Ultrasound in the 20th week of pregnancy: fetal size and other features
The 20th week of pregnancy completes the first half of the term of carrying a baby. Toxicosis retreated, the health and mood of the mother at the height. It was at this time that many begin to feel the first movements of their toddler. During this period, a woman may receive a referral for a second planned ultrasound scan. Next, we will discuss the difference between ultrasound during this period and what are the standards for the development of the baby in 20 obstetric weeks.
What is it for?
At the end of the fifth month of pregnancy, an ultrasound is not just a whim of a woman who wants to admire her growing offspring. This study is part of the second trimester screening. On the recommendation of the Ministry of Health of Russia, screening is conducted from 18 to 21 weeks. Most often, a visit to the ultrasound examination room falls on the 20th week - the period between 19th and 20th week (more than 17 weeks have passed from conception, by the standards of a woman).
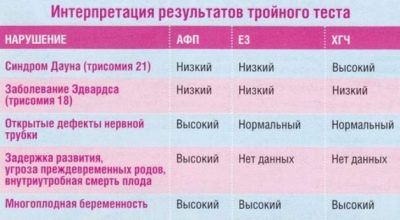
The screening includes studies of venous blood by a biochemical method using a triple or quadruple test. This study helps to establish exceeding or understating the level of hormones and proteins important for a normal pregnancy. Their change often accompanies various genetic pathologies. The picture is complemented by a survey in the office of ultrasound diagnostics.
In the first trimester, from 11 to 13 weeks, the woman has already passed the first screening, and therefore the individual risks of the birth of a baby with Edwards, Down, Turner and other incurable diseases of genetic origin are already known. Second screening allows you to judge such an unpleasant perspective on the basis of other substances in the blood, as well as other markers of pathologies on ultrasound.
In addition, ultrasound examination at this time may pursue other goals:
- child development assessment;
- assessment of the state of the placenta;
- diagnosis of possible deviations in the course of pregnancy - the risk of premature birth, fetal death;
- clarification of the timing of gestation and more accurate determination of the date of birth
Preparation for the procedure and features of
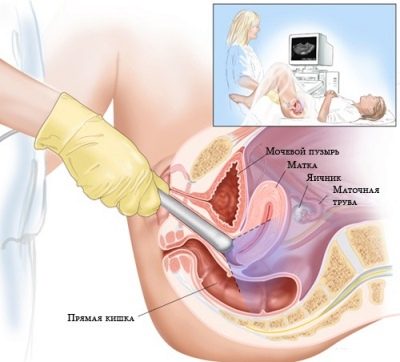
Ultrasound examination at week 20 is carried out externally, transabdominally, that is, the sensor is guided through the abdomen, an overview is available through the wall of the bushin.
There are not so many situations in which the doctor may decide to use a vaginal sensor on an ultrasound at this time. Basically, it is overweight in a pregnant woman, the presence of impressive fat deposits in the abdomen.
If the probe through the stomach to examine the baby fails, a decision is made about transvaginal ultrasound.
Internal ultrasound can also be performed if suspected premature abnormal cervical dilatation, cervical insufficiency, placenta previa.
At week 20, ultrasound is not performed in a viewing chair; for this purpose, use the couch, on which the expectant mother can sit both in a position on the back and in a position on the side, if it is not comfortable to lie on the back.
No special training for ultrasound at this time does not require. Do not drink water, follow a diet, free the intestines from gas - the uterus is already so large that the intestines, together with the gases filling it, are moved back, and the view does not interfere.
When undergoing screening ultrasound at 20 weeks, there is no need to donate blood on the same day as a visit to the diagnostician's office; during this period, these components of perinatal diagnosis can be performed on different days. The procedure lasts 5-10 minutes, it will not harm the pregnant woman and her baby.
What will the ultrasound show?
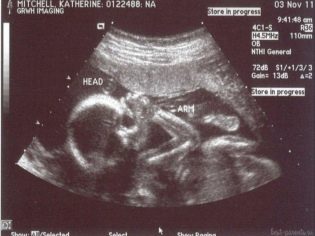
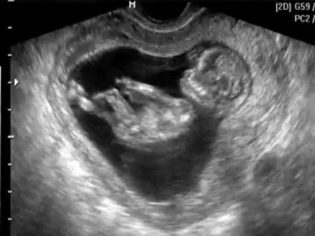
For the first half of pregnancy, the baby has done a great evolutionary path. Almost all organs are formed in it, the work of the systems is improving - nervous, in particular. The height of the crumbs this week - about 26 centimeters. The baby weighs only about 300 grams.
This week's baby has a big event - his eyes acquire photoreceptors, and now the crumb can distinguish between light and darkness. If you shine a flashlight on the stomach, the movement of the baby can increase. At the end of the fifth month, the baby learned to “make faces”, and now, with ultrasound, if you are lucky, you can see how he blinks, blinks and makes faces.
The child looks like a small, but already fully formed, little man. He is already well controlled with his pens, playing with the umbilical cord, sucking cams. His intestines are working, the baby is swallowing the amniotic fluid, the small stomach has begun to function.
At 20 weeks, the doctor carefully examines the fetus (or fetuses, if there are several of them in the uterus), assesses the size of the baby, compares the results with tables of normal values for the gestational age. This allows you to establish not only the exact date, adjust the date of delivery, if necessary, but also understand Does enough nutrition get a crumb, he has no diseasesthat may hinder its normal development.
The doctor will be able to examine the internal organs of the baby, assess the condition of the placenta, umbilical cord, amniotic fluid. If mother’s health leaves much to be desired, scanning will allow her to assess the condition of her reproductive organs, identify inflammations, cysts, possible problems with the cervix and cervical canal, which can be signs of threatening abortion.
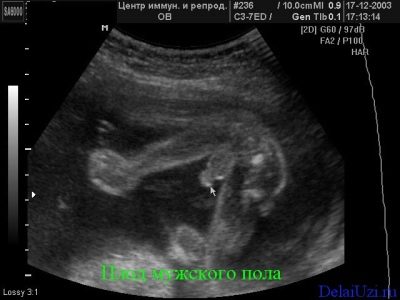
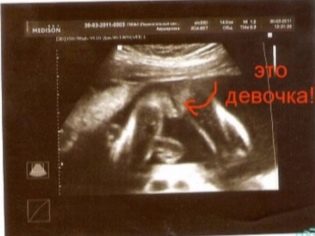
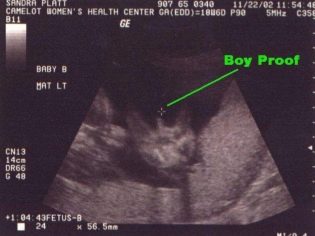
On the ultrasound at the twentieth week clearly visible sex of the child, problems with its definition should arise. On the first ultrasound, the sexual characteristics were hampered by their too small size. At the third, which is waiting at the end of pregnancy, with the diagnosis of gender also can be difficult. The child will become big, “curl up” in a compact pose and it will be very difficult to see a boy or a girl in a baby.
Now is the right time to find out who to expect - a son or daughter.
Indicators, norm, transcript
All standards are given solely for informational purposes, and can not be the basis for self-diagnosis of problems. Not always the deviation from the mean values indicates diseases, almost all parameters are evaluated by doctors in proportion to each other.
In the protocol of ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor notes the number of babies found in the uterus and always indicates whether they are alive. A living fruit is considered such a fruit which has recorded motor activity and heartbeat. On this period, the type of baby's position in space is indicated - headache presentation, pelvic or transverse.
If the doctor writes that the baby is in the pelvic or transverse position, do not be afraid and worry.During the day, the baby, who feels well and freely in the uterus, makes dozens of coups from head to foot and back.
If at the time of the mother's diagnosis, the doctor “caught” him in a transverse position, this does not mean that the child will remain in this position until the very birth. Presentation at week 20 does not matter much.
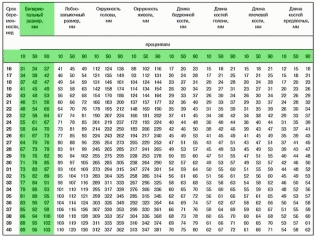
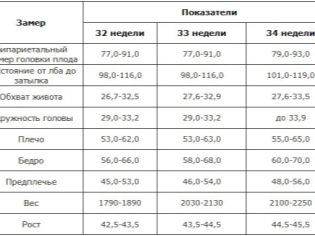
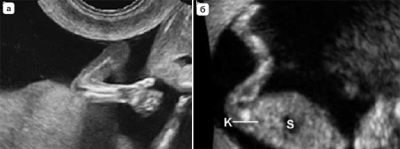
In the protocol section “Fetometric indicators”, pregnant women will receive various letter abbreviations and numbers, which are not so easy to understand. At the twentieth week, the doctor measures the length of the bones, the circumference of the head, abdomen, transverse and longitudinal dimensions of the head, as well as the cerebellum.
Rates fetometrii on week 20 (summary table):
Week of pregnancy | BPR (bipariented size in mm) | LZR (frontal-occipital size in mm) | OG (head circumference in mm) | Coolant (abdominal circumference in mm) |
19-20 | 44-47 | 58-62 | 158-170 | 134-144 |
Bone length:
Week of pregnancy | DBK (thigh length in mm) | DKG (calf length in mm) | WPC (shoulder length in mm) | DKP (forearm length in mm) |
19-20 | 30-33 | 27-30 | 27-30 | 23-26 |
Based on fetometry data, the ultrasound scanner independently calculates the estimated weight of the fetus. Values from 200 to 350 grams are typical for this period. Girls are more likely to weigh less than boys, even if the gestational age in both cases coincides with up to a day.
In the section "Anatomy of the fetus" the doctor describes the condition of the internal organs of the child. The lateral ventricles of the brain, the facial bones, the spine, the orbits, the heart, the kidneys, the stomach, the intestines, the lungs, the gall bladder and are considered and described. If the doctor does not see the pronounced malformations of these organs, then Latin N will stand opposite the name of this or that organ, which means “norm”.
If pathologies are detected, and ultrasound at this time allows you to see the underdevelopment of an organ or its absence, the doctor describes the type of pathology opposite the name of the organ. So, opposite to the line “Intestines” a record may appear - “Atresia of the anus” or “Extended loops”.
Theoretically, any pathology of internal organs can be a marker of chromosomal abnormalities; therefore, each specific situation should be considered separately. Several additional ultrasounds will be required, possibly invasive diagnostics (cordocentesis or amniocentesis) to determine if the baby has chromosomal illnesses.
After that, the doctors will decide how and when to treat a child if his illness is considered treatable. If these are total syndromes, then the mother will be given some time to think about the possibility of terminating the pregnancy for medical reasons. The final decision remains for the pregnant woman and her family.
At the end of the examination certificate, the doctor indicates characteristics of the placenta - how high it is located from the inner throat, on which uterine wall attachment occurred. Most often, the "baby seat" is mounted on the back wall. The normal for this period, the degree of maturity of the placenta is 0. At this stage, low placentation or placenta previa is often detected. The doctor assesses the size of the cervix, the state of the cervical canal and the presence or absence of uterine muscle tone.
Possible problems
BPR and LZR of the head is less than the norm
A slight deviation from the average table values of the size of the baby’s head does not indicate anything alarming. All children in the middle of pregnancy grow at different rates, besides, no one excludes a hereditary feature of appearance - a small head. Anxiety is considered a deviation from the lower threshold of the norm for 2 weeks (if the fetal BPR, for example, corresponds, not to the twentieth, but to the eighteenth week of gestation).
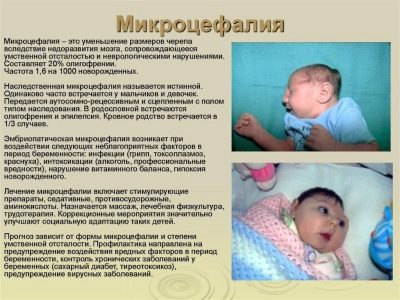
Head reduction may be caused microcephalyas well as inadequate nutrition. In this case, doctors will be talking about intrauterine growth retardation. Additional studies will help to identify the exact cause, with delayed development, prognoses are favorable - vitamin preparations help as well as medicines that improve uteroplacental blood flow.
The head of the baby more than the age norm
Excess normal fetal head size this week is sometimes a sign of hydrocephalus, swelling due to infectious processes or malformations. A slight excess of indicators (less than 2 obstetric weeks) may indicate that with this pregnancy there is a tendency for large (about 4 kg) or giant (more than 5 kg) fetus.
Again, the doctor needs to look at mom and dad, perhaps they have big heads - a family trait, and then no correction will be required.
The abdominal circumference of the child is less than gestation
This indicator may be a feature of the child's build, because thin mothers and fathers usually have the same slender children. As is the case with the size of the fetal head, it is critical to lag behind the norm by more than 2 weeks.
This situation requires careful study of the uteroplacental blood flow, the particular placenta, in time to identify possible causes of malnutrition. The thinness of the fetus itself is not dangerous. The task of doctors - find its true cause, which may pose a risk to the further development of the child.
Bone length does not match age
An indirect marker of genetic pathologies during the second ultrasound is the shortening of the bones of the lower leg, the length of the remaining bones is measured only in order to imagine the proportions of the baby, as well as to track its development.
Shorter or longer forearms or thighs in most cases turn out to be features of the child's appearance, because he may have genetically laid long legs or short arms. Such changes are considered physiological.
Pathological abnormalities and shortening of the limbs can not go unnoticed, and the woman will immediately be sent to the genetics for consultation.
Low placenta
The uterus grows, the placenta still has every chance to rise to a normal height, which most often happens if the pregnant woman observes all appointments of her doctor.
Common Questions
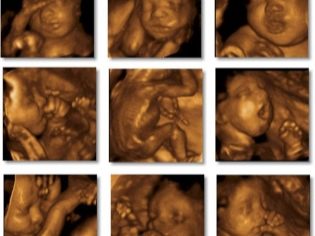
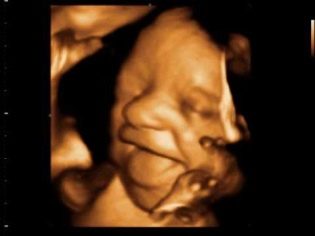
3D ultrasound
This type of ultrasound diagnosis at this time is carried out, and it allows you to take a closer look at the baby, to get beautiful pictures of the fetus. An obstetrician or geneticist sends women to an expert-class ultrasound if alarm markers or abnormalities are identified. Visit a 3D ultrasound a woman can voluntarily.
Fetus snapshots
On ordinary shots, you can see quite well what the crumb is doing - the outlines of the arms and legs are clear, the profile of the face is visible. But 3D ultrasounds and pictures that are obtained on such a device, if the baby “agrees” to pose, give a more complete picture of what a son or daughter looks like. If lives in the tummy twinsthen at week 20 it looks like this.
Gender Mistakes
Mistakes in determining sex at this time unlikely. It is still possible to confuse a boy with a girl in rare cases if the baby had a umbilical cord clamped between the legs. Such a girl will be mistakenly considered a little boy. And the shy boy, who squeezed his genitals between the legs, will be considered a girl for the time being. The probability of such a “confusion” is no more than 1.5-3%.
Unfortunately, there are situations when the floor cannot be seen, because the child is facing in, back and back to the ultrasound sensor. If no external influences (clapping, tapping) help the baby turn around, the doctor will have to admit that it is impossible to determine the sex at the moment, and will advise you to come to the appointment later.
Gender determination is not included in standard diagnostic actions during screening, and therefore this service will be paid for by the most pregnant woman at the rates for the provision of paid medical services for a specific antenatal clinic.