The causes and consequences of the presence of menstruation in the first month of pregnancy
The female body is rather complicated, and sometimes it behaves unpredictably. This is how women try to explain the onset of menstruation after conception, during the first months of pregnancy. But each mysterious phenomenon has its own logical explanation.
Female cycle after conception and without it
Everyone knows that lack of menstruation and is the main sign of pregnancy in the early period. Therefore, there are only two options: either the woman has already received confirmation of her pregnancy (a positive test, a positive blood test for hCG) and after this the spotting began, or she calmly took on her regular menstrual periods, and after a while she learned that she was pregnant and clearly indicated the period that conception took place in the last cycle.
To understand this issue, you need to very well understand how and why menstruation occurs at all. Another women's cycle starts from the first day of menstrual bleeding. With menstrual fluid particles of endometrial tissue are removed. It was not useful because conception did not happen in the last cycle.
The uterus cavity is self-cleaned in about 5–7 days, by this time the body begins hormonal adjustment - additional shells of the inner surface of the reproductive organ are formed again in case conception occurs in this cycle. The follicles on the ovary mature and one of them, which grows faster than the others, becomes dominant. The growth of the rest is suspended.
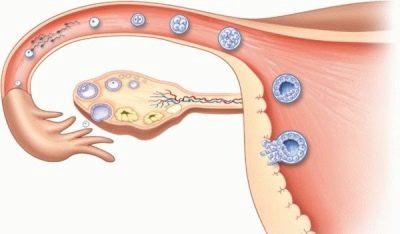
Approximately in the middle of the cycle (on the 14th day with a 28-day cycle or on the 15th - with a 30-day), the follicle bursts and releases into the ampullary part of the fallopian tube on the right or left side - at the location of the ovary - a mature egg. Its life span is very short - in one day the oocyte will be incapable of fertilization.
At the same time, regardless of whether the egg had met with the spermatozoon in the days set aside for this or did not happen, the level of progesterone in the female body rises. This hormone, which is “not in the know”, was conceived or not, begins to actively prepare the endometrium, build it up so that the fertilized egg can sink to the uterus after 5-7 days and find shelter on one of the uterine walls, that is, implant ( to gain a foothold). If this does not occur 10 days after ovulation, progesterone begins to decline, it gives way to estrogen, and 14 days after ovulation, the endometrium, which has so diligently expanded under the action of progesterone, begins to reject. Begins a new menstruation.
However, if the conception took place, then the periods normally do not come. With the timely passage of the zygotes through the pipes and timely implantation, after two days, the villi of the outer layer of the ovum (chorion) begin to produce a special hormone, hCG. Its main task is to maintain the level of progesterone in order to prevent its decline, because the embryo must develop in the most favorable conditions.
It is precisely because progesterone does not decrease 14 days after ovulation, there is no menstruation, which makes a woman think of a possible “interesting position”.
HCG remains high throughout the first trimester, and then begins to decline gradually. Progesterone remains high almost until the end of pregnancy. It is only in the last weeks before the birth begins to decline, giving way to estrogen and oxytocin, which starts the process of childbirth.
According to statistics, this is what happens in the vast majority of women, but there are about 5% of future mothers who claim that they had menstruation after conception.
Why does this happen?
Popular rumor calls bleeding after conception "washing the fetus" and sees nothing wrong with that.
Traditional medicine does not consider bleeding after conception to be the norm, although it allows for the occurrence of such a circumstance, but only exclusively in the first month of pregnancy. The bleeding from the genital tract in any other period is a threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
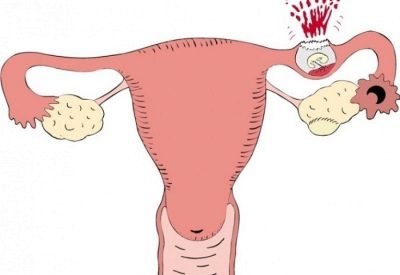
Small bleeding that is difficult to explain, which is very similar to menstruation, but less abundant, can be in approximate periods when menstruation is expected (possibly with some delay) then when a woman has a two-horned uterus from birth, or in one cycle two oocytes have ripened at once.
Some hormonal disruptions at the stage of maturation of the follicles can indeed lead to the fact that the follicles mature on two ovaries or on one, but sequentially. They may come out, perhaps not at the same time, but with a difference of several days. In this case, one oocyte will be fertilized, and the second will not. In this case, there may be some spot bleeding that will end very quickly. Next month nothing like this will happen again.
Quite often, women are interested in the issues of "normality" of menstruation after conception, already faced with such a problem: the test has already shown the cherished two stripes, and after a few days a bleeding, very reminiscent of menstruation, appeared. In this case, the reason, most likely, lies, not in double ovulation, but in violation of implantation. At the same time, the fertilized egg was able to gain a foothold and developed normally for several days, increased hCG appeared in the body, which colored the test zone of the strip. But then something went wrong, the fertilized egg died or was rejected and now leaves the body (the uterus is cleansed again).
The most common cause of such rejection are chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus. At such an early date, embryos that are not viable thus stop in development, for example, if an egg cell was fertilized not one but two spermatozoids at once, and the chromosome set of the new organism is not 46, but 69. Such an organism cannot develop further. Chromosomal abnormalities can be very different, if at the confluence of the genital cells of the parents total errors occurred at the genetic level.
Rejection of the ovum may occur due to the contact of a woman with toxins, poisons, radioactive substances, due to the inflammatory process in the endometrium, ovaries, cervix.
In addition, there are other reasons for bleeding in the first month of pregnancy. Consider them in more detail.
Implant bleeding
In about 30% of women, 6–8 days after the onset of ovulation and the completed conception, poor bleeding begins, which can be regarded as a sign of successful implantation. During implantation of the outer shell of the embryo into the wall of the uterus, endometrial cells are dissolved so that the fetal egg can sink into the shell as deeply as possible. During this, small blood vessels are injured.
Implantation bleeding is not common to all.Allocations can go for about a day - they are not large and completely harmless.
Puzzled ladies usually take them for a failure in the cycle, but after a week they see quite bright stripes in the pregnancy test. It is not worth experiencing, since what happened 7–8 days after fertilization is normal. Small bleeding during implantation does not harm the formation and maturation of the child, does not affect the possible complications of gestation, does not speak about pathology.
Endocrine disorders
During pregnancy, especially in the very early stages, some hormonal disorders may occur. Usually spotting bloody nature (pink, brown, cream) appear with a low level of progesterone, as well as an insufficient level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). In this case, the pregnancy is at risk - without the proper concentration of progesterone, the embryo will die. The hormones of the thyroid gland can also have a negative effect on the development of the embryo in the first month if its function is excessive or insufficient.
The consequences of a hormonal disorder can be the death of the fetus and miscarriage, as well as the death and subsequent stay in the uterus (missed abortion).
The hormones themselves will not come back to normal, such a probability is very low. A woman necessarily needs the help of a medical specialist - the treatment is carried out with progesterone drugs, artificially creating the hormones necessary for the development of the baby in the body.
Quite often, it is necessary to take the prescribed hormonal agents until the end of the first trimester.
Mechanical injury to the genital tract
Progesterone, which preserves and protects the embryo, has another side effect - it makes the mucous membranes in the female body more friable. That is why it is so easy to injure the blood vessels of the genital tract. Even with normal intercourse, a woman may notice small blood-like discharge from the genitals. If symptoms such as nagging pain appear, then a cervical injury is possible. True, in this case, it should come not as a discharge of a scanty scanty character, but a more abundant spotting with clots of mucus.
If this happens, you should not worry too much, although consulting a doctor will also not hurt. Usually, everything ends quite safely - mucous membranes are easy to injure, but they also heal quite quickly. Only in some cases there is a need for sanation of the genital tract. In the overwhelming majority of cases, after a few hours the discharge stops themselves.
Such injuries are not dangerous if the damaged mucous membranes are not infected with the pathogenic flora.
If a few days after the injury, atypical discharge, itching, pain, there should be a visit to the female doctor.
Spontaneous miscarriage
According to statistics, every fourth pregnancy is interrupted in the early stages. The reasons for this can be any number from the unfavorable ecological situation to the inflammatory processes and endocrine disorders in the mother's body, from severe stress to chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo. Usually, the true reason is not established.
At the same time, the lower abdomen is strongly drawn, pains of the cramping type can be observed, copious discharge with clots, since not only the microscopic fertilized egg is released, but also the enlarged endometrium. Do not confuse the threat of miscarriage, when in the first month there are bloody spotting scanty discharge, with a miscarriage that began with abundant secretions. In the second case, saving the pregnancy is usually not possible.
The most frequently lost embryo in the early period leaves the uterine cavity itself, but sometimes the self-cleaning of the reproductive organ cavity can be difficult.
In this case, medical assistance may be required.If the particles of the ovum remain in the uterus, the case may result in severe inflammation, the development of sepsis, which will lead to the need to remove the uterus.
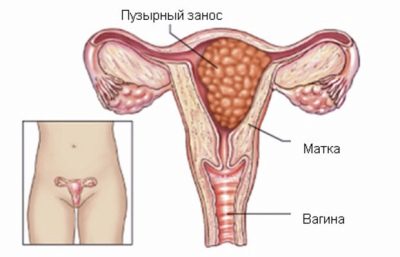
Bubble skid
If the oocyte was defective, then the process of crushing the fertilized female germ cell may be impaired. In this case, instead of the embryo inside the ovum, there are many cysts that are located close to each other, like a bunch of grapes. The genetic component of male germ cells begins to share, which leads to the formation of a multitude of bubbles.
This phenomenon is called a bubble skid. It is dangerous for a woman. From the first month, this condition is accompanied by drawing pains in the lower abdomen and blood discharge.
It is necessary as soon as possible to eliminate the accumulation of cysts from the uterus. Pass yourself a skid can not.
Reviews
Women in the topical forums about pregnancy and childbirth quite often say that bleeding in the first month does happen. And what caused it, then, when it comes time to get registered, it is no longer possible to establish.
Leaving such signs without attention, knowing all the possible causes of abnormal discharge, it is impossible. A woman must be examined. Up to 90% of all threats of miscarriage are usually managed by the joint efforts of the doctors and the very future mother. If the doctors do not see the alarming reasons, then it will be possible to relax and not think about what happened, because not always bleeding in the early period necessarily indicate a disease, pathology, or disturbance.