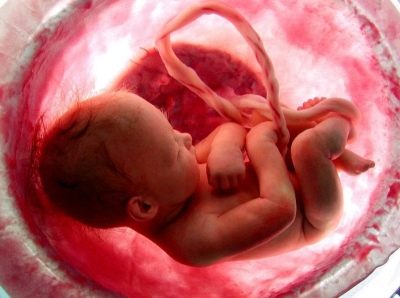
A characteristic feature of the umbilical cord is how it looks. The umbilical cord is a fairly long "cord" that can form loops. The longer the umbilical cord, the more loops it can form.
The umbilical cord, as a rule, has a gray-blue color. The presence of a blue tint due to the fact that inside the umbilical cord are veins. The umbilical cord is a truly unique organ, as it appears only during pregnancy. After the baby is born, the umbilical cord is cut. This means the birth of a new person.
The outer surface of the umbilical cord is quite smooth and even. The mucous membranes are quite brilliant in appearance. The umbilical cord has good elasticity. This can be felt after the birth of the child when cutting the umbilical cord. The density of the umbilical cord is somewhat similar to soft rubber.
Structure
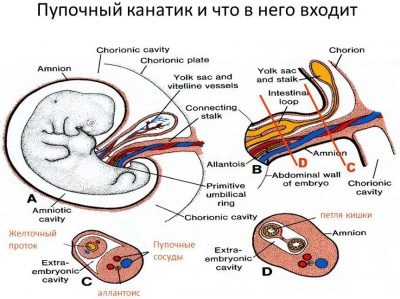
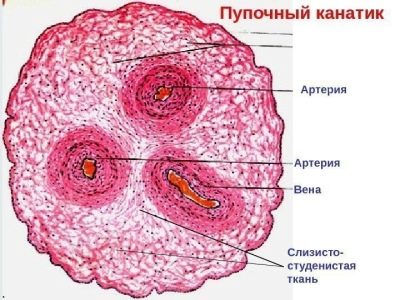
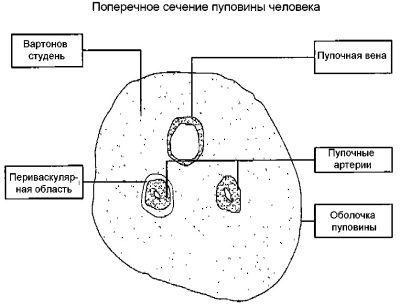
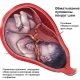
Despite the fact that the umbilical cord resembles a simple cord in its appearance, its anatomical “device” is rather complicated. So, inside the umbilical cord pass blood vessels, as well as other anatomical elements. Each of them has its own structural features, and also performs certain functions.
Arteries
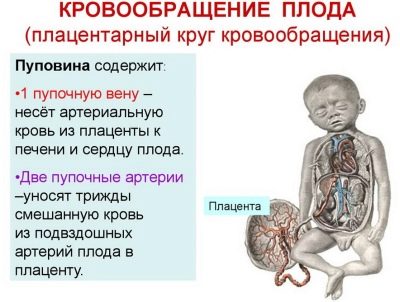
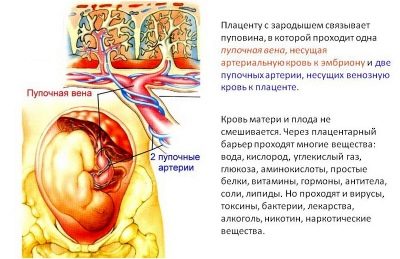
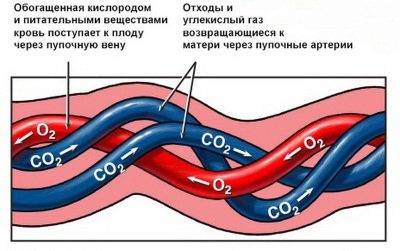
Through the umbilical arteries, fetal blood containing a lot of carbon dioxide flows to the placental tissue. Also in this blood are metabolites, which are formed in the children's body.
The umbilical arteries are the branches of the internal iliac arteries of the mother. Scientists have determined that in each period of pregnancy a certain amount of blood flows through the umbilical cord. So, by the 20th week of pregnancy about 35 ml of blood per minute flows through the umbilical arteries.How much blood flows through the arteries, as much blood flows through the veins. This biological principle underlies the functioning of the child’s body.
Gradually, the amount of blood flowing to the placenta increases. So, by the final weeks of pregnancy, this figure is already 240 ml per minute. The more a baby becomes, the more blood flows through the system of umbilical blood vessels.
The umbilical arteries function only in the period of pregnancy. After the birth of the child into the world, they "close" and turn into special weights. Experts also call them medial umbilical folds (ligamenta medialis umbilicalis). These cicatricial bands pass under the parietal leaf of the peritoneum on the anterior abdominal wall on the side of the bladder. Medial umbilical folds stretch to the navel.
Veins
Initially, the umbilical veins are paired. Over time, obliteration (closing) of the right umbilical vein occurs. Blood flows from them to placental tissue, enriched with oxygen and nutrients. At the same time, most of the blood enters the system of the inferior vena cava by means of a special venous (aransia) duct. The smaller part enters the portal blood flow. This happens through the anastomosis between the left branch of the portal vein and directly the umbilical vein itself. This blood is necessary for the blood supply to the liver tissue.
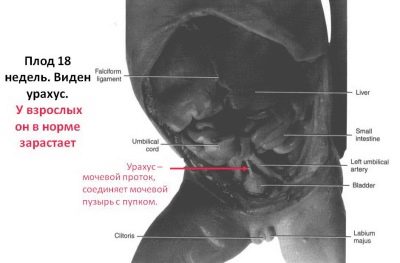
Urachus
This special thin duct connects the bladder and placenta. By the time the baby is born, the urachus closes completely. It turns into cicatricial bandage, which is called the median umbilical cord (ligamentum medianum umbilicale). It is a long strip that runs along the midline of the abdominal cavity.
In practice, there are cases when urachus does not close completely. In such a situation, the risk of developing pathology is quite high. A urachus cyst is a pathological condition in which an incomplete closure of this embryonic duct occurs.
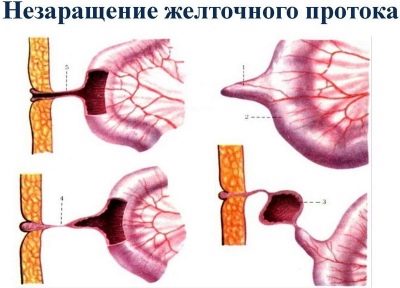
Yolk duct
This anatomical element is an elongated cord that connects the intestines of the embryo with the yolk sac. The yolk sac contains nutrients that are important for intrauterine development. They are stocked with an egg before conception. The main nutrient is lecithin.
This anatomical element is preserved only in early pregnancy. Subsequently, the yolk duct gradually grows. It can also be associated with certain pathologies. So, if it is not closed by a certain date, it can lead to the development of a pathological condition - the formation of Meckel's diverticulum.
Varton jelly
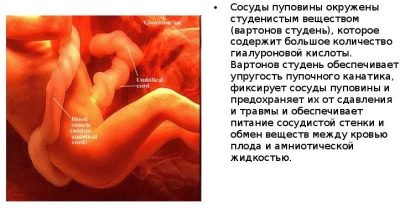
This anatomical element is very important. It performs many different functions that are necessary for the full intrauterine development of the fetus. The basis of Varton's jelly is connective tissue. The appearance of this anatomical element is peculiar. It has a gelatinous or gelatinous consistency, which in its chemical composition is mainly represented by mucopolysaccharides.
The main function of varton jell is to protect the blood vessels, which are inside the umbilical cord, from various mechanical effects. Also gelatinous fluid protects the umbilical arteries and veins from various kinks and compression.
It should be noted that varton jelly contains its own blood vessels. They are quite sensitive to the important hormone of pregnancy - oxytocin. This sensitivity is especially pronounced during childbirth.When a baby comes to light, the level of oxytocin in the female body decreases, which leads to the fact that the blood vessels located in the varton's jelly begin to close. This reaction leads to the fact that the umbilical cord begins to atrophy rather quickly. The blood flow through it persists only for a certain time.
Normal Length
This indicator may be different. The length of the umbilical cord - an individual value. Even in one woman during different pregnancies, the length of the umbilical cord can vary. Scientists have determined that, normally, approximately the length of the umbilical cord is 40-70 cm.
This length of the umbilical cord is necessary so that the baby can make active movements without hindrance. During the prenatal development of the child, his amplitude and the number of movements he makes increases significantly.
Active locomotor activity and an excessively long or short umbilical cord can cause the development of dangerous pathologies.
Elongation can be caused by a variety of reasons. Doctors believe that the length of the umbilical cord may even depend on genetic predisposition. Statistics show that the length of the umbilical cord during re-pregnancy may be greater than the first.
There are a lot of reasons that can lead to an elongation of the umbilical cord during pregnancy. In each case, they are different. If the umbilical cord lengthens excessively, certain pathologies of pregnancy may develop. In this case, doctors conduct careful monitoring of the development of pregnancy.
Functions
The main function of the umbilical cord is to provide the fetus with all nutrients and oxygen for its nutrition. A baby during its intrauterine life in the womb cannot eat on its own. He "eats" proteins, fats and carbohydrates, which he receives through blood from his mother. The fetus feeds in this way throughout its prenatal life.
The umbilical cord is also a kind of “bridge” between the mother and the baby. During the fetal life of the fetus, not only a biological, but also a mental connection is formed between him and his mother. Many scientific studies have shown that at a certain period of its development, the baby is able to feel the experiences of the mother and even react to changes in her mood.
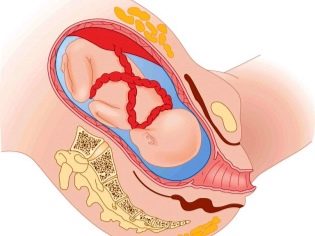
How is attached to the placenta?
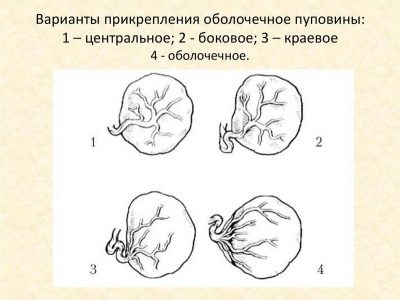
Attaching the umbilical cord to the placenta is a very important clinical criterion. The nature of the intrauterine development of the baby depends on how the umbilical cord attaches to the placental tissue.
The most physiological option is to attach the umbilical cord to the middle of the placenta. Doctors call this option the central one. In this situation, the risk of developing any complications during the course of pregnancy is quite low.
However, in obstetric practice, there are also cases when the umbilical cord is attached to the placenta "wrong." Attaching can occur in the region of the edge or even to the shells. In this case, during pregnancy, dangerous complications may develop that may affect the well-being of the child in the womb.
Various pathologies
The umbilical cord is a very important organ. Its physiological structure provides full growth and development of the baby, who "lives" in my mother's tummy. If any defects appear in the structure of the umbilical cord, this may contribute to the development of dangerous pathologies.
Entwining
A rather unfavorable pathology that can develop during pregnancy is the entanglement of the umbilical cord of the baby’s neck. Usually this situation develops if the length of the umbilical cord exceeds 70 cm. A cord that is too long begins to curl up into loops that entangle the child.
The umbilical loops can twist around not only the neck, but also the abdomen, as well as the limbs of the fetus.The prognosis of the course of pregnancy and the upcoming births depends on how the umbilical loops are located on the body of the child.
So, if the umbilical cord loop is in the baby's cervical sulcus and squeezes it strongly, then this can lead to the development of asphyxiation during natural childbirth. If there are several loops, then this situation can be extremely dangerous. As a rule, with a strong multiple entanglement, doctors try to prevent natural childbirth, and plan a cesarean section in advance.
The entanglement by the umbilical cord is not always the absolute indication for the surgical method of delivery. A caesarean section in such a pathology is performed if the risk of developing various injuries and injuries during natural independent labor is rather high.
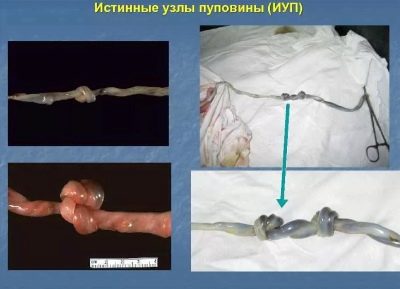
Knots
Another possible pathology that can lead to disruption of the course of a normal pregnancy is the appearance of nodes on the umbilical cord. Experts identify several types of such formations. So, nodes can be true and false.
True nodes are formed, as a rule, in the first half of pregnancy. The child at this time is still quite small and very mobile. Stormy physical activity of the baby can lead to the fact that the umbilical cord begins to "get tangled" and nodules appear on it.
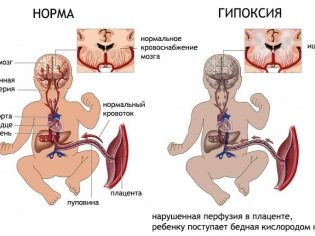
The consequences of this pathology may be different. The presence of a large number of nodes on the umbilical cord can lead to disruption of the blood supply of the child's body with oxygen and nutrients, which contributes to the development of intrauterine hypoxia. In this case, the internal organs of the child can not fully function, which contributes to the formation of pathologies.
Also true knots can also become a certain “obstacle” in natural childbirth. During the passage of the baby through the birth canal, such nodules on the umbilical cord can be very prolonged, leading to a threat to the life of the child.
In such a situation, emergency surgical intervention is required. It so happens that every minute of delay with the provision of medical care is crucial.
In obstetric practice, there are also false nodes. In this case, the diameter of the umbilical cord increases. The prognosis of pregnancy in the presence of false nodules on the umbilical cord, as a rule, is favorable.
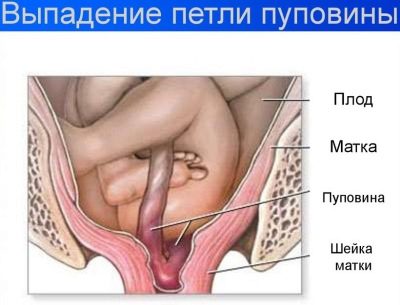
Dropping out
The biomechanism of labor has strict sequential steps. Due to the fact that the child is gradually moving through the birth canal, his birth is not accompanied by the development of any injuries or dangerous injuries. However, if the biomechanics of labor is violated, then in such a situation during childbirth very dangerous states can develop.
One of them is the loss of umbilical cord loops. In this case, the umbilical cord penetrates into the cervix and even into the vagina immediately with the discharge of amniotic fluid. In such a situation, when the fetus moves through the birth canal, dangerous states can occur. The child may simply pinch the umbilical cord, which will lead to a sharp decrease in the level of oxygen in his blood. Oxygen deficiency in this case will lead to the development of hypoxia, which ultimately can even lead to disruption of cardiac activity in the fetus.
Obstetricians and gynecologists point out that the risk of umbilical cord loops is quite high during preterm labor complicated by presentation. A pregnant woman may face this situation while not in a hospital. The outpouring of amniotic fluid with the loss of umbilical cord loops can occur anywhere - for example, on the street, at home, in the park or at the cottage. In this situation, you should urgently call the ambulance brigade.
A pregnant woman who has had an early loss of umbilical cord loops should be urgently hospitalized.
Cysts
It is usually possible to determine the cystic formation in the umbilical cord only, as a rule, when a child is born.Unfortunately, even modern ultrasound devices do not allow doctors to find out about the presence of this pathology during pregnancy. Diagnosis of umbilical cord cysts is quite complicated.
According to statistics, cysts in the umbilical cord are most often formed in the varton jelly. The number of cystic formations may be different. So, only one or several cysts can be present.
Note that not always in the presence of a cyst in the umbilical cord in a pregnant woman, there are any complications during pregnancy. Quite often, with a small and solitary cyst, the expectant mother and her baby do not experience any adverse symptoms.
If there are many cysts and they pinch the blood vessels that are in the umbilical cord, then in such a situation, the child will have discomfort symptoms. So, the baby may change the heart rate or even its physical activity.
Experts identify several clinical variants of cysts. So, they can be true and false. False cystic formation, which is in the Varton's jelly, does not have a capsule. Scientists have not yet determined the cause that leads to their appearance.
True cyst is often formed from the elements of the yolk duct. She usually has a capsule. The size of a true cyst is different - from a few millimeters to 1.5 cm.
To conduct a differential diagnosis of a false and true cyst is often extremely difficult. This can be done only after the birth of the baby, when the umbilical cord is sent for histological examination.
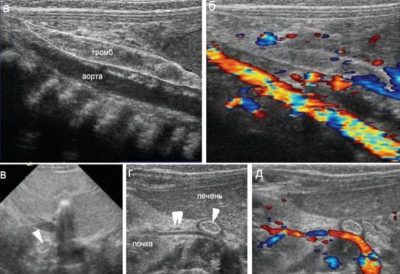
Vascular thrombosis
Identification of this pathology during pregnancy was made possible by modern ultrasound techniques. During the ultrasound, the doctor may determine the thrombosis (blockage) of the umbilical vessels. The cause of this occlusion is a thrombus that blocks the lumen of the umbilical cord blood vessel.
Some scientists believe that diabetes mellitus, which the expectant mother suffers during pregnancy, can lead to the development of this pathology. Also, the risk of umbilical cord blood vessel thrombosis is high in women who suffer from bleeding pathologies.
Thrombosis, according to statistics, most often develops in the umbilical vein. The prognosis of the development of pregnancy with such a pathology is usually unfavorable. The development of further pregnancy largely depends on how large the blood clot is and how strongly the functional impairments are expressed.
Cord Blood Test
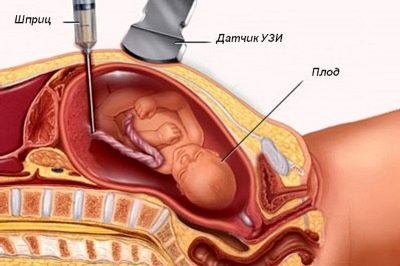
In certain cases during pregnancy, cordocentesis is required. This diagnostic procedure involves taking blood from the blood vessels that are in the umbilical cord.
Cordocentesis is an invasive procedure. This means that the risk of developing possible complications is quite high. One of these is infection of the fetus. Given the risk of such severe complications, cordocentesis is carried out only under strict medical indications.
After childbirth
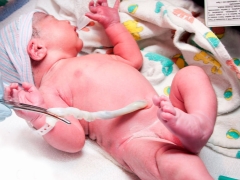
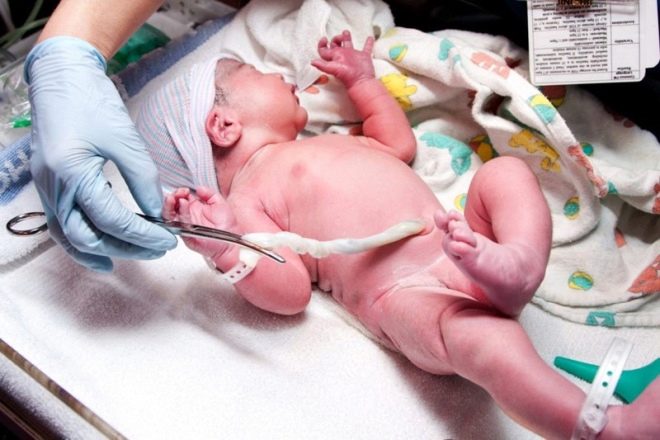
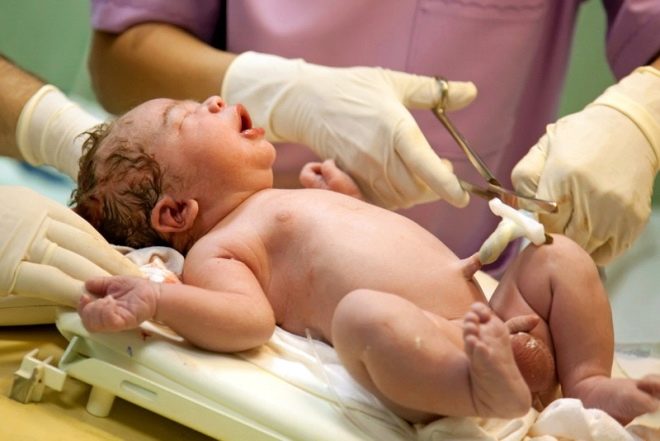
After the baby is born, doctors must evaluate the state of the umbilical cord. In order to “separate” the baby from his mother, it is necessary to cut the umbilical cord.
Previously, this was done only by doctors. Now the baby's father can also cut the umbilical cord if he is in the labor hall during the birth of the baby. This unique opportunity is currently used by more and more parents. Usually, in the process of cutting the umbilical cord, the father of the baby feels real pride, joy and emotion.
How are they cut?
Many women think that only a pair of scissors is used to cross the umbilical cord. In practice, this is not entirely true. Obstetricians and gynecologists can use various tools for cutting the umbilical cord after the baby is born. Before cutting the umbilical cord, the doctor imposes special clamps or clips on it. This is necessary in order to "limit" the blood flow through the blood vessels.
When cutting the umbilical cord, it is important to remember that it still contains arteries and veins.The blood that is in the umbilical vein is used to determine the Rh factor and blood type in a newborn baby.
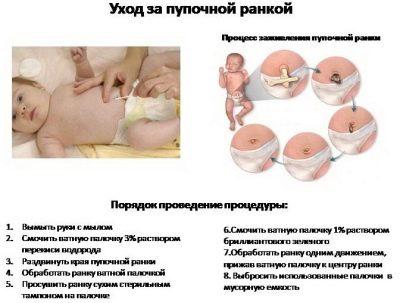
The stump, which is next to the umbilical ring in a born child, gradually begins to dry out and then completely departs. However, in the care of a newborn, it is important to remember that it is quite easy to bring a dangerous infection to this area. For the prevention of such dangerous infectious complications, doctors make up a set of recommendations for the expectant mother and will explain to her how to monitor the umbilical cord stump.
Note that for some time after birth, the umbilical cord in the child pulsates. This is absolutely normal. At this time, hurry with cutting the cord is not worth it. Too quick intervention can lead to the fact that oxygen-rich cord blood cannot fully enter the children's body. In this case, the baby can have a reduced hemoglobin level.
American scientists believe that the umbilical cord should be cut with a certain delay of a couple of minutes. Their research shows that in this case the baby’s hemoglobin level is slightly higher. Also, according to American experts, a baby with such a “delayed” cutting of the umbilical cord will be better to gain weight, and the risk of developing various pathologies that are possible in the first six months of a child’s life will be significantly lower.
Note that not all obstetrician-gynecologists share the opinion of American colleagues. Quite a lot of doctors practicing in Europe, cut the umbilical cord within the first minute since the birth of the child. They justify this by saying that such an “early” cutting of the umbilical cord reduces the risk of infection during childbirth.
On the structure and purpose of the umbilical cord, see the following video.