Symptoms and treatment of otitis in children
There are no parents in the world who have never encountered otitis media. Ears in children, indeed, often inflamed. And for this, kids have many reasons - physiological and pathological.
We will tell about how to recognize otitis in a child, how to help him and how to treat inflammation of the ears.
What it is
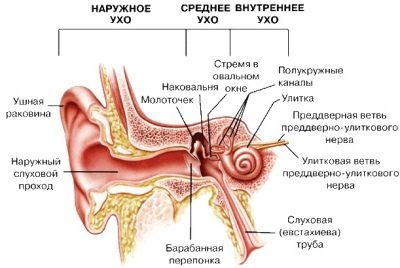
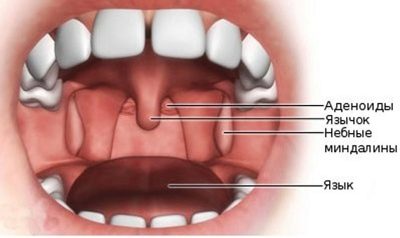
The organs of hearing have in their structure three divisions. Directly, the auricle and the auditory meatus are the external part, the middle part of the auditory analyzer is represented by the eardrum, the eponymous cavity and the auditory ossicles, the deep inner ear is a complex system of labyrinths that extend further into the brain, the acoustic nerve fibers.
When inflammation of any of these departments develops a disease called otitis.
The disease is more characteristic of children than adults. According to available medical statistics, almost 85% of babies up to 2-3 years at least once suffered a catarrhal form of this ailment. Overwhelmingly, small patients show inflammation. middle ear.
By the age of 7, almost no child remains who has never complained of ear pain. In 25% of children, the disease becomes recurrent in nature.
Otitis is considered one of the most painful ailments, since it is always accompanied by extremely unpleasant symptoms.
In the absence of adequate medical care, the inflammation of the ears can lead to serious consequences - inflammation of the meninges, hearing loss until the onset of deafness.
Causes
Hearing organs can be inflamed by external and internal causes. To external can be attributed to mechanical injury, hypothermia. The main internal reason - the penetration into the departments of auditory analyzers of pathogenic microbes, fluids.
Usually otitis is caused by such microorganisms as the pyocyanic stick, staphylococcus, some aggressive representatives of the intestinal microflora, as well as disease causing fungi.
In a healthy child, many of the bacteria live on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and do not show aggression towards the host. However, it is necessary for the baby to get sick, inadvertently sniff the nose, blow the nose incorrectly, sneeze unsuccessfully, and now the contents of the nasopharynx fall into the auditory tube, where the microbes have all the conditions for the start of reproduction.
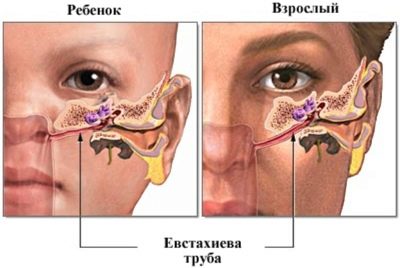
In adults, the disease does not have such a wide prevalence due to the fact that their auditory tube is located almost vertically, and the injection of fluids into it is hampered.
In children, the auditory tube is shorter, wider, it is located almost horizontally, so there is nothing surprising in the fact that inflammation occurs frequently. Any ingress of water, for example, at sea, causes an acute painful process. This explains why children often complain of earaches after a pool.
The mechanism of the disease is simple and clear. The list of reasons that can “start” the pathological process looks much more complicated:
- SARS, flu. During illnesses of viral origin, which, by the way, are very common in childhood, the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx almost always swell and increase in size.
The swollen mucosa closes the entrance to the auditory tube, it creates a "greenhouse" environment in which microbes multiply rapidly.
- Children's infectious diseases. Measles, diphtheriachicken pox adenovirus infection - All these diseases are often accompanied by otitis. Inflammation of the hearing organs acts as a complication.
- Pathologies of upper respiratory tract. Various pathologies directly affecting the likelihood and incidence of otitis directly affect the folded ear-throat-nose mechanism, such as adenoiditis, tonsillitis, nasopharyngeal tumors and polyps. In children with adenoids, the ears become inflamed more often.
- Injuries. Microbes can get into the middle part of the ear from the outside. This becomes possible with trauma to the eardrum. And external injuries of the auricle often lead to local inflammation - the external form of the disease.
At risk - all children, without exception. But children born prematurely, children with severely weakened immunity, for example, often sick toddlers, children who are subject to sudden pressure jumps - often traveling on airplanes diving into the water - are especially susceptible to otitis.
Contribute to the development of the inflammatory process in the organs of hearing and chronic diseases that are present in the child, as well as fatigue, strong nervous stress.
The child grows, and with it the structures of the hearing organs grow. The auditory tube is gradually verticalized, lengthened, becomes narrow, and otitis retreats. This usually happens by 12-14 years old. After this age, ear inflammation is no longer a common occurrence.
Psychosomatic causes
Such a direction as medical psychosomatics examines other causes of otitis media in children. The basic principle of psychosomatics says that all diseases are in close connection with the emotional sphere of a person, with his mental state. Regarding otitis, psychotherapists consider several possible causes:
- The child does not want to hear something or someone from his environment. This usually happens in families where they adhere to too strict rules of upbringing, where quarrels and scandals are constantly heard, and adults arrange their showdowns right in front of the child. With a strong sudden pain, the child “attracts” the attention of scandalous adults to his own person, and with some deterioration of the auditory function, he “protects” from streams of negative information that is constantly being heard from outside.
- The child does not know how to control his anger, his resentment on parents and other relatives. He cannot express them for some reason (due to age or the rules of decency), but anger finds a way out in limiting the ability to hear, even if only temporarily.
There are other, individual reasons that a psychotherapist or a psychosomatist can understand. It becomes relevant when the doctors after a series of various tests could not find out the true cause of the inflammation of the ears.
Analyzes are normal, prescribed medications do not help or help, but not for long - all these are reasons to think about what psychosomatic causes may arise for a particular child to start ear disease.
Types and classification
Inflamed can any of the three sections of the child’s ear. Thus, medicine distinguishes between otitis:
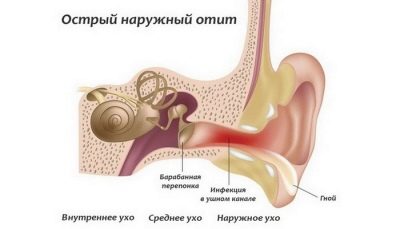
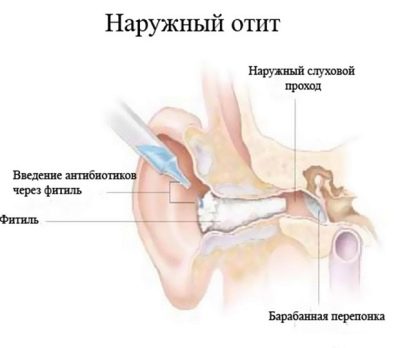
- Pathological process in the outer ear, auricle, ear space - external otitis.
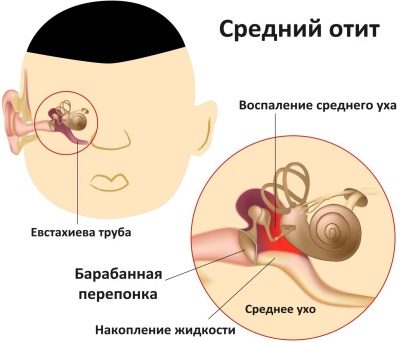
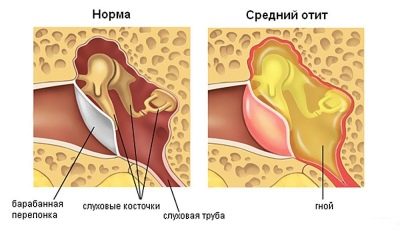
- The inflammatory process of the middle part organs of hearing - otitis of the middle ear.
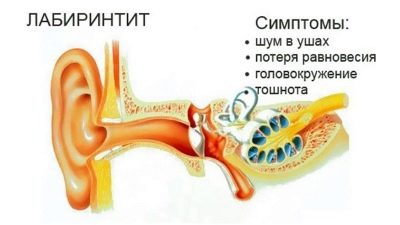
- Inflammation of deep structures, inner ear - labyrinthitis.
The external form of the disease often acts as a completely independent ailment, but pathological changes in the middle or inner section usually are nothing but complications after inflammation of the airways caused by viruses, pathogens, fungi or other causes.
Labyrinthitis is the most dangerous, but fortunately the rarest of otitis, often develops as a complication of severe otitis media.
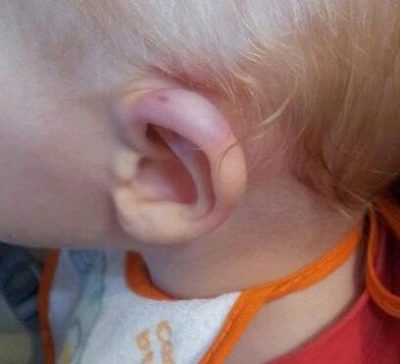
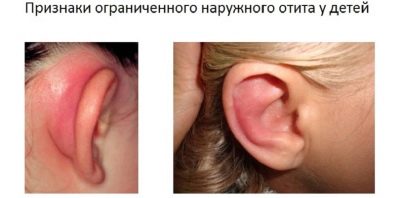
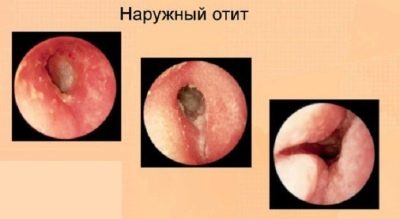
External otitis is usually manifested in the form of furunculosis - local inflammation of the auricle, ear canal, space behind the ears. Redness, suppuration may well be strictly localized - limited when there is one or two boils, or it can be quite diffuse, so-called diffuse.
With this form of the disease, the entire area of the auricle and the auditory canal is drawn into the inflammatory process. Sometimes even the eardrum becomes inflamed.
If a child has chronic suppurative otitis, then a diffuse spillage may be a complication, since pathogens with a constant breakthrough of pus from the middle ear can get into the subcutaneous space.
Otitis media is acute and chronic.
In children, in 95% of cases the disease is in the acute form. The inflammation itself can occur with the formation of pus and without it. Usual inflammation is called catarrhal, and purulent otitis called exudative.
Acute inflammation of the middle ear in its development goes through several stages:
- development of the process, accompanied by congestion in the ears;
- a sense of subjective noise;
- the appearance of a sharp unbearable painful attack, the body temperature rises, suppuration is formed, followed by a breakthrough of the membrane and the expiration of purulent masses to the outside.
Chronic otitis media often has the form of purulent. If inflammation affects only the tubular area (auditory tube), then doctors talk about the appearance of tubo-otitis.
Internal otitis, too, is acute and chronic. The inflammation itself in the deep sections can occur as serous, purulent, and necrotic. This form of the disease is often the result of frequent suppurative inflammation in the middle ear.
Inflammation of any part of the hearing analyzers can affect one ear or both. Children often have unilateral otitis, but bilateral, too, is also a fairly common phenomenon.
Depending on the cause of the inflammation, all otitis are divided into several groups. The most common are:
- viral forms;
- bacterial forms;
- traumatic and post-traumatic forms;
- allergic forms.
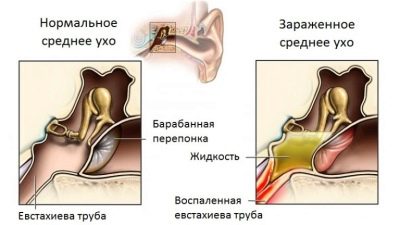
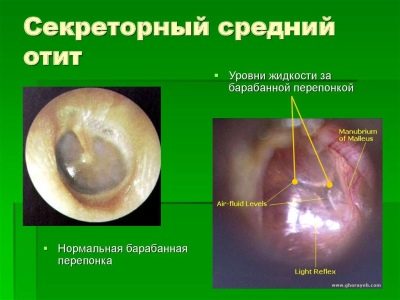
Inflammation, which is localized in the cavity behind the membrane because of obstruction of the auditory tube, which, as already mentioned, may well occur with strong rhinitis or flu, is called secretory otitis. Although it belongs to the non-purulent forms of the disease, it can entail very unpleasant consequences - persistent hearing loss and the development of hearing loss.
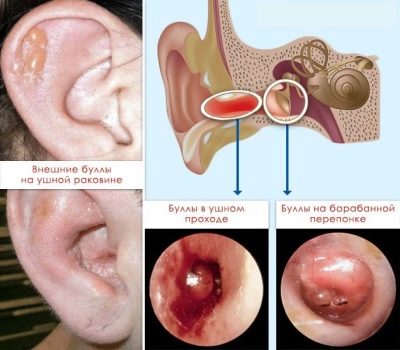
In a special group, such viral otitis can be taken out, in which infection occurs not through a tubular route or through a damaged membrane, but through the bloodstream. For example, bullous otitis is characterized not only by inflammation, but by the formation of bubbles on the membrane-septum and in the auditory canal - the bull. It feels like the occurrence of unpleasant obsessive itchy sensations inside the ear. The bubbles burst with time, and the itching gradually decreases.
The otites, which are provoked by changes in atmospheric pressure, also have their own names.
So, air otitis, which can begin with frequent takeoffs and landings of the aircraft, as well as during the practice of parachuting in adolescents, is called aerootite.
And jumpers in the water know that careless diving can lead to mareotite.
Regardless of the cause and nature of the inflammation, as well as whether it is a two-way or one-way process, the child needs expert help.
Treatment of all types and types of otitis without exception should be carried out only under medical supervision.
Symptoms and signs of otitis media
Manifestations of otitis are generally quite difficult to confuse with other diseases. Too characteristic clinical picture has this disease.
Outer
With such a lesion, the pain is not deeply sharp. Usually, the child complains of the pains that are pulling and aching outside.
On examination, you can see a furuncle or several furuncles. They can be located both in the auditory opening and on the sink. Sometimes the boil is manifested behind the ear in the form of an inflamed lump.
The temperature in this form of the disease does not always increase, and not in all cases it is high, even if the rise is observed. However, inflammation gives a lot of unpleasant moments to the child - when chewing, talking, straining the facial muscles (in a smile, for example), the pain syndrome increases.
The auditory canal is inflamed, it looks puffy and reddened. Sometimes redness and swelling extend to the entire ear completely.
The lumen of the passage as a result is narrowed, the appearance of subjective noise in the ear, a slight decrease in the perception of sounds is possible. These symptoms are temporary, some time after recovery, hearing is completely restored. External otitis almost never leads to permanent hearing loss.
Average
The child usually does not feel the onset of the pathological process in the middle part of the organ of hearing. But the height of this process manifests itself in all its glory - suddenly, brightly, usually in the evening or in the middle of the night.
The first sign is a sharp sharp pain in the ear, which is difficult to endure. If a child tries to turn his head, change its position in space, then the painful sensations become even stronger.
Attempts to drink, eat, talk and even make grimaces are made with great difficulty, because any of these actions cause an aggravation of the already debilitating pain.
The temperature rises immediately or within an hour after the onset of intense painful symptoms.
High temperature at otitis does not mean yet that process will surely be purulent. On average, the thermometer readings during the acute stage are 38.0-39.0 degrees.
The perception of sounds is reduced, there is a feeling of congestion, "wool in the ear," the child can hear a constant low-frequency noise, the baby needs to be addressed louder, because he does not recognize many sounds. Intoxicating may begin in young children at this stage. Almost everyone has headaches.
If the development of acute otitis media reaches the exudative form, then the last hours before the eardrum breakthrough become the peak of suffering. It is perforated and releases purulent contents. After that, the children lose a sharp pain, the symptoms begin to gradually disappear, the kids feel a significant investment.
However, a breakthrough under pressure of exudate can occur not only outside, but also inward, then the child begins to quickly develop symptoms of inflammation of the meninges - body temperature rises, seizures may occur, frequent severe vomiting, episodes of loss of consciousness.
After the symptoms of secondary inflammation begin to subside, there is a lack of auditory function for some time. Do not be afraid, hearing will be restored after a couple of months in full. The only exceptions are cases of severe and complicated disease, in which irreversible changes and damage to the tissues and structures inside the middle ear in the process of strong suppuration have occurred.
The fact that the ear disease has acquired a recurrent form can be said if the relapses recur several times a year, in other words, the child reacts to each or almost every illness with such a complication.
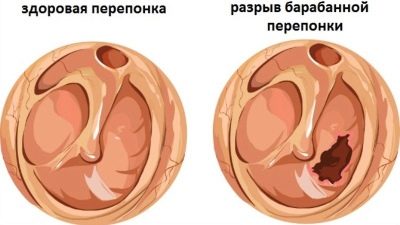
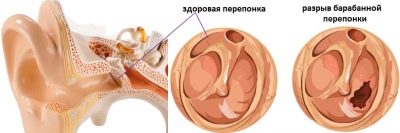
After acute otitis the eardrum, which "survived" the gap, quickly restored, cicatrization, and this does not affect the human auditory function afterwards.
However, if the disease becomes chronic, the membrane often does not heal anymore, this causes a progressive hearing loss until the onset of deafness.
Interior
The processes that occur in this form of disease, such as labyrinthitis, are very complex and subtle, because we are talking about damage to such small and important structures as the auditory and vestibular receptors, the auditory nerve, the cochlea.
This form is rare in children.
In 95% of cases, it is a consequence of chronic otitis media. The remaining 5% are other reasons, such as meningitis, sinusitis and even a systemic allergic reaction.
The initial symptoms of labyrinthitis may appear in a rather erased form. A child may experience tinnitus — from low to high-frequency squeaking; there may be bouts of dizziness or sudden nakes of nausea, as well as an unreasonable loss of balance.
Only in the presence of pus in the internal part of the organ of hearing can a high temperature rise, sometimes higher than 40 degrees. At the same time, the child almost completely loses hearing. His recovery is a big question, usually it is no longer possible to return the auditory perception after the transferred labyrinthitis by 100%.
How to recognize otitis media in infants?
Children who, because of their age, can tell or show where it hurts, make it much easier for their parents. Most of the questions from moms and dads arise in relation to infants, who are more susceptible to inflammation of the ears more than others, but they cannot show and tell anything.
Recognizing the inflammation of the hearing organs in babies is not as difficult as it seems at first glance.
In otitis externa, inflammation will be noticeable visually, since the clinical signs are similar to those observed in older children, adolescents and adults.
Otitis media a baby is always experiencing hard. The baby becomes capricious and restless, the kids from six months begin to almost constantly touch and rub their ear.
When the inflammation reaches the acute stage, the child starts screaming in response to the onset of acute pain, refusing to eat and drink, because it hurts him to suck and swallow.
Hunger as a result will only increase the cry. Against the background of the temperature, the baby shows signs of intoxication - it is sluggish, apathetic, it can start to feel sick, diarrhea can be observed.
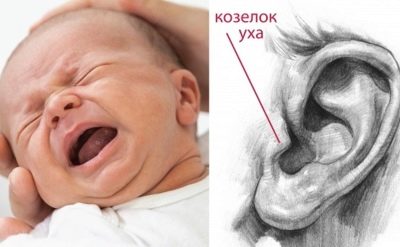
In case of any sharp cry and piercing crying, especially if they happened at night, parents are recommended to carry out a peculiar test for otitis.
The index fingers of the hands need to slightly press on the "trestle" - this is a cartilage, which is located right in the center at the entrance to the auditory opening. If a child has otitis, such a pressing will cause an even more violent reaction, because it increases the pain.
To carry out such a test is best at rest when the baby is dozing off.
Otherwise, it will be quite difficult to draw the line between crying before pressing and crying after, especially if the parents have not yet had time to study all the shades of their baby’s crying. First check one ear, then another, because the disease can be bilateral.
Internal otitis in infants during the first year of life is very rare, and its symptoms, like in older children, begin with the appearance of nausea and dizziness. In the crumbs, the oculomotor muscle on the part of the patient's ear can spontaneously contract, this will be manifested by trembling or twitching of the eyeball.
The baby’s hearing is drastically reduced, it stops reviving in response to my mother’s voice, doesn’t turn his head and doesn’t follow his eyes with a loud rattle or a squeaker, doesn’t scare and does not flinch, as all babies do if the door or window vent suddenly slam.
Danger and consequences
Otitis media is not as dangerous as its complications. Every doctor knows this truth. I would like her parents to learn it. External and average otitis have sufficiently favorable prognoses, provided that there is no self-treatment, traditional medicine and amateur performance.
The earlier it is possible to identify the pathology, the sooner the proper treatment should be started.
If the therapy was wrong, untimely or not at all, the risk of acute otitis media becoming chronic increases by 40-60%. There is nothing good in the fact that the child’s ear is constantly inflamed, no, because sooner or later it will also have its negative consequences.
The younger the child, the more dangerous for him the otitis. In children under the age of one, prognosis for purulent inflammation is less favorable than in children after 3 years.
Conditionally unfavorable forecasts almost always have labyrinthitis, after which the child does not hear well or loses the ability to hear without any special chance of recovery.
Hearing loss at an early age makes the child’s intellectual and emotional development difficult, and his speech skills are difficult to develop.
Special development and training methods for the hearing impaired and the deaf will be required, which will allow the child to at least somehow socialize in the outside world.
The most common complications of ear inflammation are:
- hearing loss;
- deafness;
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- hydrocephalus (with otitis at an early age);
- paralytic changes of the facial and ternary nerve.
A fatal outcome, although unlikely, is also possible, especially if the breakthrough of purulent masses inside is accompanied by the development of general sepsis, brain abscess.
In a family where several children are brought up, it is always a reasonable question to ask whether otitis media is contagious, whether it is dangerous for other babies if someone is sick.
Viral, allergic, traumatic forms of the disease do not pose any danger from the point of view of infection.
Only some types of inflammation, such as staphylococcal otitis, for example, can be contagious.
The infection spreads through the household, contact, with common toys and dishes, especially dangerous external and otitis media with separation of pus.
If the doctor came to the conclusion that it is bacteria or fungi that multiply in the ear of the baby, then it is better to isolate the baby from communicating with other children until recovery, to provide him with separate dishes, bedding, towels, toys, to prevent close physical contact with the healthy.
Diagnostics
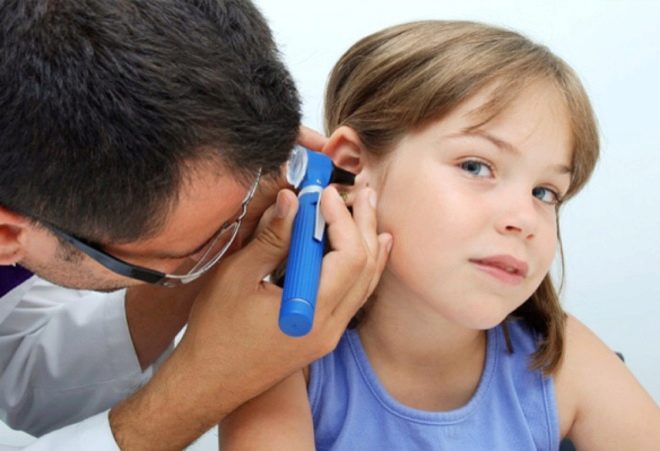
At the first signs of otitis or suspicion of them, parents must show the child to the pediatrician and otolaryngologist. If the child is an infant, then it is better to call him a doctor at home.
With the help of an otoscope device, the doctor will examine the state of the eardrum, be able to find out if it is intact, whether there are signs of protrusion, retraction of the septum, puffiness and purulent inflammation.
If at the time of inspection pus or another liquid flows from the eye, its sample must be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Additionally, blood tests are carried out for the presence of antibodies to viruses, some bacteria, allergen proteins. The ENT examines the tonsils, nasal passages, larynx to exclude concomitant pathologies.
If the reason remains unclear, then the child is recommended to undergo a CT scan of the temporal bones.
In case of severe hearing loss, special audiological research methods are prescribed - audiometry, acoustic impedancemetry.
In general, after undergoing a course of treatment, it is advisable to visit a pediatric audiologist (a hearing specialist) for all children who have had otitis.
After all, some forms of loss of sound perception develop imperceptibly and gradually, and without proper control of the situation, it is easy to miss the signs of incipient hearing loss.
If otitis is complicated, with the involvement of the membranes of the brain, damage to the ganglia, then another doctor, a neurologist, must be connected to the diagnosis. His task is to prevent the development of total neurological effects.
First aid
The younger the child, the less time the parents have to ensure that he has qualified medical care. In infants, purulent otitis can develop from the catarrhal form in just 5-7 hours, so you need to act quickly.
If the pain in the ears appeared at night, the ambulance can be called up for the child up to one year old, and the older child can be given emergency care on their own. Its effect should be enough at least until the morning when the clinic opens or you can call the pediatrician to the house.
In the framework of first aid parents should not bury any medication in their ears. Even if there are good and effective ear drops in the home medicine cabinet, you should not use them at the pre-medical level, since there is no certainty that the eardrum is intact.
If any liquid flows out of the ear, it is definitely not possible to apply drops, the discharge of exudate indicates perforation of the membrane.
If nothing follows, it is not necessary to drip either, until the doctor examines the membrane with an otoscope and confirms that it is intact. Otherwise, the instilled liquid can get directly into the inner ear and cause irreversible changes there with serious consequences.
It is also not necessary to impose warming compresses during the first-aid phase, since it is not possible at home with improvised means to determine whether there is pus accumulation in the inflamed ear section or not.
When a cavity filled with pus is heated, the inflammation only intensifies, which also threatens with serious complications.
Proper first aid should be:
- try to calm the child, hug him, take him in your arms if he is small;
- drip into the spout for 2-3 drops of vasoconstrictor nasal drops (“Nazol”, “Nazivin” will do), this will allow to reduce the swelling in the nose, nasopharynx and the auditory tube;
- give the child an age dose of an antihistamine ("Suprastin", "Loratadine», «Tavegil"," Erius "or any other), it will also reduce the swelling and reduce the manifestations of intoxication;
- give the child a fever reducing agentif the temperature has increased by 38.0 degrees (you can choose any drug based on paracetamol, you should absolutely not give acetylsalicylic acid based drugs);
- with severe pain, you can give a dose of drugs with painkillers effect ("Nurofen", "Ibuprofen", Older children -"Analgin»).
On this algorithm of actions of parents can be considered complete and as complete as possible. All the rest will be prescribed by the doctor after he determines the nature and causes of the disease, the degree of the inflammatory process, the features of the baby’s body.
Treatment
Treatment of otitis externa, as well as most cases of moderate inflammation, is permitted in home conditions.
In case of severe purulent otitis or labyrinthitis, the child is hospitalized. and provide him with all the necessary assistance in the hospital. For the treatment used mainly conservative methods - drugs, physiotherapy.
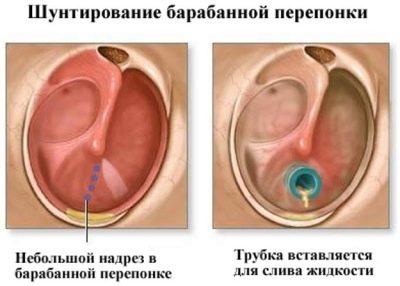
Sometimes, if the doctor has concerns that purulent masses can penetrate into the lining of the brain, they make a puncture of the ear, or rather the eardrum, to release the exudate outside.Do not be afraid of such a mini-operation, everything goes quickly, painlessly, and within a few minutes after the puncture the child feels much better.
Otitis media treatment lasts on average from 10 to 14 days. During this time, parents should closely monitor changes in the condition of the child, as well as to strictly follow all medical recommendations.
External otitis media is treated topically, in rare cases, antibiotics are prescribed for oral administration. Otitis media is a complex treatment with the use of medications, physiotherapy.
Internal otitis needs medical treatment, and at times in surgical intervention.
Medicines
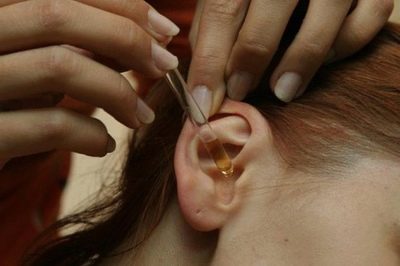
Drops
Ear drops, which are prescribed for otitis media with an average, if the eardrum is intact and unharmed, are of two types - antibacterial and osmotic-active (containing painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs).
On the shelves of pharmacies today presents a huge selection of such drugs, but it should be remembered that not every medicine, effective for ear pain in adults, is also useful and effective when used in children.
In pediatric practice, drugs that work against a wide range of fungi and bacteria have proven themselves in the best possible way. These drugs include:
Instillation is carried out 2-3 times a day at a dosage by age. Drops before that warm in the palm of your hand.
Often with unilateral otitis it is recommended to instill in both ears, starting with a healthy one, in order to avoid the spread of infection to the second organ of hearing.
Usually, children of any age tolerate such treatment well, except for a brief burning sensation and itching in the ear immediately after dropping into it, no other side effects are observed.
Often parents can hear recommendations from their parents and neighbors to drip boric acid into their ears. If you believe the instructions from the manufacturer, this drug is not prescribed until the age of 15. But if you really want to use such an antiseptic as boric acid, then you should definitely ask for permission from your doctor.
There are specialists who trust this medicine and prescribe it to children who have not even reached adolescence. But if the doctor is categorically against it, one should not insist, let alone conduct experiments on the tolerance of aggressive boric acid on his own sick child.
Antibiotics
Antimicrobial drugs are prescribed for otitis practically always - a place or systemically, and sometimes in combination of these two methods of administration.
The choice of a specific antibiotic is the task of the doctor.
In the treatment of otitis media, penicillin group drugs, as well as antibiotics, cephalosporins, have proven to be the best. In some cases, antibiotics are recommended macrolides.
Most often, children are prescribed:
- «Flemoxine Solutab»;
- «Sumamed»;
- «Amoxiclav»;
- Augmentin;
- «Suprax»;
- «Ceftriaxone».
Antibiotic therapy for otitis media is prescribed on average for 5-7 days, in difficult cases it can be extended to 10 days.
Usually, 2-3 days after the start of taking such medicines, the child becomes noticeably better, and many parents are tempted to stop giving the baby pills or suspensions.
It is absolutely impossible to stop taking it without completing the course, since this can lead to the fact that the surviving bacteria develop resistant resistance (resistance) to this type of antibiotic. The inflammation that recurs will be caused by the “enhanced” version of the microbes, and it will be much more difficult to cope with it.
The question of the advisability of the appointment “Dioxidine"At otitis The child has. Some doctors, especially representatives of the old pediatric school, are the true "fans" of this tool.However, current trends in medicine say that "Dioxidine"Besides benefits, brings a lot of harm in childhood, and therefore give preference to the antibiotics listed above.
Treatment of different types of otitis
Outer
In the external form of the disease, most often enough local treatments with antiseptics, for example, with a drug such as "Miramistin».
The doctor may advise parents to introduce the child in the eye gauze turunda with "Dioxidine"Or" Norfloxacin ". The child will benefit from physiotherapy, such as irradiation of the ear with infrared rays.
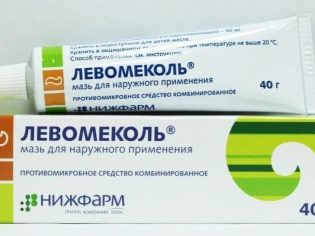
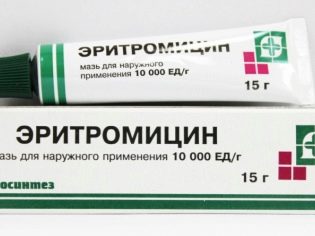
If the boil is not opened, and the pain does not go away, the abscess can be opened surgically, clean the cavity and prescribe an ointment with antibiotics "Erythromycin", "Tetracycline" or "Levomekol».
When the temperature rises, systemic internal antimicrobials may be prescribed.
Average
The basis of the treatment is ear drops, if the eardrum is intact. Antibiotics are also prescribed by mouth if otitis is severe.
To suppress the inflammatory process, it is recommended to take anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal agents, for example, "Ibuprofen" in the age dosage 1-2 times a day.
Only antibiotics inside without instillation into the ears are appointed only after the procedure of paracentesis of the membrane (puncture, which was mentioned above).
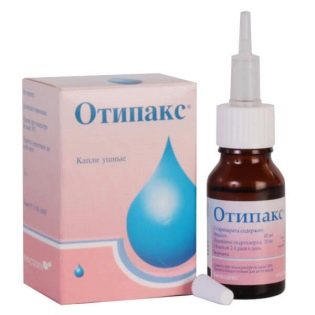
If ear inflammation is caused by allergic edema, the treatment is based on ear drops with an analgesic effect (with lidocaine, for example, "Otipaks"), And at the same time the child takes antihistamines.
With non-purulent acute otitis, you can do a warming compress at home. Below we will explain how to do this.
After recovery, it is desirable for the child to carry out procedures that will improve the functional abilities of the auditory tube - blowing, pneumomassage membranes, electrophoresis on the ear area with lidocaine.
Labyrinthitis
The child is shown bed rest in a hospital. He is given the necessary antibiotics, usually injections. The drops are instilled into the ears with an anesthetic effect; the paramedic injects anti-inflammatory drugs into the middle ear.
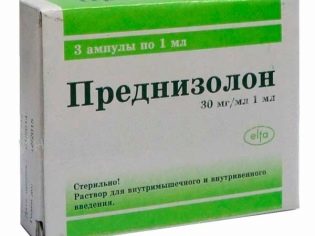
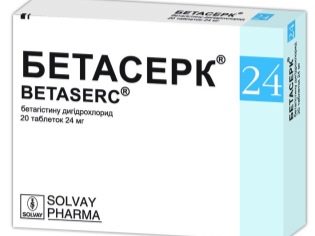
To enhance hearing, an emergency introduction can be given.Prednisolone", And a little later - drugs that improve the blood supply and metabolic processes in the inner ear -" Betaserk "," Vestibo "," Neyromidin "and others.
If conservative treatment does not work, and after removing the inflammation, hearing loss continues to progress, despite hearing improvement therapy, the child may be shown wearing hearing aids or surgery aimed at prosthetics of the damaged parts of the auditory ossicles, cochlea.
Cochlear implantation allows you to restore a portion of hearing sufficient for a child to learn, speak, and communicate.
Compress
Dry compress can be applied to the ear with external otitis. It does not require any drugs.
The treatment compress is more difficult to perform with moderate acute otitis media, which is not accompanied by pus leakage or purulent processes inside the ear cavities.
If the doctor confirms that otitis media is catarrhal, then he will most likely give the nod to compresses.
Vodka and alcohol compresses apply only to adults and adolescents. Children use alcohol and alcohol is generally prohibited.
For them, this compress ingredient is replaced with heated vegetable oil.
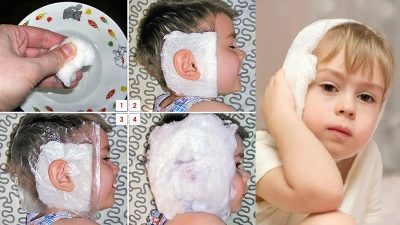
In short, the compression setting algorithm looks like this:
- in warm oil, wet a piece of gauze in the form of a square measuring 10x10 cm;
- a square is applied to the diseased ear by inserting the auricle into a vertical hole cut in gauze in advance;
- Next, a layer of paraffinized compressed paper (sold in any pharmacy) 12x12 cm in size with a similar vertical incision for the ear is put;
- both layers are covered with a layer of dry cotton 14x14 cm;
- the whole “construction” is fixed with a bandage around the head so tightly that it is almost impossible to insert a finger under the compress.
Warming compress superimposed on 6-8 hours, for infants, the time of therapeutic warm exposure can be reduced to 4-5 hours. Such procedures help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, improve the child’s condition.
Treatment of folk remedies
Given the likelihood and severity of possible complications, doctors rarely give permission for the use of folk remedies in the treatment of inflammation of the hearing organs. And all because, in their opinion, burdock or plantain, no doctor wants to take responsibility for the desire of parents to replace the prescribed antibiotics with a safer, in their opinion, burdock or plantain.
However, if it is not about replacing traditional treatment with unconventional, but only about supplementing medical prescriptions with some recipes of traditional medicine, the doctor may well meet the wishes of the parents.
The basic conditions that allow the use of folk remedies are:
- the child does not have high fever and severe pain;
- otitis is not purulent or complicated;
- eardrum is not damaged, there was no surgery and puncture;
- child over 3 years.
As a means for instillation in the ears, you can use aloe juice, diluted in half with saline.
Good help warming compresses with water propolis tincture.
Instead of vegetable oil in the classic warming compress, the method of setting which is described above, you can add camphor oil, under the conditions that the child already has 3 years and he does not have allergies.
A complete ban on the treatment of folk remedies is imposed on the use inside the ears (in drops or turundas) of any homemade drops, tinctures on vodka, alcohol.
But the "green light" traditional medicine provides folk drinks and means for the nose and throat based on medicinal herbs.
So, when otitis is useful twice a day to gargle with a decoction of chamomile, rinse their nose before instilling vasoconstrictor drops.
Throughout the course of treatment, fruit drinks from fresh or frozen sour berries containing a large amount of vitamin C, which is necessary for the restoration of auditory function, are useful.
It should be remembered that all herbal remedies, herbal preparations and drinks are contraindicated for otitis media having an allergic origin.
Any plant component on the background of sensitization of the body can cause a new “round” of the immune response, and the child’s condition in this case may worsen.
Prevention
Prevention otitis need to deal with immediately after returning from the hospital. At the initial stage of the child's life, it is important to observe the following rules.
You can not clean the ears of the newborn and the baby with cotton sticks, as this increases the risk of injury to the eardrum, and the cotton wool fibers from the sticks often remain inside the ear canal, gradually causing irritation and inflammation.
Hygienic treatments are best done using gauze turunda, which should not be injected too deep. It is quite enough to clean the outer part of the ear canal, because babies produce earwax less than adults.
Nasal congestion and rhinitis, as well as any other respiratory diseases, are conditions to which parents must respond quickly and correctly in order to prevent the development of hearing inflammation.
Runny nose should be treated on time and properly. Treatment will be facilitated by washing with saline and maintaining the humidity level necessary for the health of the mucous membranes - 50-70%, as well as the air temperature - not higher than 21 degrees heat. Only under these conditions, the nasal mucus does not dry out, and the prerequisites for the swelling of the nasal passages are not created.
When choosing clothes for walking with a baby, it is important to bear in mind that even in summer the baby’s ears should be reliably protected from strong wind, dust and sand. Headgear should provide this opportunity.
If it is too windy outside, then walk with the baby should be postponed to a more suitable time.
After the baby has eaten or drank, it is important to hold it vertically for a while.
This is useful not only from the point of view of prevention of colic and regurgitation, but also from the point of view of prevention of otitis, because very often in infants the part of the masses that he belched in the prone position falls into the auditory tube. And milk and the mixture are favorable environments for the life of a variety of microbes.
Older children need to learn to blow their nose properly. At a cold nose, first gently release the nose from the accumulated mucus, blow out one nostril, closing the second finger or handkerchief, and then perform similar actions from the second nostril.
Sniffing nose - also harmful from the point of view of the possibility of developing otitis habit.
Treat the adenoids in time for the child, and if necessary, agree to their full or partial removal, so that the child’s nasal breathing is not difficult.
To maintain a healthy ear, you should just as resolutely deal with polyps in the nose and nasopharynx and with chronic tonsillitis, especially if the doctor strongly recommends prompt resolution of the problem.
Make sure that the child does not put foreign objects in his ears, especially sharp and small parts of toys, pins. Inspect the auditory canal regularly.
When relaxing on the beach, explain to your child that you should not swallow or inhale sea or river water with your nose. And when visiting the pool, the baby must wear a rubber cap, which will protect the auditory passages from ingress of chlorinated water, which can cause inflammation in the ear and a strong allergic reaction.
The child should always dress according to the weather, especially for teenagers, who in tribute to fashion often refuse to wear hats during the cold season and during the off-season. This does not mean that the child should be confused, because excessive sweating does not contribute to the normal functioning of the body and increases the likelihood of allergic otitis.
For children of any age, a normal state of immunity is of considerable importance in the prevention of inflammatory processes of the hearing organs. Therefore, the child should spend enough time in the fresh air, his day should be planned, and the workload - educational, sports, home - evenly distributed.
Food should be sufficient and complete. Hardening and douche will strengthen the immune system, and timely preventive vaccinations will reduce the risk of infection with dangerous infections, many of which are complicated by otitis.
More about otitis will tell Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.