Pneumonia in premature babies
Pneumonia is a very common pathology in children who were born ahead of time. Why can such a disease develop in such babies, how is it treated and is it possible to prevent its appearance in babies?
Special features
- Congenital pneumonia in prematurity is much more common than in children who were born on time.
- The frequency of aspiration pneumonia in these children is also increased due to their tendency to regurgitation.
- The disease is often combined with circulatory problems, intestinal infection, hemolytic disease, and other pathologies.
- The acute period of the disease in preterm babies lasts longer.
- The dominant symptoms of the disease in newborns are manifestations of respiratory failure and intoxication.
- Fever in premature babies is less common in hypothermia.
- Very often there are complications that can be extrapulmonary.
- Pneumonia with prematurity often leads to the development of sepsis.
The reasons
Inflammation of the lungs in premature babies is caused by bacteria, parasites, fungi or viruses. Various factors contribute to their entry into the airways of the infant, among which the main ones are called pulmonary immaturity, aspiration during labor, infection during fetal development and SARS.
Alveoli in the lungs of an infant who was born before the prescribed time are generally not sufficiently straightened, and the surfactant may be of poor quality or immature. Besidessuch babies in the lungs immediately after childbirth disrupt metabolic processes and circulatory disorders are observed.
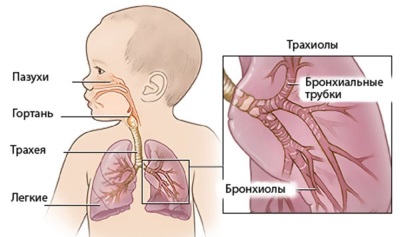
With regard to predisposing factors, the appearance of pneumonia in premature babies can be triggered by:
- Cesarean section.
- Problems with gestation, which led to hypoxia or asphyxia.
- Infectious diseases in a pregnant woman, affecting the respiratory or urinary system.
- Hereditary diseases of the respiratory system (pneumopathies).
- Lesions of the child's central nervous system, as well as birth injuries affecting the spinal cord or brain.
- Resuscitation during childbirth.
- Developmental defects in the baby.
- Improper care of the baby, for example, a long stay of the baby in one position, poor ventilation of the room, overcooling of the baby or its overheating.
- Poor sanitary and epidemiological conditions in the hospital.
How is resuscitation of newborns, see the training video:
Parasitic pneumonia babies born premature are most often caused pneumocysts who can get to the baby from a sick person or carrier (often from the staff in the hospital).
Fungal pneumoniathat most often cause candida, appear due to candidiasis in the mother or as the result of irrational treatment of premature broad spectrum antibiotics.
Pneumonia forms
Depending on the cause and circumstances contributing to the occurrence of pneumonia, pneumonia is:
- Congenital. The baby is infected transplacentally, that is, from the mother the pathogen enters the body crumbs through the placenta. Most often it is pneumonia caused by the rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasma, listeria, herpes virus, mycoplasma and other pathogens.
- Antenatal. A child becomes infected during childbirth, when it passes through an infected birth canal or the amniotic fluid containing the pathogen enters its lungs. Typically, such pneumonia causes mycoplasmas, streptococci, hemophilus bacilli, candida, trichomonads, ureaplasmas, listeria, tubercle bacilli, herpes viruses, chlamydia and other infectious agents.
- Postnatal. Baby gets infected after giving birth in a hospital or at home. Such inflammations are mainly caused by Klebsiella, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Proteus, Pseudomonas bacillus, Enterobacteria and other pathogens.
Symptoms
At the onset of the disease, non-specific signs may prevail. The general condition of the infant is deteriorating, body weight can change dramatically due to the appearance of edema. Also, pneumonia can manifest itself:
- Subfebrile or low fever.
- Inhibition.
- Bad sucking.
- Irritability.
- Pale skin.
- Bloating.
Further to such symptoms join breathing disorders. The baby begins to breathe often, the wings of the nose swell, wheezing becomes audible, there are attacks apnea, periodic breathing, coughing, there are retractions of gaps between the ribs, the frequency of contractions of the heart increases, frothy mucus can be released from the mouth.

Diagnostics
To identify pneumonia in a premature baby, use:
- Anamnestic data.
- The clinical picture.
- X-ray examination. On the radiograph in places of inflammation detect darkening.
- Laboratory data. In the blood of a child with pneumonia, a stab shift, a decrease in hemoglobin, a decrease in platelet count, and leukopenia will be noted. In addition to the clinical analysis of blood, children with suspected pneumonia are prescribed virological or bacteriological examination, urinalysis, and blood gas analysis.
Treatment
Pneumonia in preterm babies is treated only in a hospital setting. In this case, the babies should stay in special wards in the intensive care wards, and the mother is next to the crumbs and helps care for the baby.
The newborn should be in optimal conditions for him, to prevent either overheating or hypothermia baby. During the day, the position of the child is often changed, and clothing should not hamper the movements of the baby. The type of feeding and the amount of food received is determined by the doctor taking into account the condition of the infant, but nutrients are often administered to children with pneumonia parenterally.
Such methods are especially important in the treatment of such ailment of the newborn:
- Antibacterial drugs. In the first days of the antibiotic picked at random, using a wide range of tools. As soon as they receive the results of sowing and antibiogram, prescribe a drug to which the pathogen is sensitive. The drug is injected parenterally.
- Oxygen therapy. The baby is dosed with 35% preheated oxygen using a mask, a catheter or other devices.
- Passive immunization. The infant is prescribed the introduction of immunoglobulins and plasma.
- Other medications according to indications. If required, the child is given medications for the heart, probiotics, bronchodilators, glucocorticoids, and other medicines.
Some babies are assigned bronchoscopy for the rehabilitation of the lungs.Many children are recommended to perform massage - both general and vibratory.
Possible consequences and complications
Inflammation of the lungs in a premature infant may be complicated by atelectasis, pleurisy, pneumothorax, and other pulmonary pathologies. Among extrapulmonary complications in premature babies, they often diagnose hypotrophy, otitis media, hemodynamic disorders, sclerama, adrenal insufficiency, bleeding, and various metabolic disorders. One of the most dangerous complications of pneumonia in a premature baby is sepsis.
Babies with pneumonia increase the risk of anemia, thrush and rickets.. In addition, many babies develop pneumonia. bronchopulmonary dysplasia, which causes recurrent diseases of the lungs and bronchi.
Prevention
To prevent pneumonia in a premature baby, it is important to eliminate the factors that trigger the disease:
- Expectant mothers should monitor their health and promptly treat infections.
- In the maternity hospital and children's hospitals, it is important to strictly observe the sanitary and epidemiological regime.
- Born with asphyxia to the newborn should be timely and proper resuscitation.
- The babies should be applied immediately after birth to the breast and fed with breast milk.
- If a newborn, born prematurely, has respiratory disorders, and there are predisposing factors (difficult birth, maternal illness, and others), it is advisable to prescribe an antibiotic immediately after birth.
- At home, you need to monitor hygiene, microclimate and mode of the day of the newborn.