Symptoms and treatment of ARVI in children
ARVI is the most common cause of childhood ailments, especially in the cold season and in the offseason. Some kids manage to get SARS 8-10 times a year. Despite the fact that this diagnosis is widely known, parents do not know as much about acute respiratory viral infections as we would like. This large group of diseases similar to each other, how to recognize them in a child, what to properly treat and how to prevent the disease, will be described in this article.
What it is?
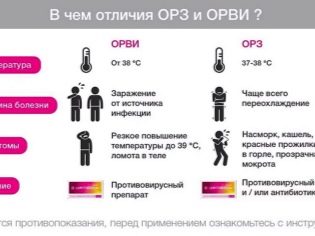
ARVI is an acute respiratory viral infection. However, it is not about any one infectious "contagion" at all. Under this abbreviation hides a whole group of diseases that are caused by pneumotropic viruses. They have only one thing in common - the clinical picture.
With ARVI viruses infect the respiratory system. The group of acute respiratory viral infections can include adenoviral and rhinovirus infections, respiratory syncytial infection, parainfluenza and a number of other diseases that affect the respiratory tract.
Accurately calculate how often children are infected with ARVI is almost impossible, because this group of ailments is considered to be the most common on the globe, and parents do not always call the doctor, and, therefore, many cases remain unaccounted for. Epidemiologists claim that in childhood, about 90% of all cases of diseases, in fact, are precisely SARS caused by a particular pathogen virus.
In the newborn and infants until six months, ARVI is less common. Such babies are protected by passive innate immunity. Antibodies to the most "running" viruses crumbs get in the womb with blood, as well as after birth with breast milk. Most often, children with preschool and primary school age are sick with ARVI, because they attend large children's groups, where any viral infection spreads with great speed.
Adolescents suffer from ARVI less frequently, because they form their own specific immunity to most pathogens. Adult ARVI threatens even less. According to statistics, every adult Russian has an acute viral infection about 2 times a year.
Often this group of illnesses is mistakenly called a cold. In order to better understand the nature of the disease, you should know that the common cold is a decrease in immunity under the influence of low temperatures, hypothermia. A viral infection has nothing to do with colds.
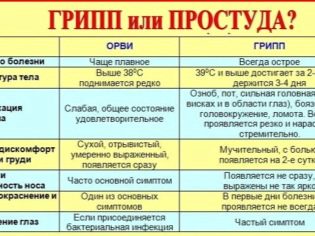
You can find several official names, synonyms: ARI, ORZ. Do not confuse SARS with the flu. Influenza belongs to the group of acute respiratory viral infections, but takes a separate place in it. When doctors talk about the incidence of influenza in the current year, they do not take into account cases of SARS. The general epidemiological situation takes into account acute respiratory infectious diseases, in 2018 the rise in the incidence rate, according to doctors, will occur in the spring and the period from September to December.
The weaker the child’s immunity, the worse his health, the more difficult the ARVI may be. Much depends on age - at 2 years the disease is more pronounced, and at 14 years old everything can do with a mild form, which theoretically can be transferred “on the feet”.
The main danger lies not in the virus that hit the child, but in the likelihood of complications. Often, a viral infection so weakens the already weak children's immunity, which creates favorable conditions for infection with bacteria, for example, staphylococci or E. coli.
Every virus that causes diseases of the ARVI group is extremely contagious. That is why the incidence is increasing exponentially, especially in closed children's groups. Almost every year, schools and kindergartens are quarantined by ORVI. This is the only way to temporarily and locally stop the spread of the virus.
Immunity to pneumotropic viruses is not lifelong, which means that after an illness after a while, the baby may get sick again, however, the disease will flow with each successive time easier. In addition, the viruses themselves, there are several hundred, and antibodies to one will in no way protect the child from another pathogen.
How does the infection occur?
Most often the insidious virus-pathogen ARVI is transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. An adult who quite easily transfers ARVI “on his feet”, during his morning trip to the subway or trolleybus, during a working day in a team infects dozens of other people, who, in turn, spread the infection further.
A person is considered contagious from the beginning of the incubation period to the moment of complete recovery, the end of the acute febrile process. The incubation period for various viruses of the ORVI group is about the same - from several hours to 2-3 days. The younger the child, the shorter the incubation period.
A child can become infected not only in a bus or subway, but also in a contact way - through common toys, objects, things in a kindergarten or school, at home, through kisses and even handshakes. The susceptibility to viruses is high, it does not depend on gender, nationality. This does not mean that every child who will be in contact with the sick person will also certainly fall ill. The virus prefers weakened organisms and can begin to act destructively only in “favorable” circumstances.
Children most often get sick:
- with a weakened immune system, often ill;
- not complying with preventive measures, walking in wet shoes, often overcooling;
- suffering anemia and deficiency of essential vitamins;
- sedentary, predominantly sedentary;
- surrounded by excessive guardianship, which are wrapped and protected from any draft;
- whose parents too often give them different medicines.
The virus enters the body mainly through the upper respiratory tract. Once in the nose, nasopharynx and larynx, the virus begins to settle down and control it. It is embedded in the cells of the ciliated epithelium, rearranging their structure for their own needs. Quite quickly, epithelial cells are destroyed, their detachment occurs, the virus enters the bloodstream, spreads throughout the body, causing intoxication symptoms, and headache.
At the time when the child becomes ill, that is, showing clinical symptoms, the virus is usually already spread throughout the body. Its dislocation exclusively in the upper respiratory tract most often occurs only at the stage of the incubation period and the early acute period of the disease.
After a few days of the acute stage, the child’s immunity, having completed the “study” of the foreign agent, forms specific antibodies, with the result that the immune response begins. The blood is gradually cleared of viral particles, the baby begins to recover.The final stage is the release of the respiratory tract from the dead ciliated epithelium. Cells that have fallen in an unequal battle with the virus are brought out by a runny nose and expectoration of sputum.
All this time, the child remains infectious. Some viruses can be transmitted to others even a week after recovery. That is why parents are not recommended immediately after recovery to lead the child to kindergarten or send to school.
The optimal is a small recovery period of 7-10 days, during which the child will be able to cope with residual effects - cough, weakness, dizziness and will not pose a danger of infection to others.
Symptomatology
ARVI causes different viruses, and therefore the symptoms may differ, but only slightly. The classic "viral" picture is as follows.
- Signs of malaise. These include the feeling of chills, muscle pain. Often, children complain that their hands, calves, back hurt, there is an ache in the knee and elbow joints. Lymph nodes may increase.
- Signs of intoxication. Severe headaches, pressing pains in the eyeballs. Often, babies on the background of acute respiratory viral infections have a stomachache, vomiting and diarrhea can open.
- Temperature. Viral infections always begin with a rise in body temperature. Different viruses cause different fevers. The highest fever is observed with the flu, a moderate, gradually increasing temperature is characteristic of rhinovirus infection. On average, the temperature in acute respiratory viral infections reaches 37.5-39.0 degrees.
- Respiratory symptoms. The defeat of the ciliated epithelium of the respiratory tract at an early stage is manifested by a sensation, which is often described as "itching in the nose," sneezing. A runny nose, dry cough appears a little later, discharge of nasal mucus begins. If no bacterial infection has joined, the snot will be transparent. If complications could not be avoided, the snot will quickly thicken and turn greenish.
- Other symptoms. ARVI may be accompanied viral conjunctivitis, increased tearing, photophobia. A child may complain of ear congestion, sore throat when swallowing.
The onset of the disease with ARVI is always acute, sudden. An hour ago, the baby was cheerful and cheerful, and now lies with the temperature and complains of a headache. If the child has become infected with adenovirus infection or parainfluenza, then the disease starts not with a general malaise, but with the appearance of a sudden cold or conjunctivitis, with sneezing, coughing.
The acute period in most diseases in the ORVI group usually lasts from 3 to 7 days, then the recovery period begins. All children are individual, and therefore the course of the disease will be individual and completely unpredictable.
Some of the symptoms listed above occur easily and do not worry the child very much, others quickly develop a severe, toxic form that requires hospitalization and the provision of skilled medical care.
Parents are often wondering if it is necessary to call a doctor if a child has ARVI? If the child is not 3 years old, then the doctor must be called even if the disease is mild and almost asymptomatic. Children older than three years old need medical advice in those cases if:
- body temperature exceeded the limit of 38.0 degrees and is not easily knocked down by antipyretic drugs;
- the child is very weak, he has signs of clouding of consciousness;
- the baby cannot turn his head to the side because of a sharp pain, or bring his chin closer to his chest;
- rash appeared;
- the child's breathing becomes hard, heavy, obstructive, pain in the sternum, severe shortness of breath;
- on the body and face of the child showed swelling of tissues;
- began convulsions.
In all these cases, the doctor should provide the necessary assistance and find out which virus has infected the baby, what complications have appeared or are threatening to appear. The classic acute respiratory viral infection, which all children are ill with, is not accompanied by the listed alarming symptoms, can be successfully cured on their own at home, guided by basic knowledge of viral ailments and common parental sense.
If you suspect your child's ARVI, in no case should you go with him to the clinic in your place of residence to see a doctor. Until the child reaches this room, he will transmit the virus to several other children. Stay at home by telling the clinic about your suspicions of a viral infection. The doctor will come to the house, examine the child and confirm or deny your suspicions. In this case, the probability of becoming active participants in the process of spreading the virus will be reduced.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of SARS is differential. That is, it is very important to distinguish ARVI from other diseases and conditions manifested by similar symptoms and signs. It is very important to be able to distinguish a viral infection from hepatitis, which can also manifest as malaise, chills, anorexia, a sense of unreasonable tiredness. In about 80% of cases, viral hepatitis at the very beginning manifests itself as ARVI or ARI.
The presence of nausea and vomiting can be not only a manifestation of intoxication, but also a sign of rotavirus infection, which is often called vomiting virus in people. A rash on the skin can also be a manifestation allergies or hemorrhages, and a concomitant fungal disease.
That is why when signs appear that go beyond the classical clinical picture of acute respiratory viral infections, consultation with a doctor and laboratory tests are recommended.
Under the "mask" of ARVI can hide dangerous flu viruses and even some bacterial inflammatory processes. That is why in case of non-standard flow of ARVI, it is recommended to carry out diagnostic measures aimed at identifying the exact causative agent of childhood malaise. For the initial diagnosis is enough three tests:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- immunological examination of a blood sample to determine the presence of antiviral antibodies.
The study protocol will be able to answer the main question - ARVI is a disease or another. In general, the blood test for SARS red blood cells are normal or slightly elevated. This increase may indicate slight dehydration. In viral disease, the number of leukocytes is somewhat reduced. Eosinophils practically disappear in the blood of a child with SARS, and ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) slightly increases.
Urinalysis for acute respiratory viral infection sometimes shows traces of protein, but this is considered to be completely normal at elevated temperatures. An immunological blood test is not always carried out, but only when the course of an ARVI is very severe or toxic. The study should be done twice - at the very beginning of the disease and at the end. Detected antibodies allow us to establish the exact pathogen.
In case of severe respiratory symptoms, as well as in case of suspicion of complications, consultation and examination of the ENT doctor are necessary, and if an outbreak of rash appears, the child may need to consult an infectious disease specialist and an allergist.
Treatment
To treat mild and moderate forms of ARVI is permissible at home. Hospitalization is subject mainly to children who have severe or toxic forms with chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, musculoskeletal system, as well as children under 1 year old, from 1 to 3 years old.
Home treatment of ARVI is a subject of controversy and discussion in the professional medical environment. So, the famous children's doctor, the favorite of millions of mothers, Evgeny Komarovsky, argues that it is not necessary to treat ORVI in the standard sense.It is enough to create conditions for the child in which his immunity can more quickly produce the antibodies to the virus necessary for recovery. To optimal conditions, he refers maintaining coolness in the room where the sick person is located, moistening the air, irrigation of the nasal mucous membranes with saline or drops based on seawater, as well as abundant warm drinks. In most cases, this is actually quite enough for the child to cope with the disease in the allotted 3-5 days.
However, invited home pediatricians from district policlinics always write out a long list of medicines, which, according to manufacturers, should "quickly cure the flu and ARVI." In this list of drugs are always present antiviral drugs, vitamins.
Most antiviral drugs, unfortunately, have no proven efficacy. And popular homeopathic remedies, such as "Anaferon", "Oscillococcinum"Are not drugs at all and traditional medicine tends to attribute their effect to the placebo effect. Parents dutifully shell out the medicines against viruses prescribed by a doctor, give their children and sincerely believe that they are doing everything possible to recover their children.
In this situation, everyone is happy - pharmacists earn money by selling ineffective or ineffective syrups and pills, the local doctor is not afraid of the anger of patients for whom he did not make an appointment, and parents actively treat their son or daughter. In fact Antiviral drugs for an hour do not bring recovery, the baby will not be better from pills, but when the active immune response begins in his body.
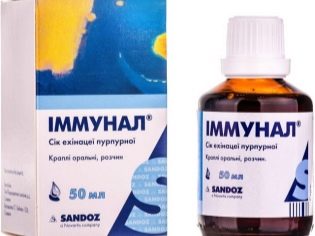
Antiviral drugs that act precisely and seriously, whose effectiveness cannot be doubted, are mainly used only in hospitals of infectious diseases hospitals, they are used for severe forms of influenza and other infections, they have a lot of side effects. "Isoprinosine», «Kagocel"," Theraflu ","Immunal"," Ergoferon "," Viburkol "," Viferon "and other popular and widely advertised means to such treatment are not relevant. They are a great way to make money on an epidemic, make a profit from sales and nothing more.
The standard treatment regimen for SARS includes several main points.
- Reduced intoxication. This is the first thing parents should do. Intoxication in case of acute viral infection is inevitable, you can help the child with abundant warm drink, the temperature of which is at room temperature. It is this fluid that is absorbed faster in the intestines. The condition is stabilized more quickly if the child abides in bed at least for the time of the acute period with fever.
- Control of body temperature. A rise in temperature is a clear indication that immunity fights the virus. To reduce the temperature to 38.0 degrees is not necessary. She is a faithful assistant and a factor that stimulates the production of natural interferons in the body. If the thermometer shows higher values, a paracetamol-based antipyretic agent should be given.
Acetylsalicylic acid is prohibited in childhood because its use increases the likelihood of liver damage and lethal Ray's syndrome. Antipyretic, depending on the age of the child, can be used in tablets, syrup, rectal suppositories.
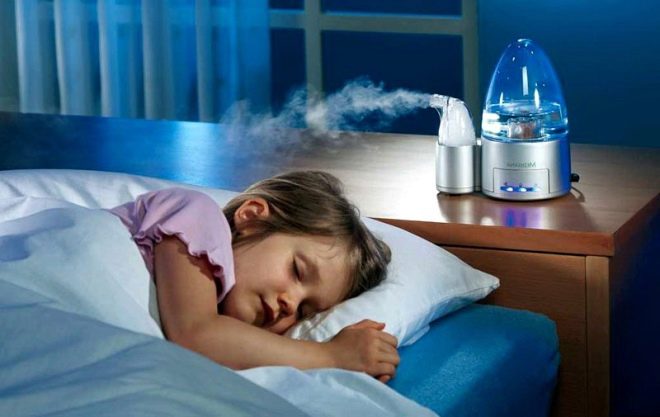
- Immunity support. Vitamins will help to cope with this task. A local immunity will help support the irrigation of mucous membranes. On dry shells, the virus multiplies many times faster. Therefore, you need to instill saline or Aquamaris in your nose, rinse your throat with warm boiled water or furatsilina solution, if there is an inflammatory process, and again - drink more warm fluids.
- Symptomatic treatment. If a child has a bad cold and nasal breathing is significantly hampered, he is prescribed vasoconstrictor nasal drops (Nazol, Nazivin).They allow you to temporarily narrow the lumen of the vessels and to ensure unobstructed inhalation. When dry cough, drugs are recommended that have a mucolytic effect and promote expectoration of sputum. With the defeat of blood vessels with viruses and the appearance of a rash resembling small red dots, can be assigned aminocaproic acid inside.
If the disease is accompanied by an exacerbation of a herpetic infection and the child has a characteristic “cold” on the lips and chin, a topical ointment is prescribed. ”Acyclovir».
If the child was nauseous or had loose stools, dehydration should be prevented, for this purpose enterosorbents can be used (“Enterosgel", Activated carbon), as well as funds to replenish lost fluid and mineral salts in the body -"Regidron», «Smecta, Humana Electrolyte. For an uncomplicated respiratory viral infection, such therapy will be more than enough.
If after 5 days, when the child is already feeling better, the “second wave” of the disease suddenly begins, then we are most likely talking about the accession of a secondary bacterial infection. It will require the use of antibiotics after compulsory medical consultation and laboratory tests.
Common mistakes
The worst mistake is made by parents and doctors who are trying to treat a viral respiratory infection with antibiotics. An antibiotic designed to resist bacteria, these drugs do not have the slightest effect on viruses. Doctors know this, of course, but sometimes they still prescribe an antibiotic for ARVI. They do this for "safety net" because it is quite difficult for kids to recognize incipient complications.
Such antibiotics “just in case” only increases the likelihood of complications. Therefore, be sure to check with your doctor if he recommends “Flemoxine Solutab"Or another drug popular in pediatric practice, why was an antibiotic prescribed. If there are complications, it is necessary to take it. If ARVI proceeds without complications, then you should not try to hedge yourself with the help of such serious medications as antibacterial drugs.
Quite often, you can encounter such a mistake as improper care for a sick child. Sometimes parents themselves increase the likelihood of developing complications by wrapping the baby, covering the sick man with several warm blankets and blankets, putting a heater near the patient's bed and tightly closing all the windows and air vents. As a result, the child breathes dry air, which additionally dries the mucous membranes of his respiratory tract, the virus gets the opportunity to spread faster and more aggressively. It is with this "care" that most often develop severe bronchitis and pneumonia.
Another common mistake is to force-feed a child with oranges, sour lemons and other citrus fruits. For a long time, it was really believed that vitamin C promotes healing. However, recent studies have shown that Ascorbic acid in no way accelerates recovery, does not fight the virus. If the child himself loves sour lemons, let him eat, but if he is made to “heal” with them, the effect of them can not be expected.
Categorically, you should not rub baby with high temperature with vodka or vinegar, pour cold water over it, apply ice to your head, since such actions can lead to vasospasm.
You can not rub the child badger fat or fat, because it against the background of temperature can lead to hyperthermia - overheating of the body. Any inhalation is also prohibited if the child has a fever.
Food and folk remedies
It is not necessary to force the child, a patient with ARVI, to eat at any cost. Moreover, you need to avoid a lot of sweets, chocolate, soda.The appetite for a viral infection is inevitably reduced, and there is a certain natural wisdom in this - if the patient's body does not spend energy on digesting food, he quickly deals with the causative agent of the disease.
Feed your son or daughter only when the child himself asks for it.. And at the time of illness should avoid dairy products, fatty and fried foods, smoked meats and canned goods. The best menu for a child with a sharp respiratory viral infection is compote from dried fruits, homemade fruit juice from berries, light vegetable soup, cereals, steam cutlets from meat and fish stuffing.
With folk remedies should be more careful. Like most antiviral drugs, decoctions and infusions will not have a significant impact on the course and duration of the disease.
But some recipes of traditional medicine, aimed at eliminating the symptoms, can help in the composition of complex therapy. These recipes can be safely attributed to home-made salt solution, which can be instilled into the nose, chamomile decoction for making warm drinks and rosehip to compensate for water balance and reduce the symptoms of intoxication.
Features of the flow at a very early age
The hardest thing is to navigate what is happening to moms and dads of young children, who cannot yet express in words where and what hurts them. Therefore, it should be remembered what features are characteristic of the behavior of children with SARS. An infant always behaves restlessly at the onset of the disease, his appetite suffers and his sleep is disturbed, capriciousness and unreasonable crying can appear.
Many babies do not know how to breathe through their mouths, and therefore hindered nasal breathing will immediately affect the child’s behavior. An aspirator will come to the aid of the mother, which will help release the nasal passages from the accumulated mucus. If the child is less than half a year, he may have an acute respiratory viral infection with a so-called wheezing breath. Respiratory disorders always occur on the background of high temperature and general intoxication.
Breastfeeding at the time of treatment is not stopped. With mother's milk, the baby will receive the necessary additional antibodies to fight a viral infection. Age up to a year is the most dangerous one in terms of the possibility of complications. Especially carefully you need to treat the child at night, it is at night most often develops a life-threatening condition, like croup.
With the appearance of barking cough, blue lips, difficulty in breathing in and out, you should immediately contact the ambulance.
In children older than 6 months, ARVI often occurs with concomitant digestive disorders. And children older than 2 years often exhibit tracheitis symptoms. At any age up to 3 years the disease most often manifests itself for the first time at night. The first signs, such as high temperature and difficulty in breathing, are detected in 90% of cases at night.
Possible complications
You should not forget about the probability of complications, although their frequency is not so great according to statistics. Approximately 85% of children suffer from acute respiratory viral infections without complications, and only 15% of cases develop certain effects. The development of complications indicates a prolonged period of fever. If the temperature lasts more than five days, the child is more likely to have complications.
Residual coughing, which does not stop thinking, may indicate that a child has developed bronchitis or even pneumonia. Against the background of increased prolonged temperature, the child may experience shortness of breath, sweating, and increased fatigue. These symptoms are a reason for immediate visits to the doctor and a thorough examination.
Often, after SARS in children, a rash appears. Be sure to consult with a pediatrician or infectious diseases, which will prevent the addition of other viral infections associated with rashes, such as chickenpox, roseola. Often the rash is associated with allergies for medications with which the baby was treated during the acute period of acute respiratory viral infection, especially if parents gave large quantities of antipyretic drugs and expectorant drugs in sweet syrups.
Sometimes after a few days or even weeks after an acute respiratory viral infection, the child begins to complain that he has sore feet or one leg. Joint pain associated with the development of such complications as reactive arthritis. To help the little patient can a rheumatologist.
Other complications that also occur after ARVI include:
- sinusitis;
- neuritis of the auditory nerve, hearing loss;
- otitis;
- chronic rhinitis;
- meningitis.
Proper treatment, reasonable care for a sick child, timely access to medical specialists will help reduce the likelihood of developing dangerous complications.
Prevention
Measures of prevention of ARVI should be recorded in the memo to parents, which it is desirable to memorize even before the child is born. Since the group of diseases is very widespread, it is impossible to protect a child by 100% from viral infections no matter how hard mom and dad try. However, basic knowledge of prevention will help to protect the child as much as possible.
There are no vaccinations for most viruses in the ARVI group.. The only way to protect a child is from birth to take care that his immunity is strong and hardened. To do this, Evgeny Komarovsky recommends bathing your baby in cool water, walking more often in the open air, making sure that there is enough vitamins and minerals in the food of the younger children.
Useful "antiviral" activities are walking barefoot on the floor, in the summer - on the grass, swimming in open water, playing in the fresh air, playing sports. If a child attends a boxing section in which he will train in a stuffy room or a chess school, this is unlikely to significantly strengthen his immunity. But cycling, skiing, athletics, swimming, figure skating, hockey and football will affect the state of immune protection in the best possible way.
In order for a child to be able to oppose a virus threat, he must sleep a sufficient number of hours per day according to his age. The mode of work and rest is important not only for the student, but also for the kindergarten student.
In the child’s room year round there should be enough humid air - about 50-70%. The air temperature should be kept at 21 degrees of heat, not higher. Hardening, training and active lifestyle should be constant and systematic.
Under no circumstances and ailments parents should not self-medicate. Children who are often given pills, syrups, capsules and potions are sick more often. To prevent ARVI, it will be quite enough to stay away from public transport and crowded places during periods of seasonal increase in incidence.
It is better to walk to the kindergarten or school during such periods on the street, if you don’t go so far or take a private car to minimize the contact of the child with possible infected people in public transport.
Gauze bandages - a subject necessary for the diseased. They somewhat reduce the entry into the environment of virus particles with exhaled air, saliva, nasal mucus particles. For healthy people, gauze dressings are not needed, they do not protect against infection.
Drugs that are often marketed as prophylactic usually refer to homeopathic or antiviral remedies described above (“Immunal"," Anaferon "). The effectiveness of their reception for the prevention of SARS is also not proven and is not subject to evaluation.. But taking vitamins approved by your pediatrician for a particular children's age can have a beneficial effect on the child’s immunity.When choosing, preference should be given to those complexes that contain a sufficiently large amount of vitamins C, A, group B.
Although personal hygiene measures are insignificant in the extent of viral respiratory infection, they should also not be forgotten.
There is nothing wrong with the child being accustomed from childhood to washing his hands after returning from the street, before eating, not to put other people's toys and personal items in his mouth. Such good habits will definitely not contribute to the incidence of ARVI.
If the children who visit the child get sick, it is best to find the opportunity to sit with the child for a week at home.
How to treat ARVI in children, see the following video.