Furadonin for children
In the treatment of urological diseases, a drug called Furadonin is widely used. But is it possible to give children this medicine and how to use it correctly in childhood?
Composition
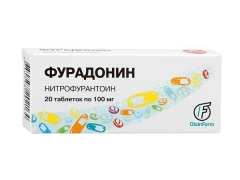
The active ingredient in Furadonine is nitrofurantoin, which in each tablet may contain 50 or 100 mg. Calcium stearate and silica, as well as potato starch, are medications.
Release form
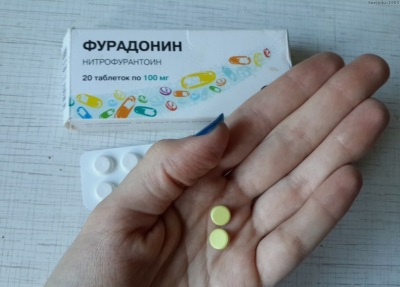
The drug is available in the form of round flat tablets with a greenish-yellow or yellow color. They are packaged in 10 pieces in cells of foil and polyvinyl chloride, and are sold in carton packs of 1-5 blister packs (10-50 tablets).
Operating principle
Furadonin is an antimicrobial agent, which is included in the group of nitrofurans. Its active substance penetrates into bacteria and disrupts their vital activity, blocking protein synthesis and reducing membrane permeability. The drug is especially effective in cystitis, which is caused by staphylococci, shigella, escherichia, streptococci, Proteus and other bacteria. About 30-50% of the drug in an unchanged state is excreted through the kidneys, providing an effect in the urinary tract.
At what age is it allowed to take?
Furadonin can be given to children older than one month. In the neonatal period, this medicine is not used. In the annotation to Furadonin, some manufacturers have a restriction in the use of such a drug up to 3 years of age, therefore prescription of medication at 2 years and younger children should be monitored by a doctor. Most often, the drug is prescribed at the age of 5 years, when a child can swallow a pill without any problems.

Indications
Furadonin is prescribed in children with infectious inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract, if they are triggered by microorganisms that are sensitive to its active substance.
This medicine is indicated for the development of a child:
- Cystitis
- Pyelonephritis.
- Urethritis.
- Pyelitis
- Pyelocystitis.
It can also be prescribed to prevent infections during urinary catheterization, cystoscopy, or any urological surgery, for example, if a child of 10 years old requires surgical treatment of ureteral reflux.
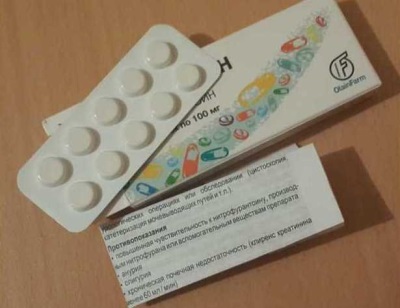
Contraindications
The use of furadonin is not recommended if the child:
- Renal failure began and the excretory function was significantly impaired.
- Identified oliguria.
- Heart failure detected (second or third stage).
- There is chronic liver inflammation or cirrhosis.
- The sensitivity to the components of the drug is increased.
- Revealed acute porphyria.
- Lack of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Age less than one month.
- Diagnosed with glomerulonephritis.
Adults do not prescribe medication during pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding, because the medicine will get into the body when the baby is fed.
Side effects
Furadonin often has a side effect on various organ systems of the child:
- The drug may cause shortness of breath and cough, as well as the appearance of chest pain. In some children, this medication provokes the occurrence of pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonitis or fibrosis. If a child has asthma, Furadonin can cause seizures.
- The digestive system may respond to Furadonin intake by nausea, abdominal discomfort or vomiting. Somewhat less pain, diarrhea or jaundice occurs. Occasionally, a child may develop hepatitis.
- Taking Furadonin may cause headaches, drowsiness, or dizziness. In children with hypovitaminosis, anemia, impaired water-salt balance, renal failure, or diabetes mellitus, this medicine causes peripheral neuropathy.
- The drug can adversely affect blood formation, provoking a decrease in the number of leukocytes due to granulocytes (sometimes until complete agranulocytosis), as well as thrombocytopenia. In addition, megaloblastic or hemolytic anemia can be a side effect of Furadonin. Note that such changes in blood are reversible and disappear after discontinuation of the drug.
- Dermatitis can occur as well as erythema from taking furadonin.
- The drug can cause allergies, for example, in the form of an itchy rash, urticaria or angioedema. In rare cases, an anaphylactic reaction is possible.
- Occasionally, after taking Furadonin, a child may experience fever, joint pain, and other flu-like symptoms.
- The use of such drugs can cause superinfection of the urinary tract (often due to the activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Instructions for use and dosage
The medicine is taken orally in a single dose prescribed by a doctor and washed down with a significant amount of water. Since the tablet is bitter, you should not chew it. For young children, a suspension is used, for the preparation of which the drug is dissolved in water, sweet juice or milk.
In children, the dosage of Furadonin is calculated on the basis of the baby’s body weight. For every kilogram of child's weight, from 5 to 7-8 mg of the drug is needed. Multiplying the weight of the selected dose, get a daily amount of Furadonin, which is divided into four doses. For example, the weight of a child at the age of 6 years old is 20 kg, when multiplied by 5, a daily dose of 100 mg is obtained, therefore we give the child 25 mg four times a day.
The duration of treatment with furadonin is 1 week. If after 7 days the doctor sees the need to extend therapy (evaluates urine analysis for sterility), the drug may be prescribed for another three days.
Overdose
If you exceed the dose of furadonin for a child, vomiting occurs. In such a situation, the baby needs to be given a lot of fluid so that the medicine is cleared more quickly with urine. In severe cases, dialysis is possible, which will quickly eliminate the effects of overdose.
Interaction with other drugs
- If antacids with magnesium trisilicate or nalidixic acid are given to the child at the same time as using furadonin, the antibacterial effect of the drug will decrease.
- The drug should not be given in conjunction with drugs of the fluoroquinolone group.
- A reduction in the antibacterial effect was also observed when coadministered Furadonine with drugs that block tubular secretion. This combination of drugs will reduce the concentration of the active substance in the urine, as well as increase its amount in the blood, because of which the drug for the child will be toxic.
Terms of sale
The medication is sold in pharmacies by prescription.
Storage conditions and shelf life
Packaging Furadonina should be stored in a place where children do not have access. It must be protected from direct sunlight and a dry place in which the temperature will not be above 25 degrees Celsius. The shelf life of the drug is indicated on the package and is 4 years from the date of issue.
Reviews
Parents of young patients who had to give Furadonin often respond positively to the medicine. They note that with cystitis, the drug eliminates unpleasant symptoms in a few days. A plus means is called its low price. As for the minuses, they include frequent side effects. According to parents, the children's body often reacts to the appearance of Furadonine nausea, dizziness, headaches, or vomiting.
Analogs
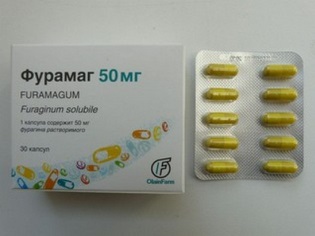
If the use of furadonin is impossible, it can be replaced with other drugs from the same group of drugs (nitrofurans).
A child can take: