Vaccination against pneumonia in children from pneumococcal infection
Vaccination against diseases caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is called a pneumococcal infection, began in our country not so long ago. Therefore, this vaccine raises many questions from parents. Why vaccinate babies for pneumonia and other pneumococcal infections and how should such a vaccination be carried out correctly?
pros
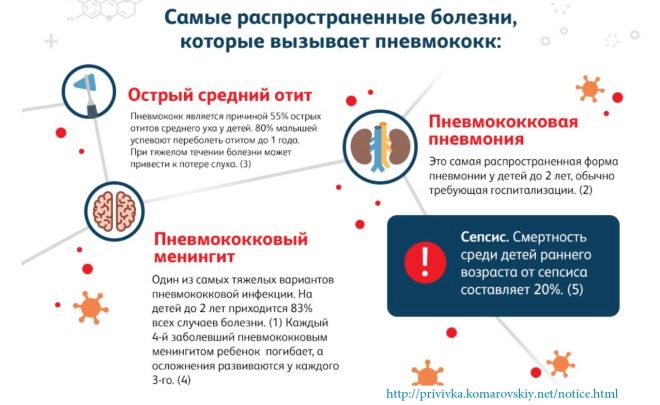
- The vaccine acts on pneumococci, protecting the child from pneumonia, endocarditis, otitis, meningitis, arthritis and other infections caused by this type of streptococcus. Even if the disease appears, its course will be easy.
- Pneumococcal vaccines rarely cause adverse reactions.
- There are very few contraindications for this vaccine.
Minuses
- Vaccine components, although extremely rare, can cause severe allergic reactions.
- In Prevenar vaccine, there are not all pneumococcal serotypes that can cause infections in children.
- Immunocompromised children suffer poorly from this vaccine.
Contraindications
Vaccination is not done if:
- The child revealed intolerance to pneumococcal vaccine.
- The baby has an acute illness or any chronic illness has become exacerbated.
- The body temperature of the child is elevated.
In case of intolerance, vaccination with pneumococcal vaccine is canceled, and in other cases it is postponed until the baby recovers. After a blood transfusion, vaccination is carried out in 3-4 months. If you ignore the contraindications and instill a sick baby, his condition will worsen dramatically.
You can learn more about pneumococcus by watching the following video.
Side effect
Pneumococcal vaccine rarely produces side effects; they are usually presented:
- The appearance of a seal at the injection site, pain, and redness. It happens in 5% of kids.
- A slight increase in temperature in 1% of children.
- Drowsiness, tearfulness, irritability, decreased appetite, lethargy.
Possible complications
The introduction of pneumococcal vaccine can cause an immediate allergic reaction - urticaria, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock. If the vaccine is given to a premature baby, he may stop breathing.
Other complications can be:
- Severe local reaction - on the limbs, there is redness and swelling more than 8 mm.
- High body temperature - more than 39 degrees.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Abscess at the injection site.
- Diarrhea and bouts of vomiting.
- Exacerbation of chronic disease.
Is it possible to prevent complications?
To prevent the occurrence of a reaction to pneumococcal vaccine, you need to monitor the baby for 2-3 weeks before the vaccination date. Making sure that the baby is completely healthy, his body temperature is normal, the oropharynx is not hyperemic, there is no rhinitis, and chronic diseases are under control, we can safely inoculate against pneumococcus.
Having put the vaccine, you do not need to leave the medical facility for at least 30 minutes to make sure that there will be no immediate allergic reaction to the vaccine. Immediately after vaccination, it is better to limit the contact of the baby with strangers for several days.
Should I vaccinate?
Since studies have shown that babies up to 2 years old are most susceptible to pneumococci, vaccination against such bacteria can be called a justified step. All the diseases that this vaccine protects against are very serious and pose a great danger to young children.
Any illness, even a simple cold, can lead to the activation of pneumococci. And the best prevention can be called timely immunization with pneumococcal vaccine. This vaccine is especially important for weakened children, because they have a higher risk of developing pneumonia.
Vaccination scheme
Currently, vaccination against pneumococcal infection is carried out with two foreign drugs - the American vaccine Prevenar and the French drug Pneumo-23. The first vaccine can be administered to babies from 2-3 months, and the second - only from 2 years of age.
The introduction of pneumococcal vaccine can be combined with any other vaccinations, except BCG. In this case, injections are made in different parts of the body.
Depending on the age of the baby, the pneumococcal vaccine is administered according to this scheme:
- Babies from two to six months are given the vaccine 3 times (the interval between vaccinations is from 1 to 1.5 months), after which revaccination is performed at 11-15 months.
- Children over the age of seven months up to 23 months are vaccinated twice (the interval between vaccinations is the same), and the child is revaccinated by the age of two.
- After 2 years, the vaccine is administered once.
Opinion E. Komarovsky
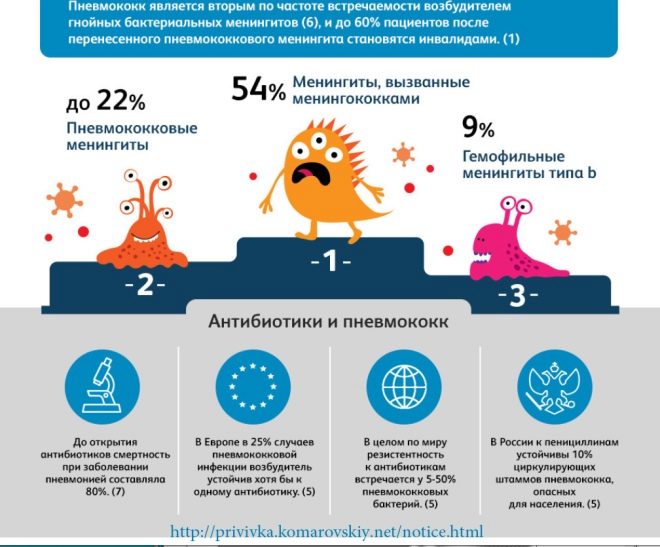
A popular pediatrician advises vaccinating children against pneumococcal infection, as this will help to avoid serious diseases. The most severe pathology caused by pneumococci is meningitis. Such a disease often ends in death, and 30% of the surviving babies still have neurological problems. Vaccination helps reduce the occurrence of meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae by 90%.
Also for young children, pneumonia is very dangerous. In babies up to 2 years, the risk of respiratory failure and pulmonary edema with such infectious lesions is very high. And the infection otitis is unpleasant for a baby and dangerous for hearing. These diseases can also be prevented or alleviated if the child is vaccinated in a timely manner. Komarovsky considers pneumococcal vaccine a safe drug.
Vaccination up to a year
In the first year of a child’s life, only Prevenar is vaccinated. The vaccine is administered three times before the year - usually babies are vaccinated at three, four and five months of age.
Training
Before the baby is vaccinated against pneumococcus, the child should be examined and determined whether he is completely healthy at the moment. It is best to get vaccinated on the day your pediatrician takes healthy children. This will prevent the simultaneous infection of ARVI from sick children in the queue. Antihistamine drugs are indicated only for children with allergies.
How to make an injection?
Pneumococcal vaccine is administered intramuscularly. Children younger than two years old are given a shot in the muscles of the anterior surface of the thigh, and babies older than 2 years of age are injected into the shoulder (the deltoid muscle).
What if there are adverse reactions?
If the injection site becomes red, it becomes dense and painful, you need to take care of it properly. You can bathe the child, but the treatment of the injection site antiseptics It is not recommended, as is the use of a compress or patch.
When the temperature rises, the child can be given an approved antipyretic drug. If parents notice that the condition of the baby is worsening and the side effects of vaccination do not go away, it is important to immediately contact a pediatrician.
Reviews
Some parents are opposed to such vaccinations, because they believe that the vaccination schedule for children under 2 years of age includes too many vaccinations.At the same time, they agree to learn more about the vaccine and, if necessary, for example, with frequent diseases, vaccinate their children.
Other parents treat the pneumococcal vaccine positively, believing that it is better to protect their baby from possible risks than to later regret the lost opportunity. And since such a vaccine is included in the national calendar, this cannot be an accident, respectively, the drug was checked and the need for such vaccination for Russian children was assessed.
Watch the following video from the Union of Pediatricians of Russia about pneumococcal infection.