Symptoms and treatment of pneumonia in children
Pick up pneumonia can absolutely any child. Every mom with horror thinks about how dangerous the complications of this disease can be. How should parents behave if the baby has picked up pneumonia, as described in this article.
What it is?
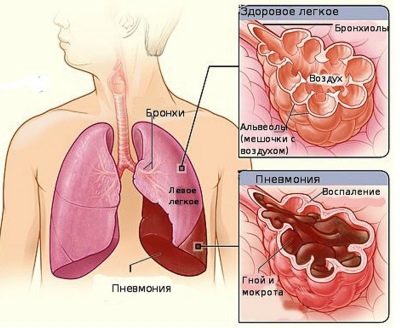
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung tissue. The development of this condition in a child can lead a variety of reasons.
In childhood, as a rule, the disease is very difficult.
At high risk of possible complications of the disease are weakened children and children suffering from concomitant chronic diseases.
The inflammatory process in the lungs triggers a cascade of various reactions that have a very adverse effect on the entire body. The complex of these disorders and leads to the appearance of numerous respiratory disorders in the baby.
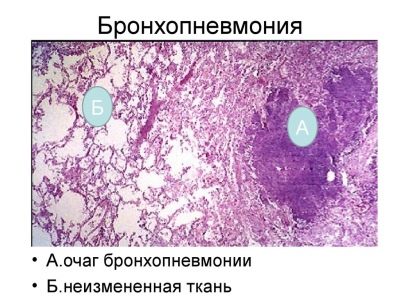
The severity of the disease depends largely on the initial state of health of the child. With local inflammation only in the lung tissue, doctors talk about the presence of pneumonia. If the bronchi are also involved in the inflammatory process, then this condition is already called bronchopneumonia.
The prevalence of this disease in the pediatric population is different. According to statistics, younger children are sick more often. Thus, the incidence of this disease in children under 5 years old is 20-25 cases per 1000 children. At an older age, this figure decreases and is 6-8 cases of 1 thousand children.
Among newborn babies, the prevalence of pneumonia is relatively rare. This feature in infants is largely due to the presence of specific antibodies, which they receive from mom during breastfeeding.
Maternal immunoglobulins protect the infant's fragile organism from a variety of infectious pathogens, which in most cases cause pneumonia.
Causes
Currently, there is a huge variety of different causal factors that contribute to the appearance of these symptoms in a child.
In the development of bronchopneumonia, infection of the baby with beta-hemolytic streptococcus plays a huge role. Also, these microbes often cause interstitial forms of the disease. Streptococcal pneumonia is very contagious to others.
The presence of streptococcus in the throat of a child is an extremely unfavorable situation. In this case, an infected baby can easily infect a healthy one. A decrease in immunity in such a situation leads to the rapid infection of the child’s body and the development of adverse symptoms.
Streptococcal infection, as a rule, is rapidly spreading in crowded groups that are visited by a large number of children.
It is important to note that streptococcal pneumonia in a baby may also occur during the period of intrauterine development.
In this case, the infected mother passes the infection to her baby.Infection occurs through the placental blood flow system. Streptococci have a very small size, which allows them to quite easily get into the common system of placental arteries and reach the lungs and bronchi of the fetus.
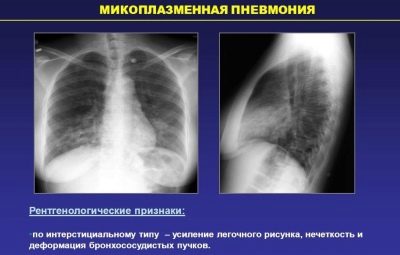
Every third pneumonia in babies, according to statistics, occurs due to infection with mycoplasma. Infection with these microorganisms can occur in many different ways.
Many scientists believe that the development of a mycoplasmal variant of pneumonia requires additional aggravating conditions. These include a general decrease in immunity or the initially weakened condition of the child.
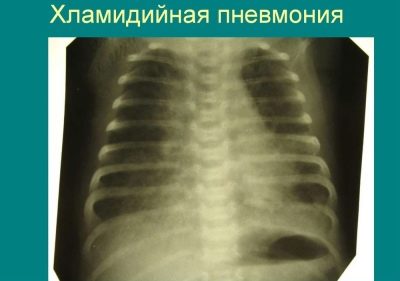
Another similar microorganism that leads to the development of pneumonia in babies is chlamydia. It causes infection much less frequently. In most cases, cases of infection with chlamydia infection through the blood are recorded.
Pediatric doctors allocate a lot of cases of intrauterine infection. Chlamydial pneumonia is usually sluggish and is manifested by the appearance of very blurred adverse symptoms of the disease.
In almost a quarter of all cases, pneumonia is caused by pneumococci. These microorganisms "prefer" to live and multiply in the lung tissue, since there for them there are the most optimal conditions for life.
The course of pneumococcal infection is usually accompanied by the development of violent adverse symptoms of the disease. The disease proceeds quite brightly. This clinical variant of the disease can cause the appearance of various complications in a sick child.
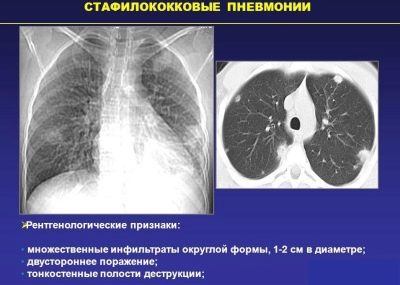
Staphylococcal flora can also cause disease in babies. The most aggressive pathogen is Staphylococcus aureus.
According to statistics, the peak incidence occurs in the preschool age. Toddlers attending educational institutions have a higher risk of infection with staphylococcal flora. Quite often, massive outbreaks of staphylococcal pneumonia are recorded in children during the cold season.
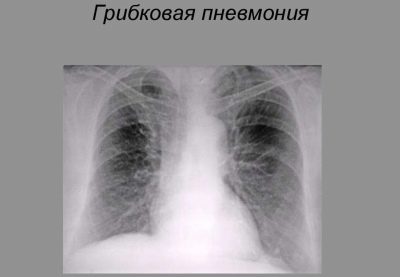
Rarely infection of the fungal flora leads to the development of pneumonia. This form of the disease is often found in children who suffer from diabetes.
Immunodeficiency pathologies are also important in the development of pneumonia in a child.
The course of the disease is usually long and is accompanied by a long development of all uncomfortable clinical manifestations of the disease. To eliminate them, a course of special antifungal drugs, as well as immunostimulating agents, is required.
There are alternative microorganisms that can cause pneumonia in babies. It should be noted that they lead to the formation of pneumonia less frequently. These include: E. coli, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, hemophilic and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pneumocystis and legionella.
In some cases, pneumonia occurs as a complication of previously transferred viral infections. Specific childhood diseases are often the causes of the development of inflammation in the lungs. Such infections include rubella, influenza and parainfluenza, cytomegalovirus and adenovirus infection, chickenpox, herpes infection of different origin.
The course of viral pneumonia is accompanied, as a rule, by the development of numerous symptoms of the disease, which are manifested in a sick baby quite rapidly.
Doctors identify several options for the development of the course of this disease:
- Children who become ill at home are most often infected with a hemophilic rod or pneumococcus.
- Kids attending preschool educational institutions quite often develop the mycoplasma and streptococcal form of the disease.
- Schoolchildren and adolescents are at high risk of developing chlamydial disease.
The course and development of the disease are also influenced by a variety of factors.Their impact greatly weakens the children's body and leads to the progression of the disease. These factors include:
- Frequent colds. If a baby is sick with ARVI or ORZ several times over the course of a year, then he has a rather high risk of developing pneumonia.
- Concomitant chronic diseases of internal organs. Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases top the list of pathologies affecting the general condition of the child’s body.
Cardiovascular diseases, which are quite difficult, also lead to a weakening of the health of the child.
- Psychosomatics. This factor is most significant in adolescents. Strong or prolonged psycho-emotional stress contributes to the depletion of the immune system, which ultimately leads to the possible development of pneumonia in the baby.
- Severe hypothermia. Some children only need to soak their feet strongly in order to catch pneumonia. Ineffective immune system in babies and inadequate thermoregulation only exacerbate the process.
- Inadequate intake of trace elements. Reducing the intake of vitamins with food contributes to the violation of metabolic processes in the body. This is especially dangerous during periods of intensive growth and development of the baby.
- Immunodeficiency states. They can be either congenital or acquired pathologies. Reduced work of the immune system contributes to the active reproduction in the children's body of various microorganisms, which are the root cause of the development of this disease.
- Aspiration. The ingress of the acidic contents of the stomach into the respiratory tract causes damage to the lung tissue in babies. Most often this situation occurs in the smallest patients during regurgitation. Inhalation of a foreign body also contributes to the development of aspiration in children and contributes to the appearance of adverse symptoms.
Classification
The variety of causes of pneumonia in children contributes to the presence of a wide variety of clinical options. This classification is used by doctors to establish the diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Every year all new types of diseases are introduced into it.
Given the initial manifestation of symptoms pneumonia can be acute or chronic. It must be said that the first variant of the disease occurs in children more often. Acute pneumonia is characterized by the appearance of a huge number of a variety of symptoms that manifest themselves in a sick child quite clearly.
The inflammatory process can be either on the one hand, or move on to the other. Most often, babies develop right-sided pneumonia.
This feature is due to the anatomical structure.
The right-sided bronchus, which is part of the bronchial tree, is usually somewhat shorter and thicker than the left one. This causes the fact that microorganisms usually penetrate into it and develop subsequently in the right lung.
Left-sided pneumonia is usually less common. Unilateral pneumonia has a more favorable prognosis.
In some cases, a two-way process may also occur. Inflammation in both lungs usually occurs in a child rather severely and causes multiple adverse symptoms. To eliminate them, a whole treatment complex is required.
Given the localization of the inflammatory focus, there are several clinical variants of the disease:
- Focal. It is characterized by the presence of a lesion, which can be localized in various parts of the lung.
- Radical. Inflammation is localized mainly in the lung root area.
- Segmental. The inflammatory process extends to some anatomical zone of the lung.
- Share Inflammation captures a whole lobe of the affected lung.
In some cases, pneumonia is asymptomatic or hidden. To determine the disease in such a situation is possible only with the help of additional diagnostic methods.
To establish the correct diagnosis allows, as a rule, complete blood count and chest radiography. These studies reveal inflammation in the lung tissue even at the earliest stages.
Given the causative agent of the disease, the following clinical forms of pneumonia are most common:
- Viral. Various viruses lead to the development of the disease, which penetrate the lung tissue well, causing inflammation in it.
- Bacterial. Accompanied by a rather severe course and the emergence of a huge number of adverse symptoms that bring severe discomfort to a sick child. The most dangerous clinical options turn into destructive forms, accompanied by massive death of lung tissue.
- Atypical. Caused by microorganisms that have certain structural features. Such microbes are also called "atypical." These include: chlamydia, mycoplasma, legionella and others. Mycoplasma pneumonia occurs with the development of many adverse symptoms.
The course of the disease is usually quite long.
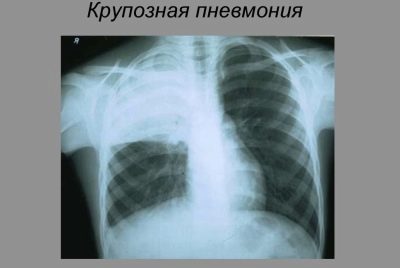
Doctors distinguish several specific types of the disease. Croupous pneumonia is accompanied by the appearance of fluid exudate in several parts of the lungs. The course of the disease is quite difficult.
This pathology occurs in children with the development of pronounced intoxication syndrome. This clinical option is more common in older children and adolescents.
Community-acquired pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs that has developed in a child when it is located outside the walls of hospitals. This form of the disease is quite common among toddlers of very different ages. It is characterized by the development of pronounced symptoms and a specific pattern on the radiograph.
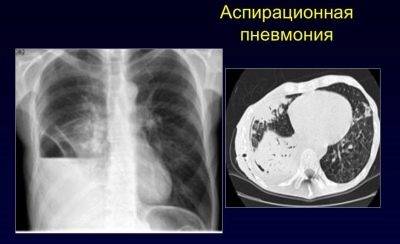
Aspiration pneumonia occurs predominantly in babies from the very first years of life. The reason for the development of this clinical option is the aspiration of the lungs by a foreign body or the ingress of the acidic contents of the stomach into the respiratory tract.
The disease develops rapidly. Sick baby requires mandatory emergency medical care.
Symptoms
The incubation period for pneumonia can be very different. This is due to the huge variety of causes that contribute to the development of the disease.
Incubation period bacterial forms usually 7-10 days.
The appearance of adverse symptoms for viral infections usually occurs within a couple of days.
The incubation period of some forms of fungal pneumonia can take 2-3 weeks.
Pneumonia in a baby is manifested by the development of a complex of respiratory disorders. The severity of these symptoms is a significant difference between this disease and bronchitis.
More severe course of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of pronounced clinical signs of the disease, which significantly impair the child's well-being.
The most characteristic symptom of pneumonia is pronounced intoxication syndrome. This pathological condition occurs in more than 75% of all cases. Intoxication is characterized by fever.
With pneumonia, febrile is quite often recorded. In this case, the body temperature of the sick baby rises to 38-39 degrees. Against the background of high febrile, the child feels a fever or a pronounced chill.
Some clinical forms of pneumonia occur without a temperature rise to high values.
In this case, the child appears only subfebrile. Usually this option is characteristic of fungal pneumonia.
A protracted course of the disease can also be accompanied by a rise in body temperature only up to 37-37.5 degrees.
Sick baby feels increased weakness and fatigue. Even the usual activities lead to the fact that the child quickly gets tired. The baby's appetite decreases.
Infants in the acute period, as a rule, are poorly attached to the maternal breast. Expressed intoxication syndrome may be accompanied by increased thirst. This symptom is well manifested in babies in 2-4 years.
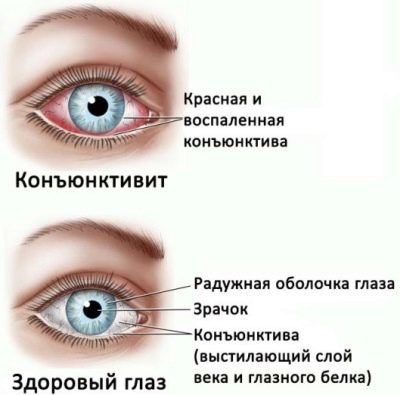
Viral pneumonia caused by adenoviruses, occur in violation of nasal breathing. Viruses settled on the mucous membranes of the nose, contribute to the development of a strong cold. Allocation with mucous, abundant. In some cases, the child also has associated symptoms. conjunctivitis.
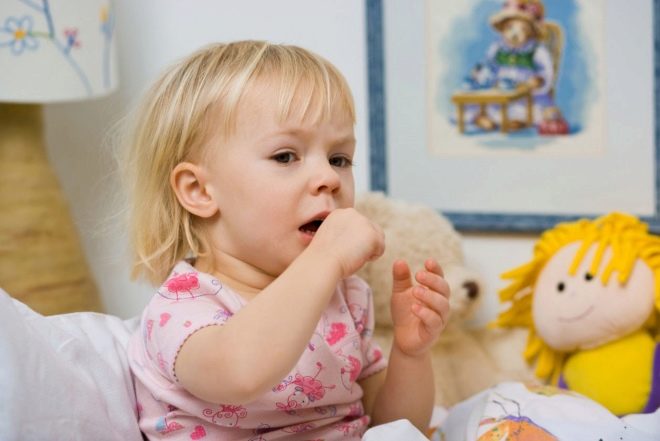
A sick baby usually has a cough. In most cases, it is productive with sputum discharge.
Protracted forms of pneumonia are often accompanied by just a dry cough. Phlegm in this situation, the child almost does not appear. The course of prolonged pneumonia can be quite long.
The color and consistency of sputum may be different:
- Staphylococcal and Streptococcal flora leads to the fact that the discharge from the lungs has a yellow or greenish color.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis contribute to the secretion of gray and foamy sputum, which in the active stage of the disease has bloody streaks.
- Viral pneumonia usually accompanied by sputum discharge of white or milky color.
In case of mild disease, the amount of sputum per day may be insignificant. In this case, the amount of discharge does not exceed a tablespoon. With a more severe course of the disease, sputum leaves in a sufficiently large amount. In some situations, its amount may be ½ cup or more.
Breast tenderness or congestion also occurs in various types of pneumonia. Usually, pain syndrome increases after coughing or when changing the position of the body. The severity of pain is significantly reduced against the background of the treatment.
The presence of inflammatory fluid inside the lungs leads to the fact that the child appears characteristic rales.
They can occur both on the inhale and on the exhale.
With a severe course of the disease, parents hear the child wheezing from the side. The appearance of shortness of breath - a very unfavorable symptom, indicating that the crumbs show the first signs of respiratory failure.
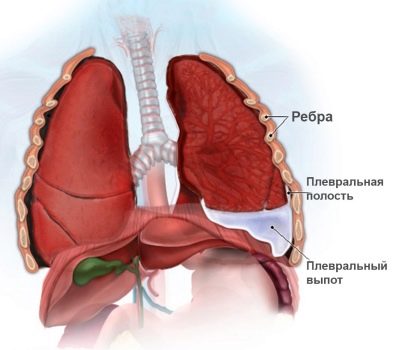
If inflammation from the lung tissue goes to the pleura, then the baby has pleurisy. This pathological condition quite often accompanies pneumonia.
Pleurisy can be suspected by increasing chest pain. Usually this symptom can already be identified in a child aged 3 years.
Pronounced intoxication syndrome significantly violates the general health of the crumbs. The baby becomes more capricious, whiny.
A sick child tries to spend more time at home. Active games with peers baby tries to avoid. A sick child significantly increases drowsiness, especially during the daytime.
Intoxication leads to increased cardiovascular function. This is manifested in a child by an increase in heart rate and pulse. Tachycardia is a fairly frequent symptom of a severe course of the disease. Infants suffering from cardiovascular abnormalities may also experience blood pressure spikes.
In some cases, the appearance of a child with pneumonia also changes. The baby's face becomes pale and his cheeks turn red. Severe course of the disease, accompanied by the development of respiratory failure, is accompanied by a blue nasolabial triangle area. Visible mucous membranes and lips become dry, with areas of high peeling.
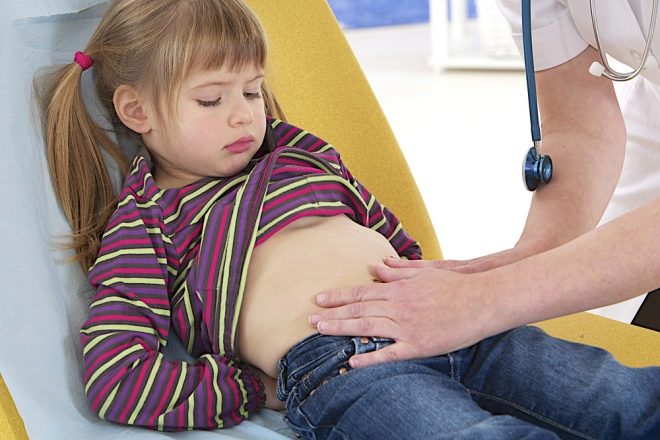
Some, especially atypically flowing forms of pneumonia, are accompanied by the appearance of symptoms not related to respiratory manifestations. Such clinical signs include: the appearance of pain in the abdomen, pain in muscles and joints, impaired stool, and others.
The severity of these symptoms depends largely on the underlying cause of the disease.
For information on the types and symptoms of pneumonia, see the following video.
The first signs of a one year old child
According to statistics, the peak of the disease in babies up to one year falls at the age of 3.5 to 10 months. This is largely due to the peculiarities of the children's body.
The bronchi of newborns and babies are much shorter than those of older children. All the anatomical elements of the respiratory tree are very well supplied with blood.
This leads to the fact that any infection that gets there goes through rapid development.
Recognizing pneumonia in infants is a rather difficult task. To cope with this at home alone parents will not succeed. If any adverse symptoms associated with respiratory disorders appear, they should always seek advice from your doctor. Often, the diagnosis of pneumonia in young children is carried out rather late.
Manifestation of pneumonia in a one-year-old child is usually non-specific. Many fathers and mothers mistakenly "write off" the symptoms of the disease to the fact that the child "just cuts teeth."
Such a false diagnosis leads to the fact that the disease is detected in children extremely late. Untimely prescribed treatment only aggravates the course of the disease and contributes to the development of complications.
Effects
Pneumonia is dangerous by the development of various complications. At the highest risk for the adverse effects of the disease are babies with concomitant chronic diseases of internal organs, and children suffering from immunodeficiency pathologies.
Quite frequent complication of the disease is the development of pleurisy. This is a condition in which the pleura is involved in the inflammatory process. The danger of this pathology is that it can lead to the transition of an acute process to a chronic one.
The combination of pleurisy and pneumonia usually has a more severe course and is accompanied by the appearance of a large number of adverse symptoms of respiratory disorders.
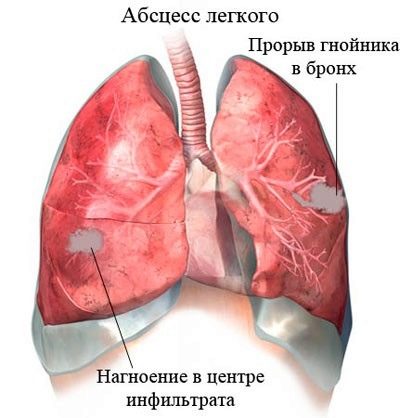
Lung abscess is one of the most dangerous complications of pneumonia. It occurs in children with severe disease. This pathology is accompanied by the appearance of an abscess, which is located in the lung tissue.
Lung abscess is treated only in stationary conditions. To eliminate such an abscess, surgery is required to remove it.
The development of broncho-obstructive syndrome often accompanies bronchopneumonia. In this case, the child, as a rule, has classical manifestations of respiratory failure.
The sick kid feels very bad: his shortness of breath increases and his general weakness increases sharply. Respiratory impairment is accompanied by the appearance of a cough that worries the baby both day and night.
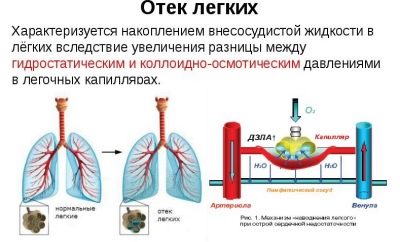
Pulmonary edema, as a complication of pneumonia, is quite rare in children.
This emergency may occur in a sick child against the background of complete well-being. Symptoms of pulmonary edema appear in a baby suddenly. Treatment of this pathological condition is carried out only in the conditions of the intensive care unit and intensive care.
Bacterial infections can cause infectious-toxic shock in sick babies. This emergency is characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Toddlers with signs of infectious-toxic shock may lose consciousness. Some babies begin to have cramps and severe dizziness.Treatment of toxic shock is carried out without delay only in the hospital.
Bacterial complications of the organs of the cardiovascular system and other vital organs are also quite common in children who have had severe pneumonia.
Inflammation of the heart muscle is accompanied by the development of myocarditis or endocarditis. These conditions are manifested by the development of arrhythmias - cardiac arrhythmias. Quite often, these pathologies have a chronic course and significantly violate the health of babies.
The spread of microorganisms that cause pneumonia in babies throughout the body leads to the development of sepsis. This extremely unfavorable condition is characterized by a pronounced intoxication syndrome.
Baby body temperature jumps to 39.5-40 degrees. Consciousness crumbs become confused, and in some cases, the child may even fall into a coma. Treatment of bacterial sepsis is carried out in the intensive care unit of the hospital.
Diagnostics
Recognize pneumonia can be at the earliest stages. For this, it is necessary for the attending physician to have sufficient experience in identifying such diseases in babies.
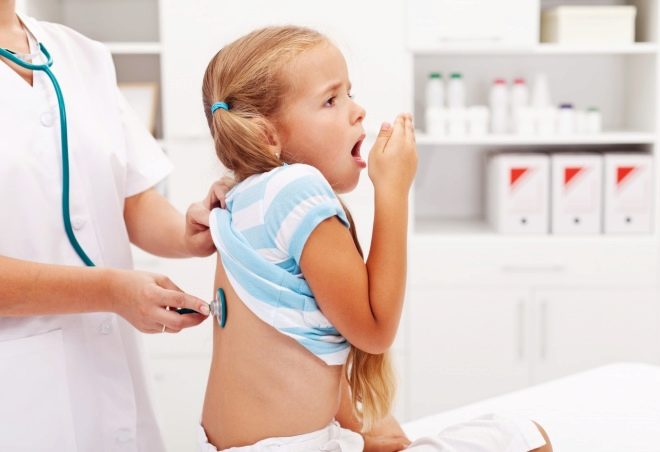
The correct algorithm of the clinical examination is very important in the diagnosis of pneumonia. During this study, the doctor reveals the presence in the chest of pathological wheezing, and also determines the hidden signs of respiratory failure.
A suspicion of pneumonia should appear in the parents if they have found several symptoms of impaired breathing in their sick child.
Long-term current acute respiratory viral infections in a baby should also be alerted, parents should think about conducting an advanced diagnostic complex.
To clarify the diagnosis conducted a variety of laboratory tests. They help to identify various signs of infection in the children's body and to establish the severity of functional respiratory disorders.
Complete blood count is a basic study that is performed on all babies with suspected pneumonia. Increased leukocyte levels and accelerated ESR quite often indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the children's body.
Bacterial infections lead to the fact that in the general analysis of the blood normal values in the leukocyte formula change.
A change in the number of stab neutrophils occurs when a child’s body is infected with various types of bacteria. For most clinical variants of pneumonia, an increase in the total number of lymphocytes is characteristic. These immune cells normally prevent the body from various infections.
For more accurate diagnosis of sick babies, various bacteriological studies are conducted. Biological material for such analyzes can be a variety of departments from the nasal cavity, throat, oropharynx.
After 5-7 days, doctors get an accurate result, allowing you to identify the causative agents of a particular disease. For the accuracy of the study requires the mandatory conduct of technically correct sampling of biomaterial.
For the detection of "atypical" pathogens, ELISA and PCR methods are used. These studies reveal microbes intracellularly. These tests are well and successfully used for the diagnosis of chlamydial and mycoplasmal infections.
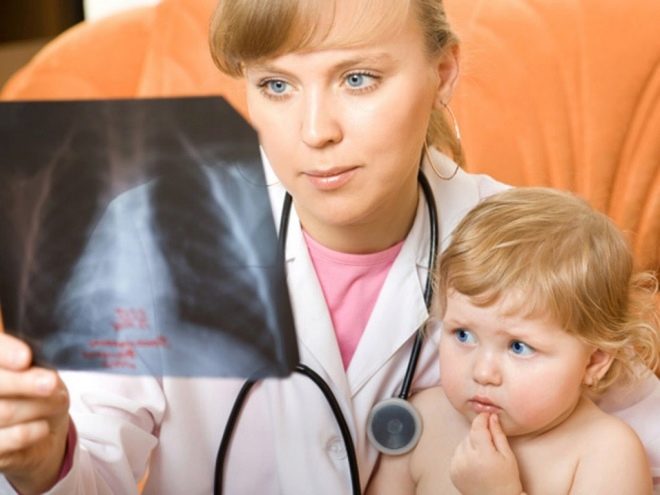
The “gold” diagnostic standard for determining pulmonary inflammation is radiography.
On the radiograph, doctors can see various pathological areas of the lung tissue, in which there are signs of pronounced inflammation. These zones look different than healthy lung tissue. A chest X-ray also reveals some complications, such as pleurisy and abscess.
In some difficult diagnostic cases, more accurate diagnostic methods are required.Such studies include computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Survey data can identify the affected areas of the lung tissue quite effectively.
The resolution of modern devices used for tomography, allows you to identify pneumonia at the stage of growth of the nidus of several centimeters.
For the formulation of the correct diagnosis requires a whole range of diagnostics. Unfortunately, it will not be possible to identify pneumonia with only one blood test. The importance of the diagnosis of pneumonia is very serious.
Timely diagnostic complex diagnostic measures allows doctors to prescribe the necessary scheme of drug therapy.
Treatment
Inflammation of the lungs in children younger than three years old is treated in a hospital. Also, hospitalization is carried out in severe disease.
Kids who cannot be properly cared for at home are also hospitalized in a children's hospital for the necessary treatment complex.
The pneumonia treatment regimen includes not only the prescription of drugs. Observance of the day regimen plays an important role in the treatment of pneumonia. The entire acute period of the illness the child should be in bed. Such forced bed rest is necessary to prevent multiple complications of the disease. Doctors recommend the baby to be in bed throughout the entire period of high temperature.
For the rapid recovery of the sick child is assigned a special therapeutic food. Such a diet includes the use of products that have passed the gentle treatment.
Meals are best steamed or boiled. It is also allowed to bake in the oven or use a slow cooker. Frying in butter with the formation of a dense crisp is completely prohibited.
The basis of the nutrition of the sick child are various protein foods and cereals. For younger children, these products should be finely chopped. Eating sparing food is necessary. This allows you to optimize digestion. Pre-ground food is better absorbed, which is required during the period of acute illness.
To recover from pneumonia, the child must receive the necessary amount of vitamins and trace elements. These chemical components are necessary for the child's body to actively combat the disease.
In the summer, you can use various fruits and berries as sources of vitamins and microelements. In winter, the appointment of multivitamin complexes is necessary.
Drinking regimen also plays an important role in the treatment of pneumonia. The incoming fluid washes away from the child’s body the toxic decomposition products of substances that are formed in large quantities during the inflammatory process in the lungs.
Severe thirst only provokes the use of large amounts of fluid.
To fill the water in the body of a sick child requires at least 1-1.5 liters of fluid.
As drinks, various fruit drinks and compotes are well suited. They can be easily prepared at home. Cranberries or lingonberries, dried fruits and various fruits are great for making drinks. Ready juice can be further sweetened. Honey can be a substitute for the usual sugar.
To improve breathing it is necessary to observe certain indicators of the microclimate in the room. Normal humidity in the nursery should vary from 55 to 60%.
Too dry air only contributes to difficulty breathing and the development of dryness of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. To maintain optimum humidity in the nursery, special devices are used - room humidifiers.
Compliance with quarantine is a necessary measure, which is necessary for all babies with signs of pneumonia.This will help prevent the development of mass outbreaks of the disease in organized children's groups.
Quarantine should be observed not only for kids, but also for schoolchildren. The baby should be at home until full recovery. After the treatment, the doctor monitors the effectiveness of the therapy and gives the child a certificate of the possibility of visiting the educational institution when the baby has recovered.
Drug therapy
Prescription drugs - a necessary condition for the recovery of the baby. When pneumonia is used a whole range of different drugs.
The scheme of treatment is built individually for each child. In this case, the attending physician necessarily takes into account the presence of a co-existing disease in a particular child, which may be contraindications to the use of any drugs.
Given that bacterial pneumonia is the most common, the appointment of antibacterial drugs is a prerequisite when drawing up a treatment regimen.
Doctors prefer antibiotics with a wide spectrum of action.
They allow you to quickly achieve a successful result. Modern drugs are well tolerated and have less adverse effects in babies.
During antibiotic therapy, the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment is monitored. Usually it is held for 2-3 days after the start of the use of drugs.
With a positive result, the child's overall health improves, the body temperature begins to decrease, and the indicators in the general blood count normalize. At this stage, significant changes on the radiograph does not yet occur.
If the result after the prescription of antibacterial drugs is not achieved, the basic therapy is subject to correction. In this situation, one drug is replaced by an alternative.
In some cases, combination therapy is used when several antibiotics are prescribed at the same time. Selection of antibacterial drugs is an individual situation, which is carried out only by the attending physician.
Parents should remember that they should not give their children antibiotics for pneumonia under any circumstances!
The choice of basic therapy is largely determined by the initial state of the baby, as well as his age.
In the treatment of pneumonia in children, several groups of drugs are currently used, which include:
- clavulanic acid-protected penicillins;
- the latest generation cephalosporins;
- macrolides.
These drugs are related to first line therapy. The remaining drugs are used only in exceptional cases where the effect of the primary basic therapy is not.
The babies of the first months of life are usually prescribed semi-synthetic penicillins to eliminate the adverse symptoms.
"Amicillin" or "Amoxiclav"In combination with cephalosporins are used in infants with developed pneumonia in the very first days after birth.
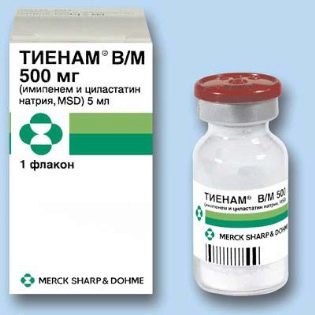
If the pathology was caused by Pseudo-Pseudo-chopsticks, then Ceftazidime, Cefaperazon, Tienam,Ceftriaxone" other.
Macrolides are used to treat pneumonia caused by atypical microorganisms.
These funds have a detrimental effect on microbes, which are located intracellularly. Such drugs will be effective for the treatment of pneumonia caused by mycoplasmas or chlamydia.
Also, these medicines are used for babies with signs of HIV pneumonia. "Suprax», «Sumamed», «Klacid"Quite successfully used in complex treatment of some forms of pneumonia.
Fungal forms of pneumonia are treated by prescribing antifungal drugs.Systemic use of "Flucanazole" allows you to effectively deal with various types of fungi that can cause damage to the lung tissue in children. Also for the treatment of fungal infections, you can use "Diflucan"And" Amphotericin B ". The purpose of these funds is based on the age of the sick child and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The choice of the form of the drug is made by the attending physician. In severe pneumonia, antibiotics are used in the form of various injections. Frequency, course dosage and duration of use are determined individually.
On average, treatment of bacterial pneumonia takes 10-14 days. To achieve a lasting effect from the treatment carried out, it is very important to observe the necessary periods for using antibacterial drugs.
To prevent the development in the child of disorders of the intestinal microflora, he is prescribed various pro- and prebiotic preparations. These medicines help to normalize the amount of lacto - and bifidobacteria necessary for good digestion.
The use of these funds is also applied after completion of the course of antibiotic therapy to normalize the biocenosis in the intestine. As such drugs in children effectively used: "Linex", "Atsipol"," Bifidumbakterin "and many others.
Various anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs are used to normalize body temperature. Parents should remember that such drugs should be used only with the development of febrile in the baby.
Medicines based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are widely used as antipyretic drugs in babies. Usually, to achieve a stable effect, these drugs are prescribed 2-3 times a day.
For the prevention of massive destructive changes in the lungs, medicines are prescribed that have a protective effect on the effects of various enzymes.
These drugs include: "Contrykal" and "Gordoks". The appointment of these drugs is possible only in a hospital.
If the baby has pronounced signs of respiratory failure, in this case, oxygen therapy may be required. Persistent respiratory failure helps reduce the flow of oxygen to all internal organs, which leads to the development of oxygen starvation (hypoxia). Oxygen therapy allows you to restore all metabolic processes in the body and improve the well-being of the baby.
In some cases, the appointment of systemic glucorticosteroids. Such therapy is usually carried out with the ineffectiveness of previously prescribed drugs or with severe disease.
As a hormonal treatment, various agents based on prednisolone or hydrocortisone are used. These drugs are prescribed in the form of injections. Such therapy can be carried out only in the conditions of the intensive care unit in the hospital.
If a child has poorly separated sputum during coughing, then expectorant drugs are used. They reduce the viscosity of the discharge, which makes it easier for your baby to cough. These funds include: "ACC", "Ambroxol, Ambrobene, Fluimutsin. Parents should remember that while taking these drugs, the child needs to be given enough liquid.
Home treatment
Independently treat pneumonia should not be. Any treatment that the parents give the child at home should be coordinated with your doctor. This will save the baby from developing dangerous complications of pneumonia. A mild course of the disease in fairly strong babies implies finding a home and using various medications.
Usually treatment at home includes the appointment of various medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory and coughing effects.
Chamomile, coltsfoot, sage, plantain, as well as pharmaceutical chest fees. Brew these herbs should be according to the instructions on the package.
To achieve the effect, it is enough to use decoctions 2-3 times a day for 10-14 days.
Rehabilitation after acute illness
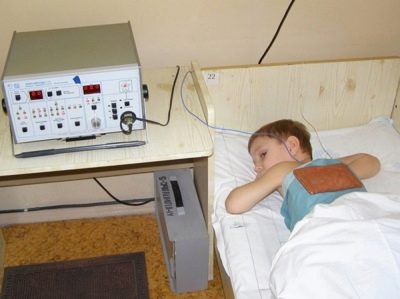
Physiotherapy helps all babies who have just had pneumonia to finally cope with the residual manifestations of the disease. UHF therapy, light and magnetic therapy improve the recovery of the child after an illness.
The course of physiotherapy is built individually. To achieve a positive effect usually requires 10-15 procedures that are carried out daily or every other day.
Percussion massage, which is carried out with the help of tapping movements on the chest, improves sputum outflow and improves the performance of external respiration. To achieve a positive effect, it is necessary to conduct it daily for 1-2 weeks.
Perform a percussion massage to the baby can both parents and pediatric massage therapists at home or in the clinic (as recommended by the doctor).
To improve the general well-being, pulmology doctors prescribe a complex of physical therapy quite early. The kid can do this kind of gymnastics at home, but under the obligatory supervision of parents.
Breathing exercises help sputum discharge, as well as reduce the manifestations of respiratory disorders that have developed as a result of the disease.
On how to properly massage the children, see the following video.
Prevention
Compliance with quarantine will help prevent mass outbreaks of the disease in teams. All babies with signs of pneumonia must be at home throughout the height of the illness.
Most infections are transmitted by airborne droplets. Wearing a mask during the recovery period of respiratory seasonal diseases will prevent the development of pneumonia in all family members.
Vaccination can save the child's body from various viral and bacterial infections. Currently, vaccination against pneumococcal infection is being actively used. This vaccination is based on the age of the child. The risk of developing a disease in a vaccinated baby is significantly reduced.
You can strengthen the immune system without the use of drugs. Proper nutrition, walking in the fresh air and hardening contribute to the activation of the immune system. The use of multivitamin complexes helps strengthen the children's body to combat various infections.