What is cervical insufficiency during pregnancy and how to treat it?
Cervical insufficiency is a common cause of losing a baby during pregnancy. Especially often due to this pathology occur miscarriages in the middle of the gestational period.
At the end of the term of carrying a baby, the ICN often leads to premature birth. What is this pathology and what methods of correction during pregnancy exist, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
The cervix performs an important function - it inhibits the developing baby inside the uterus. The cervical canal located inside the cervix is filled immediately after fertilization. thick mucus-stopper, which does not allow penetration of infections and viruses to the baby.
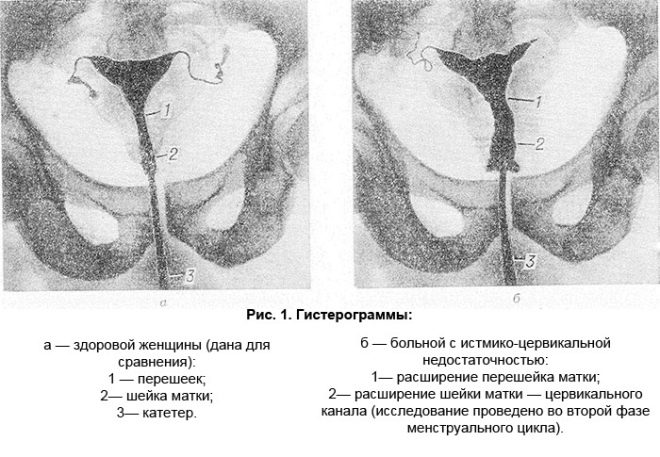
If the cervix does not fully cope with the goals set for it, they are talking about isthmic-cervical insufficiency. With it, the neck is simply not able to withstand the pressure of growing crumbs and amniotic fluid, as a result of which miscarriages and early births can occur, and during full-term pregnancy, births with ICNs can be dangerous and swift.
The neck itself in a state of deficiency shortens, softens. Normally, the process of shortening and smoothing begins just before the birth. With isthmic-cervical insufficiency, shortening occurs much earlier. Internal pharynx expands. There is a threat of falling out of the uterus of the parts of the fetal membranes and the subsequent death of the baby.
According to obstetrician-gynecologists, the pathological condition occurs in approximately 2-3% of all pregnancies. Every third woman with ICN has preterm labor. Every second death of a child in the late period of gestation is caused by this very reason.
Causes
There are three large groups of causes that can lead to pathology of the cervix and isthmus.
Congenital factors
This is the rarest reason. Infantile development of the genital organs, the uterus and its cervix is not as common. Often, sexual infantilism is combined with other congenital anomalies and defects, such as Down syndrome, for example.
Functional factors
If the tissues of the cervix are in the wrong balance between the connective and muscle fibers, if they inadequately respond to hormonal stimulation, then the functions of the cervix are impaired. This can happen to a woman whose ovaries are depleted, the functions of the sex glands are reduced, and the content of male sex hormones, such as testosterone, is increased in the blood.
If a woman was prepared for conception by stimulating ovulation with gonadotropic hormones, then she can have elevated hormone relaxin. Under his action, the musculature of the main reproductive female organ relaxes. The same relaxing hormone is also exceeded in a woman who carries several babies at the same time under her heart.
Gynecological diseases
Often the cause of cervical failure lies in gynecological diseases that have not been treated for a long time and which have passed into the chronic stage.
The risk of functional CI increases in women who decide to become mothers after 30 years, women who have extra pounds or are obese, as well as women who have become pregnant through in vitro fertilization.
Organic factors
This is the most common cause of cervical insolvency in the period of gestation of the baby. It may be associated with injuries that the cervix underwent earlier.
This usually happens in the birth process if the lady produced a large child, twins or triplets in a natural way, and the birth was difficult. Former ruptures can not affect the health of the cervix during the subsequent pregnancy.
If the previous pregnancy was accompanied by high water, if the birth process was rapid, if the placenta had to be separated manually, all this also increases the risk of injury to the cervix and the occurrence of subsequent isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
All operations that were performed with mechanical expansion of the cervix, affect its subsequent state. Such operations include abortion, curettage, including diagnostic, as well as neck surgery.
Symptoms and signs
The pathology has no expressed symptoms. Pregnant women often do not realize that they have a weak neck, there are pathological changes and there is a serious danger of miscarriage. No discomfort for the ICE patients delivers.
Infrequently, at the very beginning of gestation, some symptoms of the threat of miscarriage may appear - poor abnormal blood or bloody daub of the vagina, slight pulling sensations in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region.
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to diagnose cervical insufficiency, since it has no obvious symptoms. The doctor may suspect that something was wrong during a gynecological examination, but it is rarely performed for pregnant women. Basically only when registering.
However, if a woman is in the risk group for the likelihood of developing a CNI, examinations can be performed more often. On the gynecological chair using obstetric mirrors and normal palpation, the doctor can determine only the consistency of the neck, see the condition of the external os and the condition of the cervical canal - it is closed or ajar. This information is extremely small for making an appropriate diagnosis.
At the very beginning of pregnancy, women are prescribed colposcopy, with this study using a special device - a colposcope - it is possible to obtain more information about the cervical canal and the structure of the cervical tissues. According to the results of the passage of this survey may appear suspicions of weakness of the neck.
Ultrasound diagnosis helps to clarify the situation. Ultrasound allows you to measure the length of the cervix, compare it with normal average values and confirm or deny the presence of ICN.
It is reasonable to carry out measurements of such a parameter as neck length after 20 weeks, because by this time this indicator becomes important for diagnosis.
The length of the cervix during pregnancy - norms and fluctuations within the norms:
Gestational age (weeks) | Average length, mm | Length of primiparous, mm | Length of multiparous, mm | Limits of the norm, mm | Allowable vibrations, mm |
10-14 | 35,4 | 35,3 | 35,6 | 28-45 | 5,1 |
15-19 | 36,2 | 36,5 | 36,7 | 30-48 | 5,3 |
20-24 | 40,3 | 40,4 | 40,1 | 32-48 | 4,5 |
25-29 | 41 | 40,9 | 42,3 | 34-49 | 4,3 |
30-34 | 36,4 | 35,8 | 36,3 | 34-43 | 3,7 |
35-40 | 28,6 | 28,1 | 28,4 | 20-37 | 4,5 |
Ultrasound is done internally, intravaginally. This is the only way to find out the answer to the main question - what is the state of the internal cervix of the cervix. If it begins to open, then the uterus on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner acquires a characteristic V-shaped view.
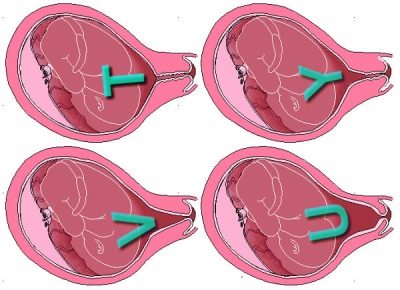
In this case, it is important to diagnose such a thing as bladder prolapse. A bubble may bulge out to varying degrees, and an assessment of the real threat to pregnancy and prognoses will depend on it.
- If the fetal bladder is located above the internal pharynx, this is considered the most favorable according to forecasts. the first degree of threat.
- If the bubble is already at the level of the inner throat, talk about ICN 2 degrees,.
- If the bladder is already partially bulging into the cervical lumen - o ICN 3 degrees.
- The heaviest is the fourth with her, the prolapse of the fetal bladder is already in the vagina.
When making a diagnosis, the obstetric history of this future mother is taken into account - how many births and abortions were, how they went, whether there were complications, what chronic diseases of the gynecological plan she has. Special attention will be paid to the facts of habitual miscarriage, if each pregnancy was interrupted before it preceded.
If pregnant women who are not at risk of developing isthmic-cervical insufficiency, studies of the cervix by exposure to ultrasound waves are conducted simultaneously with prenatal screening at the beginning of pregnancy, in the middle and in the third trimester, then women with ICN or prerequisites for the occurrence of such failure will have to visit the ultrasound cabinet a little more often.
Danger and complications
The main and most dangerous complication of cervical failure is the loss of a long-awaited crumb in any gestation week. Miscarriage or premature birth in this case develop rapidly, quickly.
Quite often, it all starts with the discharge of amniotic fluid, and it can be either full or partial. Abundant watery discharge may indicate water leakage.
Often, cervical insufficiency leads to infection of the fetus inside the mother's womb, because the cervical canal, normally tightly closed, is ajar, and there are practically no barriers to pathogenic bacteria and viruses. Intrauterine infection is dangerous for the development of the baby, it can lead to the birth of a child with severe pathologies, diseases, as well as the death of a child before birth.
Treatment
The treatment regimen depends on the degree and characteristics of cervical insufficiency in a particular woman. In some cases, it is possible to get along with drug therapy, often having to resort to surgical correction.
Surgical correction methods
It helps to impose a baby before the prescribed time by stitching the cervix. The operation is strongly recommended to women suffering from chronic miscarriage in both early and late periods, as well as with premature shortening of the cervix.
The operation is contraindicated if the expectant mother has chronic gynecological diseases, profuse bleeding, if the uterus is in a state of increased tone and cannot be removed with medicines.
Impose stitches on the cervix taken for a period of 14-15 weeks to 20-22 weeks. Overlay after 22 weeks is considered inappropriate. The child grows quickly, the walls of the uterus are stretched, the closure can end up with the cutting of sutures and tearing of tissues.
The method of operation is quite simple. Manipulations are performed under general or epidural anesthesia. The anesthesiologist selects the dosage of drugs for drug sleep and anesthesia, taking into account the patient's “interesting situation” in order not to harm the baby. Stitches can be on the outer or inner mouth.
Before surgery, a woman should be thoroughly examined for infections, if necessary, treatment of an existing infection is carried out.
Only being sure that there is no inflammation in the uterus, surgeons will begin to close the cervix.
After removal of stitches, and this happens at a period of 36-37 weeks or earlier, if the situation requires it, childbirth can begin within a short time. The neck can be badly affected if the birth has already started and the seams have not yet been removed. therefore it is recommended that women go to the hospital for obstetric facilities with sutures on the neck in advance.
Conservative treatment
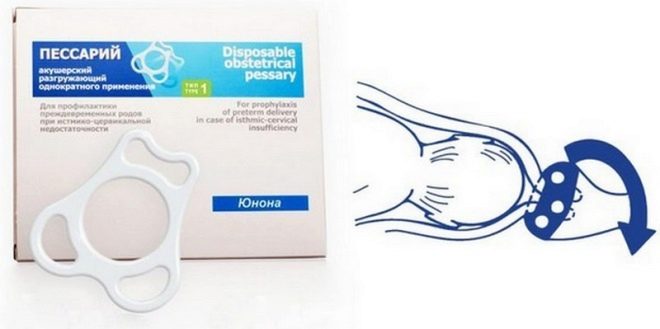
One of the most common ways to correct cervical insufficiency is to install obstetric pessary. This method is widely used when a woman has functional deficiency from 14–15 weeks to 32–34 weeks of gestation.
A pessary is a rubber or latex ring that is put on the neck in such a way that its edges abut against the walls of the vagina. This allows you to keep the cervix in a stable position, and the load on it, which has a growing in the uterus baby is significantly reduced.
The pessary is not imposed if the cervical canal is slightly open. In this case, stitches are imposed, and as a supplement to the surgical method, a pessary can also be used.
The pessary, as well as the stitches, is removed before delivery in the hospital. In pregnant women, the question often arises whether the cervix can lengthen after applying a pessary. Elongation as this does not occur, but the risk of abortion after the installation of the fixing ring is significantly reduced.
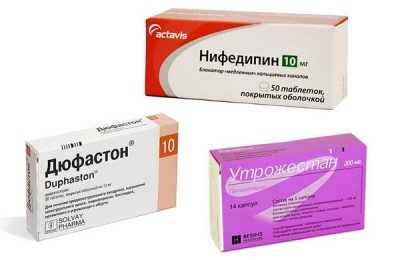
Conservative treatment also includes medication. At the initial stage, a woman with diagnosed cervical failure is treated with antibiotics and "Dexamethasone", Specific antibacterial drugs selects a doctor. This helps to reduce the likelihood of intrauterine infection of the baby.
Drugs that relieve the tone of the uterine muscles help reduce the pressure inside the uterus. For this purpose, women are prescribed "No-shpu", "Papaverine». If these drugs in tablets, injections or suppositories did not help, a woman may be prescribed "Nifedipine."
For the prevention of miscarriage, hormone therapy is used - "Duphaston", "Utrozhestan" in individual dosage and on an individual scheme, sometimes up to 34 weeks of pregnancy.
Take medications prescribed by a doctor should be strictly, without disturbing the dose and frequency, without missing a regular dose.
Prevention
Planning of pregnancy is considered the best prevention of cervical insufficiency. If you turn to a gynecologist not on the fact of pregnancy, but even before its occurrence, with high probability the doctor will be able to tell whether the woman is threatened with pathological cervical dysfunction.
The doctor inserts a special dilator into the neck and measures the width of the internal os. This is desirable to do on the 19-20 day of the cycle.
If there are no problems, then the internal pharynx has normal sizes (within 2.5 mm). If there is an abnormal expansion, this number will be exceeded. The most unfavorable size of the internal pharynx is more than 6-7 mm.
A woman who wants to properly communicate and give birth to a baby on time should not have abortions and scraping without the urgent medical need. To do this, with the onset of sexual activity, take a responsible approach to contraceptive issues.
All gynecological diseases need to be examined and treated in time, not “starting up” to a chronic condition.
Clinical guidelines
Women who are diagnosed with cervical insufficiency usually take them by surprise, it is recommended to seek help from a psychologist who accepts every female consultation. This specialist will be able to give them the right attitude and will explain that this diagnosis is not a sentence, and in most cases such pregnancies end quite safely with the birth of a healthy baby.
The psychological attitude of the pregnant is of great importance in the treatment, because stresses affect hormonal background, increase the tone of the uterine musclesthat makes it difficult for doctors.
Physical activity should also be reduced up to their full restriction - in case of a serious threat, bed rest helps.Women with less danger are prohibited from long walks, as well as the rise of everything that is heavier than 2 kilograms.
The longer the period of pregnancy, the more attention should be paid to a woman in her position in space. You can not sit or stand for a long time, it increases the pressure in the uterus, and the load on the cervix increases significantly.
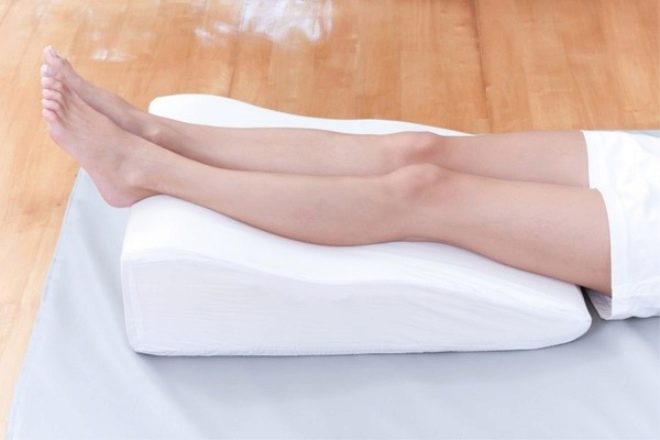
To lie to a woman should also be correct - on the back and legs slightly raised. To do this, under them you can put a small pillow or roller, this will help reduce uterine pressure.
From 24-26 weeks of pregnancy, weekly monitoring of the condition of the cervix is needed. After 30-31 weeks, a woman may be shown prophylactic hospitalization, since a large number of preterm births occur during this period.
At 37 weeks, it is necessary to go to the hospital in advance, since the birth at ICN often passes rapidly. Without constant monitoring of the future mother can come very negative consequences.
A woman with cervical failure should not make love.
If you experience pain in the abdomen, atypical discharge, you should immediately consult a doctor. This does not mean that preterm labor or miscarriage has begun, but in this matter it is always better to be safe.
Reviews
Most of the women who left their reviews and stories about overcoming cervical insufficiency during pregnancy in the maternity forums note that the doctors' efforts were crowned with success, and the baby was saved and communicated to the proper time. With repeated pregnancy, the situation with cervical insufficiency usually recurs, but a woman who is already ready for anything knows exactly the importance of diagnostic examinations and agrees to unconditionally take all prescribed medications.
Positive feedback was given on both the pessary and the suturing operation. In both cases, women diagnosed with cervical failure after 18 weeks were able to carry the babies up to 37-39 weeks.
In the next video you will hear the story of a difficult pregnancy, as well as learn about what is ICN.