Ultrasound in the third trimester during pregnancy
Screening ultrasound helps to identify many pathologies. Conducting such a study in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy allows doctors to evaluate the final period of intrauterine development of the baby. In more detail about the third ultrasonography which is carried out to future mummies, this article will tell.
Purpose of the study
Ultrasound in this period of pregnancy is necessary for the functional assessment of fetal development. The last period of pregnancy is very important for the baby. It was at this time that his body was preparing for an independent life outside the maternal organism.
Ultrasound also allows you to evaluate intrauterine development of the fetus and features of its anatomy. Ultrasound specialist determines the length of the body of the baby, as well as its estimated weight. Also with the help of this study, the doctor can determine the length of the main bone elements.
The placenta is a very important fetal element. It is through this organ that the child receives all the necessary nutrients and oxygen. They are necessary for the baby for its active growth and development.
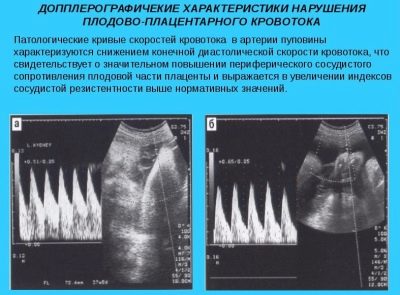
Assessment of placental blood flow is very important, especially in this period of pregnancy. During the study, a specialist can identify the formed pathology of blood vessels of the placenta. Torsion or abnormal constriction of the blood vessels are frequent “findings” during an ultrasound scan in this trimester of pregnancy.
With the help of a screening study, you can also determine fetal position in the uterus and identify the attendant diseases of internal genital organs. Ultrasound also reveals intrauterine developmental defects that are already formed during the final weeks of pregnancy. The most dangerous abnormalities in the structure of the heart.
Forming heart defects are a serious cause for concern. In some situations, it may even be necessary to perform a surgical treatment to eliminate this defect. In this case, operations are carried out after the birth of the baby.
A special study is used to determine signs of placental insufficiency. using doppler. This test allows you to identify the pathological decrease in blood flow in the blood vessels supplying the placenta. Using the Doppler study, you can also determine the speed of pulse waves in the placental and uterine arteries.
Dates
Routine ultrasound in the third trimester is usually carried out at 28-34 weeks of pregnancy. In some cases, a complex of studies can be carried out earlier in 7-14 days. Usually, the duration of the screening ultrasound is set by an obstetrician-gynecologist who monitors a pregnant woman.
In the normal course of pregnancy, the third screening may not be necessary. Usually ultrasound in this period is assigned to future moms, who during the first two studies had any violations. Also, screening must necessarily be carried out on pregnant women who, for whatever reason, have missed previous studies.
The main parameters studied
The position of the baby in the uterus is a very important indicator, which is evaluated during the third screening ultrasound. The error rate of measurement of this criterion is usually much lower than when conducting research during 1 screening. If a multiple pregnancy, in this case, doctors determine the position of all babies in the womb.
Presentation - a very important criterion, which is also noted during the screening ultrasound. Usually, the baby begins to actively move in the mother’s tummy already in the middle of the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. This leads to the fact that the presentation that was established during the second screening study may change.
The definition of this parameter is very important to hold on the third trimester of pregnancy before giving birth. It will help doctors determine the optimal tactics of obstetric aid.
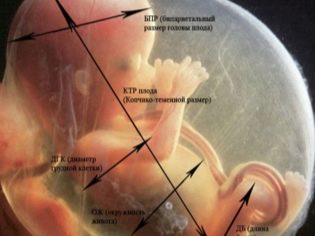
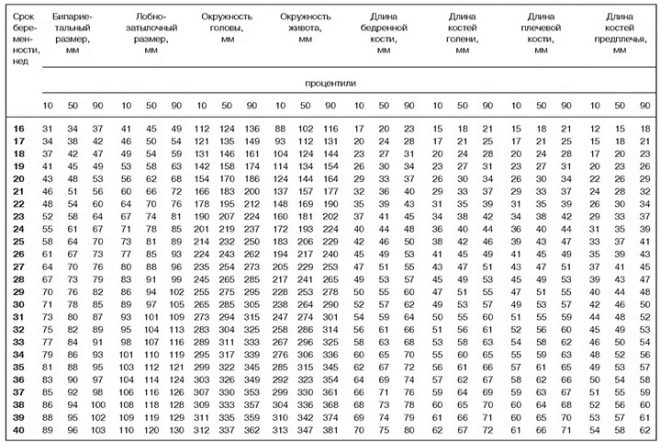
Doctors identify several key clinical parameters that allow to assess the intrauterine development of the fetus. To do this, they always evaluate biparietal size of baby's head. Also measured and abdominal circumference.
Normally, there is a certain relationship between these indicators. If the circumference of the baby’s tummy significantly exceeds the size of the head, this may indicate the development of a dangerous liver pathology and be a sign of accumulation of excess fluid (ascites) in the abdominal cavity.
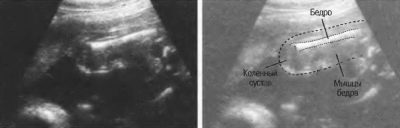
Also to identify certain orthopedic pathologies is carried out determination of the length of the femoral pits. Shortening the lengths of these tubular bones can also appear in some genetic diseases.
If during the screening ultrasound, any deviations from the norm were detected, then in this case the specialists also calculate some special factors. For this, the frontal-occipital and cephalic ratios are estimated. Also determined indices of the ratio of the circumference of the abdomen to the head.
To assess the performance of the brain, ultrasound doctors determine some of its structural elements. To do this, they necessarily explore the lateral cisterns and ventricles. Additionally, the main linear dimensions of the cerebellum are measured. Visual bumps (thalamus), choroid plexuses, and a transparent septum are also evaluated.
During the study, the main anatomical elements of the face are determined. It should be noted that The face of the fetus is examined both in front and in profile. The nasal bone is an important bone element that is evaluated in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Also during the study, the area of the nasolabial triangle is necessarily evaluated. To eliminate anomalies, eye sockets are necessarily examined.
Experienced ultrasound specialists can also determine the thickness and bone density of the frontal bone. The upper and lower jaws are also examined.
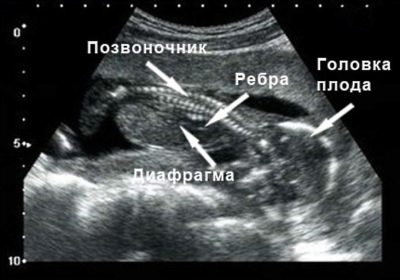
Longitudinal section of the spine - A very important criterion, assessed during the third screening. With the help of this study, it is possible to identify various anomalies of the development of the musculoskeletal system in children. A shortening of the lengths of the spinous processes may be a sign of some chromosomal pathologies.
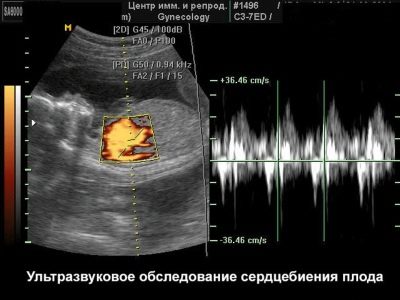
During the examination of the chest, multiple respiratory system diseasesas well as the diaphragm of the fetus. During this study, you can view all the elements of the heart. Ultrasonography allows to reveal various valve defects. Doppler sonography is used to detect regurgitation. During the third screening ultrasound, the fetal heartbeat is also evaluated.
All major blood vessels are necessarily examined. During the study, various pathologies of the aorta, pulmonary trunk and superior vena cava can be identified. A high-resolution ultrasound machine also reveals the pathological attachment of blood vessels to the placenta.
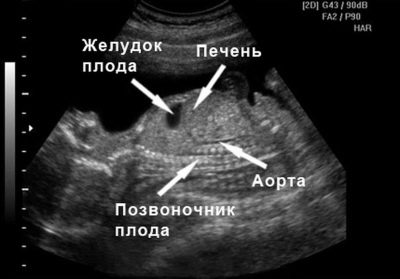
Assessment of internal organs is very important when conducting the third screening ultrasound.During the study, the doctor assesses the structure and the presence of pathologies of the liver, gall and bladder, as well as the intestinal fetus. Modern research methods also allow to determine the size of the kidneys in longitudinal and cross-section. Also with the help of ultrasound can be identified and various abnormalities of the urinary tract.
Fetal structures are very important anatomical elements, which are also necessarily evaluated. In this case, the thickness of the placenta is measured, and the amniotic fluid index is determined. In each trimester, a pregnant woman during a screening ultrasound examination necessarily identifies the pathology of the uterus and its appendages, as well as the ovaries. At 34 weeks gestation, the normal values of the determined parameters are as follows:
- The biparietal size is 7.5-9.1 cm.
- Abdominal circumference - 8.1-10 cm.
- Head circumference - 8.6-10.5 cm.
- Frontal-occipital size - 10-11.7 cm.
- The length of the femur is 5.7-7 cm.
- Fruit weight - 2.2-2.7 kg.
With multiple pregnancies, the weight of babies is usually somewhat less. With the identified tendency to bear a large fetus, doctors may recommend to the future mom to conduct another study. Usually it is carried out immediately before birth. A large fetus with a narrow mother's pelvis is a rather dangerous condition, which in some cases can lead to cesarean section.
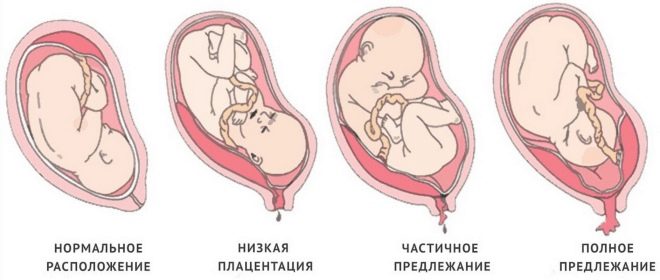
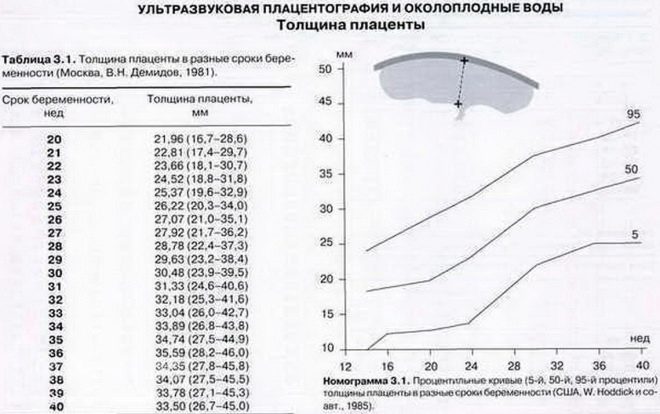
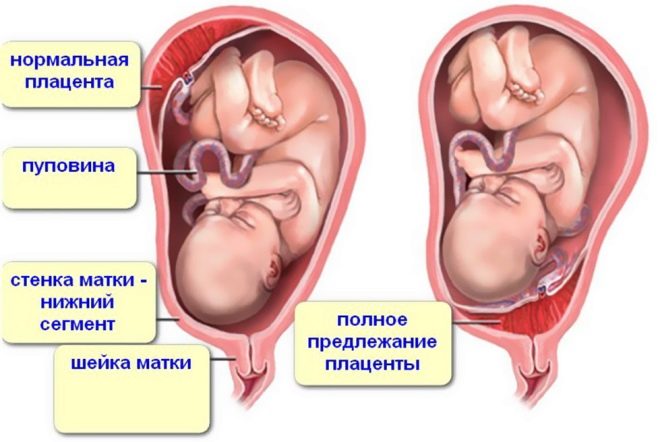
The normal thickness of the placenta at this stage of pregnancy is 27-44 mm. Usually, by the end of the final period of intrauterine development, the “baby” place no longer changes its localization. Migration of the placenta in the third trimester of pregnancy is possible only with the development of pathologies.
The linear distance from the lower edge of the placenta to the internal os is also an important diagnostic criterion. Normally, this value should be greater than 60 mm. If during the study of the placenta almost covers the internal pharynx, it may indicate an increment or low its location. This pathology can be quite dangerous and contributes to complicated childbirth.
Placental maturity is another important criterion that is determined during the third screening. This indicator in different periods of pregnancy may be different. The placenta is "ripening" closer to childbirth. Her immaturity in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy is a pathology, which can lead to various complications.
With excessively early maturation of the placenta in the early stages of fetal development, various intrauterine pathologies may also form. Overheating of this organ can lead to the development of severe hypoxia in the fetus.
It is considered normal if the maturity of the placenta before 30 weeks of pregnancy is zero. The first degree of maturity is normal already at the 27-34th week. The second degree is determined at 34-39 week. The third degree is normal with a gestation period of 39 weeks.
The amount of amniotic fluid is a very important criterion, which is evaluated during the third ultrasound screening. In this period of pregnancy, the rate of this indicator is 1.7 liters. Doctors talk about pathologies in such a situation if these indicators deviate from normal values.
Decoding results
Polyhydration is a pathological condition that is accompanied by an excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid. In the case of this pathology, this figure increases to 2 liters.
Excess volume of amniotic fluid more than 3 liters is accompanied by the development of adverse symptoms. Also, this condition usually leads to the formation of dangerous pathologies. These include: pathological presentation of the fetus, loss of umbilical cord loops, generic bleeding, as well as various postpartum diseases. In this case, the probability of fetal death rises to 45%.
A newborn baby, who was born with signs of polyhydramnios, immediately after his birth, must exclude signs of esophageal or stomach atresia, as well as other anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract. However, it often happens that the high water does not lead to any pathologies of either the mother or the fetus.
Malovodie - a pathology, which is established with a pronounced decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid. Such a pathological condition often occurs during a protracted pregnancy, when the expectant mother bears a baby for more than 40 weeks. In this situation, the risk of fetal abnormalities in the fetus increases significantly.
To assess the degree of impairment, a comprehensive assessment of the mother-placenta-fetus is performed. All the identified deviations are divided into several categories:
- First degree offense. Characterized by a compensated course. In this case, the expressed violations of the fetus is not diagnosed. If any insignificant abnormalities were identified during the study, then pathogenetic treatment may be prescribed. Dynamics of the fetus in this case is required.
- Second degree violations. Also called subcompensated state. In this case, pathology of placental blood flow is detected. Treatment of these disorders in this situation is carried out in the clinic. Hospitalization of the future mother in the hospital, as a rule, is not required.
- Third degree violations. Characterized by decompensated course. Accompanied by severe disorders in the placental circulation. Such pathologies are quite rare. Hospitalization is required to eliminate adverse symptoms in this case.
In the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, the placenta should be located on the back wall. In this case, normal placental blood flow is ensured. For normal delivery, it is better for the placenta to be 4 cm higher than the internal uterine os.
The length of the cervix is a very important criterion, which is evaluated during the third screening. During this period of pregnancy, the normal values of this indicator are more than 3 cm. If this criterion is less than the norm, then this is usually a manifestation of isthmic-cervical insufficiency. To eliminate this pathology, a special suture is required.
Elevated uterus tone - a very dangerous condition that is assessed during the third screening. This pathology can lead to premature birth and also to the development of dangerous conditions that can manifest during childbirth.
A decrease in the heart rate of the fetus, detected during the third screening ultrasound, is a manifestation of the pathology of the cardiovascular system. In this situation, the heart rate drops below 130 beats per minute. Tachycardia is also a dangerous symptom that can be a manifestation of fetal hypoxia. In this case, it is required Mandatory appointment of therapy which picks up the gynecologist together with the therapist.
During the third scheduled ultrasound scan, performance indicators are also necessarily evaluated. respiratory system. The decrease in the frequency of respiratory movements of the fetus is an extremely unfavorable symptom, indicating that its respiratory organs are underdeveloped. Too frequent breathing can be a manifestation of severe hypoxia. Doctors consider the respiration rate at 40-70 movements per minute to be the norm at this stage.
About the final period of intrauterine development of the baby in the third trimester, see the following video.