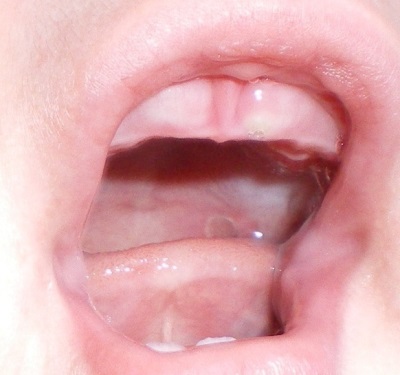
Symptoms and signs of teething in children
Before the parents had time to solve the problem with gas and colic, the time had come for cutting teeth. Rarely when a baby has each new tooth appears painlessly and easily, and mom finds out about it only when she sees it in the mouth of a toddler or hears a knock on the spoon. Many babies have a teething process restless and difficult. And for parents during this period it is important to learn to distinguish which symptoms relate to cutting teeth, and when you need to suspect the disease and show the baby to the doctor.

When do the first symptoms of eruption appear?
Parents can notice the signs of cutting teeth long before the baby's first milk teeth “hatch”, because before the new white tooth rises above the gums, it has a long way to go through bone tissue and gums. Symptoms usually appear about 2-4 weeks before the tooth crown cuts through the gum.
In some cases, for example, when fangs are cut, the teeth begin to disturb the child even earlier.
How much do your teeth bother?
The severity of teething signs for each child will be individual. Some babies tolerate cutting teeth more easily, stay awake and cheerful, others are naughty, often crying, do not sleep at night or have a fever. The first teeth (incisors) often appear without obvious symptoms, and teething with large crowns is often more painful for toddler, for example, when the first molars climb.
As for the change of teeth, falling out often does not bring the child much discomfort, and the molars of most children are painlessly cut.

The most common symptoms
Are common
For many babies with teething, a general malaise caused by severe stress in the child’s body is characteristic. During the eruption period, babies are lethargic and tired, their sleep can worsen, which also affects their parental sleep. Children often wake up at night with a loud cry, and sometimes refuse to bed at all, preferring to be always close to mom and dad.
For cutting teeth, such common symptoms as moodiness and irritability are not uncommon. In addition, most children tend to constantly nibble or suck on various objects ranging from toys to their fingers. Some children calm down with an orthodontic pacifier, others begin to bite her mother's breast. All these are signs of itchy gums that bother the little ones.
The most common sign that a baby tooth will soon appear in the baby can be called increased salivation. It is a response to irritation of the sensory nerves in the gums. Saliva is sometimes excreted in so large quantities that the baby’s clothing is constantly wet, and a rash may appear on the chest and chin.
The most unpleasant and uncomfortable common symptom that occurs during teething is pain. She is worried about the baby at the moment when the tooth is ready to cut through the gum to the surface. It is with pain that sleep and mood disorders of the child are associated.
The appetite of many babies with cutting teeth goes down, and some tots are generally refusing any food due to pronounced discomfort in the mouth. Because of this, weight gain in babies for a period of teething may be absent.
Separately, it is necessary to talk about the symptoms characteristic for the eruption of the upper canines. They are called "eye teeth" not only because of the anatomical position, but also because the appearance of this pair of teeth can be accompanied by symptoms resembling conjunctivitis. This is due to the proximity of the cranial nerves.
Local
Looking into the mouth of the baby, the mother can notice redness and swelling of the gums in the place where the tooth will soon erupt. When the crown of the tooth moves as close as possible to the surface of the gum, it will look like a white dot under the gum.
Controversial symptoms
This group of symptoms includes signs that may occur not only during the period of teething. These include:
- Runny nose It is usually small, and the discharge is colorless and watery. In addition, if it is associated with teething, then other symptoms of ARVI will be absent. Such a runny nose almost does not bother the baby and goes away on its own in a few days.
- Cough. Its appearance is caused by the accumulation of excess saliva in the throat. Such a cough manifests itself infrequently, is not accompanied by wheezing and breathing problems, and also quickly passes in a few days.
- Vomiting or diarrhea. The reason for the enhancement of the gag reflex and the slightly liquefied stool is the swallowed excess of saliva. If these symptoms appear, an intestinal infection should be excluded, the risk of which increases during teething increases due to weakened local immunity of the infant. In addition, the crumb pulls into the mouth various objects that are not always clean.
- Increased temperature. In most babies, it can rise to +37 or +37.5 degrees, so it is not knocked down. In some babies, the increase is more pronounced, and occasionally the temperature can reach 39-40 degrees. As a rule, the fever is observed in babies with cutting teeth for one to three days, and if the temperature lasts longer, it is more likely that the child is sick.
How to distinguish eruption from the disease?
When the crumbs teeth are cut, the risk of infection with various infectious agents increases. Often, during the period of teething, the baby may have an acute respiratory viral infection, stomatitis, intestinal infection or another illness. In order to respond to her appearance in time, parents should be vigilant and watch the baby:
- If the baby refuses to eat, the temperature of the child has risen, it is capricious, and sores develop in the mouth, these are signs of stomatitis and the baby needs to be shown to the doctor as soon as possible.
- If parents looked into the mouth of a toddler with fever and a runny nose, and noticed a reddened throat, then, most likely, the symptoms are not associated with cutting teeth, but with SARS or a sore throat.
- If your baby has a loose stool, high fever, stomach pain is swollen and sore, you should immediately call a doctor to rule out an intestinal infection.
When to consult a doctor?
Consultation with a pediatrician and sometimes a pediatric dentist is needed if:
- The child is already one year old, and not a single baby tooth has yet appeared.
- The teeth of the crumbs are cut in a modified order.
- The temperature has risen significantly or does not fall for more than three days.
- The child has severe diarrhea or repeated vomiting.
- The child is hard to swallow and he refuses to eat.
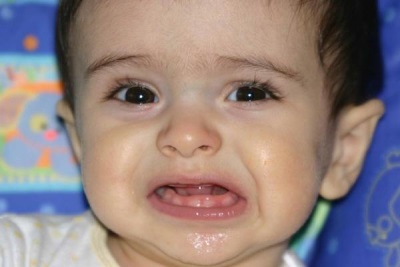
How to facilitate the process of eruption?
To help babies with painful teeth, use:
- Teethers So called toys that a child can safely nibbling and scratching their itchy gums. Inside such toys there is usually a filler in the form of water or gel. After being placed in the refrigerator, the filler cools, and when the child starts to nibble a cool teether, this partially relieves the discomfort in the gums.
- Massage. Mom can regularly massage the gums of a karapuz with a finger wrapped in gauze soaked in water or a silicone brush for the first teeth.
- Gels Kamistad, Dentinox, Doctor Baby, Calgel other. Such drugs have local anesthetic and anti-inflammatory effects, so their use helps to make the process of teething of milk teeth less painful for the crumbs.
- Antipyretic drugs. They are given when the temperature rises above +38 degrees, as well as at lower rates for babies with diseases of the nervous system or a tendency to seizures. Most often, children are prescribed paracetamol preparations, which are found in the form of a sweet syrup, as well as in the form of rectal suppositories. Instead of paracetamol, ibuprofen is used in some cases.
In the next video you can see how to help your baby survive the difficult period of teething and relieve pain.
Tips
- Saliva that comes out of the baby’s mouth with incisive teeth should be wiped regularly with a soft cloth to prevent rashes and irritation.
- Do not try to eat baby with his spoon. It is also unacceptable to lick the toddler nipple.
- Do not give your child any medication without consulting a doctor.
- Take care of the first teeth, using special fingertips and baby brushes to clean them. Pasta for the child should be chosen according to his age.
- In the diet of the crumbs should be enough products containing calcium, and the excess sweets should be limited. In addition, do not give the child before bed sweet drinks.
For more information about teething, see Dr. Komarovsky’s program.