What are the signs of pregnancy before the delay of menstruation?
From the very first hours after the conception of a baby, large changes begin to occur in the woman's body. Realizing this, many planners of the birth of a baby begin to expect the first signs to appear even before a monthly delay. Interest is fueled by those who claim that literally from the first day they felt “somehow different.” In this article, we will examine in detail whether it is possible to feel a pregnancy before a delay and what symptoms may indicate it.
Conception and implantation
To feel the process of conception is impossible, because it involves two tiny germ cells and the whole process takes place exclusively at the cellular level. On the day of ovulation a ripe egg leaves the follicle. Even during the day she retains the ability to be fertilized. If spermatozoa are nearby at this time, then it is quite possible that one of the millions of sperm will still be able to break the integrity of the oocyte membranes and get inside.
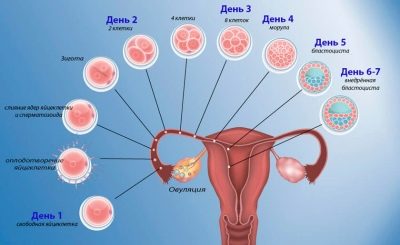
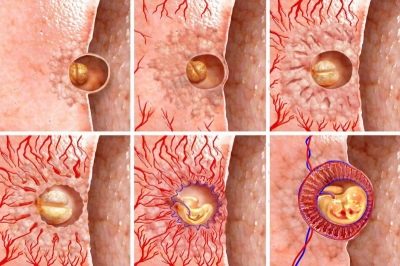
Immediately after this, the process of fusion begins, the two cells combine their DNA and the development of a new life begins. The egg cell turns into a zygote, and then into a blastocyst. Every day it is crushed, the number of cells in it increases. At the same time, the blastocyst moves along the fallopian tube from the ampullary part in which the fusion took place, into the uterine cavity. She is actively "helped" by the villus, with which the fallopian tubes are littered from the inside. With their movements they push the fertilized egg forward. First, it enters the mouth of the pipe, and then it turns out in the uterus.
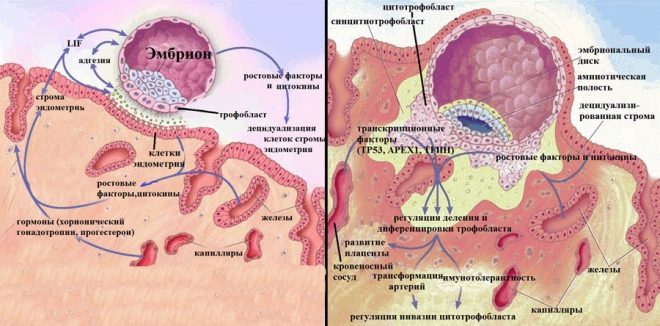
This process lasts on average 7-9 days after conception. In the uterus, the ovum must be fixed in order to get chances for further development. The process of attachment is called implantation. It has two stages. On the first, the blastocyst sticks to the endometrium. This stage is called adhesion. Egg membranes secrete certain enzymes that partially “dissolve” endometrial cells.
Then begins the second stage - invasion. When it is, the egg “breaks” into the endometrium, the chorionic villi unite with the small blood vessels, and the fetal egg begins to receive oxygen and nutrients from the maternal blood.
Only from this point on, pregnancy is considered to have occurred. therefore, the first signs quite logically can appear only after implantation, that is, 7-10 days after conception. However, some claim that they began to feel changes in their body earlier. Such feelings can be attributed to the subjective. But there is a scientific explanation for them - while the egg cell moves towards the uterine cavity, hormonal changes are initiated in the body.
Also, early signs may be psychosomatic. This occurs in women who have long and unsuccessfully planning to have a baby. In any unusual sensation, they tend to see a sign of an “interesting position." They are often told about the symptoms that they “invent” for themselves. These ladies do not cheat at all, they really feel the pregnancy, but they have inspired these feelings themselves.
In order to better understand her own feelings, a woman should know exactly what changes in terms of official medicine occur inside her body during these two weeks, which separate ovulation from the date of the next menstruation.
What happens in a woman's body?
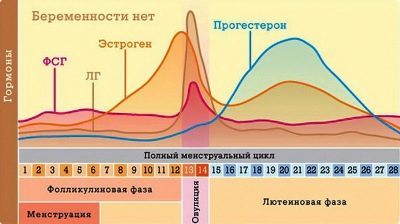
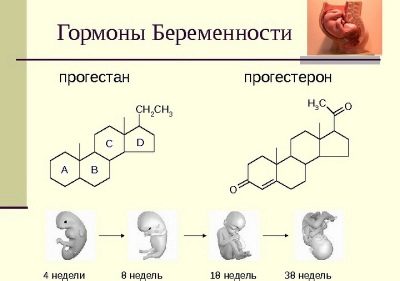
After ovulation, regardless of whether it was conceived or not, the concentration of the hormone progesterone in the blood plasma increases. In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, this substance regulates all processes — first, the endometrium under its influence thickens, becomes more loose, prepares for implantation. If there was no fertilization, then in two weeks, when progesterone drops and estrogens begin to predominate, menstruation begins - the very overgrown endometrium is rejected, which this time "was not useful."
If conception took place, progesterone is produced more actively. Even before implantation, this substance triggers some biochemical changes - the endometrium thickens, the smooth muscles of the uterus relaxes somewhat, the cervical canal is tightly closed with a thick mucus plug to prevent sperm, bacteria and viruses from entering the uterine cavity.
"Explanatory work" is carried out by progesterone and with female immunity. The germ consists of half of the native genetic material. Its second half is the paternal genes, and they can be perceived by the vigilant immune protection of an adult woman as hostile. So that the immunity does not reject the embryo, progesterone begins to have an immunosuppressive effect on it, which partially inhibits the activity of antibodies.
Immediately after implantation, the changes become more widespread. The chorionic villi, which connect the membranes of the ovum to the wall of the uterus, begin to produce their own hormonal substance, the name of which is well known to all those who plan to become pregnant - this is hCG. Chorionic gonadotropic hormone stimulates the production of progesterone. If in a non-pregnant cycle, the hormone level begins to fall to the monthly, then now the hCG will not allow him to do this, and the monthly will not come as a result.
Chorionic hormone increases with the growth of the ovum, while the rate of increase in its concentration is quite clear - every two days the concentration of hCG in the blood plasma increases exactly 2 times. If a woman becomes pregnant with twins, then the hormone level will increase not by 2, but 4 times relative to previous values.
Two hormones together affect almost all organs and systems. Progesterone increases the appetite, because its task is to preserve pregnancy, and for this evolution involves the creation of nutritious fat and carbohydrate reserves in case of situations with nutritional deficiencies. The mucous membranes under the action of two hormones become more loose and vulnerable. The pelvic organs are beginning to be better supplied with blood, increasing the load on the heart and blood vessels.
A new functional center is formed in the cerebral cortex - the center of pregnancy. Within nine months, he will have to be responsible for the consistency of all processes that are designed to help in carrying the fetus. It is this center that will regulate the growth of the uterus, mammary glands, control hormonal balance and compensate for all the inconveniences that the fetus grows in the womb of the woman’s internal organs.
All this happens about a week before the next month. And this last week may well bring something new and unusual to the woman’s usual sensations. However, much depends on individual sensitivity, on the state of immunity.
The stronger the immunity, the more pronounced the first sensations and signs can be (the body will begin to resist some changes). Immunocompromised women may not notice anything unusual.
Symptoms and feelings before the delay
Knowing about biochemical processes, it will not be so difficult to understand which sensations are justified, and which ones are contrived by a woman.Most often, early pregnancy symptoms resemble the common cold. A woman may feel overwhelmed, tired, and the runny nose will completely convince her that she is sick. In fact, this is the effect of progesterone on immunity. Among the other first symptoms of pregnancy discussed at the earliest stages are the following.
Trouble falling asleep or constant sleepiness
Obsessive desire to sleep a week longer before the end of the menstrual cycle is a normal phenomenon if conception took place. The internal processes described above lead to higher energy costs. Fatigue and drowsiness - a protective mechanism that is designed to compensate for these costs.
Lack of opportunity to fully sleep enough notes about half of pregnant women. The woman still does not know whether the pregnancy has come, but the woman’s body already knows the answer to this question. A new impulse center, which has arisen in the cerebral cortex, gives the neighboring centers a lot of discomfort. One of the "suffering" is the center of regulation of sleep.
That is why after implantation, a week before the date of the next menstruation, a woman can pay attention to the fact that she does not get enough sleep, even if she is sleeping for a sufficient amount of time, or cannot fall asleep when it is time. Frequent awakening, sensitive and shallow sleep may also indirectly indicate a possible pregnancy.
On the other hand, insomnia may well be caused not by pregnancy, but by stress, feelings, problems at work or at home, financial difficulties, and even an abundant dinner before bedtime and stuffiness in the bedroom.
Mental and Emotional Instability
Progesterone has one unpleasant side effect - it causes mental and emotional instability. The central nervous system is partially suppressed by the hormone to provide a more favorable psychological background for the development of pregnancy. But without a “fight”, the central nervous system does not give up, and because of this, a woman, about a week after conception, can feel sudden mood swings. Many become weepy, more touchy, and some even aggressive.
Women who experience premenstrual syndrome on a monthly basis know about this effect of progesterone firsthand. However, with PMS, mood changes usually begin two to three days before menstruation. With the onset of pregnancy, the instability of emotions and reactions usually manifests itself somewhat earlier.
This symptom also cannot be regarded as specific, since it depends on the individual characteristics of the woman’s psyche, on her temperament and lifestyle. Some people have no sign, some have it even outside of pregnancy
Heaviness in the stomach
If the severity appeared the day after conception, it is most likely associated with food. But 3-4 days before the expected menstruation, the feeling of an incessant heaviness in the lower abdomen may already be one of the earliest signs of an “interesting position." The fact is that the amount of circulating blood begins to gradually increase, because the pelvic organs already require increased blood supply.
Often, women perceive the feeling of “fullness” as a sign of early menstruation, and therefore do not pay enough attention to it.
Strange sensations in the uterus
Uterine muscles under the action of progesterone becomes more relaxed and soft. This is necessary for the full development of the baby in the womb. It is the process of softening that sometimes feels like “tingling” or small “lumbago” in the uterus. Usually, women begin to mark this symptom several days after conception.
Do not regard this symptom as mandatory. Even if there is no pregnancy, a slight softening of the uterus in the second half of the female cycle is the physiological norm, and therefore tingling can occur.
Breast soreness
Planned conception women love to explore the breast, to find the answer to the question whether the pregnancy has occurred. From the point of view of medicine, there is some common sense in this. Hormonal changes in the body after implantation of the ovum cause small changes in the concentration of other hormones. Breast sensitivity may increase, and may, conversely, decrease.
There is no single standard for assessing a breast before a delay. However, women note that it is very likely that the breasts in the “pregnant” cycle will behave differently than in the “non-pregnant” one. In other words, if usually in the second half of the cycle, the nipples were more sensitive, then after conception they may stop being ill and vice versa.
Other signs
Other indirect signs of the initial stage of pregnancy include headaches, which are also a "side effect" from the effects of progesterone and hCG. They usually begin either in the morning or in the evening and rarely last a long time.
Progesterone softens not only the muscles of the uterus, but also partially removes the intestinal tone. Because of this, constipation, heartburn. Similarly, the hormone also affects the bladder, and therefore many women notice frequent urination before the delay.
The idea of a cold can visit a woman not only because of the physiological rhinitis and the feeling of fatigue. After implantation, that is, about a week after ovulation, a woman may notice that in the evenings her body temperature rises, chills appear. However, in the morning the temperature drops to return in the evening. This is not a cold, but a way of immune protection to adapt to the new conditions in which the body is to be.
Many pregnant women before the test and blood test will find out about his position on the characteristic drooling. Saliva is usually excreted in large quantities at night when a woman is sleeping. Thus, a certain center in the cerebral cortex, which regulates the production of this fluid, “revolts”. With the advent of the new center - the center of regulation of pregnancy, its work is disrupted by the new "neighbor".
Allotment
After ovulation in the second half of the cycle, excretions become less plentiful. Under the action of progesterone, the so-called “dry period” begins. Allocations normally remain light, thickish. Under the influence of progesterone may be yellowish shades of vaginal secretions.
In some women, the implantation process itself is accompanied by a rather obvious symptom, which is called “implant bleeding”. About a week or more after ovulation, a woman may notice a scanty brown discharge, a “daub”, which she may mistaken for the earlier onset of menstruation.
Implantation bleeding occurs due to the integrity of the endometrial layer during invasion of the ovum into it. The discharge does not pose any danger to the health of the woman or the development of her baby. Usually they end in a few hours or a maximum in a day.
Symptom occurs not in all pregnant women. Therefore, the absence of such secretions in the right time frame is not a reason to be upset, believing that conception did not occur.
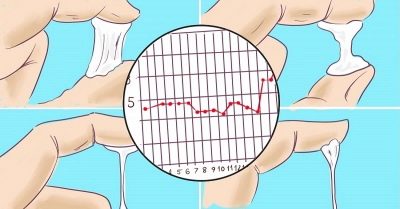
Basal temperature
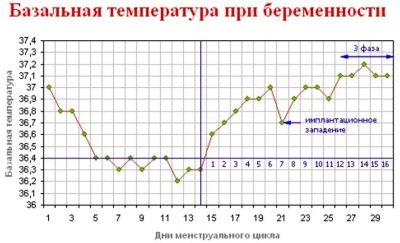
Measurement of the basal temperature can give food for thought only to women who have systematically taken daily temperature measurements in the rectum for at least the last three cycles and entered them into special graphs.
Two weeks before menstruation, basal temperature rises. This is the ovulation peak. If conception took place, then the temperature does not return to the values of the first phase of the cycle and is elevated — above 37.0 degrees.
Sometimes at the onset of pregnancy, the temperature remains below 37.0 degrees, and this is an individual feature of the woman’s body, most often associated with an insufficient level of progesterone.
Sometimes an elevated basal temperature may not indicate a pregnancy, but an inflammatory process in a woman’s body, and therefore the measurement method is not 100% accurate diagnosis.
External and physical changes
No doctor will not give an affirmative answer to the question of how the appearance of a woman changes after conception to a delay. The medicine does not have such data. But the representatives of the fair sex themselves have noticed long ago that some changes are quite possible. So, according to reviews, the first signs may appear within a week after conception. In the morning, may swell a little face, hands. Acne may appear, as this is how a woman’s body can react to changes in hormonal levels.
Women who have previously been treated for thrush can have an itch in the area of the external genital organs, accompanied by thick, cheesy white discharge, within a week after conception. The manifestation of thrush is a frequent sign of pregnancy before a delay, as the immunity under the action of progesterone becomes weakened.
Those who suffer from chronic hemorrhoids, note that an exacerbation of an unpleasant disease may begin. This is due to an increase in the blood supply to the pelvic organs.
When to do the test?
Considering that the hormone hCG, which is determined by rapid tests, increases every two days, its concentration in the urine begins to exceed the sensitivity thresholds of the tests only a couple of days before the menstruation or on the first day of the delay. Earlier testing only increases stress. A woman worries, fears failure, stress hormones disrupt the normal course of pregnancy and may well cause detachment of the ovum from the uterine wall.
With late ovulation, tests may show a negative result for several days after the delay. Therefore, it is the absence of menstruation that is considered the most objective sign of pregnancy.
If you really want to know about your situation earlier, it is worth doing a blood test for hCG. This analysis can be taken in any clinic, its cost is low (500-600 rubles), accuracy - almost 100%. Approximately 4 days before the delay, the laboratory test will detect hCG in the blood plasma.
Reviews
Many women, who left feedback on their early signs in the thematic forums, indicate that one of the first was unusual sensations in the mammary glands and mood swings. In most cases, they were manifested by an increased reaction to films, books, and touching photos. Women say they cried over and without. A common symptom of frequent urination is also quite common - many note that even a week before the expected date of their monthly periods, they began to wake up at night to go to the toilet.
But nausea, a change in taste preferences and a special sensitivity to odors usually appears a little later - after a delay.
It is not necessary that the signs and symptoms that were in the first pregnancy be repeated with accuracy in subsequent ones. Symptoms may be different, and what signs will appear first, no one ever predicts. All individually. Therefore, it is not necessary to “wind yourself up” comparing other people's symptoms with yours. You can not feel absolutely nothing and be pregnant, but you can find every one of the signs listed in this article, and not to be pregnant. Numerous reviews fully confirm this.
On the first signs of pregnancy before the delay of menstruation, see the following video.