Symptoms and treatment of symphysitis during pregnancy
No pregnant women are insured against symphysitis. This painful and dangerous condition can significantly complicate the last months of carrying a baby. In this material we will tell you how to recognize and how to treat the symphysitis in pregnancy.
What it is?
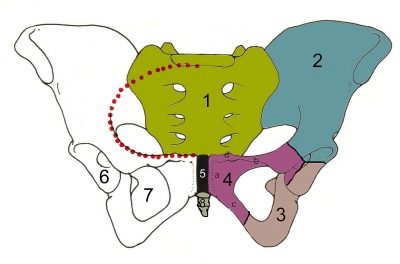
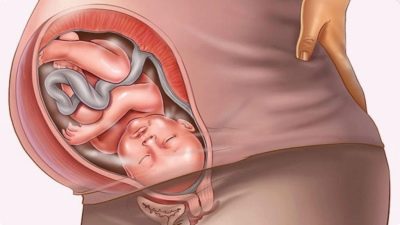
In both women and men, the pubic bones are connected by a small vertical symphysis. This connection lies right in the center, the bladder is located behind the symphysis, and the external genital organs are below. Normally, this connection is quite mobile, which is a fibro-cartilaginous disk with a slit-like fluid cavity inside.
The pelvic bones can be held firmly due to ligaments growing into the disc. The strongest of them - the top and bottom. Anterior and posterior ligaments somewhat weaker. The pubic articulation (the pubic symphysis) ensures the stability of the pelvic bones.
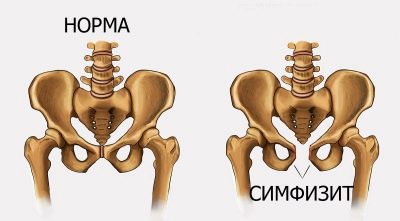
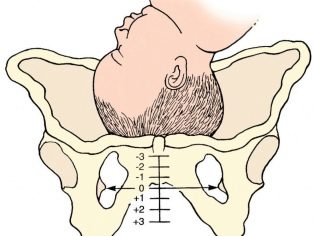
During pregnancy, the load on all the anatomical components of the pelvic zone is increased tenfold. Changes undergo ligaments, muscles, bones, including "gets" and symphysis. Nature has conceived so that the bones of the pelvis, which form the visual ring, should miss the head of the baby during childbirth. To make this possible, the symphysis softens and the pubic bones become more mobile. Sometimes during this process inflammation occurs, pelvic bones begin to disperse. It is this phenomenon that received the name symphysitis in medicine.
In varying degrees, new, not always pleasant sensations in the pubic bone area are visited by all pregnant women in the later periods. But not every future mom is diagnosed with symphysitis.
A disease is discussed when the divergence of the bones reaches certain values and is accompanied by inflammation.
Causes
As already mentioned, softening of the pubic symphysis is a natural process and necessary for the normal flow of labor. The expansion of the pelvis is the preparation of the female body for the upcoming important event - the birth of a new man. The main question is why for some women this process takes place without peculiarities, within the framework of the program established by nature, while for others it turns into a painful and dangerous state.
The true causes that lead to symphysitis, science and medicine today are not known for certain. But there are several versions that are still considered as probable prerequisites:
- First, it is calcium deficiency. In pregnant women, this mineral mainly goes to the structure of the bones of the child, many expectant mothers, especially in the second half of pregnancy, experience marked calcium deficiency.
- The second probable cause is excessive release of relaxin. This hormone, as the name implies, is designed to soften the bones, ligaments of the pelvis before childbirth. It is produced by the placenta, and also in some quantities - the ovaries of the expectant mother. If for a number of reasons the hormone is produced more than necessary, then the joints, ligaments and cartilages soften to a greater degree, which, combined with the load on the pelvis caused by the bearing of an already large child, produces such an unpleasant effect.
In the first half of pregnancy, the fetus is small, it does not exert strong pressure on the pelvic bones. However, the closer to childbirth, the greater its weight. The closer the date of delivery, the stronger the crumb pressed against the head to the exit of the small pelvis, therefore pressure on the pubic joint increases.
Risk group
About the likelihood of developing symphysitis woman can warn in advance. And all because most often the divergence of the pelvic bones with painful inflammation occurs in certain categories of pregnant women.
Long years of observation of future mothers allowed doctors to get an idea of the risk group. It includes:
- Women with diseases of the musculoskeletal system. These include both acquired diseases and hereditary pathologies - congenital bone weakness, increased bone fragility, and collagen deficiency.
- Women who give birth more than 2 times. The more births in history, the higher the likelihood of instability of the symphysis. Especially dangerous are situations in which the time between births is small - no more than three years.
- Women who have suffered pelvic injuries. Any fractures, dislocations, cracks in the pelvic region, if they occurred in the past, increase the chances of developing symphysitis. Often such injuries are inherent in ladies who are professionally engaged in athletics (run).
- Women who have had symphysitis in the past. If during the previous pregnancy the woman developed a similar pathology, the probability of relapse is almost 100%.
- Pregnant, leading a sedentary lifestyle. If the expectant mother does not physically stress herself and tries to lie down or sit more, avoids hiking, does not engage in gymnastics, then the symphysis in late periods is very likely.
- Future mothers who have a large or giant fruit. A large child is considered, whose estimated body weight at birth will be more than 4 kilograms. They call the giant a baby, which, according to preliminary estimates, will weigh more than 5 kilograms at birth.
If a woman falls into the risk group, this does not mean that the symphysis is bound to begin. You need a coincidence of risk factors, for example, carrying a large fetus against a background of calcium deficiency or a pelvic injury in the past against an increased production of relaxin.
Symptoms and signs
The symphysis is manifested by rather characteristic sensations, to determine which labor does not make up. It all begins with a pronounced pain syndrome. The further, the more pain. Women complain of pain in the pubic area. She becomes stronger at night when the woman relaxes, and is somewhat dulled during the day. With the progression of the disease pain syndrome begins to persist in the daytime.
The divergence of the pelvic bones leads to the appearance of pain in the lumbar and sacral areas. A woman may complain about the appearance of unpleasant painful sensations in the hip joints. Walking begins to be given with difficulty. The very “duck-like” gait appears, in which the woman clearly rolls from side to side when walking, and she also feels “clicks” in the pelvic joints during the step.
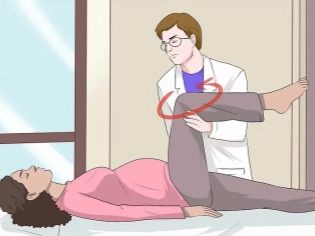
To diagnose a symphysis is possible by asking a woman to spread her legs to the side. When breeding pain in the pubic joint increases.
The most difficult for a woman with a symphysitis is to climb the stairs, bending forward. There is practically no opportunity to lift up straight legs from a supine position. All attempts to do this end with the occurrence of severe acute pain and a sense of limited movement. Pain can also occur during sex. Sometimes a woman has problems with defecation - it hurts to hurt, constipation occurs. Most expectant mothers with a symphysitis can get out of bed only from a side position in a few steps, independent lifting from a horizontal position on the back becomes impossible.
At the beginning of the inflammatory process in the pubic area, edema can be visualized. The more neglected the disease, the greater the swelling. With the divergence of the bones there is a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. Many of his future mothers take him for the threat of preterm birth and seek medical attention for this very reason.
The severity becomes more pronounced after a long stay in an upright position. If you lie down, it temporarily decreases somewhat.
Most often, the first symptoms of symphysitis manifest in the period 28-36 weeks and later. In some cases, the symptoms characteristic of this disease develops earlier than 28 weeks, but this is extremely rare. Also, the first symptoms of symphysitis can appear after childbirth, and then the appearance of the problem will be associated with injury to the symphysis joint during the passage through the birth canal of the baby.
More than 70% of future mothers are characterized by discomfort in the pubic area in the last 2-3 months of pregnancy, do not confuse them with the symphysitis. The true symphysitis differs from physiologically sound whining discomfort by the fact that there is a limited range of movement, pain becomes unbearable.
Types of disease and forms
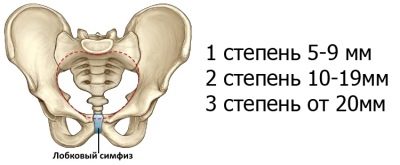
Problems with the divergence of the pelvic bone may be associated with pregnancy and the postpartum period. There are several degrees, which are determined by the magnitude of the discrepancy:
- The discrepancy from 5 to 9 mm allows to establish a symphysite of the first degree.
- The discrepancy from 10 to 19 mm is the basis for establishing a second-degree symphysitis.
- A discrepancy of 20 mm is the third degree of the symphysitis.
Danger and consequences
Symphysis for the child is absolutely not dangerous. To a greater extent, it threatens the health of a woman, because after childbirth she may remain disabled. If the discrepancy is less than 1 centimeter, the forecasts are most favorable, with such a symphysitis even natural childbirth is allowed. Symphysitis 1 degree - the easiest, and therefore easy to treat.
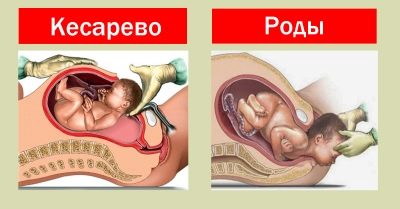
A discrepancy of more than 1 centimeter, which corresponds to degrees 2 and 3, does not cause such rosy forecasts of doctors. It all depends on how quickly this distance increases. Usually, a woman is recommended caesarean delivery.
Excessive divergence of the symphysis can lead to rupture of the ligaments, and this is considered a severe pathology of the musculoskeletal system. A woman who has survived a gap cannot stand, raise her legs, walk. She can get a disability.
A discrepancy of more than 5 centimeters is considered the most dangerous. In this case, in addition to injury to the pubic joint, the edges of the bones can injure the bladder, urethra. In the area of the hip joints, hemorrhage occurs. Later, it almost invariably leads to the development of arthritis.
A rupture may occur at the time of delivery if the cartilage disc is excessively depleted. It is for this reason that natural childbirth with a discrepancy of more than one centimeter (11 mm, 12 mm, and so on) is considered undesirable. Caesarean section avoids possible rupture of the symphysis.
The probability of rupture is influenced by the nature of the birth. With a violent and rapid delivery, the probability increases. Also, natural childbirth in a woman with a symphysitis who is pregnant with twins or triplets is considered to be risk factors for undesirable consequences. Such an anatomical feature as a narrow pelvis, is also a factor that provokes rupture of the heart.
Most often, the gap occurs gradually during childbirth, and you can guess that it happened at 2-3 days after the baby is born. The pain will increase, and the ability to move will disappear. Much less often the gap occurs suddenly, then the woman in the process of childbirth can hear the characteristic sound that accompanies ligament damage.
A woman after a break can not independently roll over on her side. She has access to the only posture in which she feels some relief - the so-called "Frog pose".
If bladder injury occurs, urine flow becomes difficult, edema and symptoms of intoxication appear.
Diagnostics
If a woman has characteristic symptoms and complaints, she should definitely consult a doctor.If a symphysitis is suspected, an examination is scheduled. The fact is that the magnitude of the divergence of the pubic joint is not always directly related to the intensity of pain. With a small discrepancy, a woman may experience a rather strong pain syndrome, and with a large discrepancy, the pain may be insignificant. That is why it is important to find out exactly what the discrepancy is and to what degree of the symphysite does it correspond.
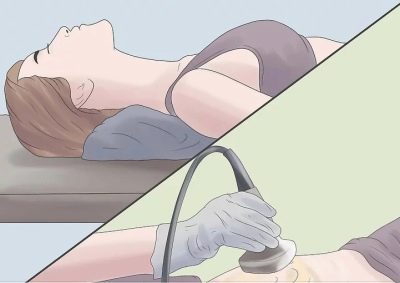
To do this, held Ultrasonography of the symphysis joint. Diagnosis is carried out by an external sensor, it allows you to measure the discrepancy and determine whether the expectant mother has signs of inflammation. After the examination, it is possible to choose further tactics of pregnancy management and choose the optimal and safe for the woman's health mode of delivery.
Significantly more diagnostic information can be given by methods such as radiography and MRI. But for pregnant women, for obvious reasons, they are not prescribed. Such diagnostic methods are widely used after childbirth, if the symptoms of the symphysitis do not disappear or there is a suspicion of an articular rupture.
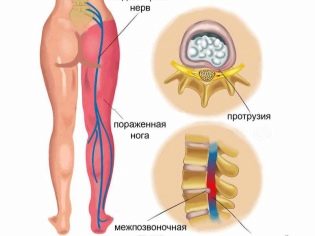
In the process of diagnosis in pregnant women It is important for the doctor to distinguish the symphysitis from some other pathologies that are similar in their manifestations. Pain in the pubic area can be caused by problems with the sciatic nerve (ischialgia), pain in the spine (lumbago), infections of the genitourinary system, as well as tuberculous lesions of the bones.
Treatment
The usual uncomplicated symphysitis does not need special medical treatment. It disappears on its own several months after giving birth, less often the clinical symptoms of softening of the symphysis persist for the first year after the birth of the baby. But without fail it is necessary to treat the rupture of the pubic symphysis, if it occurred. Without proper and timely treatment, a woman can remain disabled for life. Gap is treated exclusively by surgery and prolonged (for several months) fixation. The operation aims to recreate the affected ligaments.
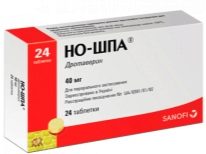
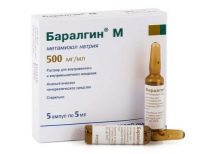
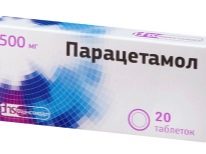
In case of symphysitis during pregnancy, the therapy is aimed primarily at alleviating the pain and preventing the rupture of the ligaments. In the treatment regimen may be included analgesic anti-inflammatory drugs - antispasmodics, such as «No-shpa"," Baralgin ","Paracetamol». They are allowed to be taken only in doses approved by a doctor and only in cases where a woman has to be held upright for a long time. Uncontrolled and frequent use of painkillers can cause drug addiction.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments are often recommended, for example, Indomethacin ointment. It is used topically to relieve pain and swelling in the pubic area.
Regardless of the degree of illness, a relative rest is prescribed for a pregnant woman. The pubic joint should not be under heavy loads. With a mild degree of symphysitis, it may be recommended to reduce the usual load, with 2 and 3 degrees often bed rest is prescribed. Expectant mothers with suspected symphysitis or a confirmed ailment are not recommended to walk up the stairs up and down, long sitting, standing in one position, long walking.
A woman is recommended to take multivitamins, complexes designed specifically for expectant mothers with a high calcium content, or calcium supplements in addition to the vitamins she takes. Unauthorized to start taking calcium in any form - means to endanger the baby, because an overabundance of this mineral in the body of the future mother can harm the baby, especially in the third trimester of pregnancy. Calcium is not recommended at all before delivery for several weeks.
With an insignificant degree of symphysite, it is enough to add to the diet foods with a high content of mineral - milk, cottage cheese, chicken eggs, spinach, fresh greens, nuts.
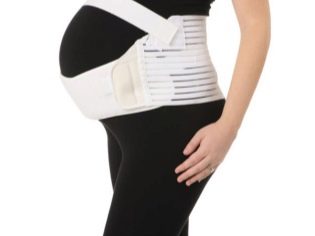
If diagnosed with symphysitis, more careful weight control will be required. Excessive weight gain increases the load on the weakened symphysis, the risk of rupture increases proportionally. A woman is recommended a universal diet for pregnant women, the correct drinking regimen, and fasting days. Starting from 6-7 months of pregnancy, a woman can wear a prenatal bandage, she will support a growing belly and reduce the load on her womb. You can buy a bandage at any pharmacy or orthopedic salon.
After birth, you will need another bandage, the wearing of which is designed to reduce the distance between the bones of the pelvis. It can also be purchased at the orthopedic salon. In some cases, a woman after childbirth is recommended to walk with a cane or crutches.
Far from the last place in the removal of painful and painful symptoms of symphysitis is given to the physiotherapeutic effect, for example, magnetic therapy. But the gynecologist and orthopedist will give referral to such procedures only when the expectant mother does not have the threat of abortion and other contraindications.
A woman with a revealed symphysite cannot sleep on a very hard surface, during sleep you should definitely put a small pillow or roller under your feet, and a small blanket or blanket rolled up with a “straw” will do.
Similarly, raise the pelvic region - under the buttocks also put a pillow.
A pregnant woman is prescribed a set of special gymnastic exercises that are effective for symphysitis. They reduce pain:
- Cat pose. A woman on a flat surface takes a knee-elbow position. Then she flexes her back and shoulders, straightens them and arches. At the same time, the chin is lowered and the abdominal muscles are slightly tense. This exercise must be repeated 10 to 15 times.
- Kegel gymnastics. These exercises are aimed at training the muscles of the pelvic floor. A woman should lie on her back and strain the muscles of the pelvis as it does when trying to keep urination. Keep tension for a few seconds, then the muscles relax. Exercise is done 15 to 20 times per session of gymnastics.
- Pose "bridge". Lying on your back, a woman should bend her knees, raise her pelvis and hold it in that position for a few seconds, then drop down gently and gently. The exercise is repeated 10-15 times per exercise.
Such gymnastics should be done only with the permission of the doctor and only if the classes do not cause an increase in pain.
If the pains become stronger, you should refuse to perform these exercises, by virtue of yourself being forced to do gymnastics in no case.
Prevention
Specific measures for the prevention of symphysitis during pregnancy does not exist. Even those future mothers who fulfill all the prescription of a doctor visit their midwife regularly and pass all the necessary tests in an “interesting position”, the risk of developing an illness exists. Reducing the likely risks will help, oddly enough, proper pregnancy planning. If a woman had diseases of the musculoskeletal system, pelvic injuries, there are problems with metabolism, planning of pregnancy should be given special attention.
Do not neglect to visit the doctor while carrying the child. It is only at first glance in such visits there is no benefit - weighed, measured the stomach and released. In fact, at each reception, the doctor controls the weight, measures the size of the pelvis, the beginning symphysis is not escaping the professional eye.
From the very first weeks of pregnancy, a woman should take care that her nutrition was correct - with a low carbohydrate content, with sufficient calcium, magnesium and other substances and vitamins necessary for healthy bones and joints. You can not overeat and "feed" the baby to large and giant sizes.
You should not limit your physical activity if the problems with the pubic joint have not yet manifested. A woman needs to do a special gymnastics for future mothers, you can practice yoga, swimming, make half-hour walks in the fresh air. Moderate exercise will help keep all muscles and ligaments, including the pubic, in a normal state.
If a woman’s work is connected with a long sitting in one place, you need to do some warm-ups every hour. But heavy loads should be abandoned, as well as climbing the stairs on foot, especially in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
If the symphysitis did happen and the doctor recommends a cesarean section, you should not insist on natural childbirth - the risks of rupture are too great.
Reviews
Feedback on the transferred symphysis young mothers leave often. Most describe their condition as associated with severe pain, which prevented sleep, walk, dress themselves. However, there are also cases when a woman had no complaints up to the very birth, and the symphysis had broken during the birth.
According to reviews, doctors most often prescribe calcium and indomethacin in tablets and ointments. After giving birth, the painful sensations of the majority of mothers who left their comments passed in about 1-2 months.
Reviews of real people about symphysis during pregnancy, see the following video.