Symptoms and treatment of pseudotuberculosis in children
The child had a fever, a runny nose, a cough, a stomach ache and diarrhea started. Most parents begin to look for the cause of hypothermia or viral infection. But in practice everything may turn out differently, and the doctor will install pseudotuberculosis in the baby. Should I be afraid of such a diagnosis and how to treat a child, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
Pseudotuberculosis is also called Far Eastern scarlet-like fever or extraintestinal yersiniosis. The causative agent of the disease is enterobacteria Yersiniae pseudotuberculosis. It does cause the child to have symptoms similar to those of most acute respiratory viral infections and flu — fever, muscle and joint pain, rash, and respiratory symptoms. In some cases, the disease causes severe complications - inflammation of the lining of the heart, pneumonia, renal failure.
Every year in Russia, about 10 thousand people become ill with pseudotuberculosis, most of them are children under 14 years of age.
The peak incidence traditionally occurs in winter and the beginning of spring. Enterobacterium affects not only humans, but also horses, cows and goats, as well as mice and other rodents. It is rodents that are considered the main carriers of the bacteria.
The reasons
Infection occurs through the mouth, with dirty hands, with food that has gotten germs. They are rather persistent and durable - they cannot be killed in boiling water, in open sunlight, and when treated with disinfectant solutions. Enterobacteria Yersiniae pseudotuberculosis survives well in the refrigerator on products.
Many people mistakenly believe that if there are no mice and rats in the house, then the infection to the child and adults is not threatened. The presence of mice is not required. Rodents contaminate the soil, water, vegetables and fruits with enterobacteria in the place of their growth. And contaminated food and water then get into people's apartments. In water, the bacterium lives up to 8 months, and in the soil it lasts up to a year.
Dairy products, meat, vegetables and fruits that have not been sufficiently sanitized, may well be the cause of pseudotuberculosis infection. Winter and the beginning of spring are the most dangerous months, because people begin to buy and eat vegetables, which were stored in vegetable storehouses for several months, during which the enterobacterium is disseminated and retains its aggressive properties perfectly.
After entering the stomach, bacteria pass the path to the ileum, where they cause inflammation. Then begins the spread of infection through the lymph nodes. Symptoms appear when toxins that produce enterobacteria in the course of their vital activity enter the child’s blood.
If the pathological process is increasing, suffer the liver, spleen. The immune response is formed for a long time, it takes several days for the child’s natural protection to develop the necessary antibodies and start exterminating the microbes.
Immunity is formed not resistant, therefore repeated infection is possible.
The incubation period from the moment of ingress of bacteria through the mouth to the onset of intoxication phase is up to 20 days, but most often in children it is much shorter - 8-10 days.
Types of illness
Depending on which part of the body suffers the most, there are several types of pseudotuberculosis in children:
Abdominal. This type of manifest enterocolitis, often resembles appendicitis.
Arthralgic. With this type of pseudotuberculosis, the joints ache, fever is combined with manifestations of polyarthritis.
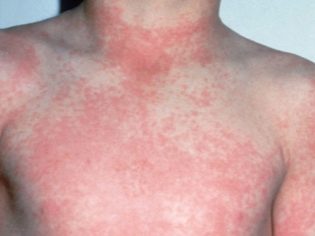
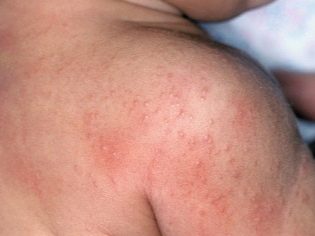
Scarlet-like. This type of disease is a manifestation of a rash, very similar to a rash with scarlet fever.
Mixed. May combine the signs and symptoms of all types of pweed tuberculosis.
Septic. The type of disease is associated with the development of toxic shock.
In severity, the disease can be mild, moderate and severe, as well as complicated and uncomplicated.
Symptoms and signs
Most often in children, pseudotuberculosis develops according to the scenario of a localized form of the disease. The disease always begins suddenly, with a sharp jump in body temperature to 38.0-39.0 degrees.
The child complains of chills and abdominal pain. He may have vomiting. The stool becomes fluid and frequent. Baby can run to the toilet up to 10-12 times a day.
Fecal masses have a greenish tint, foamy structure and a very unpleasant odor. If blood or large fragments of mucus appear in them, this may indicate that the lesion has also affected the large intestine.
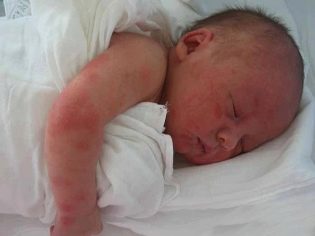
After a few hours or a day, pain in the joints may appear, and they will look a bit swollen. At about the same time (maximum for 3 days), scarlet-like rash - rashes in the form of small nodules.
The condition of the child is characterized by the following symptoms:
Strong headache;
weakness and intoxication;
dehydration is not excluded;
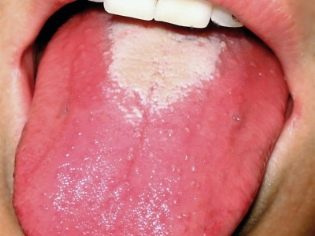
the tongue is covered with white bloom, after 14 days the bloom becomes crimson;
there is redness with a slight blueness of the hands, feet, face;
sometimes pain in the iliac region to the right;
swollen lymph nodes.
With arthralgic type pseudotuberculosis diarrhea and vomiting not. There is fever and soreness of the joints. The condition may, but not necessarily, be accompanied by a rash.
If the disease starts to develop by generalized form, then the temperature rises to 40.0 degrees, vomiting occurs, and almost immediately rash appears on the body.
The most severe is the septic form of the disease.
In babies and children suffering from chronic diseases, the immunity works “to the limit,” it is not sufficient by itself.
With septic-type pseudotuberculosis, the temperature rises above 40.0 degrees, the child sweats a lot, and may faint. He quickly develops anemia. Mortality in this disease is high - about 40% of cases.
For any type of disease at the initial stage, respiratory symptoms appear - sore throat, cough, runny nose. The location of the rash in any type of disease is invariable - the lower abdomen, axillary zones and sides. Larger rashes are observed around the joints. The rash lasts about a week.
If the disease is not complicated and proceeds easily enough, after 5-6 days the child will feel better and the manifestations of the disease will begin to recede. The first one gradually and gradually decreases the temperature, then the signs of intoxication disappear, the joints cease to hurt, the swelling drops, the lymph nodes become normal in size. In case of a complicated disease, recovery may take up to one and a half months; with rapid reinfection, the child may be ill for up to 3 months.
Diagnostics
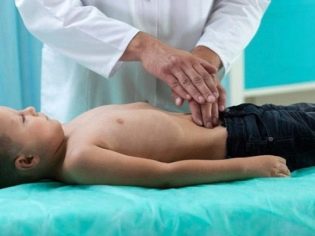
A combination of four symptoms — an abnormality in the gastrointestinal tract, fever, a rash, and pain in the joints — should help the physician make the correct diagnosis. Doctors must be called to the house when the initial signs, as mentioned above. A pediatrician may suspect pseudotuberculosis, but only a laboratory technician can confirm the diagnosis and he will do all the necessary tests.
The child takes an analysis of feces, urine, smear from the pharynx and sputum on bacpery. Growing on special nutrient media will allow you to get a sample of the pathogen and test it for sensitivity to different antibiotics. This information is needed to choose the right drug for treatment.
Pseudotuberculosis is very similar in clinical picture to measles, scarlet fever, rubella, acute respiratory viral infections, intestinal infection, so a blood test for the presence of antibodies to viral infections is sure to be done.
Do not be afraid if the doctor offers hospitalization, at least a day. The fact is that careless attitude to the symptoms can lead to the fact that such pathology as appendicitis, and it requires urgent surgical intervention. In the conditions of a hospital there is an opportunity to carry out a laparoscopic diagnosis to a child.
Treatment
The main danger of pseudotuberculosis in childhood lies in the possibility of rapid dehydration. With high temperature and repeated vomiting and diarrhea, the state of dehydration can develop in a few hours. It is deadly for the child, especially for the baby.
In order to prevent dehydration, parents must often and often give the child a drink of warm water, tea, and water. If vomiting does not give the child to drink, and every sip causes a new fit of nausea, and if the child refuses to drink outright, you can try to drink the baby from the disposable syringe in small portions.
If this is not possible, you should immediately call an ambulance, doctors will be able to provide the child with intravenous fluids of saline and glucose to fill the fluid deficit.
In the stage of acute intoxication, the child should be given funds for oral rehydration - “Smektu”, “Regidron"," Humana Electrolyte "and others. From the first symptoms associated with fever, you need a strict bed rest with the control of body temperature and the admission of antipyretic. Parents, just in case, should be ready to provide emergency care for febrile seizures, which can also develop in the acute period.
To feed a child by force is impossible. But if he himself asks for food, then you should be given only diet food, porridge-mash, vegetable soup with crackers, jelly. Spicy and salty foods, smoked meats and pickles, as well as dairy products should be avoided.
Mild forms of pseudotuberculosis do not need antibiotics. Recovery can be achieved by giving the child a feasible home help in the form of abundant drinking and pureed food, the rest of the immunity will do itself when it forms a sufficient amount of the necessary antibodies to penetrated enterobacteria.
Moderate and severe forms of the disease are not complete without antibiotics. Usually, the child is prescribed a drug from a number of penicillin antibiotics.
They are most easily perceived by the child's body. In case of ineffectiveness or resistance of the bacterium to penicillin shown in the laboratory, the doctor recommends preparations of the tetracycline group of antimicrobial agents.
Enterobacteria is very sensitive to antibiotics-aminoglycosides, for example, to "Gentamicin" and "Neomycin". But parents from such an appointment, if it suddenly happens, it is better to refuse. The fact is that these antibiotics are ototoxic for children, their use can cause the development of partial hearing loss or complete persistent deafness. After the end of treatment, hearing is not returned.
The course of taking the recommended antibiotics for pseudotuberculosis is from 7 to 14 days, depending on the type of the disease and the characteristics of its course.
For joint pain, doctors often recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as "Ibuprofen". Topical anti-inflammatory ointments, such as “Indomethacin”, can be administered locally. Symptomatic treatment may include nasal drops with a vasoconstrictor effect on a head cold, rinses and throat antiseptics, when a sore throat appears, as well as antipyretics - Paracetamol and Ibuprofen. "Aspirin" and all funds that have acetylsalicylic acid in their composition are prohibited for children, as they can cause dangerous Ray's syndrome.
To relieve gastrointestinal symptoms, enterosorbents are prescribed, for example, “Smecta” or “Enterosgel". Multivitamins can be prescribed at the final stage of the disease. To relieve joint pain and pain in the lymph nodes, dry heat is shown - a scarf or a warm shawl. Compresses - oil or alcohol - is strictly prohibited.
Prevention
The prevention of this disease is given a lot of attention at the state level. Owners of vegetable stores and food warehouses are obliged to comply with certain security measures, in particular, to ensure that there are no mice and rats in the warehouse, as well as to destroy them in a timely manner.
Water supply organizations evaluate the presence of enterobacteria in water samples, and public catering institutions, organizations that prepare food for children's groups, are obliged to regularly take samples of products for analysis to comply with the recommended rules for processing products.
On their own, parents can add home-based preventive measures to measures across the state. It is necessary to thoroughly wash all the vegetables and fruits, both purchased in the market and purchased in the store. It is not necessary to give the child ready-made vegetable salads and vinaigrettes bought in the supermarket. Milk that has not been pasteurized, for example, purchased from private farmers, should be boiled.
When rodents are found in the house or traces of their stay, it is important to quickly take measures to eliminate mice and rats by any available means.
It is important to teach the child to wash his hands, especially after walking on the street, where he could contact the soil, water, and animals contaminated with enterobacteria. It is equally important to teach the child not to take his hands in his mouth or at home, much less on a walk. If dangerous symptoms appear, isolate the baby from other children.
See also the following video for what pseudotuberculosis is.