Intrauterine infections: from causes to effects
Often, hearing about intrauterine infection, parents can hardly imagine what it is about. If a pregnant woman has the flu, is it an infection or not? And if there is a thrush - can a baby be infected? This article will discuss intrauterine infections of the fetus and how to avoid them.
What it is?
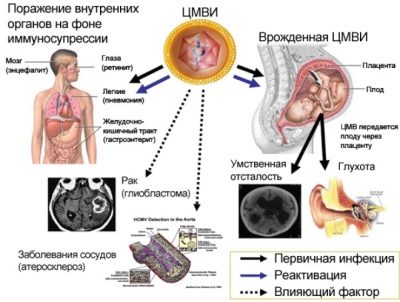
Intrauterine infections are called a fairly large group of ailments of the fetus and the newly born crumbs. Such infections become possible as a result of infecting a child during pregnancy (during his intrauterine stay), as well as during childbirth. Such infection can cause the death of the baby before birth, as well as the lag of the baby in development. The presence of intrauterine infection in women increases the likelihood of miscarriage and premature birth. Great risks anomalies and malformations of the child’s formation, damage to its organs and systems, especially nervous ones.
Viral agents, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, and sometimes some parasites can cause fetal disease in the womb and during birth. The transmission path is always vertical, i.e. the disease goes from mother to baby. It is difficult to say how often such infections occur, there are no more or less reliable statistics, however, according to the World Health Organization, every tenth newborn baby has been exposed to intrauterine infection.
In a quarter of infant deaths in Russia, intrauterine infections are “guilty”. They also cause anomalies and gross flaws in about 80% of toddlers born with certain deviations. Among the children who died before they reach the age of one, with congenital anomalies of development, in about 30% of cases the main cause of the tragedy also lies in the intrauterine infection.
What kind of infections are we talking about? It is usually in TORCH infections (TORCH). This reduction was introduced in 1971 by experts from the World Health Organization:
- T - toxoplasmosis;
- O - mycoplasma, syphilis, hepatitis, streptococcal infection (streptococci), candida and other viral and bacterial infections;
- R - rubella;
- C, cytomegalovirus;
- H - herpes.
Moreover, all infectious pathogens are divided into separate groups:
- viruses: rubella (rubella), cytomegalovirus, herpetic viruses, viral hepatitis;
- bacteria: syphilis, listeriosis, tuberculosis, sexually transmitted diseases, sepsis;
- parasites: toxoplasmosis and some others;
- fungi: Candida and others;
- co-infections caused by several different pathogens.
Causes, ways and mechanisms of transmission
These infectious diseases develop in the fetus in case of infection from the mother before birth or during the process of delivery. Almost always the source of infection is a woman. Before birth, a baby can become infected through the blood circulating in the mother-placenta-fetus system through infected amniotic waters. In the process of birth - by contact and aspiration. Infectious infection can also affect the baby with the prescribed invasive prenatal diagnosis: during cordocentesis, amniocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy, as well as during procedures involving the introduction of blood plasma and other drugs to the baby through the umbilical cord.
In the birth process, infection occurs due to the presence of infection in the mother's birth canal.The placenta is created by nature not only for food, but also to protect the child from viruses, bacteria, fungi. And for most pathogens, placenta is indeed an insurmountable barrier. But only if the “children's place” is not damaged, it functions normally.
If fetoplacental insufficiency is diagnosed in a woman, then infection of the child is not at all excluded.
At risk include pregnant women who have problems with women's health, for example, colpitis, endocervicitis or sexually transmitted diseases. The likelihood that a child will become infected with an intrauterine infection increases if the woman has a diagnosed miscarriage threat, preeclampsia, if she, already in an interesting position, suffered in acute form the above infections. Premature babies are at a greater risk of becoming infected intrauterinely.
If a child becomes infected at the stage of organogenesis during the first 2-3 months of pregnancy, the pregnancy usually ends in miscarriage, since many of the malformations are incompatible with life and further development. If the infection occurs before 12 weeks, then often this leads to the birth of a dead baby or a baby with severe defects. If the infection happens in the middle of the gestational period or in the final third trimester, then usually the lesion is limited to a single organ or the infection becomes generalized.
If a pregnant woman is seriously ill with a viral illness or a disease caused by pathogenic bacteria, this does not mean that the baby is seriously ill, and, conversely, a mild illness of the expectant mother does not guarantee that her baby has an intrauterine infection. The severity of the leakage may well not coincide.
Symptoms and signs
On the possible presence of intrauterine infection crumbs medical workers can already guess during the birth process. Opaque, turbid amniotic waters with meconium impurities will induce them to such an idea. Usually, the original feces of dark green color come out of the intestine of the fetus after birth, but when infected, defecation often occurs involuntarily while still in the womb, therefore the waters have a dark color and a very pronounced putrid odor.
The fact that the risk of infection is high is indicated by obstetricians and the characteristics of the “children's place”. The placenta with intrauterine infection has signs of plethora, there are microthrombi, areas of necrotic nature.
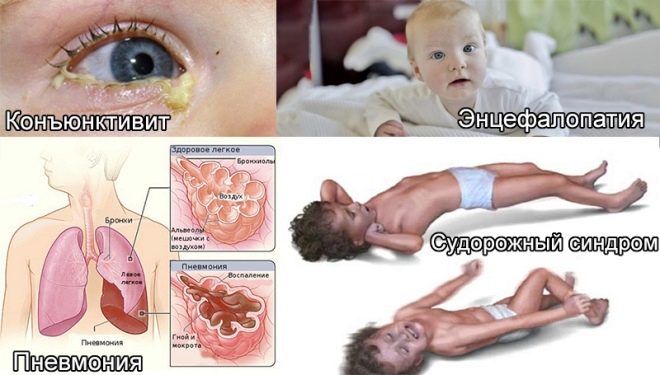
Many babies with intrauterine infection are born with asphyxia, they have less weight than necessary, there are signs of a hypotrophic physique. They have a slightly enlarged liver, some developmental abnormalities can be observed, sometimes microcephaly or hydrocephalus is observed at birth.
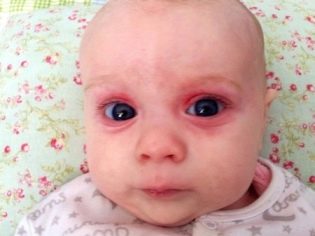
From the first hours of life, these babies have jaundice, there may be pustules on the skin, various eruptions in the form of roseol or vesicles, fever and fever, convulsions, breathing problems. From the first days, pneumonia, omphalitis, inflammation of the heart muscle can develop, the amount of hemoglobin in the child’s blood is reduced, the eyes are often affected by conjunctivitis or keratoconjunctivitis, multiple hemorrhages can occur on the skin - hemorrhagic syndrome. Examination in the maternity hospital can show congenital glaucoma, cataracts, heart and vascular defects, problems with the brain.
Newborn babies with intrauterine infections regularly burp, this is abundant, their muscles are weakened, there are signs of depression of the central nervous system, the skin has a grayish tint. These are common signs for all children with intrauterine infections. But each specific infection can have its own, distinctive clinical manifestations.
Toxoplasmosis - congenital form
If a child in the womb is affected by a unicellular parasite - Toxoplasma, then this leads to serious consequences, which are manifested in a significant developmental delay, malformations of the brain, organs of sight, heart and skeleton bones.
After a baby with congenital toxoplasmosis is born, he has fever, severe jaundice, edema, reddening of the skin by exanthema, hemorrhagic rash, loose stools, cramps, and inflammation of the heart muscle, kidney, lungs. Much depends on the time of infection. If it happened recently, and the child’s disease has a subacute course, then it is usually manifested by meningitis or encephalitis.
If the baby has become infected for a relatively long time, and the disease has become chronic, then hydrocephalus, a decrease in brain volume, is most often observed. Often children are born with a squint, complete or partial atrophy of the optic nerve.
The consequences of congenital toxoplasmosis can be oligophrenia, the development of epilepsy and blindness.
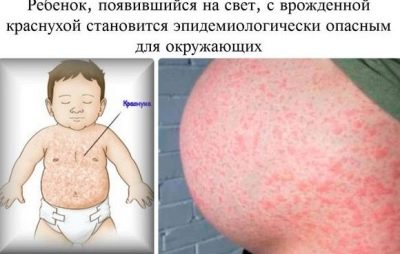
Rubella
A child can be born with this infectious disease when his mother fell ill with rubella during the period of gestation. You need to know that the risks that the child also gets infected are directly dependent on the specific period:
- on initial terms - risk is estimated at 85% or more;
- second trimester - probability is approximately 20%;
- in third - about 10%.
At any stage of childbearing a rubella can lead to abortion due to the death of the baby.
Babies who are lucky enough to survive in the womb with congenital rubella are born with low body mass, childbirth usually bear the status of premature. In the first hours they have a profuse hemorrhagic rash on the body, jaundice associated with the breakdown of red blood cells, it lasts a long time. As a rule, co-morbid infections are called a triad, because they are usually presented to one degree or another.
It can be:
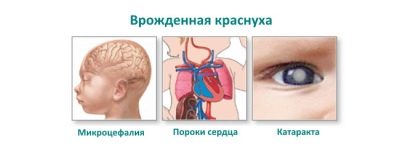
- abnormalities of the organs of vision: cataract, glaucoma or microophthalmia;
- heart damage: various defects, for example, open arterial duct or stenosis of the pulmonary artery;
- hearing abnormalities: congenital abnormalities of the auditory nerves and hair cells, congenital hearing loss or deafness.
If a woman has contracted rubella already for long periods, there may be no congenital heart disease, and the set of symptoms will be limited only to damage to the organs of sight and hearing.
These signs are basic. They are found in the vast majority of newborns with a congenital form of Rubella. But there are other symptoms that can be observed - for example, a decrease in brain volume, brain edema, cleft palate, skeletal bone malformations, abnormal development of the urinary organs and the reproductive system.
A child with such a congenital disease develops with a significant lag from his peers, while he is lagging behind both physically and mentally.
CMV infection (cytomegaly)
A child's disease in the womb with cytomegalovirus after birth is manifested by a lesion of a single or extensive abnormality of many organs. Causes this virus to pathological decrease in immunity, purulent and septic effects.
Cytomegalovirus is often the main cause of a decrease in the volume of a child’s brain, the development of retinopathy, and cataracts. Infection in the first trimester usually leads to the fact that children have heart defects and the vascular system. After birth, bilateral pneumonia and kidney damage usually develop. Suffer from this virus and nerves: visual and auditory. Therefore, the occurrence of blindness, deafness is not excluded.
Congenital herpes infection
Herpes viruses can affect the child’s body in different ways: a generalized infection develops in about half the cases, the nervous system suffers in every fifth case,skin and mucous membranes are affected in 20% of cases.
A child born to the world with a generalized form of herpes infection, usually experiencing significant problems with spontaneous breathing - the so-called distress syndrome is developing. Its condition is complicated by pneumonia, liver enlargement, and thrombocytopenia. With the defeat of nerve endings encephalitis and meningoencephalitis most often develops. When the skin form of the child is born with a profuse rash of the type of vesicles, with a rash affected are not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes, and internal organs. If a bacterial infection is added to this form, then sepsis usually develops.
Herpes viruses can cause a decrease in brain volume, blindness, hypoplasia of the extremities, and mental and psychomotor retardation.
Chlamydia - congenital form
Chlamydia infected mothers transmit to their children in about 45-50% of cases. Every fifth child born with chlamydia develops pneumonia, almost all have chlamydia eye damage. Infants are infected mainly during the passage through the birth canal at the time of their birth. And the first symptoms of infection appear as early as 1-2 weeks after delivery.
Every fourth child, doctors ascertain nasopharyngitis, every third - conjunctivitis, which can not be treated with any antibiotics, a small effect gives only tetracycline. In 15% of cases, pneumonia develops with a strong cough. Less commonly, the disease is manifested by gastroenteritis. In the 15% of cases, the urinary organs of the child are also affected - girls have vulvitis and urethritis in children of both sexes.
Mycoplasmosis
The child becomes infected with mycoplasma during childbirth. If mycoplasma is detected in a pregnant woman, treatment must necessarily be carried out after 16 weeks of time, which helps to reduce the incidence of infection in children.
Mycoplasmosis in newborns makes itself felt pneumonia, which develops very slowly. The child is pale, shortness of breath appears and increases gradually. About 15% of children in the first months of life from such pneumonia die.
Candidiasis - congenital form
Recognizing congenital candidiasis is the most difficult, because it often proceeds hidden, and the diagnosis can be made late. Most often, fungal lesions are found in babies who are in a hurry to be born prematurely, as well as in babies whose mothers suffered from diabetes during the gestation period, in the presence of candidiasis in the analyzes of the future mother.
Fungi can lead to a wide variety of lesions: skin, mucosal lesions, and a generalized candidal infection can be observed. Candida infection can be visceral, with fungal infections of the heart muscle, liver, and kidneys. The disease can flow easily and hard.
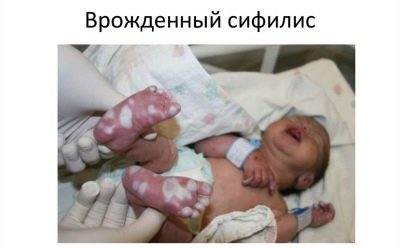
Congenital syphilis
The cause of the disease in a child who has just given birth is a similar disease in the mother while waiting for the baby. That is why all expectant mothers are carried out a threefold examination on the RV during the carrying of the baby.
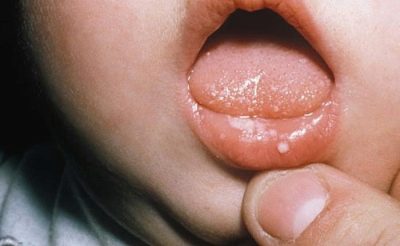
Signs of congenital syphilis in the toddler may not appear immediately, but during the first two years of life. Typically, the disease makes itself felt syphilitic rhinitis, pemphigus, osteoporosis and liver enlargement.
If during the pregnancy, the future mother was diagnosed with syphilis, then the baby is taken for analysis of umbilical cord blood immediately after birth. Congenital syphilis can be indicated by a placental pathologically enlarged and modified by its structure.
Diagnostics
Given the severity of the possible consequences of such infections for the baby, health workers are involved in identifying infectious diseases as soon as a woman “in position” comes to the hospital to get registered. TORCH-complex tests, smears from the vagina on the microflora, bakposiv carried out several times during the waiting period of the child, starting with the first trimester.
The doctor may suspect an intrauterine infection in a child at any time. In this case, the woman will be given a referral to the invasive diagnostic procedure. Cord blood of a fetus or a sample of amniotic fluid after an in vitro study (in vitro - "in vitro") will be able to give an exact answer to the question of whether the baby has an infection or not.
There are markers that are visible on ultrasound. Very often, intrauterine infection of the crumbs is accompanied by a change in the quantity of amniotic fluid to a greater or lesser side, therefore the question of a possible infection is necessarily raised in the case of low water or polyhydramnios. In the waters of the ultrasound is often found so-called suspension.
Premature maturation of the placenta, as well as edema of the fetus itself, which become apparent from the measurement of fetometry, indicates an infection in a child.
An experienced doctor of ultrasound diagnostics will definitely pay attention to the developmental abnormalities of some of the internal organs of the baby, to impaired blood flow in the umbilical cord, placenta. On CTG after 29-30 weeks of gestation, possible infectious illnesses of the fetus may indicate a change and deviation from the PSP standards.
After the baby is born, there will be much more opportunities for diagnostics at the disposal of health workers - this is the whole range of laboratory tests, both bacteriological and virological. The histology of placental tissues is considered to be a very informative method.
During the first day of a newborn with suspected intrauterine infection, a neurologist, a cardiologist, an ophthalmologist, must be examined by the auditory function on a third day along with the rest of the newborn.
Treatment
All babies born with intrauterine infections immediately begin to receive treatment. If the lesion is recorded viral, treatment with interferons, immunoglobulins is prescribed, and the child is given immunomodulators. Herpes viruses require the use of a special drug, which was developed against them - "Acyclovir". If the infection in a child is of a bacterial nature, antibiotic treatment is prescribed.
All these measures are designed to eliminate and neutralize the body, which is responsible for infection and all pathological processes. In addition to the main drug, prescribed and symptomatic treatment. And it depends on what specific symptoms of the toddler is accompanied by infection.
It is necessary to understand that some of the effects require surgical intervention, for example, congenital heart defects. And for children with deafness, cochlear implantation and other methods of correcting hearing impairment are indicated.
No doctor will be able to confidently answer the question, what are the predictions for a child who was born with an intrauterine infection.- it all depends on the nature of the disease, the degree of damage to the small organism, its own immunity, and even on the child’s desire to survive. But statistics show that in 80% of cases with a generalized congenital infection, the baby’s death occurs regardless of how well the maternity hospital and the children's department are technically equipped.
Medicine can easily cope with the lesions of individual organs, but a substantial correction of the CNS lesions practically does not exist. And then the predictions will depend on how disturbed the functioning of the brain is, how damaged the brain structures are.
Prevention
The main way to avoid intrauterine infection of the fetus is considered to be a detailed examination of a woman before pregnancy. It is necessary to determine in time, to identify all possible infections in a woman and her sexual partner, many diseases are easily and fairly quickly treated, the main thing is that this should be done before two stripes appear on the test, indicating that a new period is starting in the life of a couple - the waiting period baby
A woman who is planning a pregnancy, as well as having a child under her heart, should exclude communication and contact with infectious patients. The majority of infections in the body have recovered antibodies form that protect against reinfection, as happens with rubella and chickenpox. And if a woman who plans to become a mother, before such diseases did not hurt, she must be done 3-4 months before pregnancy appropriate vaccinations. This will help avoid infection while waiting for the baby.
After suffering an infectious disease in the first trimester, the doctor may offer an abortion for medical reasons. This is also one of the methods of prevention of intrauterine infectious diseases in children.
If it becomes clear that the infection of the child has occurred, which is confirmed by tests and invasive diagnostics, then the woman and her family should decide whether to terminate the pregnancy. Everyone has the right to both agree and refuse.
For information about which intrauterine infections are dangerous for women and for the future baby, see the following video.