Staph infection in newborns and infants
A staph infection awaits a child from the first minutes of his independent life in this world. Even in the maternity hospital, even with careful decontamination, staphylococci live and wait for their prey. In 95 - 97% of newborns in the first hours after birth, staphylococcus is detected. But not all kids microbes cause disease. About who and why sick staph infection and how to treat it, we will tell in this material.
What it is
A staph infection is a single name for a huge group of diseases that are caused by staphylococcal microbes. These microorganisms can provoke a wide variety of pathologies - from pimples and pustules on the skin to severe bacterial pneumonia and sepsis.
For many parents, the information that almost every newborn gets infected in the maternity hospital, can be a real discovery. In fact, there is no reason to panic. Not every child has Staphylococcus ailments, because babies are well protected from this germ by innate maternal immunity. A person encounters this microbe throughout life, and adults develop strong immunity to staphylococcus. During pregnancy, the baby receives ready-made antibodies from the mother.
The presence of staphylococcus on mucous membranes, skin or in the fecal masses of a baby is not yet an infection.
If the condition of the child remains normal, then maternal antibodies are enough to restrain the activity of the microbe. Infection can develop in babies who were born as a result of a very difficult and problematic pregnancy. The risk group is:
- premature and low birth weight babies;
- children with congenital immunodeficiency disorders (for example, people infected with HIV);
- children whose mother in the process of gestation suffered from preeclampsia, low water or high water;
- children with congenital malformations.
The innate immunity “ends” by about half a year, and from this age on, the child’s own immunity begins to “learn” and develop its antibodies to microbes and the virus. It is at this time that outbreaks of staph infection are most often diagnosed in infants. The infection itself can be localized and spread, as well as acute and chronic. Here is just an exemplary list of diseases that can be caused by staphylococci:
- pyoderma;
- felon;
- whitlow;
- furuncle or abscess;
- phlegmon;
- epidemic pemphigus of newborns;
- staph tonsillitis;
- otitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- pneumonia;
- ostriomyelitis;
- endocarditis;
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- omphalitis;
- enterocolitis;
- sepsis.
About the pathogen
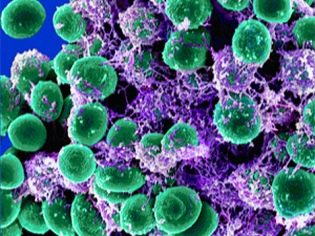
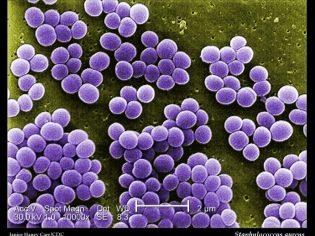
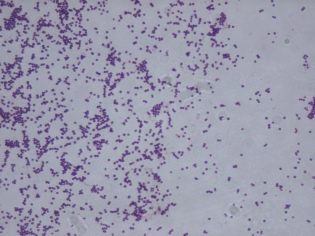
Staphylococci under a microscope resemble grape bunches, and therefore they received such a name - staphylos - grapes, coccus - grain. Each microbe has a spherical shape, together they are grouped into a bunch. The carriers of these microbes are 100% of the population of the planet.
Science today knows 27 species of staphylococcal bacteria. 24 of them are not dangerous for humans, they peacefully coexist with people. Only three types of bacteria are capable of causing diseases, as they are opportunistic. This property explains why not every child gets sick - with normal immune protection, the bacteria do not harm the person, and start pathologically activated only when there are prerequisites for this - the child is weak, the immunity fails, the baby has been operated on or instrumental manipulated, and so on.
With these three species need to get acquainted.
Staphylococcus aureus
Behind the beautiful Latin "aureus" lies, as it is easy to guess, Staphylococcus aureus. This is the most dangerous and aggressive germ that becomes the "culprit" of most staph infections. In total, it can cause more than a hundred of various ailments.
Such a poetic name was given to him for his ability to form a golden pigment. This bacterium can affect both the skin and internal organs. Its main feature is the formation of pus. The microbe is stubborn and very tenacious - it is not afraid of boiling, frost, bleach and hydrogen peroxide, it does not care for alcohol and formalin, salt and acids, and it cannot be eliminated by exposure to direct sunlight.
The only means that can instantly destroy the structure of the microbe is the most ordinary "green paint".
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is the most insidious representative of the species. He usually “lives” in medical institutions, where from constant disinfection and exposure to drugs he becomes truly unkillable. It cannot be eliminated with the help of most antibiotics - penicillins and cephalosporins. Diseases caused by such a “modified” microbe are very difficult to treat.
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Epidermal staphylococcus chooses the skin as well as the mucous membranes of a person for its vital activity. It does not manifest itself, while the child’s immunity is strong and looks completely harmless. But everything changes if the immune system is weakened.
From the skin and mucous membranes, the microbe quickly enters the body through wounds, surgical incisions, and causes severe lesions, even sepsis. Surgeon-doctors very much disliked this microbe’s behavior, because it sometimes complicates the recovery period even after a successful operation.
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Saprophytic staphylococcus in children is very rare. His favorite habitat is urinary tract of women. If a pregnant woman suffers from such an infection, then the probability of infection at the time of delivery of the child increases. This microbe causes complicated cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Causes of disease
The widest distribution of staphylococci is the main cause of infection. Laboratory tests can detect this microbe and not one, but several species at once in any person. Dangerous members of the species are distributed in various ways:
- Airborne. Microbes are quickly and easily removed from the body of a patient with exhaled air and can long exist in it and in the dust, without losing their activity at all.
- Household. A baby can get a sample of the most friendly microorganism through contact with the hands of parents, medical personnel, through tools, through objects that were held by infected people. Antiseptics and alcohol on staphylococcus will not work.
- Food. A newborn and an infant can get staphylococcus along with breast milk, drinking water, and water in which the parents mixed milk. Boiling does not help, because the germ of boiling is not afraid. A baby that is given complementary foods can become infected after eating dairy and other products with which the person carrying the bacteria has come into contact. Improper storage and insufficient heat treatment make infection even more likely.
The internal causes that contribute to the development of the infection after the bacteria hit are diverse, but, in fact, they boil down to one factor - insufficient work of immunity in general and local immunity in particular.
The body of a child weakened by anything, the presence of chronic or congenital diseases, prematurity - all this significantly reduces the ability of the child's body to resist. This is how a staph infection begins to develop in one of its many manifestations.
The probability of infection increases significantly if the child is in contact with a person who has open wounds affected by staphylococcusif the adult has an acute or chronic bacterial infection.
Symptoms and signs
The symptoms of a staphylococcal infection are due to those who, in the course of their vital activity, excrete toxins and enzymes that can destroy neutrophils and macrophages, as well as lymphocyte cells. An abscess is usually formed at the site of microbial invasion. Toxins spread through the body through the bloodstream, causing severe intoxication symptoms.
Intoxication is manifested by fever, severe weakness. The baby's behavior changes - he begins to refuse feeding, his sleep is disturbed, and a moody cry appears. The more severe the infection, the brighter the signs of intoxication will be:
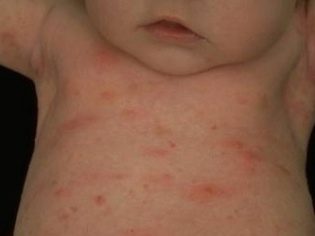
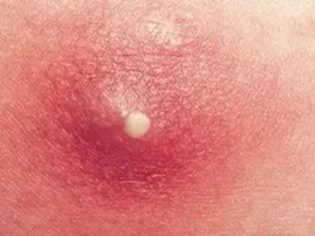
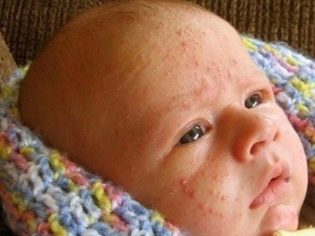
- The most common manifestations of staph infection - skin. There may be pustules and boils on the skin of the face, hands, legs, tummy. A rash is always accompanied by a purulent process. Quite often in newborns the infection begins with purulent inflammation of the umbilical wound.
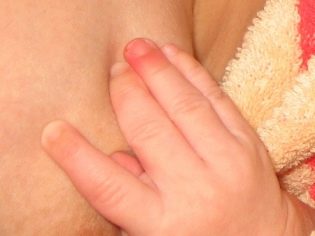
- Omphalite - The most frequent staphylococcal inflammation. The umbilical wound with it is inflamed due to infection with Staphylococcus aureus. It becomes painful, reddened, with slight pressure pus is released.
- Skin manifestation of infection is quite diverse - from single vesicles and pustules to extensive rashes on face and body. The blisters are filled with turbid liquid, burst even by a light touch, in their place a golden yellow crust forms. If the skin is affected all over the body, then we are talking about pemphigus - pemphigus of newborns.
- The bacterium can multiply not only on the skin and in the subcutaneous layer, it happens that it affects the bones and joints. Purulent inflammation of bones - osteomyelitis - manifested by pain in the limbs, which become stronger when moving. At rest, the baby may not be very anxious, but during gymnastics or laying on his tummy, he begins to act up and cry sharply. If a joint is affected, the disease is called arthritis, manifested by swelling and reddening of the joint, tenderness to palpation.
- If a staph infection affects the upper and lower respiratory tract, then the child has the characteristic symptoms of respiratory diseases - runny nose, cough, fever. Heavy leaks staph angina - with her baby can not normally eat because of pain when swallowing. Its tonsils are enlarged and inflamed, with pustular lesions visible on them. Pustules may appear in the nose.
- Bacterial pharyngitis always accompanied by a dry, painful cough. For all types of respiratory staphylococcal lesions characterized by high temperature.
- If the germ in the baby causes inflammation of the lining of the heart — endocarditisthen it is manifested by high fever - up to 40.0 degrees and higher, pain in the sternum, difficulty breathing. When listening, characteristic heart murmurs are noticeable.
- Intestinal manifestations bacterial contamination make themselves aware of abdominal pain, bloating, increased meteorism. The baby's stool is changing - there can be painful frequent diarrhea, vomiting is possible. The crumb has no appetite, his behavior and sleep are disturbed, he is capricious. At high temperatures dehydration occurs very quickly.
- Brain damage (meningitis) manifested by severe weakness, fever, nausea.The crumb becomes very sluggish, all his muscles are relaxed. Neurological disorders, convulsions, loss of consciousness may occur.
- If infection develops in the urinary tract, then the baby shows great anxiety during urination. He shouts loudly, bent. Body temperature may be elevated. When staphylococcal sepsis affects almost all the internal organs and systems of the baby.
Often enough, the germ causes conjunctivitis in newborns. Inflammation of the organs of vision is purulent and, in the absence of timely medical care, can result in loss of vision. Whatever disease staphylococcus causes, all ailments will have common signs that will allow the doctor and parents to suspect bacterial infection:
- heat;
- purulent lesions;
- severe intoxication.
Consequences and danger
A staph infection is a disease that can never be treated with folk remedies and grandmother's recipes. Not every strong antibiotic can kill a bacterium that has become aggressive; decoctions of herbs in this case cannot help a child with anything. For the formation of the forecast, it is important to know at what stage the staphylococcus was detected. If this is an early infection, and several days have passed since the beginning of the infection, then the prognosis is more favorable.
The delay and improper treatment of bacterial inflammation of almost any organ is dangerous due to the occurrence of systemic infection - sepsis.
Staphylococcal sepsis, according to medical statistics, leads to death in about 70% of cases. Mortality from endocarditis caused by staphylococci is 45-50%. Infectious toxic shock and pulmonary edema are also dangerous, which are also often observed in infants with severe bacterial infection. Mortality from such conditions ranges from 25 to 40%.
Staphylococcal acute infection quite often, unfortunately, causes chronic disease of the affected organ. So, a single staphylococcal tonsillitis can lead to chronic tonsillitis. The most unfavorable prognoses are given in relation to the nosocomial infection with which the baby becomes infected in the hospital. It is difficult to treat, the microbe is resistant to antibiotics, namely these drugs are almost the only way to provide assistance. So, nosocomial sepsis leads to death in about 90% of cases, and hospital pneumonia leads to the death of babies in 80% of infections.
Lung bacterial infections are practically non-existent. In most cases, they are complicated - a sore throat can cause damage to the kidneys or the heart membrane, and furunculosis can cause the development of severe conjunctivitis and other forms of staphylococcal infection.
Mortality of newborns and infants from staph infection is growing. This fact had to be recognized both in the Ministry of Health and in the World Health Organization. This is due to the fact that adults themselves are uncontrolledly treated with antibiotics, even when they are not necessary, for example, with the flu or ARVI. Taking antibiotics for any reason and without it gradually led to the fact that new microbial strains appear faster than the pharmaceutical industry develops drugs against them.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a bacterial infection and even just when the temperature rises to 39.0 degrees and above, as well as with the appearance of rash, pustules, parents must call a pediatrician or an ambulance. During the initial examination, the doctor will assess the general symptoms, if high fever is detected, suppurative inflammation, as well as symptoms of intoxication, the doctor will surely find out from the parents whether the baby has had any contact with the patients, has not undergone any procedures in the hospital.
If you suspect a severe bacterial lesion, the child will be hospitalized at high temperature, vomiting, diarrhea. Under the round-the-clock supervision of doctors in an infectious diseases hospital, it is recommended that all babies with a staphylococcal infection who are not one year old stay.
Leaving the child at home can only if he has a slight skin rash, localized form and no high temperature.
The main diagnosis is carried out in the laboratory. For respiratory manifestations, for example, for tonsillitis, a smear from the throat is taken; for pustular lesions, a sample of the contents of the wheal or boils, as well as a blood test. If you suspect sepsis or bacterial damage to the internal organs - a blood test.
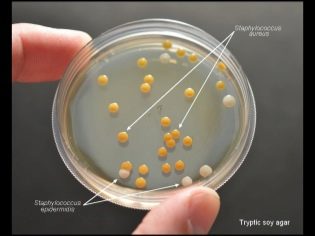
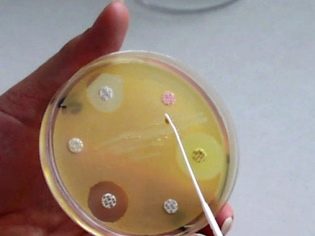
The study is called bacposevom. The collected sample is sown on a nutrient medium and waiting for a colony of bacteria to grow. Microscopic examination shows exactly which bacteria have grown. This makes it possible to confirm or refute a staph infection.
In order to understand how to deal with this, a microbial laboratory technician exposes the most common antibiotics. The drug, to which microbes show sensitivity, becomes the basis of the treatment of this child.
Depending on the symptoms, the search for bacteria is carried out in blood samples, urine samples, in the feces of an infant, and also in the breast milk of his mother.
As already mentioned, if you want to find staphylococci in any person by laboratory methods, therefore, the detection of these microbes is not considered a disease in itself. There are norms that correspond to completely healthy conditions. These standards for disease significantly exceeded:
- The rate of content of Staphylococcus aureus in a smear from a nose is 10 in 2 degrees or 10 in 3 degrees.
- The normal microbial content of a throat swab is 10 to 4 degrees.
- In the intestine, blood normally staphylococcus should not be.
Analyzes are done more than one day, but this should not frighten parents. During the entire time that laboratory technicians need to ascertain the whole picture, the child will receive treatment, he will not be left without attention. Until the exact pathogen is known, the doctor may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics or provide symptomatic treatment. To accurately diagnose an infection, consultation of other specialists is sometimes required. Gastroenterologist, surgeon, neurologist, dermatologist, hematologist, otolaryngologist.
Treatment
Treatment of staphylococcal infection includes two main areas:
- the suppression of the activity of bacteria, the elimination of pathogenic microflora;
- activation of the child's immunity.
Depending on the severity and nature of a particular microbial disease, can be shown:
- conservative treatment;
- surgical intervention.
Medication Treatment
The basis of the treatment of any form of staph infection is antibacterial drugs. Babies are usually prescribed antibiotics of the penicillin group. Considering the resistance of many microbes to penicillin, semi-synthetic penicillins, eg "Ampicillin". Well proven in the fight against staphylococcus penicillins with clavulanic acid - "Amoxiclav».
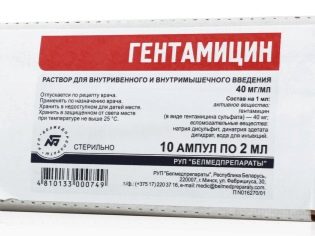
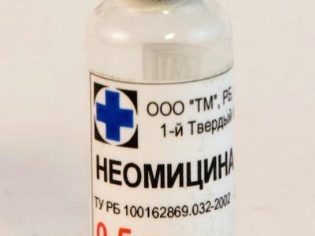
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are very effective against staphylococcus. However, parents should be aware that drugs such as Gentamicin, Neomycin are ototoxic.
In other words, their use in childhood often leads to partial hearing loss or complete deafness. Therefore, it is better to refuse such means if there is no vital necessity. The need, in fact, can be only one - severe sepsis, in which "Gentamicin" can save a child's life, even at the cost of hearing loss.
Cephalosporin antibiotics and macrolides are prescribed for staphylococcus, but not as often as penicillins.Basically, these drugs are resorted to if the child does not have relief after taking penicillin drugs, as well as in the case of nosocomial infections.
Treatment with antibacterial drugs should take place according to certain rules:
- the specific drug is chosen by the doctor;
- The doctor prescribes a course of treatment, and it is strictly forbidden to change it up or down;
- do not use two antibiotics at the same time;
- antibiotics for infants prescribed together with drugs that protect and restore the intestinal flora to avoid dysbiosis - "Bifidumbakterin", for example.
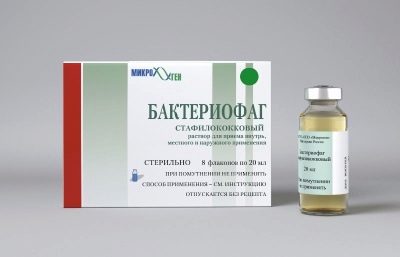
There are no alternatives to antibiotics for severe infections, unfortunately. But in mild and moderate conditions can be assigned staphylococcal bacteriophages. A bacteriophage is a virus that absorbs a pathogen. Sometimes these drugs are prescribed in conjunction with antibiotics.
Bacteriophages are applied externally in the form of compresses and lotions, for treating wounds, as well as inside - with internal inflammatory processes. They are dripping into the nose with rhinitis, into the ears with purulent otitis, and they irrigate the baby’s neck with a staphylococcal infection. Only in Russia can the doctor prescribe a bacteriophage to the child separately from the antibiotic. Nowhere in the world are bacteriophages treated as an independent method of treating a bacterial infection. In world practice, they are usually prescribed in combination with antibiotics.
If necessary, in stationary conditions, the child will be prescribed a treatment that increases immunity. It may be immunomodulatory drugs. But their purpose is not a mandatory practice, but rather the personal opinion of a particular doctor. There are still heated debates about the appropriateness of the use of immunomodulators in early childhood. If the decision on the use of such funds is made, then the child can enter antistaphylococcal plasma or immunoglobulins.
This concludes the main therapeutic program and begins an additional, but equally important, symptomatic treatment:
- With enterocolitis or gastroenteritis – «Enterofuril", Drinking heavily,"Regidron" or "Smecta»To compensate for the water-salt balance, which is disturbed by vomiting and diarrhea. At the time of illness, the diet does not change if the child is fed naturally. Babies who eat adapted mixes are advised to slightly lower the concentration of the mixes by adding a little less dry matter than expected - this will reduce the load on the digestive organs.
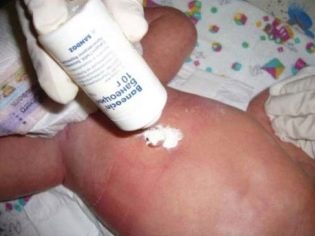
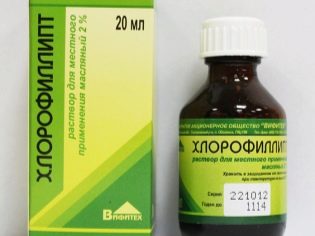
- For any skin manifestations - local treatments with antiseptics and antibiotic solutions. The umbilical wound, bursting blisters can be treated with hydrogen peroxide. According to parents, good results gives the drug "Chlorophyllipt." No alcohol-containing liquids for newborns and infants can never be used.
- Respiratory lesions are shown drops with antibiotics in the nose (in the ear), as well as aspiration of the nasal passages of the infant with the help of an aspirator, since nodules of nasal mucus in the crumbs that still cannot blow their nose are a fertile environment for the development of new colonies of staphylococcus. Additionally, vasoconstrictor nasal drops and “chlorophyllipt” can be prescribed.
- Staphylococcal tonsillitis will require parents to carry out procedures for irrigation of the throat and tonsils with an antiseptic "Miramistin"," Chlorophyllipt ", as well as lubrication with balsam"Viniline».
Surgical measures
Surgical treatment of a staphylococcal infection is required when the baby has deep furuncles, phlegmon, abscesses. In addition, surgery may be required for purulent tonsillitis, with lung abscess and pustular lesions of other internal organs.
The essence of the intervention is in instrumental dissection of purulent formation and thorough cleaning of the cavity from pus, necrotic modified tissues. The contents of the abscess are sent to the laboratory for analysis, and local treatments with antiseptics, dressings, local bacteriophages, and antibiotics are administered systemically (by mouth) to the child.
Since Staphylococcus aureus is afraid of "Zelenka", it is often recommended to treat the wound after surgery with this solution.
General recommendations for treatment
Walking with a child at a high temperature is impossible, bathing should also be postponed. After the fever subsides (usually this happens 2-3 days after the start of antibiotic use), you can walk and bathe. Should remember that a child with acute staph infections is contagious to otherstherefore, it is important to limit its contact with other children or pregnant women who live together with a sick baby.
Eating a child (this applies to babies who have already switched to complementary foods) should be light, especially carefully approach the diet for intestinal lesions. Diet and drinking mode will tell the doctor depending on the specific diagnosis.
The acute period of infection is always very dangerous, since infants have a high risk of developing febrile seizures and dehydration due to high fever and intoxication.
Reduce the risks will help plentiful drinking regime. The baby should be watered often, the water should be warm, but not hot. If the temperature of the liquid is equal to the body temperature of the patient, then the absorption of the liquid proceeds much faster.
Prevention
The spread of a staph infection directly depends on how quickly new facts of the disease are detected and how correctly and promptly doctors begin treatment. For this reason, it is not necessary to carry the child with suspicion of staphylococcus to the clinic for an examination by a doctor. Other children who will sit with you in the same queue are not to blame for anything and you should not infect them. It is more expedient to call the doctor on the house.
The baby should have its own towels, bedding, toys. The sharing of hygiene items by two or more children is unacceptable. If someone in the family has signs of purulent disease, contact with the infant by that person should be temporarily stopped. If the mother has cracks on the nipples, it is worth taking early measures to eliminate them, because staphylococcus is very often transmitted to the baby with mother's milk precisely because of cracks in the nipples.
Big parental mistake to give the child antibiotics at its discretion at every sneeze. This increases the risk of bacterial complications tenfold. Medical personnel of all medical institutions, especially maternity hospitals and children's hospitals, should regularly be tested for asymptomatic carriage of staphylococci.
It is important to understand that there is no universal way to protect a child from germs. This is not possible, next to a staphylococcus a person lives his whole life. In such conditions, the child’s immunity plays a role, only he is able to make sure that not a single staph is dangerous.
Therefore, advice to harden the baby from the very first weeks of his life, to feed properly and walk a lot is not an empty phrase, but the best ways to make the family only read about a staph infection without encountering it personally.
About what is staph in children and how to treat it, see the next video.