Antibiotics for pneumonia in children
Medicine and pharmacology step forward, develop. But some dangerous diseases keep up with them. They are also developing and gaining momentum. So it turns out, in particular, with pneumonia. The number of cases of pneumonia in children, despite a general improvement in the quality of life, is growing. This is evidenced by impartial statistics: pneumonia is the unconditional leader in infant mortality (18% of all fatal cases for children aged 1-5 years).
Almost one and a half million children die of pneumonia every year in the world. This is more than the sum of AIDS and measles. In every third sick child, the symptoms of pneumonia are confused with other symptoms, and the pneumonia goes into a prolonged form. And the most, in my opinion, is sad: with all the modern development of the pharmaceutical business, the variety of drugs, only one-third of young patients receive the necessary and proper antibiotics for treatment.
Pediatric pneumonia and its antibacterial treatment ... What should parents know about the ailment, and what antibiotics can prescribe a doctor to our little ones if pneumonia suddenly happens to them?
What it is?
In fact, pneumonia is a very dangerous and unpleasant disease. No wonder the grandmothers were so afraid of her. The main cunning of pneumonia lies in the fact that the symptoms of illness are skillfully hidden behind the symptoms of the common cold. It is difficult to recognize. And it is advisable to do it in time to cure pneumonia in the early stages.
Pneumonia in children is typical and atypical. Doctors also divide the types of the disease into hospital and community-acquired. The difference between the species - in the name of the microorganism - the causative agent of the disease. Most often, pneumonia causes pneumococci. These are the sticks living in the nasal passages and cavities. They are afraid of antibiotics, and pneumonia, caused by missed pneumococci, is usually easily treated.
Crumbs under the age of 6 years can be caused by a Hemophilus bacillus, while in schoolchildren the "culprits" of the disease are often Mycoplasma and Chlamydia pneumonia.
There is also aspiration pneumonia - inflammation of the lungs in a child occurs for "mechanical" reasons - water has got into the lungs, food, or there is an alien body in the airways.
How to recognize?
I will say right away that in it is almost impossible to determine if a child has pneumonia, because the main method of diagnosing this disease is radiography. Only after the baby takes a picture and takes blood and sputum for analysis, can we speak with confidence about the diagnosis.
When to go to the doctor?
The symptoms of pneumonia, as already mentioned, are very similar to the symptoms of most colds and viral diseases. But there are nuances. So, you can suspect pneumonia in a child if:
- Temperature the body of the baby rose above 38 degrees and lasts more than three days,
- The baby has no appetite,
- The child wants to sleep all the time and complains of fatigue,
- He has difficulty breathing, shortness of breath,
- The baby's lips and skin become blue (the so-called "cyanosis" is observed),
- The number of breaths per minute more than 40,
- The baby sweats a lot, complains of chest pain,
- On the part of the patient's lung, the skin “breathes” into the intercostal space as it breathes.
Why is it important to diagnose pneumonia in a timely manner? Because pneumonia is fraught with serious complications for the child: disorders of the heart, other organs. Pleurisy may develop, in which cavities form in the lungs with pus. We already know about the lethal outcome in pneumonia.
Treatment
Treatment of pneumonia in children is always prescribed in combination: vitamins, antihistamines and antibiotics. Although antibiotics would be worth putting on the list first, since, in fact, treatment would be built on them.
The question of hospitalization must be decided by a doctor. Now many doctors rather loyally look at the course of treatment for pneumonia at home. Of course, if the medic has no fears for the life of the young patient.
Children under 1 year must be placed in the hospital to avoid unforeseen complications of pneumonia. And to argue with the doctor is not worth it - it is a matter of life and death for your child.
In cases with older children, the doctor will assess the degree of development and form of the disease. The common perception that the treatment of pneumonia will necessarily require a huge amount of injections is wrong at the root. Many doctors, including the famous doctor Komarovsky, argue that pneumonia is perfectly treated with pills, if the disease is not protracted, not running, and proceeds without complications. In such situations, the doctor may allow you to treat the child at home.
The release of Dr. Komarovsky’s pneumonia program is below:
For kids, home treatment is definitely better. In familiar surroundings, surrounded by people close to him and understood by him, recovery occurs faster. Provided that you can provide the crumbs with good nutrition and meticulous care.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs have long proven to be highly effective in the fight against pneumonia pathogens. If the disease is detected at an early stage, then, most likely, the doctor will prescribe a baby from the penicillin group. If the disease is not severe - the drug can be taken in pills or suspensionsif the doctor insists on intramuscular or intravenous administration, do not argue - the doctor knows best. Here are the names that parents want to know:
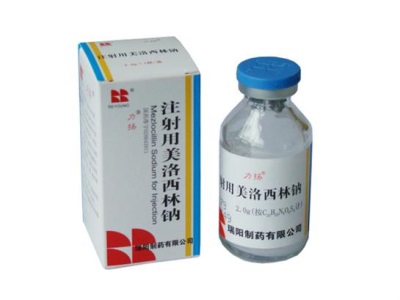
Mezlocillin - An antibiotic of the penicillin family of semi-synthetic origin. His children are only pricked, since the release form of the antibiotic is a dry substance for injection. In pharmacies you can find bottles of 0.5 g, 1 g, 2.5 g and 10 g. Small infants (whose weight is less than three kilograms) and premature babies, the drug is given in a dose of 75 mg of an agent per 1 kg of body weight twice a day. Infants weighing more than 3 kilos, as well as children up to the age of 14, are also counted on - 75 mg per 1 kg of weight, but already three times a day.
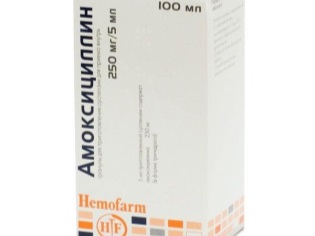
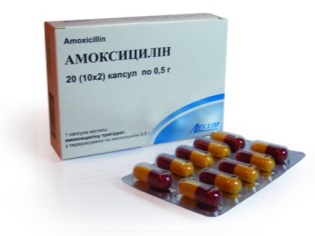
Amoxicillin - broad-spectrum antibioticwhich can not be appointed in injections, because it does not exist in this form. This drug can be taken to children from birth. Antibiotic on the shelves of pharmacies exists in the form of capsules and granules for self-preparation of the suspension. Preparing is simple - cool boiled water is added to the mark on the bottle. After thorough mixing and stirring, you get a pleasant mass for the child with strawberry or raspberry flavor and taste.
Young patients under the age of 2 years can be given a suspension at the rate of 20 mg of the drug per kg of body weight per day. Do not forget to divide the resulting dose into three equal doses. Children from 3 years old can take half a measuring spoon of the suspension three times a day, and children after 5 years of age will have to divide an entire measuring spoon into three daily doses. Remember that the bottle with the finished suspension can only be stored for 14 days.
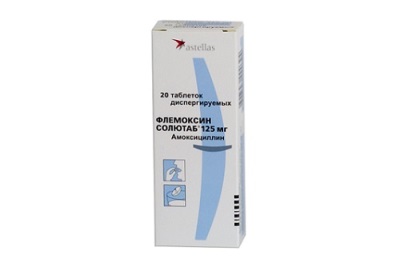
Flemoxin - semi-synthetic penicillin, improved version Amoxicillin. In suspension, this drug is not available. Children's option is tablets at a dosage of 125 and 150 mg. But these pills are easy for children to take - they are absorbed in the mouth, or they can be diluted with a small amount of water and drunk. The dose for the treatment of your child should be calculated by the doctor.
If the form of pneumonia is not strong, and the stage is not running, the doctor may also prescribe macrolide antibiotics:
Erythromycin - the most famous of the antibiotics of the Macrolides family. Available in tablets. Take the drug is not recommended for children under the age of 4 months. When pneumonia, the dose of the antibiotic to babies is calculated on the basis of the formula - 50 mg of medicine per 1 kilogram of the child’s weight, divided into four equal doses per day. The average course of treatment is 21 days.
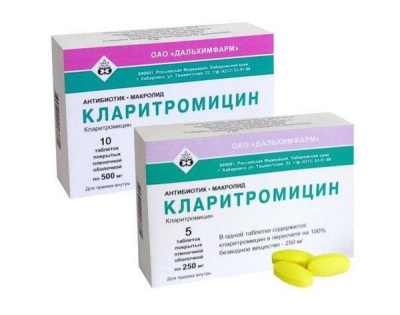
Clarithromycin - An antibiotic is a microlide, which you will find in pharmacies in the form of tablets and capsules. The drug is prescribed to babies who have reached the age of 6 months. The dosage and number of doses per day prescribed by the doctor. Children who have reached the age of 12 can drink 250 mg of antibiotic twice a day.
If the doctor considers that the child has a complicated form of pneumonia, the illness was not diagnosed immediately, then he can prescribe antibiotics - cephalosporins:
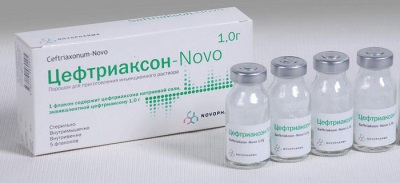
Ceftriaxone - broad-spectrum antibiotic with the strongest anti-bacterial effect. It is produced only in the form of a dry mixture for injection. Crumbs from birth to two weeks should receive the drug in the hospital and under medical supervision. The rest of the guys up to 12 years old - one injection per day (20-80 mg. Drug per kilogram of child's weight). For children whose weight has passed over the 50 kilo mark, the doctor prescribes an adult dose of antibiotic. Ceftizoxime - this antibiotic is also available only in the form of powder for injection.
If a child weighs less than 50 kg, he is allowed to administer from 50 to 180 mg of medicine per 1 kilogram of weight from 2 to 6 times a day. The duration of the course of treatment will be determined by the doctor.
What should not be done during treatment?
- Give baby antipyretic drugs. The doctor will be able to evaluate the effectiveness of the prescribed antibiotic when the natural decrease in temperature begins. Antipyretics can distort the treatment pattern.
- Limit the child to drink. In the treatment of pneumonia, it is important to prevent intoxication of the body, for this the child needs to drink a lot and abundantly - water, tea, vitamin herbal preparations, compotes.
- Abruptly cancel antibiotics after improvement.
And finally, do not “chase” antibiotics for fashion. The tool of the last generation, of course, quickly put on its feet and cope with the infection, but the children's body will become insensitive to antibiotics of previous generations.
For information on when a child should be given antibiotics and what is worth considering, see Dr. Komarovsky’s program.