Symptoms and treatment of tracheitis in children
A variety of diseases can cause cough development in children, one of which is tracheitis. How this disease manifests in babies and how it can be dangerous, this article will tell.
What it is?
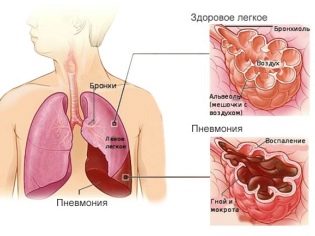
Inflammation of the mucous membranes covering the inside of the trachea is called tracheitis. This pathology is quite common, especially in babies. Both a child and an adult can become ill with tracheitis. Boys suffer as often as girls. A child residing in any country can become ill with tracheitis.
This pathology can be independent or occurs in conjunction with other diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Very often, babies have at the same time a whole “bunch” of similar diseases: pharyngitis, laryngitis and tracheitis. One pathology passes into another, which significantly violates the health and general condition of the child.
The duration of the acute period of tracheitis may be different. On average, it is 5-10 days.
After an acute period of illness, there is a rather long recovery time - convalescence. It is characterized by the persistence of residual symptoms of the disease, which gradually disappear over 1-2 weeks. The recovery period is very important. Compliance with all the recommendations of doctors at this time will prevent the transition of the acute process into a chronic one, and also reduce the likelihood of the appearance of long-term adverse effects of the disease.
Babies who attend educational institutions have a high risk of becoming infected with infectious tracheitis. It's related with a high rate of spread of pathogens from a sick child to a healthy one.
Babies of early age, due to the still insufficiently active work of the immune system, are susceptible to this disease much more than older children.
Rarely tracheitis occurs in newborns. If the one-year-old baby is breastfed, then the risk of infection with various infections leading to respiratory pathology is small.
The reasons
The development of inflammation in the trachea in children leads a variety of causal factors. They can act in isolation or simultaneously. The combined effect of several causal factors leads to the fact that the baby has a variety of adverse symptoms, which is bad for its overall well-being. The following causes contribute to the development of inflammation in the trachea:
- Bacteria. Bacterial infections top the list of causes that cause various pathologies of the respiratory tract. They are found in children's practice extremely often. Bacterial tracheitis is contagious. It is easily transmitted by airborne droplets from a sick child to a healthy one.
- Viruses. They are the causative agents of tracheitis a little less than bacteria. Influenza and parainfluenza viruses, rhino - and adenoviruses, Coxsackie and Epstein - Barr viruses and many others can lead to the development of the disease. The course of viral tracheitis is usually easier than bacterial. All adverse symptoms on the background of properly selected treatment, as a rule, pass for 5-7 days.
- Allergic Pathologies. They manifest themselves in children up to a year. Various allergens become provoking factors to the appearance of adverse symptoms of the disease. They are characterized by a wave-like course: periods of exacerbation are replaced by rather stable remission.The entry of allergens into the children's body each time provokes a worsening of the child’s well-being and the onset of the disease.
- Inhalation of too cold air. Atmospheric impurities and industrial wastes also have an adverse and irritating effect on the delicate mucous membranes of the larynx. According to statistics, children at the age of 2-3 years are most susceptible to this variant of the disease. This feature is due to insufficiently effective work of local immunity.
- Hypothermia Both local and general cooling can lead to the development of the disease. Walking in cold weather without a scarf and hats or swimming in the summer in an insufficiently well warmed body of water are often the causes of the appearance of pathologies in the respiratory tract in children.
- Long stay in a highly smoked room. The smallest components of toxic substances that are released during smoking, a negative effect on the cells of the mucous membranes of the trachea. For the development of the disease in a child, even a short stay in a smoky room is sufficient. Adults should remember that smoking in the room where the child is located should not be under any circumstances!
- Breathing in dry air. Normal breathing requires physiological microclimate parameters. To the inhaled air did not damage and "scratch" the delicate mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, you should carefully monitor the humidity in children's rooms. Inhalation of too dry air often leads to severe irritation of the trachea, which ultimately contributes to the development of the symptoms of tracheitis.
- Immune weakening. Often sick and weakened children are more susceptible to various infectious pathologies. This is due to a pathological decrease in immunity.
Toddlers with immunodeficiency conditions are also at increased risk. If a child has colds and infectious diseases more than 5-6 times a year, then this is a significant reason to turn to a child immunologist.
Kinds
The inflammatory process in the trachea may be different in duration and intensity. This is due to various reasons that lead to its development. About acute tracheitis say, when the disease appeared in the baby for the first time in life. In more than 90% of cases, this is an infectious form.
Quite often, acute tracheitis is recorded in infants and children in the very first years of life.
The most common cause of acute inflammation of the trachea in children is viruses. Bacterial flora, such as streptococci and staphylococci, leads to the development of the disease more rarely. Anaerobic microorganisms cause tracheitis in no more than 5% of cases. The acute process is characterized by the appearance of severe edema of the trachea, its infiltration with inflammatory immune cells, as well as the formation of a sufficiently large amount of mucus. These morphological features lead to the fact that the baby has clinical symptoms characteristic of the disease.
Chronic tracheitis in most cases is a consistent acute stage. In pediatric practice, it occurs mainly in babies who have abnormalities in the immune system and complicated chronic diseases of internal organs. In adolescence, the development of chronic tracheitis significantly affects long or episodic smoking.
Toddlers with severe pulmonary pathologies and congestive diseases of the cardiovascular system are at risk of developing a persistent, protracted form of tracheal pathology. In some cases, diseases of the paranasal sinuses lead to the development of the chronic variant.
Morphologically, when the process is chronized, both hypertrophic and atrophic changes can be observed on the mucous membranes of the trachea. Hypertrophy is manifested by an increased blood supply to the blood vessels and the growth of the inner lining of the respiratory tree.These changes provoke the appearance of a child cough with a lot of sputum. The amount of discharge of mucus also increases markedly.
When atrophy mucous membrane changes its color. She becomes gray, she appears uncharacteristic shine. The mucosa is noticeably thinner and can bleed easily.
In some cases, dense crusts appear on the inner epithelial lining of the trachea. They significantly increase the cough. He becomes more impressed and unbearable.
Symptoms
The adverse symptoms of infectious tracheitis do not appear in a child immediately. Before the onset of clinical signs of the disease, the incubation period first passes. It may be different in its duration.
For viral forms of tracheitis, the incubation period is usually 2-5 days. Unfavorable symptoms of bacterial infections usually appear after 3-7 days.
The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Coughing hack. This symptom is very characteristic of tracheitis. Cough can be both dry and wet. He is worried about the baby both during the day and at night. The intensity of cough may be different and depends on the cause of the disease.
- Coughing difficulties. The presence of a large amount of mucus and sputum leads to the fact that the child is difficult enough to cough. During a coughing attack, he strains, his face reddens. Some babies have tears on their faces. This is a reaction to pain, which occurs when severe coughing.
- Soreness in the chest. Pain syndrome increases markedly during coughing. Some babies feel “stuffy” in the chest, which greatly hinders them. This situation can lead to the fact that the child's breathing becomes more superficial, instinctively, the baby begins to spare the chest and limit the amplitude of the respiratory movements. Quite often, this symptom is present in children aged 5-12 years.
- Pain in the oropharynx. Appears after coughing. In the overwhelming number of cases, acute tracheitis occurs in conjunction with pharyngitis, which also contributes to persistent pain in the throat. This causes difficulty in swallowing food. Solid food when swallowing causes a marked increase in pain.
- The change in voice timbre. Usually he becomes more hoarse. The baby can hoar at the pronunciation of words. In infants, this symptom manifests itself during crying.
- The appearance of sputum. In some forms of tracheitis, this feature may be absent. Usually the sputum is thick enough, it is difficult to expectorate. The number of pathological secretions can be different: from a teaspoon to 50-100 ml per day.
The color of sputum is usually greyish or yellow, may contain bloody streaks.
- Increased body temperature. Mild disease is accompanied by subfebrilitet. In this case, the body temperature rises to 37-37.5 degrees. More severe forms of the disease are accompanied by febrile values. When joining complications, the body temperature rises above 38 degrees.
- Intoxication. As a result of the inflammatory infectious process, a large amount of a wide variety of toxic decomposition products accumulates in the children's body. Their accumulation in the internal environment leads to the appearance of the following clinical signs: the appearance of a moderate headache, an increase in weakness, apathy, and a change in mood.
- Violation of the child's behavior. In the acute period of the disease, the baby may become more sluggish, he loses interest in games with his favorite toys. A hacking cough significantly disrupts children's sleep. The child may experience severe sleepiness during the daytime, and at night almost never sleep. Decreased appetite leads to the fact that the baby begins to lose weight.
Diagnostics
If the child has the first symptoms of tracheitis - be sure to show the baby to the doctor.
If you have a high body temperature, you should not go to the clinic yourself. In this case, it is better to call the pediatrician at home. The doctor will examine the crumb and conduct the necessary clinical examination. In some cases, the pediatrician will refer the baby for a consultation. to child otolaryngologist.
To establish the correct diagnosis of a single clinical examination is not enough. To establish the causative agent, additional laboratory tests are required.
All sick children must pass a general clinical tests. In general, the analysis of blood in infectious tracheitis increases the number of leukocytes and the ESR significantly accelerates. Changes in the leukocyte formula suggest that in the children's body there is a viral or bacterial infection.
Establishing the source of the disease also helps bacteriological analysis. The material for this examination is sputum from the respiratory tract. The study is conducted in laboratory conditions. The result of the analysis shows the presence of a specific pathogen.
This laboratory test is widely distributed and successfully used in pediatric practice to identify various respiratory pathologies.
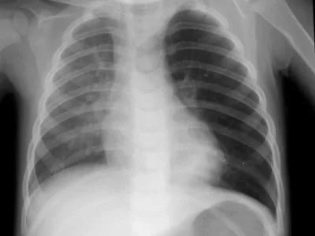
In some situations, doctors additionally prescribe x-ray of the lungs. It is carried out in the case when there is a suspicion of pneumonia. This lung pathology develops in severe tracheitis and can be a rather dangerous complication.
Radiography in very young patients is not carried out, since this method of research has a fairly high radiation load. To exclude pneumonia in this case, the doctors perform auscultation of the chest with the help of a normal phonendoscope.
Complications
The most frequent complication of the acute process is its transition to the chronic form. Chronization occurs mainly in rather weak children. Immunodeficiency states also contribute to the transition of acute tracheitis in the protracted form. Chronic tracheitis is quite exhausting for a baby and requires complex treatment.
Pneumonia is one of the most dangerous complications. It develops with the spread of the inflammatory process from the trachea through the bronchial tree. Purulent pneumonia is dangerous in the development of abscesses and sepsis. Treatment of this dangerous complication is carried out only in a hospital.
The danger of long-term allergic tracheitis is that it can cause a child to develop bronchial asthma. The risk is especially high in allergic children with hereditary predispositions. Frequent exacerbations of allergic tracheitis contribute to the occurrence of persistent respiratory failure.
The impact of allergenic factors on the children's body against the background of chronic inflammation in the trachea can cause symptoms of bronchial obstruction.
Treatment
Cure tracheitis at home is possible. However, this should be done only with the obligatory supervision of the attending physician.
Even mild forms of the disease with improperly chosen treatment can cause the child to appear rather dangerous complications.
The duration of tracheitis therapy is usually 7-10 days. In some cases, treatment may be longer.
The treatment regimen is selected individually. taking into account the age of the baby and the presence of concomitant chronic pathologies of internal organs. To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease requires the appointment of a whole range of different medicines.
Herbal medicine also helps to improve the child's well-being, which is especially effective in very young patients.
To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease are used:
- Compliance with bed rest. If the baby has a high body temperature, then he must be in bed for the entire period of fever and fever. This simple forced measure will help to avoid the development of dangerous complications in the future.
- Sufficient drinking regime. To eliminate bacterial and viral toxins from a child’s body, you need to drink plenty of fluids. Ordinary boiled water will be suitable as the main detoxifying agent. A sick child should drink at least 1-1.5 liters per day. Drinks and compotes made from berries and fruits will also be an excellent beverage option.
- Dieting. To replenish the forces needed to fight the disease, the child must receive a sufficient amount of vital nutrients. The daily caloric content of the child’s diet in the days of illness should be somewhat increased. Food should be cooked in the most gentle way - to simmer, bake or boil. All dishes should be sufficiently crushed, so as not to increase the pain when swallowing.
- Antiviral drugs. They are prescribed for viral tracheitis. The duration of their use is 5-7 days. The dosage and frequency of use is chosen by the attending physician. The use of antiviral drugs in babies has positive feedback from parents. They note that taking these medications helps improve the well-being of the baby in a shorter time.
- Antibiotics. Appointed with bacterial forms of tracheitis. Discharged for 7-10 days. In the appointment of antibacterial drugs necessarily carried out monitoring of the effectiveness of their actions. For this, the overall well-being of the child and the improvement in the overall blood count are evaluated.
- Antitussives. Help eliminate cough and improve sputum discharge. Can be discharged in the form of tablets, sweet syrups or solutions for inhalation. "Sinekod", "Lasolvan", "Gadeliks", "Mukaltin»And other drugs will help to cope with a coughing hampering and improve the child's well-being. When signs of bronchial obstruction appear, special bronchodilators are discharged, for example, “Berodual».
- Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory. Used with increasing body temperature above 38 degrees. In children, paracetamol-based and ibuprofen-based drugs are widely used. They should not be used for prophylaxis even at subfebrile temperature, since such use can significantly aggravate the course of the disease and increase the risk of side effects.
- Inhalation. Conducted only after prior consultation with your doctor. In older children, various aromatic oils can be used for inhalation. For a single procedure, a couple of drops of this tool is enough. Aromatic oils of fir, cedar, pine and eucalyptus have excellent anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating actions.
- Normalization of humidity in the children's room. Too dry air has a pronounced irritant effect on the mucous membranes of the trachea. The optimum humidity in the nursery should be 55-60%. To improve the performance of the microclimate help special devices - humidifiers. During the work they spray the smallest parts of water that promotes good moistening of dry air in the room.
- Immunostimulating Therapy. Conducted under strict indications. Interferon preparations have a pronounced stimulating effect on the immune system. They can be used in the form of nasal drops or spray, as well as by ingestion or through injections. The choice of an immunostimulating drug and the frequency of its use is chosen by a pediatric immunologist or the attending pediatrician.
- Multivitamin complexes. For a quick recovery, a child needs an adequate supply of antioxidant biologically active substances.Vitamin complexes enriched with vitamins A, C and E will be an excellent component of the complex treatment of various clinical forms of tracheitis.
- Bee products. Propolis and honey have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. These products help to combat the pronounced symptoms of intoxication of the child’s body, and also have a pronounced immunostimulating effect.
Honey should be used carefully, as quite often babies have allergic reactions to it.
- Percussion massage. Carried out by lightly tapping the fingers on the chest. This massage improves the discharge of thick sputum through the airways. It should be done daily, 2 times a day. To obtain a positive effect requires 10-12 procedures.
- Use of alkaline drinks. They make sputum more fluid, which contributes to its easy discharge through the respiratory tract. Mineral water and milk are well suited as alkaline drinks. They should be consumed 30 minutes before a meal, 50-100 ml. It is important to note that milk and mineral water should be preheated to 40-45 degrees.
Prevention
The implementation of preventive measures is very important. The main component of prevention is the prevention of infections and strengthening of the immune system in the children's body.
Enhance the immune system will help active daily walks in the fresh air, optimal physical exertion and proper healthy eating. When playing on the street, be sure to choose warm and comfortable clothes for your baby. In windy weather, do not forget to wear a scarf.
The treatment of secondary foci of infection also plays an important role in the prevention of tracheitis. Children suffering from chronic pathology of ENT organs must be observed in Laura. They should visit the pediatric otolaryngologist at least 2-3 times a year.
During mass outbreaks of infectious pathologies, children visiting educational institutions should be at home. Compliance with quarantine significantly reduces the risk of possible infection with infectious tracheitis.
For more information about this disease, its symptoms and treatment, see the following video.