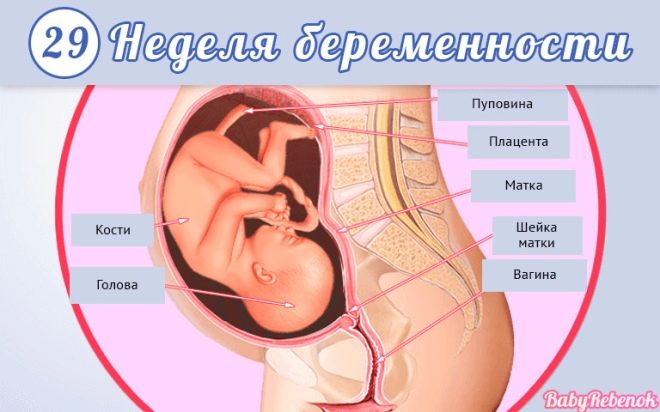
Fetal development in the 29th week of pregnancy
The 29th week of pregnancy corresponds to the beginning of the eighth obstetric and 7 calendar months of pregnancy. Recently began the third trimester, which will be the final. Childbirth is getting closer, and in a week the woman will have to go on maternity leave. If she bears twins, then she has a week of rest on maternity leave. At week 29, the 27th week of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Baby options
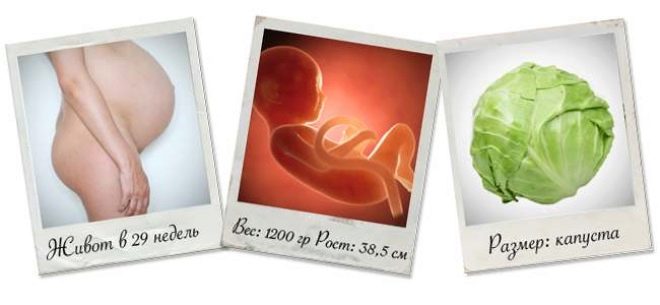
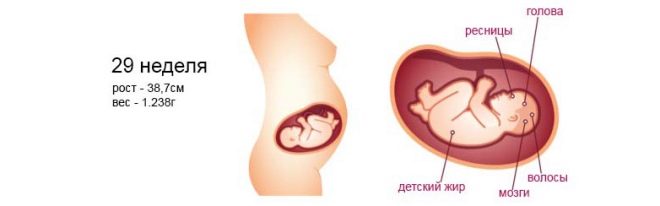
The times when the child resembled an alien creature are over. At weeks 28-29, the baby is actively gaining weight and looks like a human being. He is no longer small, but still not as big as newborns. On average a fruit on this term weighs from 1200 to 1500 grams.
The laid genetic program of height and weight is already clearly traced, and therefore already now the ultrasound specialist can see both large children and tiny crumbs, whose weight does not reach 1300 grams. Already, the estimated mass of girls is slightly less than the weight of boys, and therefore it is increasingly difficult to sum up the size of a baby under the concept of “norm”.
Growth the child now ranges from 37 to 40 centimeters, but even here a lot is due to genetics - there are high parents who have high children, and there are undersized moms and dads, the growth of babies who have less than average values.
If you use the system of parameters of the fruit with objects, fruits, vegetables, beloved by future mothers, then the baby can be compared with a sufficiently large doll. The crumb grows now much slower than before, but it is gaining weight very quickly.
The fetal fetometry on ultrasound this week is also difficult to fit into the concept of standards, because all children are already very individual. On average, the parameters are as follows:
BPR (biparietal head size) - 70-82 mm;
LZR (frontal-occipital size) - 86-102 mm;
DBK (thigh length) - 52-60 mm;
DKG (leg length) - 47-55 mm;
DKP (humerus length) - 47-55 mm;
head circumference - 255-295 mm;
abdominal circumference - 228-278 mm.
What does it look like?
For the first time in its prenatal history of existence, the baby boasts the presence of subcutaneous fat - it is not so much, not more than 5% of body weight, but this is not so little. Thanks to the fat layer, the fetus ceases to look very thin and wrinkled, the folds on the skin gradually smooth out, and it changes color from saturated red to more moderate, because now with the appearance of fat, the skin becomes four-layer, more durable, and through it does not shine through all blood vessels.
Have babies appeared quite rounded cheeks. Now the fat will be actively deposited on the chest and pope, the last will begin to "gain weight" in the arms and legs - they are still very thin.
In the children's organism, this period begins. pigment production which gives the skin the shade that is meant by the genome - from week 29, children become mulatto or dark-skinned, dark-skinned or light-skinned, as they are destined to be. Hair begins to darken if the child is destined to be born dark-haired.
If earlier the child had the head with the largest part of the body, now it is about a quarter of the proportions of the body and will be no more than one fifth to the birth. The baby ceases to fit in the space of the uterus, and therefore he is on this term starts to group - take the so-called flexion position, pressing the legs to the tummy, and the arms to the chest. This position, which is often called the “embryo posture,” makes it very difficult to identify sexually during an ultrasound examination, because the umbilical cord and the baby’s fists often appear between the legs, and therefore it’s not so easy to see the floor. The accuracy of determining the sex from this period is reduced.
The kid has well-developed mimic muscles, he owns a dozen spent and rehearsed grimaces, knows how to smile reflexively, frowns, yawns, spits, makes “offended” mines. Do not think that this is how he expresses his emotions - contractions of the mimic muscles are still poorly controlled by the central nervous system, and therefore grimaces appear spontaneously.
The baby’s body is still covered with lanugo and cheese-like lubricant, but this week begins a gradual getting rid of hair, after all, the skin of a child that has become denser is no longer so much in need of additional protection. The hairs fall out, get into the amniotic fluid, the baby can swallow them, but there is nothing wrong with that - they are not digested and in pure form, mixed with bile, get into the intestines of the fetus, where they will be present in the composition of the original feces baby
The development of organs and systems
All organs of the baby laid and formed and in the current time only continue to grow rapidly. The liver has become bigger, the heart has grown, the kidneys are not quite mature yet, but their cups and pelvis continue to grow in size, and they produce up to 450-500 ml of urine per day. The process of systemogenesis is almost complete, when the organs adjust their work according to the “rules” of the system to which they are directly related.
The digestive organs organs are better than others. They work very smoothly - the esophagus holds water swallowed by the kid into the stomach, from there the amniotic fluid is sent to the intestine.
The walls of the intestine can shrink - there is a primary peristalsis. But defecation does not occur - while meconium is only accumulating and will normally leave the intestines after the birth of a child. The feces will be dark green, sometimes even black.
Heart increased in size, it pumps more than 24 liters of blood per day. Heart rate normal is 130-160 beats per minute.
Ended liver division whether it is necessary. The ripening process is underway. lungs: tiny vesicles of the alveoli acquire a phospholipid substance called surfactant. Its production is continuous, constant. It is the surfactant that will envelop the alveoli and prevent them from collapsing and sticking together after the baby switches to a different type of breathing and makes its first independent breath.
The sex glands in girls have long been located in the pelvis, but in boys the testicles are now just on the way - they are migrating from the abdominal cavity to the scrotum, and this process is rather long.
Brain, nervous system, skills
The brain increases the mass of the medulla, and the processes of formation of the nervous system now - the main thing that happens quite intensively with the baby. Constantly emerging new nerve cells, young neurons are combined into new connections that create that invisible network of "communication" between the brain and spinal cord and internal organs, muscles.
The nervous system at the level at which it is now provides the child with the presence of basic reflexes - he sucks, swallows, hiccups, spits, pisses while filling the bladder, sleeps and is awake, shows some activity during wakeful periods, knows how to grab the umbilical cord with his hand,and also has the germ of the instinct of self-preservation - with a loud sound, a bright light directed at the stomach, when any threat threatens, the child shudders, shrinks, is grouped into a ball.
He instinctively protects the weakest point in his body - the stomach. If something, for example, the umbilical cord, touches the tummy, the baby bends. And this is also a reflex.
When tickling the palm of the hand, children in this period reflexively spread their fingers in a “fan”. The lungs perform specific respiratory movements, although the baby is not yet breathing in the usual sense. It is believed that such movements, which increase as the duration of pregnancy increases, not only contribute to the formation of the respiratory reflex (the baby will know how to breathe immediately), but also improve the blood circulation of the fetus.
The cerebral cortex in its formation goes to the finish line. The kid already hears well and is able to distinguish the taste of the amniotic fluid, trains the blink reflex, although his eyes do not fully open yet. This week is the formation of receptors, which will later be responsible for the sense of smell.
Previa
By the 29th week of pregnancy, up to 93% of children in the uterus occupy the position in which they will be at the time of the onset of labor.
Given that the child already has to be in the flexion position, reversal and upheaval are seen as less and less likely. Most of the children at this time have a headache presentation - they lie head first to the exit of the uterus. This situation is considered optimal for birth. Pelvic presentation on this term or the location of the baby across the uterus - until the sentence, there is a chance of a reversal, but they are not so great.
Usually by this time women themselves are able to distinguish where the baby has a booty and where the head is. Many note that the child in the head prevails the baby is pushed mainly in the lower abdomen, and in the pelvic region - in its upper part.
Sensations are already clear, stirring all women feel great. The transverse presentation of the fetus makes the abdomen elongated, like a rugby ball, and the tremors are mainly felt in the lateral parts of the abdomen.
Women whose children are not properly positioned should do special gymnastics, move actively. The chances of a reversal remain. Until the 34th week of pregnancy, the baby definitely has time, only then the presentation will be recognized as final and the doctors will begin to decide on the mode of delivery.
What happens if the baby is born now?
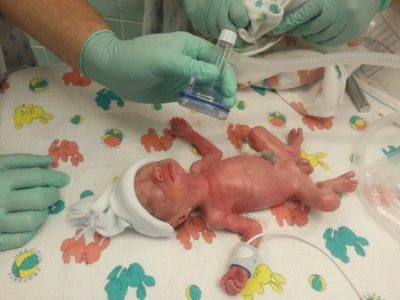
If births occur that week, they are considered premature, but survival predictions, according to WHO, exceed 95%. This means that the baby, even if it is very premature, has a high chance of survival. The risk of disability remains quite high, but not the same as for a period of 22-25 weeks.
Being born on week 29 is not the norm, and therefore the baby will definitely need qualified resuscitation care. The baby will be immediately placed in a special incubator, he will be provided with probe nutrition, constant warming, maintaining a certain humidity. His pulse, pressure will be monitored in real time. It is very likely that an artificial respiration apparatus will be needed, since the child has not yet accumulated the necessary amount of surfactants in the lung tissue and breathing on his own is a very difficult task, and sometimes impossible at all. In such conditions, the child will have to spend as much time as is necessary for the maturation of the organs and the gaining of weight to at least 1.7 kilograms.
Then the mother and the baby are usually transferred to the early childhood department of a specialized hospital or perinatal center, since the child needs to be under the supervision of specialists for quite a long time. When his weight reaches 2 kilograms, provided that there are no other health problems, the baby can be discharged with the mother home.
According to reviews of women who gave birth at this time, usually they have to spend up to 1.5-2 months in the hospital.In approximately 20% of cases, children were diagnosed with concomitant problems with the nervous system, the work of the organs of sight and hearing.
What can threaten?
The baby is not as defenseless as it used to be, it has its own immune system, it has its own hormonal background, it is still reliably protected by the placenta (its aging has not yet begun), and therefore the main threat now is premature birth. Whatever the success of modern medicine in nursing deeply premature babies, for a child it would be better to spend at least a couple of months in my mother's womb.
Despite the fact that the baby is well protected, the woman needs to take care of herself and try not to get sick, not to take medicine, so as not to cause a state of premature depletion of the placenta, in this case there is a risk of delayed development. The risk of intrauterine infection persists if a woman has untreated infections of the genital tract or water leakage occurs.
It is important to monitor the activity of the baby. Her acceleration or reduction can be a sign hypoxia.
You will learn about the features of the course of pregnancy at week 29 by watching the following video.