What is dangerous low placenta previa during pregnancy and what to do?
The low location of the placenta scares the expectant mothers and causes them a lot of fears about the outcome of pregnancy and childbirth. What is its danger and what to do if the diagnosis "low placental" has already sounded, we will tell in this material.
What it is
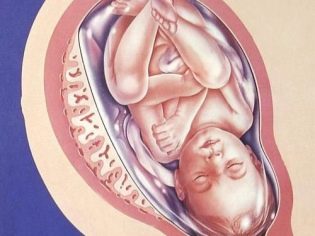
The placenta is a unique organ. It appears only during pregnancy and disappears after the birth of the child. The task of the placenta is to provide the baby with food, the delivery of all the substances necessary for its normal growth and development, vitamins, oxygen. At the same time, the placenta helps to excrete the products of the metabolism of the baby into the mother's body.
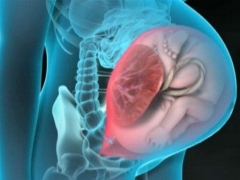
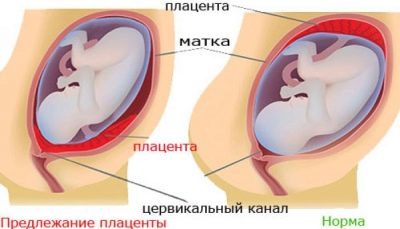
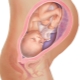
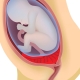
Placenta previa is a concept that designates the location of this temporary and very necessary organ in the uterine cavity. Presentation is always a pathology, because the term itself has the meaning of finding the placenta on the path that the child will need to pass during childbirth.
Normally, the place of attachment of the placenta should be such that the baby’s “baby seat” does not interfere with being born into the world. If it is a presentation, it means that the placenta is located low, partially or completely blocked the exit to the small pelvis.
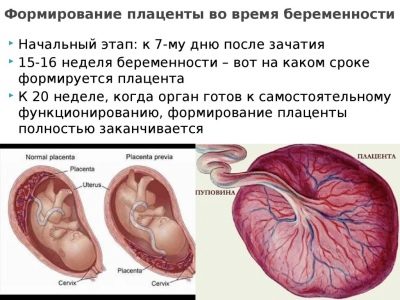
Low placentation occurs quite often in early pregnancy. Before the 20th week of pregnancy, partial or regional presentation is recorded in approximately 10% of pregnant women. But the placenta has the ability to rise above the cervical region following the uterus walls that grow along with the fetus. Therefore, by the 30th week of pregnancy, previa is present only in 3% of pregnant women, and by the 40th week - only in 0.5-1% of expectant mothers. The process of raising the placenta above is called migration.
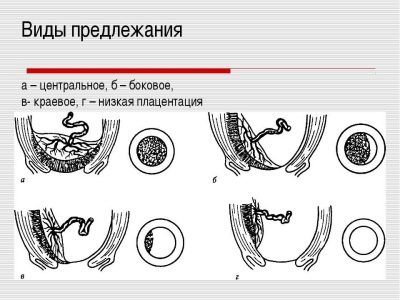
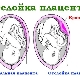
The placenta is finally formed only by 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. Prior to this, the place of "growth" of the ovum in the endometrium is called the chorion. Presentation is of three types.
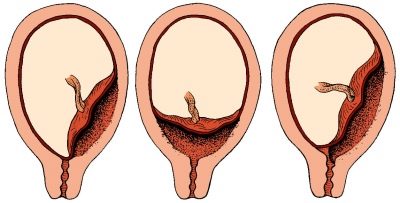
- Complete - the internal pharynx is completely blocked by the placenta. This is a very dangerous threatening condition in which independent deliveries are impossible and the fetus or mother is likely to die as a result of spontaneous massive bleeding.
- Incomplete - The placenta partially covers the internal orifice of the cervix. Independent natural childbirth, in most cases, is also impossible, the danger to the baby and mother is great.
- Low or lower - The placenta is located above the entrance to the cervical canal, but the distance from it to the "children's place" does not exceed 7 centimeters. Internal pharynx is not closed by the placenta. If the “children's place” is located too low and affects the edge of the throat, the presentation is called marginal.
Natural childbirth with such a presentation of the placenta is quite possible, however, they will require special attention from doctors, and from pregnant women - the utmost caution in the process of gestation.
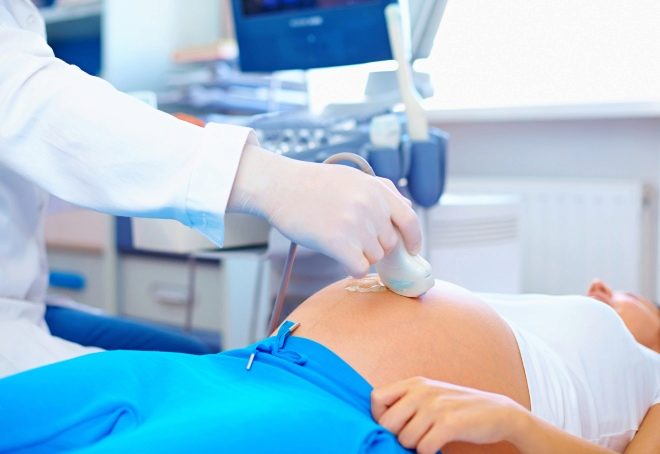
Doctors can determine the type and degree of presentation by ultrasound scanning. With each planned ultrasound placenta paid close attention. Its localization is determined by the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus, as well as the distance from the internal pharynx (entrance to the cervical canal) to the edge of the “children's place” is measured.
If it is at least 3 centimeters, the diagnosis is “low placentation” or “first placenta previa”.
It should be noted that bottom previa - the safest of all three types of presentations. The forecasts of the doctors with him are more favorable, but such an arrangement of the “children's place”, of course, is not a variant of the norm. Certain hazards and risks exist.
Causes of low placentation
By and large, it is almost impossible to somehow influence the place of formation of the placenta. It will appear where the fertilized egg can be fixed at the time of implantation.
A fertilized egg is implanted in the uterine cavity about 8-9 days after fertilization, from this moment the chorion forms, which subsequently becomes the placenta. It is impossible to determine exactly where the fertilized egg “floats”. But there are risk factors that increase the likelihood that the blastocyst will fix too low.
First of all, such factors include pathologies of the structure of the uterus, diseases of the female reproductive system, the consequences of surgical interventions.
Thus, in women suffering from endometrial inflammatory processes, undergoing abortions or other curetats, with a history of cesarean section, the chances of a low placentation during subsequent pregnancy are higher. Such causes are called uterine or intrauterine. These include:
- endometriosis;
- surgeries performed on the uterus - (abortion, removal of fibroids, diagnostic curettage, cesarean section);
- complicated previous childbirth;
- uterine fibroids;
- hypoplasia and abnormal congenital structure of the body of the uterus;
- failure of the cervix (cervical insufficiency);
- pregnancy with multiple fruits at the same time.
The reason for the fixation of the ovum in the lower part of the uterus may be the enzymatic insufficiency of the fetal membranes. Such reasons for the development of low placenta called fetal. These include:
- hormonal disorders in women;
- inflammatory diseases of the appendages, fallopian tubes, ovaries.
With repeated pregnancy, low location of the placenta is more likely than during the first pregnancy. The more a woman gives birth, the higher the probability of developing lower placentation with each subsequent pregnancy.
It is believed that women who are overweight and women who could not quit smoking with the onset of pregnancy are also at risk. If, in a previous pregnancy, the placenta was located low, with a high probability, according to experts, the “baby seat” will be located below and in the subsequent pregnancy. In addition, there is a certain genetic dependence - a woman may inherit a tendency to placenta from his own mother.
Diagnosis and symptoms
Blood flow at any time during pregnancy may indicate a low placenta previa. A doctor may be confused by elevated heights in the uterus, which are ahead of the actual gestational age, as well as improper location of the fetus in the uterine cavity - the pelvic or transverse presentation of the baby is often accompanied by low placentation.
Bleeding from the genital tract with a lower prevalence of placenta usually first appear after 12-13 weeks of pregnancy. They may be more or less abundant. Often they go on to the birth.
But the most common bleeding in the last trimester of pregnancy, when the walls of the uterus are stretched to such an extent that there are partial microvolume "baby seats" from the uterine endometrium.
In a third of pregnant women with low placentation, such bleeding occurs after 35 weeks of gestation. Six out of ten women show quite heavy bleeding during childbirth.Even unwary, severe coughing, laughter, sex, constipation, physical exertion and severe stress can provoke bleeding in pregnant women with a low position of the placenta. Any tension of the uterine muscles is dangerously small detachment and exposure of blood vessels.
In women who have low placental manifestations of episodic or persistent bleeding, the level of hemoglobin is reduced, anemia develops, low blood pressure, dizziness, and bouts of sudden weakness are often observed.
If you suspect placenta previa, the doctor does not perform a manual intravaginal examination, because it can provoke premature birth or bleeding, which can be fatal for both the fetus and the pregnant woman.
The best way to diagnose ultrasound is considered. Ultrasound allows determining the position of the “children's place” with millimeter accuracy.
Sometimes the low position of the placenta has no symptoms. The woman does not complain about anything, and only the ultrasound doctor at the next examination draws attention to the fact that the “baby seat” is lower than we would like. In this case, more careful monitoring of the state of the placenta is required: control ultrasounds, designed to track the migration process, are appointed and carried out at 12, 20 (or 21-22) a week and at 30 weeks. If necessary, more frequent scans can be recommended.
Danger and risks
What threatens the low placental location is not difficult to guess. In the early stages it is dangerous for a spontaneous miscarriage, and for a more substantial period of gestation it is threatened with premature birth. Women with this problem at the end of the second and third trimesters often develop preeclampsia, which only increases the risk of adverse outcome. Half of pregnant women have iron deficiency anemia.
If the placenta in the early stages was formed and attached low, then the probability that the child will assume an abnormal position in the uterus, increases by 50%. The child will instinctively choose a position in which his head will not come into contact with anything, including the placenta.
The baby is more likely to receive not a headache, but a pelvic presentation, which makes it very difficult for the childbirth process or will generally be an indication for a cesarean section.
For a baby, a low-lying placenta is a risk factor for the likelihood of hypoxia. Prolonged chronic oxygen deprivation can cause the death of the little ones, irreversible changes in the structures of his brain.
Also, placental insufficiency, which develops if the “baby seat” is omitted, can lead to a delay in fetal development. The lower part of the uterus is worse supplied with blood than the body and the bottom of the uterus, which is why the baby will receive less of the necessary nutrients.
The abnormal location of the organ feeding the baby is dangerous. If the placenta is attached low, the woman at any time may experience bleeding, which can have very sad consequences.
Treatment
Despite the level of modern medicine, there is no universal treatment for low placentation. There are no such pills and shots to raise the "baby seat" above. One can only hope that the migration will occur independently, and in most cases this is exactly what happens.
The task of the doctors is to quickly cope with periodic bleeding and preserve pregnancy as long as possible: until the baby is fully viable. The implementation of medical recommendations is the first priority for every pregnant woman with a low-lying placenta.
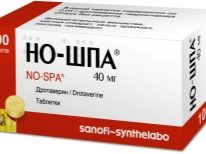
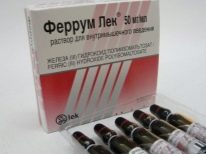
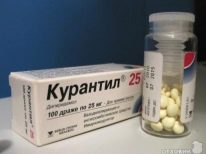
To reduce the tone of the uterus, antispasmodic drugs are prescribed: “No-shpa, Papaverine, ginipral. To compensate for the iron deficiency of a pregnant woman, it is recommended to take iron preparations in courses.Ferrum Lek"," Sorbifer ".For better uteroplacental blood flow, for eliminating the symptoms of delayed development of the baby, fetoplacental insufficiency, “Curantine”, “Trental”, as well as folic acid, B vitamins are recommended, “AskorutinAnd vitamin E in large therapeutic doses.
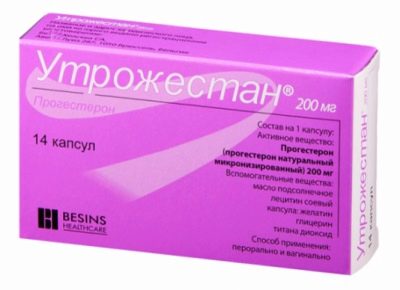
Quite often, a woman is recommended daily administration of a solution of magnesia intramuscularly (10 ml each) and “Magne B 6” in tablets twice a day. If there is a hormonal deficiency, prescribe "Utrozhestan" or "Duphaston" in individual dosage. With asymptomatic treatment, you can be treated at home, with frequent episodes of bleeding, it is recommended to undergo treatment in a day hospital at a gynecological specialized clinic.
In the later periods, a woman will have to visit a gynecologist and fetal CTG more often than other pregnant women to make sure that the baby’s heart activity is normal and there is no pronounced oxygen starvation. Drug therapy is likely to continue until the birth, if the placenta does not rise.
Recommendations to the future mother
As already mentioned, a woman will have to be extremely careful. She is prescribed a quiet mode, she is contraindicated stressful situations, exercise, weight lifting, leaning forward. With a low placenta on no time can not jump, travel on uneven roads by car or bus, because shaking can cause severe bleeding.
A woman can not have sex, because orgasm stimulates the uterine muscles, which will increase the likelihood of placental abruption. Not only sexual intercourse is prohibited, but also other forms of sexual satisfaction - oral, anal sex, and masturbation. Any action that could lead to a reduction in the uterine muscles is contraindicated.
Also undesirable travel by air. The optimal posture for relaxation (and you need to rest at any free moment) is lying on your back with your legs upside down. If you cannot lie down (the woman is at work), you should raise your legs higher in the sitting position.
To do this, you can use a small improvised stand under your feet.
How to give birth?
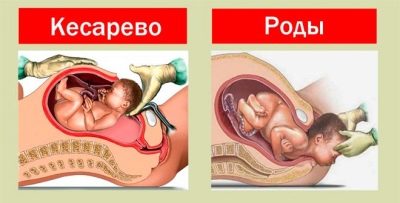
With a low placentation, labor can take place both naturally and by surgical operation - cesarean section. The final decision on the tactics of obstetric care is determined at approximately 35-36 weeks of gestation according to the results of the control ultrasound.
If the placenta has not risen, doctors will most likely recommend prompt delivery. A cesarean section is performed if a woman has a low-lying placenta combined with pelvic or transverse fetal presentation, if she is pregnant with twins or triplets, if there are scars on the uterus from previous surgical procedures.
Also, pregnant women over 30 years old who have undergone several abortions and who have a burdened gynecological history are trying to direct the operation. If the pregnancy was accompanied by regular bleeding, it may also be considered to conduct a planned cesarean section.
Sometimes the need for emergency surgery occurs already in the process of childbirth, for example, if the bleeding does not stop after the discharge of water, if there is a weakness of labor forces.
In the absence of bleeding, ready and mature cervix, normal pelvic size, a small child who is in the head occipital presentation, independent childbirth is allowed.
Stimulation of labor with medicines with low previa is not carried out in any case, labor activity must develop independently.
Reviews
According to reviews left by moms on the Internet, in most cases, by week 30, the position of the placenta was established within the normal range. This means that the violations detected at week 20-21 are not a sentence, but only a temporary difficulty.Childbirth with a low placenta also, in most cases, proceeded quite satisfactorily, healthy babies were born.
During pregnancy, according to women, it is quite difficult to constantly comply with all the recommendations, the most intimate prohibition on intimate relationships. Many because of this temporarily spoil the relationship with her spouse, pregnancy proceeds against the background of experiences and stress.
About what dangerously low placenta previa, see the following video.