Lymphadenitis in children: the symptoms and treatment of a child with inflammation of the lymph nodes
The pathology in which the lymph nodes are enlarged is called lymphadenitis. This is a fairly common disease among children of different ages.
What it is?
Enlarged lymph nodes are normal in size due to a variety of causes. In the normal state, these collectors should prevent the spread of various infections throughout the body. Each lymphatic nodule consists of many separate immune cells - lymphocytes. It is they who should stand on the protection of the body against various harmful microorganisms.
Lymphadenopathy causes severe inflammation.. It can be acute and chronic. When microbes or after exposure to a provoking factor, for the first time in their lives, they speak of an acute process. If adverse symptoms persist for a long time or reappear after a few months, then this clinical form is already called chronic.
Doctors consider lymphadenitis to be a secondary disease, since swollen lymph nodes are a consequence, not a cause.. Various pathological conditions and diseases lead to this. The child’s immune system does not function as well as in an adult. This leads to the fact that reactions from the lymph nodes are quite common.
The basis of all medical classifications of lymphadenitis is the anatomical principle. Different forms of the disease are called taking into account the localization where the enlarged lymph nodes appeared. This classification allows doctors to fully understand the area of inflammation and successfully draw up the tactics of the necessary treatment.
For the final formation of the lymphatic system takes at least ten years. Usually by adolescence, it is already fully formed.
The most dangerous age at which the lymph nodes are most susceptible to various infections and inflammation, is considered the time period before the onset of five years. It is usually at this time that the largest number of cases of illness in children is recorded.
The reasons
The development of lymphadenopathy of the lymph nodes can lead to a variety of factors. Scientists note that up to 75% of cases of this disease are caused by various bacteria. They even identified a list of the most dangerous bacterial infections, in which, with a high degree of probability, there is an increase in lymph nodes.
These include:
- inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (antritis, sinusitis);
- inflammation of the internal structures of the ear (otitis);
- furunculosis and eczema;
- pyoderma and common purulent process on the skin;
- scarlet fever and diphtheria.
According to statistics, the most often lead to the development of lymphadenitis:
- Streptococcal infection.
- Staphylococcus.
- Infection Epstein-Barr viruses.
Bacteria can reach the lymph nodes in various ways. They most often get there along with the bloodstream.. Also, microorganisms are able to reach the lymph nodes by contact or by lymph flow. Once inside the lymphoid tissue of the lymph node, they cause severe inflammation there. This inflammatory process provokes an increase in the size of the lymph node, and also causes other adverse symptoms in the child.
In pediatric practice, there are also forms of lymphadenitis caused by viruses. These microscopic microorganisms easily enter the body by airborne droplets, as well as directly into the blood. Viral lymphadenitis is usually serous. Bacterial species also cause purulent inflammation. Adverse lymphadenitis symptoms in viral infections appear, as a rule, as early as 2-5 days after the onset of the disease.
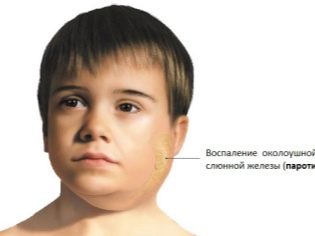
Swollen lymph nodes may even be a consequence of a simple flu infection. The following viral diseases also lead to the development of lymphadenitis in babies: rubella, viral acute tonsillitis, parotitis, chicken pox and others. After recovery, all adverse symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes disappear.
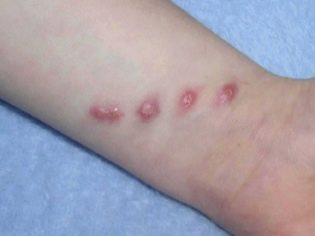
Parents with pets in their homes should be very careful. Often, normal scratches can lead to the development of lymphadenitis in a child.
Cats are carriers of a dangerous disease - felinoza. In this case, the disease they have virtually no effect. If a pet has bit or scratched a baby with this disease, the child may also become infected.
Felinoz is manifested in children with various types of lymphadenitis.
Scientists have identified the most common causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes in children older than six years. These include: toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, mononucleosis, brucellosis, actinomycosis, syphilis and osteomyelitis, as well as various dental diseases (odontogenic diseases). Late treatment of carious or pulping teeth leads to a very rapid spread of the infection to the lymph nodes. In this situation, the lymph nodes located below the jaw are predominantly affected.
Not only various infectious agents can cause lymphadenitis in babies. Swollen lymph nodes may be a secondary manifestation of other diseases.
Different variants of lymphadenitis occur when:
- various tumor neoplasms (including leukemia);
- lymphosarcoma;
- rheumatological diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and others);
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- neuroblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma;
- after traumatic lymph node injury;
- Kawasaki disease;
- various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Currently, scientists began to celebrate the emergence of "drug" lymphadenitis. This form of the disease occurs as a result of an overdose of drugs or with their excessively long use. This variant of lymphadenitis is registered in no more than 3-5% of cases. In order to eliminate the adverse symptoms, a review of the treatment being carried out and the complete abolition of the drugs provoking the disease are required.
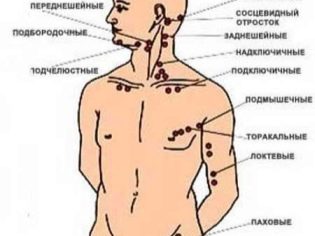
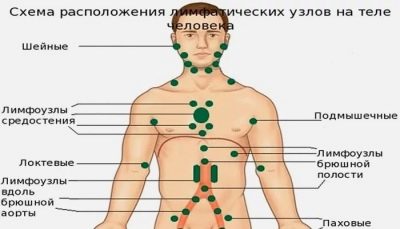
Enlarged lymph nodes due to various pathologies can occur almost anywhere: under the arm, on the neck, in the abdominal cavity, in the groin, on the head, under the jaw.
Such a variety of clinical variants of the disease entails the need to use nosological classification. It shows the various forms of the disease, taking into account the main classification features.
Kinds
Currently, doctors use several classifications. Thus, given the prevalence of the process, all lymphadenitis is divided into regional and generalized. Common forms occur mainly in weakened and frequently ill children, as well as in children with various forms of immunodeficiency states.
All regional lymphadenitis can be divided into several clinical options:
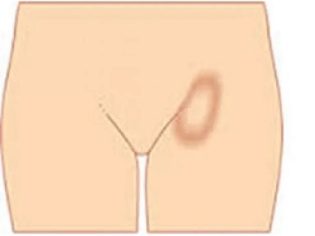
- Inguinal. Characterized by swollen lymph nodeslocated in the groin area. According to statistics, most often this form of lymphadenitis is recorded in boys. Often, inguinal lymphadenitis is the result of diseases of the urinary organs.
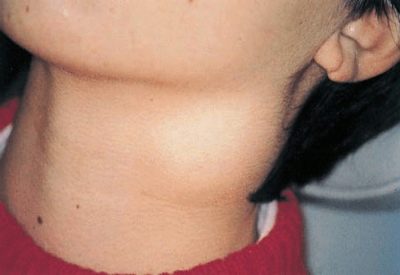
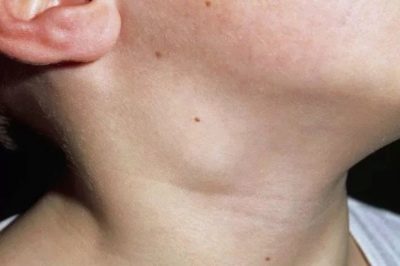
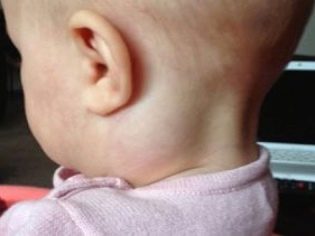
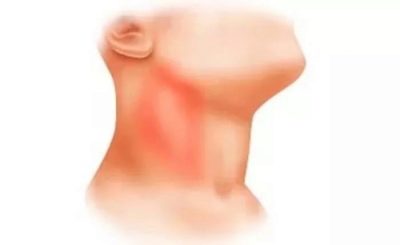
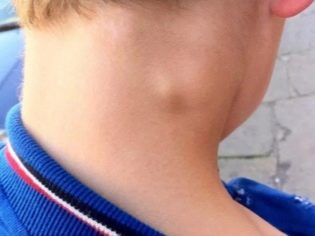
- The neck. Found in almost 80% of cases. Most often occur in babies up to 10 years. Caused by various causes, including numerous pathogens.
- Submandibular. Occur due to reactive inflammation, flowing in the lymph nodes located at the bottom of the lower jaw. Sick teeth are also a common cause of this form of lymphadenitis in children. Characterized by a persistent course, usually poorly amenable to therapy. Lymphadenitis can persist in a child for a long period of time.
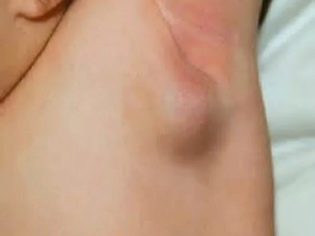
- Axillary. Most often recorded in systemic diseases. Can also occur in tumor processes, as well as in some infectious diseases. According to statistics, more often registered with girls. Often the process is one-sided.
- Mesenteric. Characterized by an increase in mesenteric lymph nodesbeing in the abdominal cavity. Overly enlarged lymph nodes cause various abnormalities in the functioning of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, including the intestines. Enlarged liver is characteristic of some forms of mesenteric lymphadenitis.
Also, doctors identify several clinical variants of the disease, differing from each other in terms of the occurrence of adverse symptoms. This classification includes the following forms:
- Spicy Usually the first adverse effects of the disease completely disappear in 2-3 weeks from the moment of their occurrence. After the acute process subsides, complete recovery occurs.
- Subacute. Adverse symptoms can persist for a couple of weeks to a month. With a favorable course of the disease also comes recovery. If the disease is severe, then a complete cure does not occur.
- Chronic. Characterized by the persistence of adverse symptoms for more than a month. Usually, this variant of the disease occurs in waves: periods of exacerbations are replaced by remission. To eliminate the adverse symptoms and prevent the long-term consequences of the disease requires the appointment of complex treatment.
- Reactive. In this case, all clinical manifestations diseases occur in the baby literally within a few hours. Due to the disease, the well-being of the child suffers. The kid can feel strong weakness, refuses to eat, starts to be very naughty.
The inflammation that occurs in the lymph nodes may have different clinical options:
- Serous. Doctors also call this form infiltration. Usually occurs with viral infections. The course of the disease is usually mild or moderate.
- Purulent. The development of this form contributes to the preceding infection with a bacterial infection. The inflammatory process is usually quite acute and causes multiple adverse symptoms. Purulent lymphadenitis is accompanied by a pronounced increase in body temperature, often to febrile numbers. To eliminate the adverse symptoms requires the appointment of high doses of antibacterial drugs.
- Necrotic. Quite unfavorable way of developing the disease. This form leads to complete necrosis (death) of the affected tissue. The course of the disease is extremely unfavorable. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital. In case of very serious condition, the baby may be hospitalized in the intensive care unit and intensive care unit.
- Adenoflegmon It is also a very unfavorable variant of the disease.. To eliminate the symptoms, a whole complex of various drugs is required. Treatment is carried out strictly in stationary conditions. The prognosis is conditionally favorable.
Acute cervical lymphadenitis. This form of the disease is the most common. Often it occurs in babies after infections.These include: influenza, acute tonsillitis, catarrhal respiratory infections, childhood infections and others. There have been cases of increase in cervical lymph nodes in pneumonia. There are also frequent variants of odontogenic lymphadenitis.
A fairly common path of inflammation - the transition of a purulent process from the paranasal sinuses.
Babies with severe sinusitis or sinusitis have a high chance of getting lymphadenitis. The development of this condition, as a rule, leads to a decrease in immunity. Often sick or weakened toddlers, according to statistics, get sick much more often than their healthy peers.
The peak incidence of cervical lymphadenitis occurs at the age of 6-10 years. At this time, the lymph nodes are most vulnerable to various infections. This feature is due to the physiology of the child's body. The overwhelming number of cases of cervical lymphadenitis occurs due to infection with bacterial infections. They account for more than 70%.
To eliminate the adverse symptoms associated with enlarged lymph nodes, a whole range of different medicinal and physiotherapeutic procedures is used. Usually, it takes at least 2-3 weeks of active treatment to normalize the condition. In some cases, it may even take several months. Monitoring the condition of the baby is carried out at all stages of the treatment of the disease.
Inguinal lymphadenitis. This clinical variant of the disease is characterized by an enlarged lymph nodes in the groin. They can be increased in both girl and boy. However, according to statistics, boys are more susceptible to inguinal lymphadenitis. The symptoms of the disease are the same as in other clinical forms.
In most cases, inguinal lymphadenitis has a serous variant. However, there are also purulent species. Late diagnosis leads to the fact that they turn into dangerous forms - abscesses. These pus formations can easily erupt with the expiration of pus from a wound. With the formation of a purulent abscess, an immediate appeal for medical care is required.
Mesenteric lymphadenitis. This clinical variant of the disease occurs with an increase in the lymph nodes located in the mesentery. It is also a secondary manifestation of many diseases of internal organs. Mesadenitis can be acute and chronic. Kids with this pathology are observed not only at the pediatrician, but also at the pediatric gastroenterologist. In some cases, you may need to consult a surgeon.
Occurs mesadenitis mainly in older age. An enlarged lymph node in the abdominal cavity leads to the appearance of various adverse symptoms. The most characteristic symptom of the disease is the appearance of cramping or spastic abdominal pain. The most dangerous course of the disease in infants is when the child cannot yet tell the mother or the doctor about his symptoms.
Inflammation in the abdominal cavity can cause many different complications. In case of a pronounced purulent process, the inflamed lymph nodes can break through with the expiration of pus inside the peritoneum. This leads to the development of purulent abscesses, and in some cases even to the occurrence of sepsis.
Starting therapy for mesenteric lymphadenitis - the appointment of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents. With the ineffectiveness of the treatment in some cases, surgical treatment is required. Indications for surgery are established by a vascular or abdominal surgeon. The prognosis of the disease is conditionally favorable.
Symptomatology
The severity of symptoms of lymphadenitis depends on many reasons. The most important are: the child's age, the presence of immunodeficiency states, prematurity at birth, and chronic comorbid diseases.In very young children, the disease proceeds, as a rule, with vivid symptoms and may even turn into a chronic form.
For various variants of lymphadenitis is characteristic:
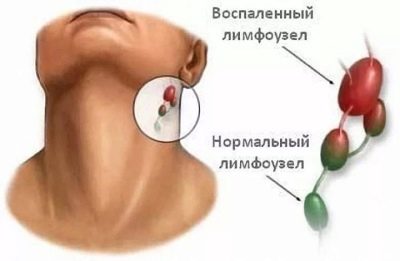
- Increase in the size of different groups of lymph nodes. In some cases, the lymph nodes become even visible upon visual inspection from the side. The skin over them can be changed or not. It depends on the clinical form of the disease. In some forms, the skin over the lymph nodes becomes bright red or even fiery scarlet.
- Soreness or sensitivity to palpation. During the feeling of the lymph nodes, it can be noted that the child has some discomfort. In severe lymphadenitis, severe pain appears. It may increase after a hot bath or bath, as well as during active physical exertion.
- Cohesion with the skin. When feeling the lymph nodes, you can notice their pronounced mobility. This is due to severe inflammation in the lymphoid tissue of the lymph node. In some diseases, the lymph nodes remain tightly welded to the skin and do not move.
- Symptoms of intoxication. All purulent lymphadenitis occur with an increase in body temperature to subfebrile or even febrile numbers. Against the background of such febrile, the baby may show signs of fever or even severe chills. The general condition worsens, thirst develops.
- Violation of child's behavior. In the acute period of the disease, the baby becomes more sluggish, plays poorly with toys. Many infants are poorly attached to the mother's breast. They often suffer from appetite and sleep disturbed. A child can become quite passive.
These symptoms are basic. They appear in almost all clinical forms of lymphadenitis. It is not always possible to suspect mild forms of the disease at home. Often, to establish the correct diagnosis requires additional expert advice.
Diagnostics
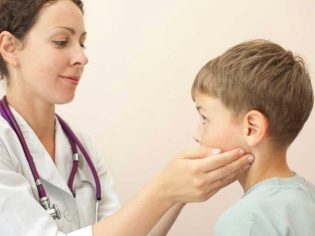
When an enlarged lymph node is found, immediately take the child to the doctor.
Sometimes lymphadenitis is the first clinical marker of very dangerous diseases, including cancer tumors. In no case should you pull with the request for medical care! This can lead to the transition of the disease into a chronic form or aggravate the course of the disease.
Lymph nodes, increasing in size, become available for palpation. When palpating, you can also set their estimated diameter. In some cases, they acquire the size of a "pea" or "bean." When conducting a home inspection, be careful! Do not try to push too hard on the inflamed lymph nodes. Such treatment can only enhance the inflammatory process.
When detecting signs of lymphadenitis in a child's parents are really confused. They do not know which doctor to ask for help. First of all, it is worth signing up for a consultation with a pediatrician. He will examine the child and make a preliminary conclusion about what kind of disease could cause an increase in the lymph nodes in the baby.
In some cases, the doctor will send the child to consult an infectious disease doctor, rheumatologist, cardiologist or gastroenterologist. These experts will help to establish the correct and accurate diagnosis. Some clinical situations are quite difficult. In this case, a real medical consultation is required, in which several physicians of various specialties will participate. Establishing the correct diagnosis is a necessary step for drawing up the correct treatment tactics.
After conducting all necessary clinical examinations, the doctor will prescribe a child several laboratory and instrumental tests. They are needed in order to further verify the diagnosis. All babies with lymphadenitis are prescribed:
- General clinical blood and urine tests. These simple tests allow you to identify a possible infectious cause of the disease, as well as to establish the degreeThe severity of functional disorders.
- Biochemical blood test. Necessary to identify the primary focus. Often appointed to exclude concomitant diseases including diseases of the kidneys and the digestive system.
- Cytological and histological examination. For this analysis, a small piece of the lymph node is preliminarily taken by puncture. In a special laboratory, laboratory doctors research material on the main clinical features. This test is highly informative and allows you to establish the cause of the disease.
- Backwater inflammatory exudate. Usually this study is carried out in conjunction with histology. This test gives a fairly accurate idea of what kind of inflammation originated in the lymph nodes. In the course of the study, it is possible to additionally establish the sensitivity of the detected microorganisms to various types of antibiotics and bacteriophages.
- Puncture of lymph nodes. After carrying out this procedure, histological examination is required. It allows you to establish the diagnosis in 98% of cases. This test is highly specific and has been successfully used in pediatric practice for many years to establish the correct diagnoses.
- X-ray. The method has a fairly high radiation load. Assigned to kids only under strict indications. Radiography usually does not apply to children under two years of age. The study provides a descriptive picture of the presence of many diseases, however, it does not have high sensitivity and specificity.
- Ultrasound procedure. Appointed to establish the true size of the inflamed lymph nodes. The method gives an accurate picture of the existing pathology in the lymph nodes.
- Computer and magnetic resonance therapy. Assigned only in complex diagnostic cases where the establishment of a diagnosis using other methods is impossible. The methods are highly informative and accurate. During the study, the child does not experience any pain.
Treatment
Therapy of the disease is usually complex. To eliminate adverse symptoms, doctors prescribe various combinations of drugs. They can be used in the form of tablets, injections, and in case of severe course of the disease - in the form of droppers and various infusions.
Treatment of any lymphadenitis - speed. First appointed means of conservative therapy. These include anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents.
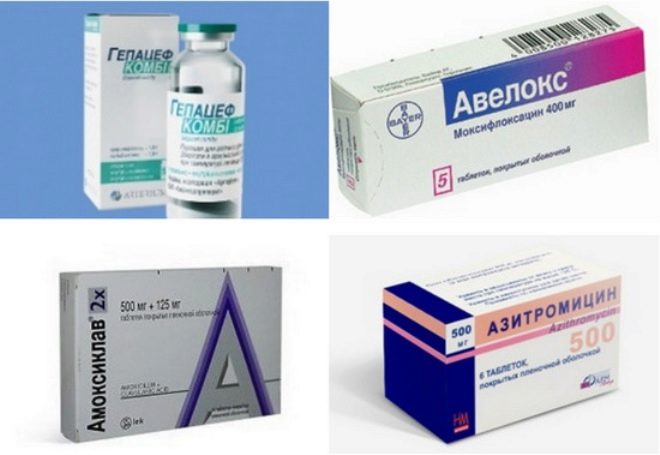
Antibiotics are prescribed only in cases where a purulent process is established or bacteria have been identified during diagnostic tests.
Currently used antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action. They effectively fight several types of bacteria at once. For the treatment of various forms of lymphadenitis are prescribed: clavulanic acid-protected penicillins, the latest generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones and others. The course of antibiotic therapy is usually 10-14 days. During treatment, mandatory monitoring of the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment is carried out.
When determining the viral cause of the disease - antiviral drugs are prescribed. They are usually recommended for use for a shorter period. On average, it is 5-7 days. Antiviral drugs are prescribed in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs. This combination allows you to achieve the best result in the shortest possible time.
Anti-inflammatory drugs help eliminate the symptoms of intoxication. Paracetamol, nimesulide, ibuprofen and others are used to reduce body temperature. These agents are prescribed for symptomatic treatment. Use medications should only be when the temperature rises above 38 degrees.
Also for removing bacterial toxins from the body abundant warm drink required. It helps to normalize the health of the child much faster. As drinks, compotes and fruit drinks made from various fruits and berries are well suited. For their preparation both fresh and frozen fruits are used.
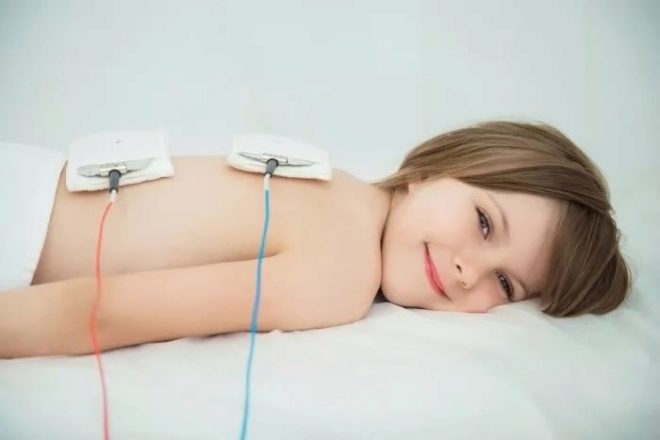
Subacute and chronic lymphadenitis can be treated using physiotherapy methods. However, please note that these methods also have a number of contraindications. For example, in babies with cancer and rheumatological diseases, their use is undesirable. Various methods of magnetic therapy, ultrasound, infrared radiation and many others are used to eliminate lymphadenitis.
With the ineffectiveness of the conservative treatment can be assigned to surgery. It is important to note that the indications for them are strictly limited.
Usually, surgery is performed only on older babies. Most cases of lymphadenitis go away alone or after a conservative treatment and do not require surgical treatment.
Prevention
An important element of preventive measures for lymphadenitis is strict control over the course of any infectious pathology in the body. All untreated infections can cause signs of lymphadenitis. To prevent inflammation in the lymph nodes requires mandatory monitoring of the state of the teeth. Caries is best treated in the earliest stages, preventing the development of pulpitis.
Kids, especially the first years of life, must be vaccinated against all childhood infections, taking into account their age.
Often the causes of lymphadenitis in preschool children are the usual "quarantine" diseases. Preventing many of them is pretty easy. For this, it is necessary only in time to deliver the child all the necessary vaccinations.
Strengthening immunity is also an important component of the prevention of lymphadenitis in children. Proper nutrition, healthy sleep and active play in the fresh air will be the guarantors of a good mood and excellent work of the immune system. To teach your baby to a healthy lifestyle should be from the very first days. This good habit will help him in the future to be active and not get sick.
About what to do if lymph nodes are enlarged, see the next video.