Symptoms and treatment of giardiasis in children
Mysterious creatures of Giardia and the ailment caused by them - giardiasis of all parents on hearing. And all because of all the parasites that can live in the human body, it is lamblia that are chosen as “extreme”. Even doctors with diplomas often blame them for the rash and diarrhea in a child, for poor sleep and poor academic performance at school. Is it really dangerous giardia in fact and how to treat giardiasis, we will tell in this article.
About the disease
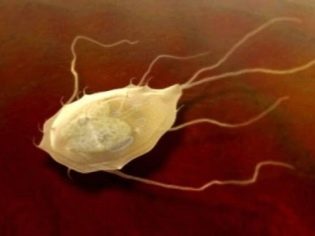
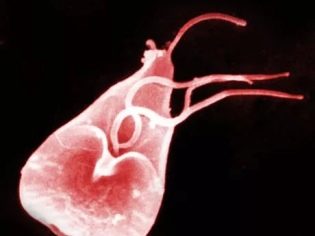
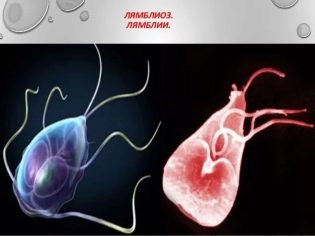
Giardiasis is a disease caused by the simplest microorganisms - Giardia. They resemble a jellyfish, have flagella and a suction disk, with which they can be attached to the walls of the small intestine. It is this section of the digestive tract that is the favorite place of Giardia, where they feel quite comfortable.
A rather cute (under a microscope) protozoa was discovered in the middle of the 19th century by a Czech doctor and researcher Dusan Lyambl. True, he did not immediately blame the organisms named after him for all the problems with human health, this was done by others and much later. The second international name of the disease is giardiasis or gairdiasis. The fact is that in Western countries, doctors categorically disagree with the fact that the discoverer of parasites was Czech Lyambl. They attribute the discovery to the French scientist Gyard, hence the international name of the diagnosis.
The World Health Organization claims that every year around 200 million people are infected with Giardia in the world, and more than 70% of them are children under 14 years old.
Giardia live in two states - they can be active and "sleeping". Fixed Giardia exists in the form of cysts. With the help of cysts, in fact, infection occurs, the transmission of the parasite. Motionless cysts, getting into a favorable environment for themselves - in the small intestine, "come to life" and begin to multiply.
If a child has a weakened immunity, if he has comorbidities, then the immunity will not have a quick reaction to new inhabitants of the small intestine. This allows Giardia to multiply by dividing at a rather rapid pace. These single-celled parasites are capable of doubling their numbers every 10-12 hours. However, the more Giardia, the less space for them, and individuals begin to fall into the large intestine.
In the large intestine, the conditions for the existence of lamblia are assessed as extreme, completely unsuitable for themselves, and therefore quickly turn back into motionless cysts and, in this form, come out with feces. In a dormant state Giardia can exist for more than three weeks in the soil, and the water even longer - about 5 weeks.
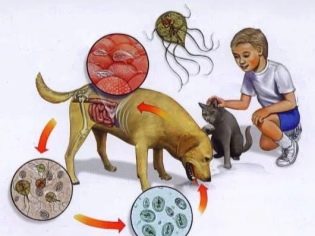
With water, vegetables and fruits, with unwashed hands, cysts penetrate into the body of another person, begin to multiply, come out in the form of cysts, and the circle closes.
The presence of Giardia in itself is not considered a disease. You can talk about giardiasis when the rapid reproduction of protozoa leads to certain changes in the children's body, because lamblia in the small intestine feed on the nutrients that are needed for the child, and, accordingly, the baby loses them. In addition, parasites excrete metabolic products, and this is also not useful for a child’s body.
At risk - children from a year to 4-5 years. It is at this age that the world is known not only in appearance, sound and smell, but also in taste, and therefore the spread of Giardia in a children's team is just a matter of time, and a small segment of it. Most negatively Giardia affect children with diseases of the stomach, especially with ailments accompanied by low acidity. At risk and children are vegetarians who are deficient in protein foods.
In the acute stage, giardiasis can be manifested by severe symptoms. But in chronic, if the infection occurs again and again or the treatment is not completed for the first time, the symptoms may not be. It is believed that the state of health of the child is deteriorating significantly, because the small parasites that are barely visible through the microscope operate around the clock and seven days a week.
Myths and truth about Giardia
It is difficult to say why, but of all the parasites, it was Giardia that was honored to be recognized almost as one of the main threats to humanity. These single-celled are well-studied, and therefore anyone interested in learning will be able to know enough about them.
Moreover, it is not clear why so many myths hover around lamblia and giardiasis, which, by the way, are actively supported by the medical workers themselves:
- "Giardia is very dangerous!". It is a myth. Even in the active vegetative stage, during the breeding season, the protozoa cannot be considered dangerous, since they do not carry any threat to the life of the child. The harm that Giardia inflicts on the child’s body is greatly exaggerated.
- "Your child has problems with the gall bladder, because he has Giardia!" This is not just a myth, but the real medical obscurantism. Nowhere, except for the small intestine, these protozoan parasites can not exist, and the bile environment for them is completely disastrous. Therefore, any problems with the digestive organs (cirrhosis, biliary dyskinesia, etc.) should not in any way be attempted to be explained by the presence of Giardia in the feces of a child.
- "If giardiasis is not treated, the child will have giardia in the liver and other organs.". This myth appears to be financially supported and warmed by manufacturers of pharmacological agents to combat parasites. And some doctors quite seriously say these words to the parents of their little patients.
As already mentioned, a suitable environment for living Giardia is an extremely small intestine. Neither in the liver, nor in the spleen, nor in the stomach can parasites survive.
- "Giardiasis can be treated with folk remedies". Broths of herbs, mashed onions and garlic and other recipes from the arsenal of alternative medicine in principle can affect Giardia, but such treatment will be long and ineffective, until the end to get rid of parasites will hardly. Therefore, it is better to resort to the course of treatment with traditional drugs, it will not take more than 5 days.
- “If you wash your hands often, you will not catch Giardia”. It is a myth. Hand washing is an excellent habit that protects a child from many pathogenic bacteria and some viruses, but it almost does not protect against lamblia. It’s enough for a baby to play in the sandbox in which the cat carrying the Giardia had sat before to bring microscopic cysts onto the shoes. And for infection enough only 10 individuals.
- "Because of Giardia, the child began to get sick more often with ARVI". It is not true. The presence of parasites in the small intestine does not affect the likelihood of being infected with a virus and has virtually no significant effect on the immune system.
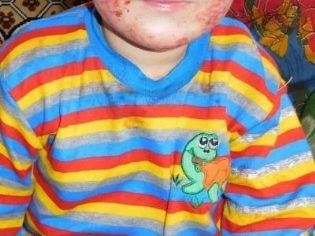
- "Giardia - a source of allergy". To cause an allergic reaction on the skin Giardia can not, because the products of their life are not strong toxins or allergens. Skin diseases, including those of allergic origin, should not be associated with giardiasis.
- "Giardiasis can be cured once and for all". This is a common misconception. Once with one batch of parasites can cope, the baby can get new, and on the same day.
- “Every fifth child has lamblia”. It's true. About 30% of the guys between the ages of 3 and 7, according to the test results, do have these parasites in their bodies. However, they have no complaints and pathologies, diseases with dire consequences. Parents will learn about lamblia only from the result of feces analysis. In this case, the lambliosis of the intestines is out of the question, because the presence of cysts is not yet a disease.
Symptomatology
The presence of cysts can not be felt in any way. The child does not complain and does not get sick. The fact that the development of pathology associated with the reproduction of Giardia begins can be said when the parasites begin to irritate the intestinal mucosa. This process may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- discomfort in the navel, in the upper abdomen, mild nagging pain, not characterized by sharp or pronounced nature, the sensations are not constant;
- loss or loss of appetite, change in taste preferences, feeling of mild nausea;
- the child’s tummy is often swollen; after a meal, a rumble can be heard;
- stool instability - diarrhea alternated with constipation and vice versa;
- prolonged diarrhea (several days);
- fecal masses have a yellow or yellowish color and uneven consistency, in some places there are blotches of mucus;
- general weakness, irritability, moodiness of the child;
- if a baby has previously been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, an exacerbation may begin;
- body temperature is usually normal, very rarely it rises to subfebrile values (37.0 - 37.9 degrees).
The most common symptom is weight loss. As we have already found out, Giardia sucks out from the small intestine many useful substances that get there with food. And if you consider that the child already has a reduced appetite, then the weight will really begin to change in a smaller direction. In children, there will be a slow weight gain or the weight will be in one place.
In acute giardiasis, if a very large number of cysts are immediately taken into the child’s body, a temperature rise up to 38.0 degrees can be observed, and all the above symptoms will be quite pronounced. Vomiting and severe headaches may occur.
Diagnostics
It is possible to establish the presence of lamblia cysts in the body of a child only by the results of fecal tests, the so-called scatological analysis. However, cysts are not always found in the material, since they do not always fall into the portion of feces that parents took for shipment to the laboratory. To get to the bottom of the truth (if you really want to get to it) you need to bring stool analysis to the clinic once a week for at least a month. Only then can lab assistants with a probability of up to 90% answer the question if a child has Giardia.
Often, pediatricians prescribe a direction for serological blood tests. To make it, the child must be raised early, not fed, and prepare for his protests, since blood is taken exclusively from a vein. To pass this analysis or not, it's only parents who decide since it is not considered informative in terms of the development of giardiasis. A certain amount of specific antibodies to Giardia in the blood when conducting a serological analysis can, in principle, be detected, but only at 3-4 weeks after infection. And since the fact of infection cannot be identified in time, a serological analysis cannot be considered a reliable diagnosis.
A rather unpleasant diagnostic method is duodenal examination. He can assign a child who is already 10 years old. During probing, the child will need to swallow a one and a half meter probe, which will take samples of bile. The method was previously widely used because medicine sincerely considered Giardia to be responsible for problems with the gallbladder and duodenum.
Numerous recent studies have shown the inconsistency of such a relationship, and therefore parents have the right to refuse agonizing diagnostic probing, even if the doctor insists on it. Surely the doctor is an adherent of the old fundamental medical school.
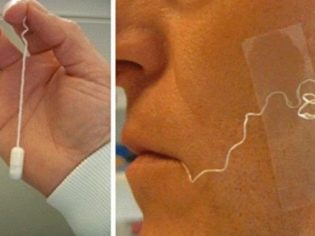
A simpler and more illustrative method is enterotest.
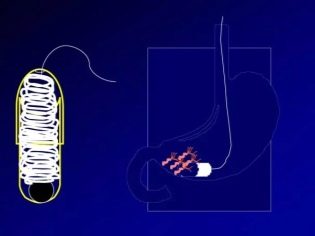
The child is given to drink a gelatin capsule. Inside the capsule is a nylon thread. It will be released after the capsule is dissolved in the stomach. The thread will pass through the small intestine, Giardia, if any, will adhere to it, after which it will be released with feces through the large intestine. Emptying is provoked by taking a laxative agent 2 hours after ingestion of the capsule.
Another method is biopsy of the small intestine. For analysis, a small fragment of the shell is taken; in it, the presence or absence of Giardia is microscopically determined. In addition to this fact, doctors can determine what changes caused the parasites in the small intestine. The procedure is quite time-consuming and expensive, it is prescribed very rarely, mainly when there is suspicion of a tumor in the small intestine. Giardia in this situation is found in parallel.
Treatment
Not every giardiasis needs special treatment. If the baby simply has lamblia cysts in the feces, this is by no means an indication to start taking medications for parasites. Doctors often choose waiting tactics. In most cases, when infected, cysts in the analyzes do exist, but there is no pronounced toxic effect on the body.
Immunity of the child "works" on this problem from the very penetration of Giardia in the small intestine. And with a high degree of probability he will be able to win a landslide victory over the parasite without outside help.
The World Health Organization gives very specific instructions for this case - you need to start treating giardiasis with medicines only when diarrhea has not stopped for 7-10 days. In this lamblia should be detected, confirmed.
In more complex cases, when prolonged diarrhea is not the only symptom, the doctor may prescribe a three-stage treatment regimen.
Elimination of intoxication and help immunity
At this stage, which usually lasts about 2-3 weeks, the child is recommended special food. In the child's menu include foods and dishes that "do not like" Giardia. These are various cereal porridges, vegetable oil, dried fruits and fresh vegetables, applesauce, dairy products - to improve intestinal motility. The better the intestines work, the more productive they are to empty, the more parasites will leave it. Under the ban - carbohydrates. They very well nourish Giardia, and therefore it is better to postpone high carbohydrate food for later.
To remove possible skin manifestations prescribe antihistamines in the age dosage. The best remedy for a child of the youngest age - 1 year, 2 years - “Suprastin". It is recommended to take pills. Bile preparations and enterosorbents may be prescribed as adjunctive therapy. As a choleretic, children over 5 years old are often prescribed a herbal preparation "Hofitol».
Antiparasitic therapy
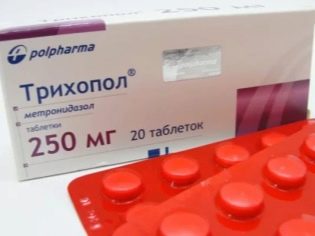
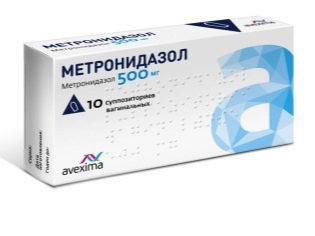
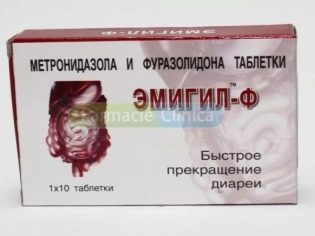
This is the main stage at which the doctor will choose the means to combat parasites. Modern drugs do not need to take weeks, in most cases, they have an effect after 3-5 days. When choosing a medicine, the doctor will draw the attention of the parents to drugs that have an effect on the simplest ones, to which lamblia are directly related. These drugs include «Trichopol», «Metronidazole», «Furazolidone"," Tiberal ","Macmiror».
A combination drug that contains both metronidazole and furazolidone is very popular. "Emigil-F". Children over 5 years old give it in pills, and babies under one year old - in suspension. Quite often, children with acute giardiasis are prescribed the drug. Nemozol. It is available in tablets only. The doctor calculates the age dose based on the child's weight. The average course of treatment is from 5 to 7 days.
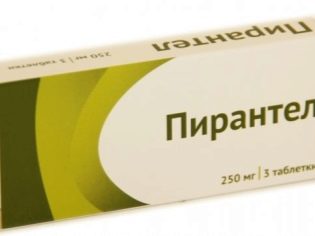
Some other known antihelmintic drugs, for example, Pyrantel with giardiasis are ineffective because they have a rather limited spectrum of action that does not apply to the simplest microorganisms.
These funds are prescribed courses in pills. If the situation is close to critical, and diarrhea in a child against giardiasis has lasted for more than 10 days, then “heavy artillery” can be used - drugs that need to be taken once, for example, Tinidazole.
At the same time with these drugs should continue taking anti-allergic agents and chelators. Of the enterosorbents in childhood allowed to use "Polysorb", "Smecta», «Enterosgel"," Polyphepan ". These tools are an effective defense against toxins, which produce dying individuals of parasites as a protective reflex.
Pinning results
The third stage repeats the first one in a lot, since it is intended to create conditions in the body in which it will be extremely uncomfortable for Giardia to settle in it again. Of course, to reduce such a risk to zero is impossible, because lamblia are widespread, but at least you can try. During the month, the child must adhere to special diets, which will include a large amount of fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as cereals, mashed potatoes, cottage cheese and kefir. The doctor will definitely advise one of the multivitamin complexes that is suitable for the child in age - the loss of vitamins caused by giardiasis needs to be compensated and replenished.
If the disease was accompanied by prolonged diarrhea, then at the final stage of therapy, probiotics and prebiotics are often prescribed. In some cases, children are shown enzyme preparations.
Efficiency
Drugs that form the basis of antiparasitic treatment, such as «Metronidazole», «Furazolidone» and all funds based on them gradually lose their effectiveness due to the fact that parasites appear, which are very resistant to the active substance of these drugs. Giardia, which have left the body at the stage of antiparasitic treatment, and not dead, but only become cysts, acquire such resistance.
The next time they cause infection, giardiasis will succumb to drug therapy is much more difficult. The modern pharmaceutical industry is working on this issue, and almost every year new drugs are on sale. Doctors are usually aware of new products, and they will promptly suggest another remedy for Giardia if “Metronidazole" It does not work.
To make treatment more effective, doctors recommend that all family members undergo it at the same time.
If parasites have been identified in a child and they have led to a disease, then adults and other children in the family should take medications prescribed to the baby. The dosage for each family member is determined by the doctor.
Sometimes there is a need for a second course of treatment. In order to make sure that all parasites have left the body, the child must, several times after the end of the first course, pass feces for analysis. Dispensary observation it is necessary for him for half a year, during this time it is desirable to make an analysis of feces for Giardia cysts at least three times.
Prevention
In terms of infection with giardiasis, every inhabitant of the planet is dangerous, since many adults are longtime carriers of Giardia. Children's immature immunity is poorly resistant to invasion, and therefore even a small number of cysts will be sufficient for infection. Prevention of this unpleasant disease is divided into two areas - personal prevention and public prevention.
All societies need to take into account that the main source of cysts is pets.
So that children do not play in the sandbox, next to which someone’s dog or cat went to the toilet, the owners of four-legged people just need to learn how to clean up after their pets what they usually leave in the courtyards. This measure alone could reduce the incidence of giardiasis by several orders of magnitude.
At the public level, it is desirable to control the state of reservoirs, to protect them from infection by parasites. In children's groups (schools and kindergartens) it is necessary to regularly conduct a scatological examination of all pupils and students in order to identify carriers of Giardia in time, who have no symptoms.
Individual measures for the prevention of giardiasis are hygienic. Wash hands a little, you still need to teach the child not to drag them into his mouth. Proper handwashing should last at least 30 seconds using baby soap. In the house where the child lives, as well as in the places where he is, there must be a merciless war with flies and cockroaches. These insects are the main carriers of lamblia cysts. The smaller flies and cockroaches in an apartment, the lower the risk of being infected with parasites.
Cysts can get into the body of a child with water, including drinking. Tap water is not the best option for baby drinking, given the fact that standard conventional water chlorination practically does not kill Giardia cysts.
It is not necessary to water the child and water from unknown and unverified sources - springs. There, in addition to Giardia, microorganisms are also more terrible.
Thus, the main prevention is to boil drinking water, to thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits bought in a store or on the market with a brush, and also to prevent children from trying to play other people's toys for playing, especially to drag them into their mouths.
About what is giardiasis and how to deal with it, Dr. E.O. Komarovsky will tell in the next video.